Abstract
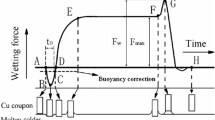
The effect of trace amounts of rare earth additions on the microstructure and properties were studied for the Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-Ag solder alloys. At the same time, the intermetallic compounds (IMCs) in the solder alloys and intermetallic layer (IML) thickness at the solder/Cu substrate interface were investigated, both as-reflowed and after high-temperature aging. The results indicate that adding trace amounts of rare earth (RE) elements has little influence on the melting temperature and microhardness of the solders investigated, but adding RE elements improves the wettability and shear strength of the Sn-58Bi and Sn-58Bi-Ag solder alloys. In addition, it was found that the addition of RE elements not only refines the microstructure and size of the IMC particles, but also decreases the IML thickness and shear strength of the Sn-58Bi solder joint after high-temperature aging. Adding trace amounts of RE elements is superior to adding trace amounts of Ag for improving the properties of the Sn-58Bi solder. The reason may be related to the modification of the microstructure of the solder alloys due to the addition of trace amounts of RE elements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C.H. Raeder, L.E. Felton, D.B. Knorr, G.B. Schmeelk, and D. Lee, IEE/CHMT Int’l Electron Manufacturing Technology Symposium (1993), p. 119
J.F. Li, S.H. Mannan, M.P. Clode, D.C. Whalley, D.A. Hutt, Acta Mater. 54, 2907 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2006.02.030
J.F. Lia, S.H. Mannan, M.P. Clode, K. Chen, D.C. Whalley, C. Liu, D.A. Hutt, Acta Mater. 55, 737 (2007). doi:10.1016/j.actamat.2006.09.003
Y. Wang, W.Y. Hu, X.L. Shu, L.H. Zhao, B.W. Zhang, Mater. Rev. 13, 23 (1999)
D.M. Zhang, G.F. Ding, H. Wang, Zh. Jiang, J.Y. Yao, J. Funct. Mater. Devices 12, 211 (2006)
H.W. Miao, J.G. Duh, Mater. Chem. Phys. 71, 255 (2001). doi:10.1016/S0254-0584(01)00298-X
X.F. Li, F.Q. Zu, H.F. Ding, et al. Phys. Lett. A 354, 325 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.physleta.2006.01.058
K. Suganuma, Lead-free Soldering Technology, X. Ning (Trans.) (Beijing Science Press, 2002), p. 51
M. Mccormack, S. Jin, G.W. Kammlat, IEEE Trans. Comp. Packag. Manuf. Technol. A 17, 452 (1994)
H.X. Jia, J.L. Huang, K.K. Zhang, J. Luoyang Inst. Technol. 25, 11 (2004)
H.M. Miao, J.G. Duh, B.S. Chiou, S. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 11, 609 (2000). doi:10.1023/A:1008928729212
Y.W. Shi, J. Tian, H. Hao, Z.D. Xia, Y.P. Lei, and F. Guo, J.␣Alloy Compd. 453, 180 (2008)
Z.G. Chen, Y.W. Shi, Z.D. Xia, Y.F. Yan, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1122 (2002). doi:10.1007/s11664-002-0052-4
B. Li, Y.W. Shi, Y.P. Lei, F. Guo, Z.D. Xia, B. Zong, J. Electron. Mater. 34, 217 (2005). doi:10.1007/s11664-005-0207-1
C.M.L. Wu, Y.W. Wong, J. Mater Sci: Mater. Electron. 18, 77 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10854-006-9022-6
JIS Z 3198-5, Japanese Industrial Standards Committee (2003)
H. Hao, J. Tian, Y.W. Shi, Y.P. Lei, Z.D. Xia, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 766 (2007). doi:10.1007/s11664-007-0138-0
J. Zhou, Y. Sun, F. Xue, J. Alloy Compd. 397, 260 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jallcom.2004.12.052
B. Huang, N.C. Lee, Int. Symp. Microelectron. Proc. 3906, 711 (1999)
Z.G. Chen, Y.W. Shi, Z.D. Xia, Y.F. Yan, Electron. Process Technol. 2, 53 (2003)
Z.D. Xia, Z.G. Chen, Y.W. Shi, N. Mu, N. Sun, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 564 (2002). doi:10.1007/s11664-002-0126-3
Ch.Zh. Liu, W. Zhang, M.L. Sui, J.K. Shang, Acta Metall. Sinica 41, 847 (2005)
C. Qin, J. Huang, K. Zhang, Y. Wang, J. Henan Univ. Sci. Technol. (Natural Science) 27, 5 (2006)
P.L. Tu, Y.C. Chan, J.K.L. Lai, IEEE. Trans. Comp. Packag. Manuf. Technol. B. 20, 87 (1997)
Z. Mei, J.W. Morris, J. Electron. Mater. 21, 599 (1992). doi:10.1007/BF02655427
H. Mayoori, A.G. Ramirez, S. Jin, J. Electron. Mater. 31, 1160 (2002). doi:10.1007/s11664-002-0005-y
A.G. Ramirez, H. Mayoori, S. Jin, Appl. Phys. Lett. 80, 398 (2002). doi:10.1063/1.1435075
T. Laurila, V. Vuorinen, J.K. Kivilahti, Mater. Sci. Semiconductor Process. 7, 307 (2004)
C.M. Chen, L.T. Chen, Y.S. Lin, J. Electron. Mater. 36, 168 (2007) doi:10.1007/s11664-006-0025-0
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dong, W., Shi, Y., Xia, Z. et al. Effects of Trace Amounts of Rare Earth Additions on Microstructure and Properties of Sn-Bi-Based Solder Alloy. J. Electron. Mater. 37, 982–991 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-008-0458-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-008-0458-8