Abstract
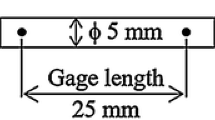
The effect of the rotating magnetic field (RMF) on the microstructure and properties of Sn-1.0Ag-0.5Cu-0.5Sb-0.07Ce alloy was investigated. The phase composition of the solder was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the grain size, shape, and phase distribution of the solder were determined by optical microscope (OM), scanning electron microscope (SEM), and energy disperse spectroscopy (EDS). Then, the differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) was employed to evaluate the thermal characteristics of the solder. Finally, the universal mechanical testing machine was used to measure the mechanical properties of the solder at different strain rates. The results showed that the size of β-Sn was refined and the distribution was more uniform, intermetallic compounds (IMCs) developed from long-strip-like or block shape to finely granular, and the layer spacing decreased after the application of a rotating magnetic field. The pasty range and the melting point of solder decreased slightly (from 5 to 4.7 °C) with the RMF. Meanwhile, RMF processing led to an increase (about 13.4%) in the elongation (El.%) of alloy, and the mechanical properties of the solder were enhanced. The research serves as a helpful reference for the development of low-content lead-free solder, which provides a potential solution to the reliability problem of the lead-free joint.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors affirm that the information/data of this research article is available inside the article.
References
I.C. Nnorom, O. Osibanjo, Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 52, 843–858 (2008)
M. Turner, D. Callaghan, Comput. Law Secur. Rev. 23, 73–76 (2007)
J. Wang, J. Chen, Z. Zhang, P. Zhang, Z. Yu, S. Zhang, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 34, 124–133 (2022)
G. Zeng, S. McDonald, K. Nogita, Microelectron. Reliab. 52, 1306–1322 (2012)
K. Zeng, K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 38, 55–105 (2002)
R.J. Coyle, K. Sweatman, B. Arfaei, JOM 67, 2394–2415 (2015)
A.M. El-Taher, S.E. Abd El Azeem, A.A. Ibrahiem, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 6199–6213 (2021)
M. Reid, J. Punch, M. Collins, C. Ryan, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. 20, 3–8 (2008)
J. Wang, L. Ma, Y. Wang, F. Guo, J. Mater. Sci. 57, 1623–1632 (2022)
K. Maslinda, A.S. Anasyida, M.S. Nurulakmal, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 489–502 (2016)
Y. Leong, A.S.M.A. Haseeb, Materials 9, 522–538 (2016)
Q.B. Tao, L. Benabou, V.N. Le, N.A.T. Nguyen, H. Nguyen-Xuan, Fatigue Fract. Eng. Mater. Struct. 43, 2883–2885 (2020)
A.E. Hammad, A.M. El-Taher, J. Electron. Mater. 43, 4146–4157 (2014)
M. Xin, X. Wang, F. Sun, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-022-09210-9
S. Chantaramanee, P. Sungkhaphaitoon, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 27607–27624 (2021)
G.Y. Li, B.L. Chen, X.Q. Shi, S.C.K. Wong, Z.F. Wang, Thin Solid Films 504, 421–425 (2006)
A.E. Hammad, Microelectron. Reliab. 87, 133–141 (2018)
X. Tu, D. Yi, J. Wu, B. Wang, J. Alloys Compd. 698, 317–328 (2017)
W. Zhu, F. Xu, X. Zhang, J. Qin, H. Lu, C. Wang, L. Tang, J. Chin. Rare ESOC. 40(02), 261–267 (2021)
A.A. El-Daly, A.A. Ibrahiem, J. Alloys Compd. 730, 47–56 (2018)
A.E. Hammad, M. Ragab, J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 18838–18847 (2019)
Z. Wang, J. Zhou, F. Liu, Y. Wu, N. Yan, Solder. Surf. Mt. Technol. (2022). https://doi.org/10.1108/SSMT-06-2022-0044
A.E. Hammad, M. Ragab, Microelectron. Reliab. 113, 113932–113940 (2020)
D.A.-A. Shnawah, S.B.M. Said, M.F.M. Sabri, I.A. Badruddin, F.X. Che, Microelectron. Reliab. 52, 2701–2708 (2012)
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, S. Gouda, J. Alloys Compd. 627, 268–275 (2015)
C. Pan, J. Zhang, K. Kou, Y. Zhang, G. Wu, Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 120, 1–8 (2018)
A.A. Ibrahiem, A.A. El-Daly, Microelectron. Reliab. 98, 10–18 (2019)
I. Abdullah, M.N. Zulkifli, A. Jalar, R. Ismail, M.A. Ambak, J. Electron. Mater. 48, 2826–2839 (2019)
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, Mater. Des. 51, 789–796 (2013)
A.A. El-Daly, A.M. El-Taher, Mater. Des. 47, 607–614 (2013)
T.G. Langdon, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 283, 266–273 (2000)
I. Shohji, T. Yoshida, T. Takahashi, S. Hioki, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 366, 50–55 (2004)
Q.S. Zhu, Z.G. Wang, S.D. Wu, J.K. Shang, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 502, 153–158 (2009)
G. Sharma, R.V. Ramanujan, T.R.G. Kutty, G.P. Tiwari, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 278, 106–112 (2000)
R. Mahmudi, A.R. Geranmayeh, H. Khanbareh, N. Jahangiri, Mater. Des. 30, 574–580 (2009)
Funding
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 51775388 and 11872048) and the Outstanding Young and Middle-aged Scientific Innovation Team of Colleges and Universities of Hubei Province (No. T2022015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. ZW contributed to experiments, data curation and writing—original draft. JZ contributed to writing—review & editing. JL, ZW and NY contributed to investigation and collection of literature. Fang Liu contributed to writing—review & editing, resources, and project administration.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest among them.
Ethical approval
The article does not involve any study performed on animals or human by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Liu, F., Liu, J. et al. Influences of rotating magnetic field on microstructure and properties of Sn–Ag–Cu–Sb–Ce solder alloy. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 34, 504 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09961-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-023-09961-z