Abstract
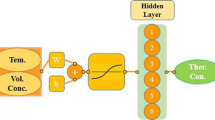
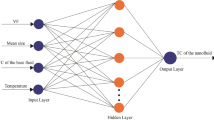
The correlations of thermal conductivity of alumina nanoparticle dispersed in pure ethylene glycol were proposed by neural network modeling using experimental data. The required input and target data have been taken from the experimental measurement to train artificial neural network (ANN). The temperatures were changed within 24–50 °C. Levenberg algorithm was used to train the ANN. Results showed that the thermal conductivity of nanofluid had a significant increase with increasing solid volume fraction of nanoparticles. The results also revealed that the ANN model can predict the thermal conductivity of Al2O3–EG nanofluid accurately with maximum deviation of 1.3 % and high correlation coefficient (R > 0.998).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Wongwises S, Toghraie D. An experimental study on the effect of diameter on thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Fe/water nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119:1817–24. doi:10.1007/s10973-014-4328-8.
Hemmat Esfe M, Arani AAA, Rezaie M, Yan WM, Karimipour A. Experimental determination of thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of Ag–MgO/water hybrid nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:189–95.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Yan WM, Afrand M, Sina N, Study on thermal conductivity of water based nanofluids with hybrid suspensions of CNTs/Al2O3 nanoparticles. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2016;124(1):455–460. doi:10.1007/s10973-015-5104-0.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Asadi A, Karimipour A. Thermal conductivity and viscosity of Mg (OH)2-ethylene glycol nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;120:1145–9.
Khanafer K, Vafai K. A critical synthesis of thermophysical characteristics of nanofluids. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2011;54(19–20):4410–28.
Mahian O, Kianifar A, Kalogirou SA, Pop I, Wongwises S. A review of the applications of nanofluids in solar energy. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2013;57(2):582–94.
Mahian O, Kianifar A, Sahin AZ, Wongwises S. Performance analysis of a minichannel-based solar collector using different nanofluids. Energy Convers Manag. 2014;88:129–38.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S. Turbulent forced convection heat transfer and thermophysical properties of Mgo–water nanofluid with consideration of different nanoparticles diameter, an empirical study. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;119(2):1205–13.
Hemmat Esfe M, Naderi A, Akbari M, Afrand M, Karimipour A. Evaluation of thermal conductivity of COOH-functionalized MWCNTs/water via temperature and solid volume fraction by using experimental data and ANN methods. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2015;121:1273–6.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Mahian O, Wongwises S. Heat transfer characteristics and pressure drop of COOH-functionalized DWCNTs/water nanofluid in turbulent flow at low concentrations. Int J Heat Mass Transf. 2014;73:186–94.
Celen A, Çebi A, Aktas M, Mahian O, Dalkilic AS, Wongwises S. A review of nanorefrigerants: flow characteristics and applications. Int J Refrig. 2014;44:125–40.
Chandrasekar M, Suresh S, Senthilkumar T. Mechanisms proposed through experimental investigations on thermophysical properties and forced convective heat transfer characteristics of various nanofluids—a review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev. 2012;16(6):3917–38.
M. Hemmat Esfe, S. Saedodin, O. Mahian, and S. Wongwises, Thermal conductivity of Al2O3/water nanofluids: measurement, correlation, sensitivity analysis, and comparisons with literature reports, J Therm Anal Calorim., 117 (2014), pp. 675–681.
M. Hemmat Esfe, S. Saedodin, M. Bahiraei, D. Toghraie, O. Mahian, and S. Wongwises, “Thermal conductivity modeling of MgO/EG nanofluids using experimental data and artificial neural network,” J. Therm. Anal. Calorim., 118 (1) (2014) pp. 287–294.
Barbés B, Páramo R, Blanco E, Casanova C. Thermal conductivity and specific heat capacity measurements of CuO nanofluids. J Therm Anal Calorim. 2014;115(2):1883–91.
Eslamloueyan R, Khademi MH. Estimation of thermal conductivity of pure gases by using artificial neural networks. Int J Therm Sci. 2009;48:1094–101.
Hemmat Esfe M, Wongwises S, Naderi A, Asadi A, Safaei MR, Rostamian H, Dahari M, Karimipour A. Thermal conductivity of Cu/TiO2–water/EG hybrid nanofluid: experimental data and modeling using artificial neural network and correlation. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;66:100–4.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Naderi A, Alirezaie A, Karimipour A, Wongwises S, Goodarzi M. Modeling of thermal conductivity of ZnO–EG using experimental data and ANN methods. Int CommunHeat Mass Transf. 2015;63:35–40.
M. Hemmat Esfe, S. Saedodin, N. Sina, and M. Afrand, Designing an artificial neural network to predict thermal conductivity and dynamic viscosity of ferromagnetic nanofluid, Int. Commun. Heat Mass Transf., doi:10.1016/j.icheatmasstransfer.2015.06.013.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Biglari M, Rostamian H. Experimental investigation of thermal conductivity of CNTs-Al2O3/water: a statistical approach. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;69:29–33.
Karimi H, Yousefi F. Application of artificial neural network–genetic algorithm (ANN–GA) to correlation of density in nanofluids. Fluid Phase Equilib. 2012;336:79–83.
Sadollah A, Ghadimi A, Metselaar IH, Bahreininejad A. Prediction and optimization of stability parameters for titanium dioxide nanofluid using response surface methodology and artificial neural networks. Sci Eng Compos Mater. 2013;20:319–30.
S. Haykin, “Adaptive filters,” Signal Process. Mag., vol. 6, 1999.
Marquardt DW. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J Soc Ind Appl Math. 1963;11:431–41.
Hemmat Esfe M, Saedodin S, Akbari M, Karimipour A, Afrand M, Wongwises S, Safaei MR, Dahari M. Experimental investigation and development of new correlations for thermal conductivity of CuO/EG–water nanofluid. Int Commun Heat Mass Transf. 2015;65:47–51.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the assistance provided by the nanofluid Laboratory of Semnan university science and technology Park for providing necessary instrumentation to carry out the sample preparation and helping in the analysis of samples to complete the article in time.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hemmat Esfe, M., Rostamian, H., Toghraie, D. et al. Using artificial neural network to predict thermal conductivity of ethylene glycol with alumina nanoparticle. J Therm Anal Calorim 126, 643–648 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5506-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-016-5506-7