Abstract
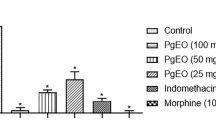
Eugenia pohliana DC.(Myrtaceae) is used in folk medicine by communities in Brazil. However, there are no reports on its biological activity. This is the first study to identify the components of E. pohliana essential oil (EpEO) and evaluate their antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities in an in vivo model at doses of 25, 50, and 100 mg/kg. The essential oil (EO) was obtained by hydrodistillation, and the analysis was performed by gas chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry. Antinociceptive activity was evaluated by writhing tests, tail movement, and formalin (neurogenic and inflammatory pain); naloxone was used to determine the nociception mechanism. Anti-inflammatory activity was assessed by oedema and peritonitis tests. We found that (E)-β-caryophyllene (BCP) (15.56%), δ-cadinene (11.24%) and α-cadinol (10.89%) were the major components. In the writhing test, there was a decrease in writing by 42.95–70.70%, in the tail movement, an increase in latency time by 69.12–86.63%, and in the formalin test, there was a reduction in pain neurogenic by 29.54–61.74%, and inflammatory pain by 37.42–64.87%. The antinociceptive effect of EpEO occurs through the activation of opioid receptors. In addition, a reduction in inflammation by 74.93‒81.41% was observed in the paw edema test and inhibition of the influx of leukocytes by 51.86‒70.38% and neutrophils by 37.74‒54.72% in the peritonitis test. It was concluded that EpEO has antinociceptive effect by the opioid pathway, as shown by the inhibitory effect of naloxone, and anti-inflammatory actions, and that its use does not cause hemolytic damage or behavioral change.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
We declare for all purposes that the National Council for Scientific Research and Development (CNPq), the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (Capes), and the Fundação de Amparo a Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco (FACEPE) have made available scholarships of research and financial support to researchers, for the acquisition of inputs and materials.
References
Adams RP (2007) Identification of essential oil components by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry, 4th edn. Allured Publ. Corp, Illinois
Aguilar-Ávila DS, Flores-Soto ME, Tapia-Vázquez C, Pastor-Zarandona OA, López-Roa RI, Viveros-Paredes JM (2019) β-caryophyllene, a natural sesquiterpene, attenuates neuropathic pain and depressive-like behavior in experimental diabetic mice. J Med Food 22(5):460–468. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2018.0157
Archer J (1973) Tests for emotionality in rats and mice: a review. Anim Behav 21:205–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0003-3472(73)80065-X
Astani A, Reichling J, Schnitzler P (2011) Screening for antiviral activities of isolated compounds from essential oils. Evidence-based complement. Altern Med 2011:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/ecam/nep187
Azevedo Neto J, Costanzini A, Giorgio R, Lambert DG, Ruzza C, Calò G (2020) Biased versus partial agonism in the search for safer opioid analgesics. Molecules 25:3870. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25173870
Bande-Borujeni S, Zandi-Sohani N, Ramezani L (2018) Chemical composition and bioactivity of essential oil from Eucalyptus occidentalis leaves against two stored product pests. Int J Trop Insect Sci 38:216–223. https://doi.org/10.1017/S1742758418000085
Barbosa DCS, Holanda VN, Assis CRD, Aguiar JCROF, Nascimento PH, Silva WV, Navarro DMAF, Silva MV, Lima VLM, Correia MTS (2020) Chemical composition and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory potential, in silico, of Myrciaria floribunda (H. West ex Willd.) O. Berg fruit peel essential oil. Ind Crops Prod 151:112372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112372
Barros FJ, Costa RJO, Cesário FRAS, Rodrigues LB, Costa JGM, Coutinho HDM, Galvao HBF, Menezes IRA (2016) Activity of essential oils of Piper aduncum anf and Cinnamomum zeylanicum by evaluating osmotic and morphologic fragility of erythrocytes. Eur J Integr Med 8:505–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2016.02.011
Bezerra Filho CM, Silva LCN, Silva MV, Løbner-Olesen A, Struve C, Krogfelt KA, Correia MTS, Oliva MLV (2020) Antimicrobial and antivirulence action of Eugenia brejoensis essential oil in vitro and in vivo invertebrate models. Front Microbiol 11:424. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2020.00424
Brito LF, Oliveira HBM, Neves Selis N, Souza CLS, Júnior MNS, Souza EP, da Silva LSC, Souza Nascimento F, Amorim AT, Campos GB, Oliveira MV, Yatsuda R, Timenetsky J, Marques LM (2019) Anti-inflammatory activity of β -caryophyllene combined with docosahexaenoic acid in a model of sepsis induced by Staphylococcus aureus in mice. J Sci Food Agric 99:5870–5880. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.9861
Chang H-J, Kim J-M, Lee J-C, Kim W-K, Chun HS (2013) Protective effect of β-caryophyllene, a natural bicyclic sesquiterpene, against cerebral ischemic injury. J Med Food 16:471–480. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2012.2283
Costa WK, Oliveira JRS, Oliveira AM, Santos IBS, Cunha RX, Freitas AFS, Silva JWLM, Silva VBG, Aguiar JCROF, Silva AG, Navarro DMAF, Lima VLM, da Silva MV (2020) Essential oil from Eugenia stipitata McVaugh leaves has antinociceptive, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic activities without showing toxicity in mice. Ind Crops Prod 144:112059. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112059
Costa WK, Nascimento MF, Santos CRB, Navarro DMAF, Napoleão TH, Correia MTS, Brayner FA, Oliveira AM, Silva MV (2022) Oral administration of essential oil from Psidium glaziovianum Kiaersk leaves alleviates pain and inflammation in mice. Inflammopharmacology 30(2):599–607
Durazzini AMS, Machado CHM, Fernandes CC, Miranda M (2019) Chemical composition and effect of hydrodistillation times on the yield of essential oil from Eugenia pyriformis leaves. Orbital Electron J Chem 11:334–338. https://doi.org/10.17807/orbital.v11i5.1221
File SE, Wardill AG (1975) Validity of head-dipping as a measure of exploration in a modified hole-board. Psychopharmacologia 44:53–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00421184
Franco CJP, Ferreira OO, Moraes ÂABM, Varela ELP, Nascimento LD, Percário S, Oliveira MS, Andrade EHA (2021) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of essential oils from Eugenia patrisii Vahl, E. punicifolia (Kunth) DC., and Myrcia tomentosa (Aubl.) DC., leaf of family myrtaceae. Molecules 26:3292. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26113292
Gertsch J, Leonti M, Raduner S, Racz I, Chen J-Z, Xie X-Q, Altmann K-H, Karsak M, Zimmer A (2008) Beta-caryophyllene is a dietary cannabinoid. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:9099–9104. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0803601105
Gonzalez MS, Lima BG, Oliveira AFR, Nunes DD, Fernandes CP, Santos MG, Tietbohl LAC, Mello CB, Rocha L, Feder D (2014) Effects of essential oil from leaves of Eugenia sulcata on the development of agricultural pest insects. Rev Bras Farmacogn 24:413–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2014.05.003
Guimarães AG, Melo MS, Bonfim RR, Passos LO, Machado SMF, Ribeiro AS, Sobral M, Thomazzi SM, Quintans-Júnior LJ (2009) Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of the essential oil of Eugenia candolleana DC., myrtaceae, on mice. Rev Bras Farmacogn 19:883–887. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2009000600016
Guo X, Shang X, Li B, Zhou XZ, Wen H, Zhang J (2017) Acaricidal activities of the essential oil from Rhododendron nivale Hook. f. and its main compund, δ-cadinene against Psoroptes cuniculi. Vet Parasitol 236:51–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vetpar.2017.01.028
Han X, Parker TL (2017) Anti-inflammatory activity of clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) essential oil in human dermal fibroblasts. Pharm Biol 55:1619–1622. https://doi.org/10.1080/13880209.2017.1314513
Hirano SI, Ichikawa Y, Sato B, Yamamoto H, Takefuji Y, Satoh F (2021) Potential therapeutic applications of hydrogen in chronic inflammatory diseases: possible inhibiting role on mitochondrial stress. Int J Mol Sci 22:2549. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052549
Hunskaar S, Hole K (1987) The formalin test in mice: dissociation between inflammatory and non-inflammatory pain. Pain 30:103–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(87)90088-1
Jacoby RP, Koprivova A, Kopriva S (2021) Pinpointing secondary metabolites that shape the composition and function of the plant microbiome. J Exp Bot 72:57–69. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eraa424
Jimenez PC, Fortier SC, Lotufo TMC, Pessoa C, Moraes MEA, Moraes MO, Costa-Lotufo LV (2003) Biological activity in extracts of ascidians (Tunicata, Ascidiacea) from the northeastern Brazilian coast. J Exp Mar Bio Ecol 287:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-0981(02)00499-9
Khatun A, Imam MZ, Rana MS (2015) Antinociceptive effect of methanol extract of leaves of Persicaria hydropiper in mice. BMC Complement Altern Med 15:63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12906-015-0558-y
Klauke AL, Racz I, Pradier B, Markert A, Zimmer AM, Gertsch J, Zimmer A (2014) The cannabinoid CB2 receptor-selective phytocannabinoid beta-caryophyllene exerts analgesic effects in mouse models of inflammatory and neuropathic pain. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:608–620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euroneuro.2013.10.008
Kotlinska JH, Gibula-Bruzda E, Witkowska E, Chung NN, Schiller PW, Izdebski J (2013) Antinociceptive effects of two deltorphins analogs in the tail-immersion test in rats. Peptides 39:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2012.11.008
Koyama S, Purk A, Kaur M, Soini H, Novotny M, Davis K, Kao C, Matsunami H, Mescher A (2019) Beta-caryophyllene enhances wound healing through multiple routes. PLoS ONE 14:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0216104
Kraeuter AK, Guest PC, Sarnyai Z (2019) The elevated plus maze test for measuring anxiety-like behavior in rodents. In: Guest P (eds) Pre-clinical models. Methods in molecular biology. Humana Press, New York, pp 69–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8994-2_4
Kujur A, Kumar A, Prakash B (2021) Elucidation of antifungal and aflatoxin B1 inhibitory mode of action of Eugenia caryophyllata L. essential oil loaded chitosan nanomatrix against Aspergillus flavus. Pestic Biochem Physiol 172:104755. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pestbp.2020.104755
Lago JHG, Souza ED, Mariane B, Pascon R, Vallim MA, Martins RCC, Baroli AA, Carvalho BA, Soares MG, dos Santos RT, Sartorelli P (2011) Chemical and biological evaluation of essential oils from two species of myrtaceae—Eugenia uniflora L. and Plinia trunciflora (O. Berg) Kausel. Molecules 16:9827–9837. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules16129827
Lazarini JG, Franchin M, Soares JC, Nani BD, Massarioli AP, Alencar SM, Rosalen PL (2020) Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant potential, in vivo toxicity, and polyphenolic composition of Eugenia selloi B.D.Jacks. (pitangatuba), a Brazilian native fruit. PLoS ONE 15:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0234157
Lee W, Lee CH, Lee J, Jeong Y, Park JH, Nam IJ, Lee DS, Lee HM, Lee J, Yun N, Song J, Choi S, Kim S (2021) Botanical formulation, TADIOS, alleviates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced acute lung injury in mice via modulation of the Nrf2-HO-1 signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 270:113795. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.113795
Lewanowitsch T, Miller JH, Irvine RJ (2006) Reversal of morphine, methadone and heroin induced effects in mice by naloxone methiodide. Life Sci 78:682–688. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2005.05.062
Maayah ZH, Takahara S, Ferdaoussi M, Dyck JRB (2020) The molecular mechanisms that underpin the biological benefits of full-spectrum cannabis extract in the treatment of neuropathic pain and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866:165771. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165771
Macedo JGF, Rangel JML, Santos MO, Camilo CJ, Costa JGM, Souza MMA (2021) Therapeutic indications, chemical composition and biological activity of native Brazilian species from Psidium genus (myrtaceae): a review. J Ethnopharmacol 278:114248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.114248
Matsuda M, Huh Y, Ji RR (2019) Roles of inflammation, neurogenic inflammation, and neuroinflammation in pain. J Anesth 33:131–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00540-018-2579-4
Mazine FF, Souza VC, Sobral M, Forest F, Lucas E (2014) A preliminary phylogenetic analysis of Eugenia (Myrtaceae: Myrteae), with a focus on neotropical species. Kew Bull 69:9497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12225-014-9497-x
McParland A, Moulton J, Brann C, Hale C, Otis Y, Ganter G (2021) The brinker repressor system regulates injury-induced nociceptive sensitization in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Pain 17:17448069211037400. https://doi.org/10.1177/17448069211037401
Meccariello R, Santoro A, D’Angelo S, Morrone R, Fasano S, Viggiano A, Pierantoni R (2020) The epigenetics of the endocannabinoid system. Int J Mol Sci 21:1113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031113
Mendes JF, Martins HHA, Otoni CG, Santana NA, Silva RCS, Silva AG, Silva MV, Correia MTS, Machado G, Pinheiro ACM, Piccoli RH, Oliveira JE (2018) Chemical composition and antibacterial activity of Eugenia brejoensis essential oil nanoemulsions against Pseudomonas fluorescens. LWT 93:659–664. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2018.04.015
Mesquita PRR, Nunes EC, Santos FN, Bastos LP, Costa MAPC, Rodrigues MF, Andrade JB (2017) Discrimination of Eugenia uniflora L. biotypes based on volatile compounds in leaves using HS-SPME/GC–MS and chemometric analysis. Microchem J 130:79–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.08.005
Mondal M, Quispe C, Sarkar C, Bepari TC, Alam MJ, Saha S, Ray P, Rahim MA, Islam MT, Setzer WN, Salehi B, Ahmadi M, Abdalla M, Sharifi-Rad J, Kundu SK (2021) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory potential of essential oil of Eucalyptus camaldulensis Leaf. In vivo and in silico studies. Nat Prod Commun 16:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/1934578X211007634
Morikawa T, Ashitani T, Kofujita H, Takahashi K (2014) Antitermitic activity of extracts from Chamaecyparis obtusa branch heartwood. Eur J Wood Wood Prod 72:651–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-014-0830-8
Mujumdar AM, Naik DG, Waghole RJ, Kulkarni DK, Kumbhojkar MS (2000) Pharmacological studies on sterculia foetida leaves. Pharm Biol 38:13–17. https://doi.org/10.1076/1388-0209(200001)3811-BFT013
Neves IA, Rezende SRF, Kirk JM, Pontes EG, Carvalho MG (2017) Composition and larvicidal activity of essential oil of Eugenia candolleana DC. (Myrtaceae) against Aedes aegypti. Rev Virtual Quim 9:2305–2315. https://doi.org/10.21577/1984-6835.20170138.
Nunes TAL, Costa LH, Sousa JMS, Souza VMR, Rodrigues RRL, Val MCA, Pereira ACTC, Ferreira GP, Silva MV, Costa JMAR, Véras LMC, Diniz RC, Rodrigues KAF (2021) Eugenia piauhiensis Vellaff. essential oil and γ-elemene its major constituent exhibit antileishmanial activity, promoting cell membrane damage and in vitro immunomodulation. Chem Biol Interact 339:109429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2021.109429
Oliveira AM, Freire MOL, Silva WAV, Ferreira MRA, Paiva PMG, Soares LAL, Medeiros PL, Carvalho BM, Napoleão TH (2018) Saline extract of Pilosocereus gounellei stem has antinociceptive effect in mice without showing acute toxicity and altering motor coordination. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 95:289–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.04.004
Oliveira AM, Nascimento MF, Ferreira MRA, Moura DF, Souza TGS, Silva GC, Ramos EHS, Paiva PMG, Medeiros PL, Silva TG, Soares LAL, Chagas CA, Souza IA, Napoleão TH (2016) Evaluation of acute toxicity, genotoxicity and inhibitory effect on acute inflammation of an ethanol extract of Morus alba L. (Moraceae) in mice. J Ethnopharmacol 194:162–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.004
Oliveira AM, Freitas AFS, Costa MDS, Torres MKS, Castro YAA, Almeida AMR, Paiva PMG, Carvalho BM, Napoleao TH (2021) Pilosocereus gounellei (Cactaceae) stem extract decreases insulin resistance, inflammation, oxidative stress, and cardio-metabolic risk in diet-induced obese mice. J Ethnopharmacol 265:113327
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463:3–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(03)01272-X
Russo C, Edwards KD, Margetts G, Kleidonas S, Zaibi NS, Clapham JC, Zaibi MS (2021) Effects of Salvia officinalis L. and Chamaemelum nobile (L.) extracts on inflammatory responses in two models of human cells: primary subcutaneous adipocytes and neuroblastoma cell line (SK-N-SH). J Ethnopharmacol 268:113614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2020.113614
Sa FAS, Paula JAM, Santos PA, Oliveira LAR, Oliveira GAR, Liao LM, Paula JR, Silva MRR (2017) Phytochemical analysis and antimicrobial activity of Myrcia tomentosa (Aubl.) DC. Leaves Mol 22:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules22071100
Sampaio MGV, Santos CRB, Vandesmet LCS, Santos BS, Santos IBS, Correia MTS, Martins ALB, Silva LCN, Menezes IRA, Gomez MCV, Silva MV (2021) Chemical composition, antioxidant and antiprotozoal activity of Eugenia gracillima Kiaersk. leaves essential oil. Nat Prod Res 35:1914–1918. https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2019.1644506
Santos IBS, Santos B, Oliveira JRS, Costa WK, Zagmignan A, Silva LCN, Ferreira MRA, Lermen VL, Lermen MSBS, Silva AG, Ximenes RM, Soares LAL, Paiva PMG, Lima VLM, Correia MTS, Silva MV (2020) Antioxidant action and in vivo anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive activities of Myrciaria floribunda fruit peels: possible involvement of opioidergic system. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci 2020:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1258707
Shah SA, Gupta AS, Kumar P (2021) Emerging role of cannabinoids and synthetic cannabinoid receptor 1/cannabinoid receptor 2 receptor agonists in cancer treatment and chemotherapy-associated cancer management. J Cancer Res Ther 17:1–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_488_18
Silva JKR, Andrade EH, Barreto LH, Silva NCF, Ribeiro A, Montenegro RC, Maia JG (2017) Chemical composition of four essential oils of Eugenia from the Brazilian Amazon and their cytotoxic and antioxidant activity. Medicines 4:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicines4030051
Silva MVSG, Silva SA, Teixera TL, Oliveira A, Morais SAL, Silva CV, Espindola LS, Sousa RMF (2021) Essential oil from leaves of Eugenia calycina Cambes: natural larvicidal against Aedes aegypti. J Sci Food Agric 101:1202–1208. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10732
Silva ROM, Castro JWG, Dantas Junior OM, Araújo ACJ, Leandro MKNS, Costa RJO, Pinto LL, Leandro LMG, Silva LE, Amaral W, Parabocz LD, Ferriani AP, Garcia B, Maia BHLNS, Rocha JE, Bezerra CF, Freitas TS, Costa MS, Campina FF, Matias EFF, Iriti M, Coutinho HDM (2019) Photoinduced antibacterial activity of the essential oils from Eugenia brasiliensis lam and Piper mosenii C. DC. by blue led light. Antibiotics 8:242. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics8040242
Silva SMM, Costa CRR, Gelfuso GM, Guerra ENS, Nóbrega YKM, Gomes SM, Pic-Taylor A, Fonseca-Bazzo YM, Silveira D, Magalhães PO (2018) Wound healing effect of essential oil extracted from Eugenia dysenterica DC (Myrtaceae) leaves. Molecules 24:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24010002
Sobeh M, El-Raey M, Rezq S, Abdelfattah MA, Petruk G, Osman S, El-Shazly AM, El-Beshbishy HA, Mahmoud MF, Wink M (2019) Chemical profiling of secondary metabolites of Eugenia uniflora and their antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, pain killing and anti-diabetic activities: a comprehensive approach. J Ethnopharmacol 240:111939. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2019.111939
Souza AM, Oliveira VB, Oliveira CF, Betim FCM, Pacheco SDG, Cogo LL, Miguel OG, Miguel MD (2021) Chemical composition and in vitro antimicrobial activity of the essential oil obtained from Eugenia pyriformis Cambess (Myrtaceae). Braz Arch Biol Technol 64:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1590/1678-4324-2021200663
Sousa RMF, Morais SAL, Vieira RBK, Napolitano DR, Guzman VB, Moraes TS, Cunha LCS, Martins CHG, Chang R, Aquino FJT, Nascimento EA, Oliveira A (2015) Chemical composition, cytotoxic, and antibacterial activity of the essential oil from Eugenia calycina Cambess. leaves against oral bacteria. Ind Crops Prod 65:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.11.050
Taher YA, Samud AM, El-Taher FE, ben-Hussin G, Elmezogi JS, Al-Mehdawi BF, Salem HA, (2015) Experimental evaluation of anti-inflammatory, antinociceptive and antipyretic activities of clove oil inmice. Libyan J Med 10:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3402/ljm.v10.28685
Trinh HKT, Pham LD, Le KM, Park HS (2021) Pharmacogenomics of hypersensitivity to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Front Genet 12:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.647257
Wang W, Zhang Y, Yang Z, He Q (2021) Effects of incorporation with clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) essential oil (CEO) on overall performance of chitosan as active coating. Int J Biol Macromol 166:578–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.215
Winter CA, Risley EA, Nuss GW (1962) Carrageenin-Induced Edema in Hind Paw of the Rat as an Assay for Antiinflammatory Drugs. Exp Biol Med 111:544–547. https://doi.org/10.3181/00379727-111-27849
Wongrakpanich S, Wongrakpanich A, Melhado K, Rangaswami J (2018) A comprehensive review of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in the elderly. Aging Dis 9:143–150. https://doi.org/10.14336/AD.2017.0306
Yoo H-J, Jwa S-K (2018) Inhibitory effects of β-caryophyllene on Streptococcus mutans biofilm. ArCh Oral Biol 88:42–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2018.01.009
Acknowledgements
The authors express their gratitude to the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq) for financial support and investigator research grants (DMAFN, THN, and MTSC). We are also grateful to the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES; Finance Code 001) and the Fundação de Amparo à Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco (FACEPE) for financial support.
Funding
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ALD, JBG, WKC, AMO performed the methodologies. WKC, AMO analyzed and interpreted the results. BOV performed the essential oil extraction. ALD, WKC, AMO wrote the article. JCROFA, DMAFN performed the analysis and chemical characterization of essential oil. AMO, MVS performed a critical review of the final version of the article. MTSC, THN, AMO, MVS contributed reagents, materials and analytical tools.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
do Nascimento, A.L., Guedes, J.B., Costa, W.K. et al. Essential oil from the leaves of Eugenia pohliana DC. (Myrtaceae) alleviate nociception and acute inflammation in mice. Inflammopharmacol 30, 2273–2284 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01067-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-022-01067-y