Abstract
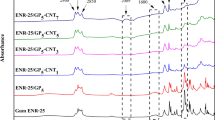
Nanocomposites of epoxidized natural rubber (ENR) filled with graphite (GP), carbon nanotubes (CNTs), and CNTs/GP hybrid fillers were prepared and characterized. It was found that both the gum and filled ENR compounds exhibit a reversion curve, attributed to the breaking of weak -O-O- linkages. Furthermore, increasing GP loadings in ENR-GP and ENR-CNTs/GP hybrid composites lead to elevated cure curves and torque differences, indicating higher crosslink density and stiffness of the vulcanizates. These changes are attributed to the increasing chemical interaction between polar functional groups in ENR molecules and nanofiller surfaces, as confirmed by FTIR analysis. That is, a decrease in OH and epoxide groups, along with an increase in ether linkages were observed. Moreover, ENR-CNTs/GP hybrid composites exhibit even higher curing curves, torque differences, Payne effect, total bound rubber content, electrical conductivity, and dielectric constant due to finer filler dispersion and distribution. This is attributed to the formation of interconnected infinite networks that rapidly reach the percolation threshold concentration. Additionally, the formation of CNTs-GP-CNTs connections enhances mechanical strength, heat conduction, and the tunneling effect of electrons. This confirms the synergistic effects of graphite and carbon nanotube hybrid fillers on key properties in ENR-CNTs/GP hybrid nanocomposites, indicating their potential applications in various fields.














Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The data are available from the corresponding author upon sensible request.
References
Phanny Y, Azura R, Ismail H (2013) Effect of different origins of natural rubber on the properties of carbon black filled natural rubber composites. ASEAN Eng J Part B 2(1):60–67
Millard E (2019) In: Schmidt M, Giovannucci D, Palekhov D, Hansmann B (eds). Recent experiences from the natural rubber industry and its movement towards sustainability. Sustainable Global Value Chains. Springer, New York p. 499–520
Matchawet S, Kaesaman A, Bomlai P, Nakason C (2016) Electrical, dielectric, and dynamic mechanical properties of conductive carbon black/epoxidized natural rubber composites. J Comp Mat 50(16):2191–2202
Shooli SA, Tavakoli M (2016) Styrene Butadiene rubber/epoxidized natural rubber (SBR/ENR50) nanocomposites containing nanoclay and carbon black as fillers for application in tire-tread compounds. J Macro Sci Part B 55(10):969–983
Teh PL, Ishak ZAM, Hashim AS, Karger-Kocsis J, Ishiaku US (2006) Physical properties of natural rubber/organoclay nanocomposites compatibilized with epoxidized natural rubber. J Appl Polym Sci 100:1083–1092
Damampai K, Pichaiyut S, Stöckelhuber KW, Das A, Nakason C (2022) Ferric ions crosslinked epoxidized natural rubber filled with carbon nanotubes and conductive carbon black hybrid fillers. Polymers 14(20):4392
Balendran BK, Yaragalla S (2022) Epoxidized natural rubber/acid functionalized carbon nanotubes composites for enhanced thermo-mechanical and oxygen barrier performance. Polym Eng Sci 62(3):861
Krainoi A, Johns J, Kalkornsurapranee E, Nakaramontri Y (2021) In: Ghosh PK, Datta, K, Rushi AD (eds) Carbon nanotubes reinforced natural rubber composites. Carbon Nanotubes-Redefining the World of Electronics. IntechOpen. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.87724
Kummerlöwe C, Vennemann N, Pieper S, Siebert A, Nakaramontri Y (2014) Preparation and properties of carbon-nanotube composites with natural rubber and epoxidized natural rubber. Polim 59(11):11–12
Nakaramontri Y, Nakason C, Kummerlöwe C, Vennemann N (2017) Enhancement of electrical conductivity and other related properties of epoxidized natural rubber/carbon nanotube composites by optimizing concentration of 3-aminopropyltriethoxy silane. Polym Eng Sci 57:381–391
Moolsin S, Sawangkan D (2022) Epoxidized natural rubber/silane modified silica nanocomposites prepared in latex stage. J Metal Mat Min 32(1):118–123
Pithaksareetham N, Hongkarnjanakul N, Suchat S (2018) Eco-nanocomposites with epoxidized natural rubber for improved mechanical properties essential to unmanned aerial vehicles propeller applications. Adv Polym Technol 37:2946–2957
Jarnthong M, Peng Z, Lopattananon N, Nakason C (2017) Nanosilica-reinforced Epoxidized natural rubber nanocomposites: Effect of Epoxidation level on morphological and mechanical properties. Polym Compos 38:1151–1157
He C, She X, Peng Z, Zhong J, Liao S, Gong W, Liaob J, Kong L (2015) Graphene networks and their influence on free-volume properties of graphene-epoxidized natural rubber composites with a segregated structure: Rheological and positron annihilation studies. Phy Chem Chem Phy 17:12175–12184
Yaragalla S, Chandran CS, Kalarikkal N, Subban RHY, Chan CH, Thomas S (2015) Effect of reinforcement on the barrier and dielectric properties of epoxidized natural rubber–graphene nanocomposites. Polym Eng Sci 55:2439–2447
Siriwas T, Pichaiyut S, Susoff M, Petersen S, Nakason C (2023) Graphene-filled natural rubber nanocomposites: Influence of the composition on curing, morphological, mechanical, and electrical properties. Exp Polym Lett 17(8):819–836
She X, He C, Peng Z, Kong L (2014) Molecular-level dispersion of graphene into epoxidized natural rubber: Morphology, interfacial interaction and mechanical reinforcement. Polymer 55(26):6803–6810
Barrios SU, Santana MH, Verdejo R, Miguel A, Manchado L (2020) Design of rubber composites with autonomous self-healing capability. ACS Omega 5:1902–1910
Kitisavetjit W, Nakaramontri Y, Pichaiyut S, Wisunthorn S, Nakason C, Kiatkamjornwong S (2021) Influences of carbon nanotubes and graphite hybrid filler on properties of natural rubber nanocomposites. Polym Test 93:106981
Cao L, Huang J, Chen K (2018) Dual cross-linked epoxidized natural rubber reinforced by tunicate cellulose nanocrystals with improved strength and extensibility. ACS Sust Chem Eng 8 6(11):14802–14811
Venkat S, Dhamodharan R (2012) Epoxidized natural rubber–magnetite nanocomposites for oil spill recovery. J Mat Chem A 1(3):868–876
Salaeh S, Kao-ian P (2022) Conductive epoxidized natural rubber nanocomposite with mechanical and electrical performance boosted by hybrid network structures. Polym Test 108:107493
Gbaguidi A, Namilae S, Kim D (2020) Synergy effect in hybrid nanocomposites based on carbon nanotubes and graphene nanoplatelets. Nanotech 31:255704
Luo X, Yang G, Schubert DW (2022) Electrically conductive polymer composite containing hybrid graphene nanoplatelets and carbon nanotubes: synergistic effect and tunable conductivity anisotropy. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 5:250–262
Krainoi A, Boonkerd K (2022) Novel hybrid natural rubber nanocomposites with carbon nanotube and cellulose nanofiber for strain-sensitive sensor. Indus Crop Pro 187:Part B, 115455
Thongkong N, Wisunthorn S, Pichaiyut S, Nakason C (2020) Natural rubber nanocomposites based on hybrid filler of zinc nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes: Electrical conductivity and other related properties. Exp Polym Lett 14(12):1137–1154
Nakaramontri Y, Pichaiyut S, Wisunthorn S, Nakason C (2017) Hybrid carbon nanotubes and conductive carbon black in natural rubber composites to enhance electrical conductivity by reducing gaps separating carbon nanotube encapsulates. Eur Polym J 90:467–484
Marinho B, Ghislandi M, Tkalya E, Koning CE, de With G (2012) Electrical conductivity of compacts of graphene, multi-wall carbon nanotubes, carbon black, and graphite powder. Powder Techno 221:351–358
Nakaramontri Y, Kummerlowe C, Vennemann N, Wisunthorn S, Pichaiyut S, Nakason C (2018) Effect of bis(triethoxysilylpropyl)tetrasulfide (TESPT) on properties of carbon nanotubes and conductive carbon black hybridized filler filled natural rubber nanocomposites. Exp Polym Lett 12(10):867–884
Krainoi A, Kummerlöwe C, Nakaramontri Y, Wisunthorn S, Vennemann N, Pichaiyut S, Kiatkamjornwong S, Nakason C (2020) Novel natural rubber composites based on silver nanoparticles and carbon nanotubes hybrid filler. Polym Comp 41:443–458
Xu Z, Song Y, Zheng Q (2019) Payne effect of carbon black-filled natural rubber compounds and their carbon black gels. Polymer 185:121953
Kaewsakul W, Sahakaro K, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2012) Optimization of mixing conditions for silica-reinforced natural rubber tire tread compounds. Rub Chem Technol 85(2):277–294
Sumfleth J, Adroher XC, Schulte K (2009) Synergistic effects in network formation and electrical properties of hybrid epoxy nanocomposites containing multiwall carbon nanotubes and carbon black. J Mater Sci 44(12):3241–3247
Cheng B, Lu X, Zhou J, Qin R, Yang Y (2019) Dual Cross-Linked Self-Healing and Recyclable Epoxidized Natural Rubber Based on Multiple Reversible Effects. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 7(4):4443–4455
Velisek J, Koplik R, Cejpek K (2020) The Chemistry of Food. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York
Barbosa R, Nunesa AT, Ambrósio JD (2017) Devulcanization of natural rubber in composites with distinct crosslink densities by twin-screw extruder. Mater Res 20(2):77–83
Damampai K, Pichaiyut S, Mandal S, Wießner S, Das A, Nakason C (2021) Internal Polymerization of Epoxy Group of Epoxidized Natural Rubber by Ferric Chloride and Formation of Strong Network Structure. Polymers 13(23):4145
Silverstein RM, Webster FX, Kiemle DJ, Bryce DL (2005) Spectrometric Identification of Organic Compounds. John Wiley & Sons Inc, New York
Krainoi A, Kummerlöwe C, Nakaramontri Y, Vennemann N, Pichaiyut S, Wisunthorn S, Nakason C (2018) Influence of critical carbon nanotube loading on mechanical and electrical properties of epoxidized natural rubber nanocomposites. Polym Test 66:122–136
Payne AR, Whittaker RE (1971) Low strain dynamic properties of filled rubbers. Rubber Chem Technol 44:440–478
Sarkawi SS, Dierkes WK, Noordermeer JWM (2014) Elucidation of filler-to-filler and filler-to-rubber interactions in silica-reinforced natural rubber by TEM network visualization. Eur Polym J 54:118–127
Wolff S, Wang MJ (1993) In: Donnet JB, Bansal RC, Wang MJ (eds). Carbon black reinforcement of elastomers. Carbon Black: Science and Technology, Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, p 290
Roychoudhury A, De PP (1995) Elastomer–carbon black interaction: Influence of elastomer chemical structure and carbon black surface chemistry on bound rubber formation. J Appl Polym Sci 55:9–15
Mohapatra S, Nando GB (2015) Analysis of carbon black–reinforced cardanol-modified natural rubber compounds. Rub Chem Tech 88(2):289–309
Niedermeier W, Fröhlich J, Luginsland HD (2002) Reinforcement mechanism in the rubber matrix by active fillers. KGK-Kaut Gum Kunst 55:356–366
Luo T, Wang Q (2021) Effects of graphite on electrically conductive cementitious composite properties: A Review. Materials 14(17):4798
Earp B, Dunn D, Phillips J, Agrawal R, Ansell T, Aceves P, De Rosa I, Xin W, Luhrs C (2020) Enhancement of electrical conductivity of carbon nanotube sheets through copper addition using reduction expansion synthesis. Mater Res Bull 131:110969
Zare Y, Rhee KY (2020) Calculation of the electrical conductivity of polymer nanocomposites assuming the interphase layer surrounding carbon nanotubes. Polymer 12(2):404
Funding
The authors gratefully acknowledge full financial support from the PSU NR-IRI (Natural Rubber Innovation Research Institute), Contract no. SIT591146S. In addition, Prince of Songkla University, Surat Thani Campus, Thailand is acknowledged for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Pichaiyut, S., Kitisavetjit, W. & Nakason, C. Synergistic effects of graphite and carbon nanotube hybrid fillers on key properties of epoxidized natural rubber nanocomposites. J Polym Res 30, 412 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03799-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-023-03799-z