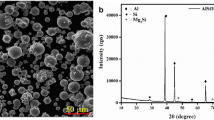
Abstract
In this study, near-amorphous multiphase intermetallic compound (IMC) particles were prepared with mass percentages of 0, 0.25, 0.5, and 1% to form composite SnBi solder alloys. Furthermore, the impact of the IMC particles amount on the melting properties, microstructure, and mechanical properties of the solder alloy was investigated. The thermal analysis data showed that the IMC particles decreased the melting range, melting temperature, and undercooling of composite solders. The microstructure of the solder alloy was significantly better than that of SnBi alloys after the addition of IMC. In the ball shear test, the microscale solder joints of the SnBi alloy comprising 0.5-wt% IMC particles exhibited the highest shear strength. Meanwhile, the ductility was improved most significantly in the SnBi alloy with 1-wt% IMC particles, the morphological characteristics of shear ports also support this phenomenon. The fracture morphology, location, and fracture mode of solder joints also changed with the increase of the IMC amount. Nanoindentation test results revealed that the enhancement of the creep resistance in SnBi-IMC microscale solder joint samples was due to the shift in creep mechanism by the presence of IMC particles. Additionally, the impact of the IMC particles amount on the hardness and elasticity modulus of SnBi-IMC solder alloys was also investigated.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
S.K. Kang, A.K. Sarkhel, J. Electron. Mater. 23, 701 (1994)
X. Hu, T. Xu, L.M. Keer, Y. Li, X. Jiang, J. Alloys Compd. 690, 720 (2017)
W.R. Osório, L.C. Peixoto, L.R. Garcia, N. Mangelinck-Noël, A. Garcia, J. Alloys Compd. 572, 97 (2013)
A.F. Abd El-Rehim, H.Y. Zahran, J. Alloys Compd. 695, 3666 (2017)
A. Nabihah, M.S. Nurulakmal, Mater. Today Proc. 17, 803 (2019)
H. Wang, X. Hu, X. Jiang, Mater. Charact. 163, 110287 (2020)
W. Dong, Y. Shi, Z. Xia, Y. Lei, F. Guo, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 982 (2008)
F. Wang, Y. Huang, C. Du, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 668, 224 (2016)
Q. Xu, X. Ding, C. Chen, J. Zhou, F. Xue, Q. Chen, Mater. Lett. 305, 130745 (2021)
W. Zhu, W. Zhang, W. Zhou, P. Wu, J. Alloys Compd. 789, 805 (2019)
W. Zhu, Y. Ma, X. Li, W. Zhou, P. Wu, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 29, 7575 (2018)
X. Li, Y. Ma, W. Zhou, P. Wu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 684, 328 (2017)
T. Feng, H. Hahn, H. Gleiter, Wuli Xuebao/Acta Physica Sinica 66, (2017)
J. Gui, X. Li, J. Wang, W. Li, H. Qin, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 32, 28454 (2021)
H. Zhang, X. Li, W. Zhou, Mater. Chem. Phys. 290, (2022)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R: Rep. 82, 1 (2014)
Y. Li, Y.C. Chan, J. Alloys Compd. 645, 566 (2015)
P. Liu, P. Yao, J. Liu, J. Electron. Mater. 37, 874 (2008)
R. Sun, Y. Sui, J. Qi, F. Wei, Y. He, X. Chen, Q. Meng, Z. Sun, J. Electron. Mater. 46, 4197 (2017)
P. Yao, P. Liu, J. Liu, J. Alloys Compd. 462, 73 (2008)
H. Zhang, X. Li, P. Yao, L. Wen, Y. Zhu, X. He, G. Yang, Mater. Charact. 186, 111791 (2022)
A.S.M.A. Haseeb, M.M. Arafat, M.R. Johan, Mater. Charact. 64, 27 (2012)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 28, 15718 (2017)
Y. Wan, S. Li, X. Hu, Y. Qiu, T. Xu, Y. Li, X. Jiang, Microelectron. Reliab. 86, 27 (2018)
F. Wang, H. Chen, Y. Huang, L. Liu, Z. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 30, 3222 (2019)
Y. Tang, S.M. Luo, W.F. Huang, Y.C. Pan, G.Y. Li, J. Alloys Compd. 719, 365 (2017)
M.L. Huang, F. Zhang, F. Yang, N. Zhao, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Electron. 26, 2278 (2015)
P.F. Yang, Y.S. Lai, S.R. Jian, J. Chen, R.S. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 485, 305 (2008)
M.J. Mayo, R.W. Siegel, A. Narayanasamya, W.D. Nix, J. Mater. Res. 5, 1073 (1990)
B.N. Lucas, W.C. Oliver, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 30, 601 (1999)
L. Shen, Z.Y. Tan, Z. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 561, 232 (2013)
R. Mahmudi, R. Roumina, B. Raeisinia, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 382, 15 (2004)
L. Shen, P. Septiwerdani, Z. Chen, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 558, 253 (2012)
D. Grivas, K.L. Murtyt, J.W. Morris, Acra Merolfurgicu. 27, 731 (1979)
Funding
This study was sponsored by the National Natural Science Foundation of China under Grant No. 52065015; the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. 2021 GXNSFAA075010; Director Fund Project of Guangxi Key Laboratory of Manufacturing System and Advanced Manufacturing Technology under Grant No. 20-065-40-002Z; Self-Topic Fund of Engineering Research Center of Electronic Information Materials and Devices under Grant No. EIMD-AB202007; Science and Technology Plan Project of Liudong New District under Grant No. Liudongkegong20210106; and Innovation Project of GUET Graduate Education under Grant Nos. 2021YCXS006 and 2021YXW06.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL participated in the conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, data curation, writing of the original draft, and writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript. JW participated in the methodology, formal analysis, and data curation. ZL contributed to methodology and formal analysis. LM participated in the conceptualization, investigation, writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript. HQ participated in the conceptualization, investigation, methodology, formal analysis, and writing, reviewing, & editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human tissues or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent to participate
This research is not related to human subjects.
Consent for publication
The author assigns non-exclusive publication rights to Springer and warrants that his contribution is unique and that he possesses all necessary authority to make this grant. The author assumes responsibility for the material’s release on behalf of all co-authors. This assignment of publication rights includes the non-exclusive right to reproduce and distribute the article in any format, including reprints, translations, photographic reproductions, microform, electronic form (offline, online), or other reproductions of a similar nature.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, J., Wang, J., Li, Z. et al. Effects of Near-amorphous multiphase intermetallic compound particles on the microstructure and mechanical properties of SnBi solders. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 1248 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10670-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-10670-w