Abstract
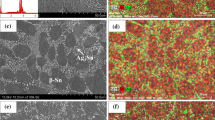
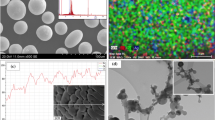
The present study investigates the changes in microstructures and their effects on electrical resistivity, moduli, hardness and damping properties in an environmental-friendly eutectic Sn–3.0Ag–0.5Cu (wt%) solder alloy when exposed to harsh service environments. A thorough microstructural investigation was conducted by scanning electron microscopy with diffraction analysis and transmission electron microscopy. In the as-received Sn–Ag–Cu solder alloy, very-fine needle-shaped Ag3Sn and Cu6Sn5 intermetallic compound (IMC) particles are found to be uniformly dispersed in the eutectic colony. However, after exposing at harsh service environments (e.g., aging temperature at 150 °C for various aging time) these IMC particles were appeared with coarse structure. This coarsening nature of IMC particles degraded the mechanical properties of electronic interconnections. This was confirmed by measuring a range of electrical and mechanical properties that included electrical resistivity, Young’s moduli, shear moduli and microhardness. A comparison between the as-received and isothermal aging solder alloy shows that the electrical resistivity of as-received and 60 days isothermal aged alloys was about 12.5 and 10.0 μΩ cm, respectively. Further, the degradation in shear moduli and hardness was about 27.3 and 25.5%, respectively. However the isothermal aged solder alloy displayed high damping property as compare to the as-received alloy.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
B.L. Silva, A. Garcia, J.E. Spinelli, J. Alloys Compd. 691, 600 (2017)
A. Fawzy, S.A. Fayek, M. Sobhy, E. Nassr, M.M. Mousa, G. Saad, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 603, 1 (2014)
Z. Yang, W. Zhou, P. Wu, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 590, 295 (2014)
Y. Plevachuk, W. Hoyer, I. Kaban, M. Kohler, R. Novakovic, J. Mater. Sci. 45, 2051 (2010)
H.R. Kotadia, P.D. Howes, S.D. Mannan, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 1253 (2014)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 781 (2016)
F. Gnecco, E. Ricci, S. Amore, D. Giuranno, G. Borzone, G. Zanicchi, R. Novakovic, Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 27, 409 (2007)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 11273 (2016)
A.K. Gain, T. Fouzder, Y.C. Chan, W.K.C. Yung, J. Alloys Compd. 509, 3319 (2011)
L. Zhang, K.N. Tu, Mater. Sci. Eng. R 82, 1 (2014)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 7524 (2016)
G. Chen, H. Peng, V.V. Silberschmidt, Y.C. Chan, C. Liu, F. Wu, J. Alloys Compd. 685, 680 (2016)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, Y.C. Chan, J. Mater. Sci. 26, 7039 (2015)
A.K. Gain, T. Fouzder, Y.C. Chan, A. Sharif, N.B. Wong, W.K.C. Yung, J. Alloys Compd. 506, 216 (2010)
E.A. Eid, A.N. Fouda, M.E.-S. Duraia, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 657, 104 (2016)
S.H. Chang, S.K. Wu, Scripta Mater. 64, 757 (2011)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Alloys Compd. 617, 779 (2014)
A.K. Gain, Y.C. Chan, Microelectron. Reliab. 54, 945 (2014)
ASTM International, Standard test method for dynamic Young’s modulus, shear Modulus, and Poisson’s ratio by impulse excitation of vibration. ASTM E1876- 09 (ASTM International, West Conshohocken, 2009)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, M.Z. Quadir, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 662, 258 (2016)
R. Novakovic, T. Lanata, S. Delsante, G. Borzone, Mater. Chem. Phys. 137, 458 (2012)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, M.Z. Quadir, Mater. Des. 110, 275 (2016)
K.D. Kim, D.D.L. Chung, J. Electron. Mater. 31(9), 933 (2002)
P. Babaghorbani, S.M.L. Nai, M. Gupta, J. Alloys Compd. 478, 458 (2009)
A.K. Gain, L. Zhang, J. Mater. Sci. 27, 3982 (2016)
Y. Sutou, T. Omori, N. Koeda, R. Kainuma, K. Ishida, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 438–440, 743 (2006)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the financial support provided by The University of New South Wales (UNSW) through the project InfoEd Ref: RG124326. The authors would also like to thank Mr. Tit Wah Chan, Department of Physics and Materials Science, City University of Hong Kong, for helping in evaluating the damping properties.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gain, A.K., Zhang, L. Effect of isothermal aging on microstructure, electrical resistivity and damping properties of Sn–Ag–Cu solder. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 28, 9363–9370 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6675-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-017-6675-2