Abstract
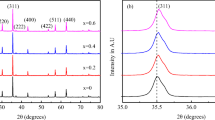
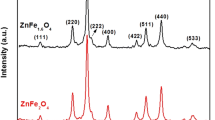
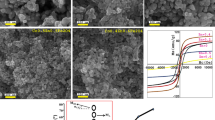
The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of annealing temperature and cobalt cation (Co2+) doping on the magnetic properties of zinc ferrite (ZFO) nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were prepared through sol-gel combustion process with citric acid as the fuel. The obtained nanoparticles were annealed at several temperatures from 300 to 1000 °C for 2 h. Spinel formation was proved by X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns, and the average crystallite size in all samples was estimated between 22 and 32 nm. It is worthwhile to mention that Fe2O3 and ZnO are detected as the medium phases. Meanwhile, Fe2O3 phase transformation to the other allotropes has happened around 400 °C and was characterized via the simultaneous thermal analysis (STA) and XRD. For higher annealing temperatures, diffusion has gradually been completed and, finally, the single phase of spinel structure was prepared at 1000 °C. In addition, field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) images revealed that the nanoparticle size after annealing was between 30 and 200 nm for the whole samples. The formation of the spinel phase was considered the most important factor on the magnetic properties of ZFO. Cobalt doping, annealing temperature, and also Fe2O3 phase were the main factors on changing magnetic properties. Paramagnetic nanoparticles with higher coercivity for doped samples rather than un-doped samples have been obtained.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Krishnan, K.M. et al.: Nanomagnetism and spin electronics: materials, microstructure and novel properties. J. Mater. Sci. 41(1), 793–815 (2006)
Berggren, K.-F., Yakimenko, I.: Effects of exchange and electron correlation on conductance and nanomagnetism in ballistic semiconductor quantum point contacts. Phys. Rev. B 66(5), 085323 (2002)
Wang, S.-B., Min, Y.-L., Yu, S.-H.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of uniform hematite nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 111(6), 3551–3554 (2007)
Niyaifar, M.: Effect of preparation on structure and magnetic properties of ZnFe2O4. J. Magn. 19(2), 101–105 (2014)
Kombaiah, K. et al.: Effect of Cd2+ concentration on ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles on the structural, optical and magnetic properties. Optik-Int. J. Light Electron. Opt. 135, 190–199 (2017)
Stewart, S., et al.: Cationic exchange in nanosized ZnFe2O4 spinel revealed by experimental and simulated near-edge absorption structure. Phys. Rev. B 75(4), 073408 (2007)
Masoudpanah, S. et al.: Structure and magnetic properties of La substituted ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 370, 122–126 (2014)
Guo, X. et al.: ZnFe2O4 nanotubes: microstructure and magnetic properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 118(51), 30145–30152 (2014)
Jeong, J.R. et al.: Magnetic properties of γ-Fe2O3 nanoparticles made by coprecipitation method. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 241(4), 1593–1596 (2004)
Sutka, A., Mezinskis, G.: Sol-gel auto-combustion synthesis of spinel-type ferrite nanomaterials. Front. Mater. Sci. 6(2), 128–141 (2012)
Kumar, Y. et al.: Effect of annealing on the magnetic properties of zinc ferrite thin films. Mater. Lett. 195, 89–91 (2017)
John, H.T., Fraih, A.J.: Preparation of nano crystalline zinc–ferrite as material for micro waves absorption by sol-gel methods. Ind. J. Sci. Technol. 10(21), 1–6 (2017)
Thankachan, R.M. et al.: Enhanced lithium storage in ZnFe2O4–C nanocomposite produced by a low-energy ball milling. J. Power. Sources 282, 462–470 (2015)
Erfaninia, N. et al.: Preparation of magnetically recyclable ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by easy single-step co-precipitation method and their catalytic performance in the synthesis of 2-aminothiophenes. Appl. Organometallic Chem. 32(2), 1–7 (2018)
Zhong, X. -B. et al.: A novel approach to facilely synthesize mesoporous ZnFe2O4 nanorods for lithium-ion batteries. J. Power. Sources 306, 718–723 (2016)
Dhiman, M. et al.: Morphology-controlled hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic properties of ZnFe2O4 nanostructures. Ceram. Int. 42(8), 12594–12605 (2016)
Singh, C. et al.: Synthesis of zinc-substituted cobalt ferrites via reverse micelle technique involving in situ template formation: a study on their structural, magnetic, optical and catalytic properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 156, 188–197 (2015)
Peng, Y. et al.: Structure and properties of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized via the sol-gel auto-combustion method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27(1), 587–591 (2016)
Monfared, A. et al.: A rapid and efficient thermal decomposition approach for the synthesis of manganese-zinc/oleylamine core/shell ferrite nanoparticles. J. Alloys Compd. 693, 1090–1095 (2017)
Martins, M.L. et al.: Mechanisms of phase formation along the synthesis of Mn–Zn ferrites by the polymeric precursor method. Ceram. Int. 40(7), 16023–16031 (2014)
Sharma, R. et al.: Improvement in magnetic behaviour of cobalt-doped magnesium zinc nano-ferrites via co-precipitation route. J. Alloys Compd. 684, 569–581 (2016)
Li, Y. et al.: Magnetic properties of Cu0.48Ni0.52Fe2O4 and thermal process of precursor. J. Supercond. Nov. Magn. 26(3), 2153–2158 (2013)
Oliver, S.A., Harris, V.G., Hamdeh, H.H., Ho, J.C.: Large zinc cation occupancy of octahedral sites in mechanically activated zinc ferrite powders. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76(16), 2761–2763 (2000)
Sivagurunathan, P., Sathiyamurthy, K.: Effect of temperatures on structural, morphological and magnetic properties of zinc ferrite nanoparticles. Can. Chem. Trans. 4(2), 244–54 (2016)
Smit, J., Wijn, H.: Ferrites Philips Technical Library, p 278. Eindhoven, The Netherlands (1959)
Raut, A.V. et al.: Effect of gamma irradiation on the structural and magnetic properties of Co–Zn spinel ferrite nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Bull 63, 123–128 (2015)
Manikandan, A. et al.: Synthesis, optical and magnetic properties of pure and Co-doped ZnFe2O4 nanoparticles by microwave combustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 349, 249–258 (2014)
Weil, L., Bertaut, F., Bochirol, L.: Propriétés magnétiques et structure de la phase quadratique du ferrite de cuivre. J. Phys. Radium 11(5), 208–212 (1950)
Nakagomi, F. et al.: Influence of the Mg-content on the cation distribution in cubic MgxFe3−xO4 nanoparticles. J. Solid State Chem. 182(6), 2423–2429 (2009)
Jadhav, S.S. et al.: Structural properties and cation distribution of Co–Zn nanoferrites. Int. J. Modern Phys. B 23(30), 5629–5638 (2009)
Gabal, M., Al Angari, Y.: Effect of chromium ion substitution on the electromagnetic properties of nickel ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 118(1), 153–160 (2009)
Singh, A.K. et al.: Dielectric properties of Mn-substituted Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 91(7), 6626–6629 (2002)
Nikam, D.S. et al.: Cation distribution, structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Co1−xZnxFe2O4 (x = 0–1) nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 5(1), 2338–2345 (2015)
Jadhav, S.S., et al.: Effect of Zn substitution on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 108(6), 093920 (2010)
Joseph, J. et al.: Structure and magnetic properties of highly textured nanocrystalline Mn–Zn ferrite thin film. Physica B 456, 293–297 (2015)
Anwar, H., Maqsood, A., Gul, I.: Effect of synthesis on structural and magnetic properties of cobalt doped Mn–Zn nano ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 626, 410–414 (2015)
Waqas, H., Qureshi, A.: Influence of pH on nanosized Mn–Zn ferrite synthesized by sol–gel auto combustion process. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 98(2), 355 (2009)
Ebrahimi, S.S., Masoudpanah, S.: Effects of pH and citric acid content on the structure and magnetic properties of Mn-Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by a sol–gel autocombustion method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 357, 77–81 (2014)
Bakhshi, H., Shokuhfar, A., Afghahi, S.S.S.: Structural, magnetic and Raman study of CoFe2O4@ C core–shell nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41(6), 10736–10744 (2015)
Li, X. -H. et al.: Synthesis and magnetic properties of nearly monodisperse CoFe2O4 nanoparticles through a simple hydrothermal condition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 5(3), 1039 (2010)
Yadav, R.S. et al.: Magnetic properties of Co1−xZnxFe2O4 spinel ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by starch-assisted sol–gel autocombustion method and its ball milling. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 378, 190–199 (2015)
Deraz, N., Abd-Elkader, O.H.: Structural, morphological and magnetic properties of Zn0.5Mg0.5Fe2O4 as anticorrosion pigment. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 10(6), 7138–7146 (2015)
Zhang, S. -H. et al.: A family of cubane cobalt and nickel clusters: syntheses, structures and magnetic properties. Inorg. Chim. Acta 396, 119–125 (2013)
Huili, H. et al.: Effect of cobalt substitution on the structure, electrical, and magnetic properties of nanorcrystalline Ni0.5Zn0.5Fe2O4 prepared by the polyol process. Ceram. Int. 40(7), 16235–16244 (2014)
Abu-Dief, A.M. et al.: Effect of chromium substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline zinc ferrite. Mater. Chem. Phys. 174, 164–171 (2016)
Chen, X. et al.: Effect of particle size on magnetic properties of zinc chromite synthesized by sol–gel method. Appl. Phys. Lett. 81(23), 4419–4421 (2002)
Upadhyay, C. et al.: Effect of size and synthesis route on the magnetic properties of chemically prepared nanosize ZnFe2O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 312(2), 271–279 (2007)
Goodenough, J.B., Loeb, A.L.: Theory of ionic ordering, crystal distortion, and magnetic exchange due to covalent forces in spinels. Phys. Rev. 98(2), 391 (1955)
Upadhyay, C., Verma, H., Anand, S.: Cation distribution in nanosized Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Appl. Phys. 95(7), 5746–5751 (2004)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tehranian, P., Shokuhfar, A. & Bakhshi, H. Tuning the Magnetic Properties of ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles Through Partial Doping and Annealing. J Supercond Nov Magn 32, 1013–1025 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4785-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4785-6