Abstract
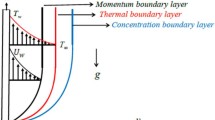
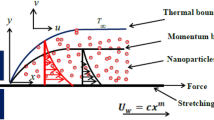
In this article we derive semi-analytical/numerical solutions for transport phenomena (momentum, heat and mass transfer) in a nanofluid regime adjacent to a nonlinearly porous stretching sheet by means of the Homotopy analysis method (HAM). The governing equations are reduced to a nonlinear, coupled, non-similar, ordinary differential equation system via appropriate similarity transformations. This system is solved under physically realistic boundary conditions to compute stream function, velocity, temperature and concentration function distributions. The results of the present study are compared with numerical quadrature solutions employing a shooting technique with excellent correlation. Furthermore the current HAM solutions demonstrate very good correlation with the non-transpiring finite element solutions of Rana and Bhargava (Commun. Nonlinear Sci. Numer. Simul. 17:212–226, 2012). The influence of stretching parameter, transpiration (wall suction/injection) Prandtl number, Brownian motion parameter, thermophoresis parameter and Lewis number on velocity, temperature and concentration functions is illustrated graphically. Transpiration is shown to exert a substantial influence on flow characteristics. Applications of the study include industrial nanotechnological fabrication processes.

















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Choi SUS, Eastman JA (1995) Enhancing thermal conductivity of fluids with nanoparticles. ASME FED, New York
Eastman JA, Choi US, Li S, Soyez G, Thompson LJ, DiMelfi RJ (1999) Novel thermal properties of nanostructured materials. Mater Sci Forum 312–314:629–634
Xuana Y, Roetzel W (2000) Conceptions for heat transfer correlation of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf 43:3701–3707
Masuda H, Ebata A, Teramae K, Hishinuma H (1993) Alteration of thermal conductivity and viscosity of liquid by dispersing ultra-fine particles (dispersion of 7-Al203, SiO2 and TiO2 ultra-fine particles). Netsu Bussei 4:227–233
Pak B, Cho Y (1998) Hydrodynamic and heat transfer study of dispersed fluids with submicron metallic oxide particles. Exp Heat Transf 11:151–170
Maïga SEB, Palm SJ, Nguyen CT, Roy G, Galanis N (2005) Heat transfer enhancement by using nanofluids in forced convection flows. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 26:530–546
Roy G, Nguyen CT, Lajoie P-R (2004) Numerical investigation of laminar flow and heat transfer in a radial flow cooling system with the use of nanofluids. Superlattices Microstruct 35:497–511
Keblinski P, Phillpot SR, Choi SUS, Eastman JA (2002) Mechanisms of heat flow in suspensions of nano-sized particles (nanofluids). Int J Heat Mass Transf 45:855–863
Abu-Nada E, Masoud Z, Oztop HF, Campo A (2010) Effect of nanofluid variable properties on natural convection in enclosures. Int J Therm Sci 49:479–491
Xuan Y, Li Q (2003) Investigation on convective heat transfer and flow features of nanofluids. J Heat Transf 125:151–155
Akbari M, Behzadmehr A, Shahraki F (2008) Fully developed mixed convection in horizontal and inclined tubes with uniform heat flux using nanofluid. Int J Heat Fluid Flow 29:545–556
Akbari M, Behzadmehr A (2007) Developing mixed convection of a nanofluid in a horizontal tube with uniform heat flux. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 17:566–586
Chang H, Chang Y-C (2008) Fabrication of Al2O3 nanofluid by a plasma arc nanoparticles synthesis system. J Mater Process Technol 207:193–199
Krajnik P, Pusavec F, Rashid A (2011) Nanofluids: Properties, applications and sustainability aspects in materials processing technologies. In: Seliger G, Khraisheh MMK, Jawahir IS (eds) Advances in sustainable manufacturing. Springer, Berlin, pp 107–113
Rana P, Bhargava R, Bég OA (2012) Numerical solution for mixed convection boundary layer flow of a nanofluid along an inclined plate embedded in a porous medium. Comput Math Appl 64:2816–2832
Rashidi MM, Abelman S, Freidoonimehr N (2013) Entropy generation in steady MHD flow due to a rotating porous disk in a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 62:515–525
Mohammadein AA, Gorla RSR (2001) Heat transfer in a micropolar fluid over a stretching sheet with viscous dissipation and internal heat generation. Int J Numer Methods Heat Fluid Flow 11:50–58
Bhargava R, Kumar L, Takhar HS (2003) Finite element solution of mixed convection micropolar flow driven by a porous stretching sheet. Int J Eng Sci 41:2161–2178
Rana P, Bhargava R (2012) Flow and heat transfer of a nanofluid over a nonlinearly stretching sheet: a numerical study. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17:212–226
Abel MS, Kumar KA, Ravikumara R (2011) MHD flow, and heat transfer with effects of buoyancy, viscous and joule dissipation over a nonlinear vertical stretching porous sheet with partial slip. Engineering 3:285–291
Nield DA, Kuznetsov AV (2009) The Cheng–Minkowycz problem for natural convective boundary-layer flow in a porous medium saturated by a nanofluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 52:5792–5795
Khan WA, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of a nanofluid past a stretching sheet. Int J Heat Mass Transf 53:2477–2483
Bachok N, Ishak A, Pop I (2010) Boundary-layer flow of nanofluids over a moving surface in a flowing fluid. Int J Therm Sci 49:1663–1668
Liao SJ (2004) Beyond perturbation: introduction to the homotopy analysis method. Chapman & Hall/CRC Press, London/Boca Raton
Liao SJ (2004) On the homotopy analysis method for nonlinear problems. Appl Math Comput 147:499–513
Liao SJ (2005) Comparison between the homotopy analysis method and homotopy perturbation method. Appl Math Comput 169:1186–1194
Turkyilmazoglu M (2010) A note on the homotopy analysis method. Appl Math Lett 23:1226–1230
Turkyilmazoglu M (2011) Numerical and analytical solutions for the flow and heat transfer near the equator of an MHD boundary layer over a porous rotating sphere. Int J Therm Sci 50:831–842
Turkyilmazoglu M (2012) Solution of the Thomas–Fermi equation with a convergent approach. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 17:4097–4103
Turkyilmazoglu M (2012) The Airy equation and its alternative analytic solution. Phys Scr 86:055004
Turkyilmazoglu M (2011) Some issues on HPM and HAM methods: a convergence scheme. Math Comput Model 53:1929–1936
Turkyilmazoglu M (2011) Convergence of the homotopy perturbation method. Int J Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 12:9–14
Hayat T, Nawaz M, Asghar S, Mesloub S (2011) Thermal-diffusion and diffusion-thermo effects on axisymmetric flow of a second grade fluid. Int J Heat Mass Transf 54:3031–3041
Rashidi MM, Hayat T, Erfani E, Mohimanian Pour SA, Hendi AA (2011) Simultaneous effects of partial slip and thermal-diffusion and diffusion-thermo on steady MHD convective flow due to a rotating disk. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 16:4303–4317
Rashidi MM, Mohimanian Pour SA, Hayat T, Obaidat S (2012) Analytic approximate solutions for steady flow over a rotating disk in porous medium with heat transfer by homotopy analysis method. Comput Fluids 54:1–9
Rashidi MM, Ali M, Freidoonimehr N, Nazari F (2013) Parametric analysis and optimization of entropy generation in unsteady MHD flow over a stretching rotating disk using artificial neural network and particle swarm optimization algorithm. Energy 55:497–510
Tripathi D, Bég OA, Curiel-Sosa JL (2012) Homotopy semi-numerical simulation of peristaltic flow of generalised Oldroyd-B fluids with slip effects. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Eng, 1–10
Liao SJ (2010) An optimal homotopy-analysis approach for strongly nonlinear differential equations. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 15:2003–2016
Rashidi MM, Mohimanian Pour SA, Abbasbandy S (2011) Analytic approximate solutions for heat transfer of a micropolar fluid through a porous medium with radiation. Commun Nonlinear Sci Numer Simul 16:1874–1889
Turkyilmazoglu M (2010) Purely analytic solutions of magnetohydrodynamic swirling boundary layer flow over a porous rotating disk. Comput Fluids 39:793–799
Cortell R (2007) Viscous flow and heat transfer over a nonlinearly stretching sheet. Appl Math Comput 184:864–873
Chen Co-K, Char M-I (1988) Heat transfer of a continuous, stretching surface with suction or blowing. J Math Anal Appl 135:568–580
Husnain S, Mehmood A, Bég OA, Ali A (2012) Suction and blowing effects on unsteady flow and heat transfer through porous media with variable viscosity. J Porous Media 15:293–302
Bég OA, Bég TA, Rashidi MM, Asadi M (2012) Homotopy semi-numerical modelling of nanofluid convection boundary layers from an isothermal spherical body in a permeable regime. Int J Microscale Nanoscale Therm Fluid Transp Phenom 3:237–266
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rashidi, M.M., Freidoonimehr, N., Hosseini, A. et al. Homotopy simulation of nanofluid dynamics from a non-linearly stretching isothermal permeable sheet with transpiration. Meccanica 49, 469–482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-013-9805-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-013-9805-9