Abstract
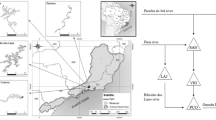
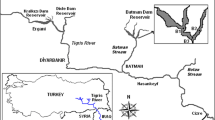
Trait-based classifications can efficiently capture species’ responses to environmental gradients and their impacts on ecosystem functioning. Thus, the clustering of phytoplankton species into functional groups can improve the understanding of their relationships with the environment and help to predict their response to environmental changes. Accordingly, this study aimed to create habitat templates of Reynolds phytoplankton functional groups (RFGs) in tropical drinking water reservoirs to describe, explain, and predict their occurrence and formation of blooms. We analyzed the structure of RFGs in 10 tropical reservoirs, in humid and semiarid regions of Brazil, and defined their relationships with 10 environmental variables. We designated the habitat template based on niche differentiation, thresholds for the occurrences and bloom formation, cluster analyses, and generalized additive models. We identified 136 species, assembled in 20 RFGs. Six groups of habitat templates were recognized based on environmental conditions and dominant RFGs, usually represented by bloom-forming species of cyanobacteria, dinoflagellates, green algae, and diatoms. The functional groups D, X1, and P presented the most restrictive occurrences, while RFGs M and SN displayed the widest, occurring in almost all sets of conditions. Moreover, salinity was the best predictor of RFGs’ biomass (higher R2), followed by depth, soluble reactive phosphorus, irradiance, water transparency, and dissolved inorganic nitrogen. Our approach improves the understanding of how RFGs interact with environmental gradients in tropical reservoirs, helping water managers to adopt sustainable practices to control algal blooms, based on predictions of the future state of dominance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amorim, C. A. & A. N. Moura, 2020. Effects of the manipulation of submerged macrophytes, large zooplankton, and nutrients on a cyanobacterial bloom: A mesocosm study in a tropical shallow reservoir. Environmental Pollution 265: 114997.
Amorim, C. A. & A. N. Moura, 2021. Ecological impacts of freshwater algal blooms on water quality, plankton biodiversity, structure, and ecosystem functioning. Science of The Total Environment 758: 143605.
Amorim, C. A., C. R. Valença, R. H. Moura-Falcão & A. N. Moura, 2019. Seasonal variations of morpho-functional phytoplankton groups influence the top-down control of a cladoceran in a tropical hypereutrophic lake. Aquatic Ecology 53: 453–464.
Amorim, C. A., Ê. W. Dantas & A. N. Moura, 2020. Modeling cyanobacterial blooms in tropical reservoirs: The role of physicochemical variables and trophic interactions. Science of The Total Environment 744: 140659.
Anagnostidis, K. & J. Komárek, 1988. Modern approach to the classification system of cyanophytes. 3 – Oscillatoriales. Algological Studies/Archiv für Hydrobiologie 50/53: 327–472.
Barbosa, L. G., C. A. Amorim, G. Parra, J. Laço Portinho, M. Morais, E. A. Morales & R. F. Menezes, 2020. Advances in limnological research in Earth’s drylands. Inland Waters 10: 429–437.
Benincà, E., B. Ballantine, S. P. Ellner & J. Huisman, 2015. Species fluctuations sustained by a cyclic succession at the edge of chaos. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 112: 6389–6394.
Borics, G., A. Abonyi, N. Salmaso & R. Ptacnik, 2021. Freshwater phytoplankton diversity: models, drivers and implications for ecosystem properties. Hydrobiologia 848: 53–75.
Borics, G., V. B. Béres, I. Bácsi, B. A. Lukács, E. T. Krasznai, Z. Botta-Dukát & G. Várbíró, 2020. Trait convergence and trait divergence in lake phytoplankton reflect community assembly rules. Scientific Reports 10: 19599.
Braga, G. G. & V. Becker, 2020. Influence of water volume reduction on the phytoplankton dynamics in a semi-arid man-made lake: A comparison of two morphofunctional approaches. Anais Da Academia Brasileira De Ciências Academia Brasileira De Ciências 92: 20181102.
Brasil, J., J. L. Attayde, F. R. Vasconcelos, D. D. F. Dantas & V. L. M. Huszar, 2016. Drought-induced water-level reduction favors cyanobacteria blooms in tropical shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 770: 145–164.
Chorus, I. & E. Spijkerman, 2021. What Colin Reynolds could tell us about nutrient limitation, N: P ratios and eutrophication control. Hydrobiologia 848: 95–111.
Costa, M. R. A., J. L. Attayde & V. Becker, 2016. Effects of water level reduction on the dynamics of phytoplankton functional groups in tropical semi-arid shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia Springer 778: 75–89.
Crossetti, L. O., D. C. Bicudo, L. M. Bini, R. B. Dala-Corte, C. Ferragut & C. E. M. Bicudo, 2019. Phytoplankton species interactions and invasion by Ceratium furcoides are influenced by extreme drought and water-hyacinth removal in a shallow tropical reservoir. Hydrobiologia 831: 71–85.
Dumont, H. J., I. Van de Velde & S. Dumont, 1975. The dry weight estimate of biomass in a selection of Cladocera, Copepoda and Rotifera from the plankton, periphyton and benthos of continental waters. Oecologia 19: 75–97.
Elliott, J. A., 2021. Modelling lake phytoplankton communities: recent applications of the PROTECH model. Hydrobiologia 848: 209–217.
Ger, K. A., P. Urrutia-Cordero, P. C. Frost, L.-A. Hansson, O. Sarnelle, A. E. Wilson & M. Lürling, 2016. The interaction between cyanobacteria and zooplankton in a more eutrophic world. Harmful Algae 54: 128–144.
Golterman, H. L., R. S. Clymo & M. A. H. Ohnstad, 1971. Chemical analysis of fresh waters, Blackwell Scientific Publishers, Oxford:
Herrman, K. S., V. Bouchard & R. H. Moore, 2008. Factors affecting denitrification in agricultural headwater streams in Northeast Ohio, USA. Hydrobiologia 598: 305–314.
Hillebrand, H., C.-D. Dürselen, D. Kirschtel, U. Pollingher & T. Zohary, 1999. Biovolume calculation for pelagic and benthic microalgae. Journal of Phycology 35: 403–424.
Hutchinson, G. E., 1961. The paradox of the plankton. The American Naturalist 95: 137–145.
Ibelings, B. W., M. Bormans, J. Fastner & P. M. Visser, 2016. CYANOCOST special issue on cyanobacterial blooms: synopsis – a critical review of the management options for their prevention, control and mitigation. Aquatic Ecology 50: 595–605.
Janssen, A. B. G., S. Hilt, S. Kosten, J. J. M. Klein, H. W. Paerl & D. B. Van de Waal, 2021. Shifting states, shifting services: linking regime shifts to changes in ecosystem services of shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 66: 1–12.
Jeppesen, E., D. E. Canfield, R. W. Bachmann, M. Søndergaard, K. E. Havens, L. S. Johansson, T. L. Lauridsen, T. Sh, R. P. Rutter, G. Warren, G. Ji & M. V. Hoyer, 2020. Toward predicting climate change effects on lakes: a comparison of 1656 shallow lakes from Florida and Denmark reveals substantial differences in nutrient dynamics, metabolism, trophic structure, and top-down control. Inland Waters 10: 197–211.
John, D. M., B. A. Whitton & A. J. Brook, 2002. The Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Keddy, P. & E. Weiher, 1999. The scope and goals of research on asssembly rules. In Weiher, E. & P. Keddy (eds), Ecological Assembly Rules: Perspectives, Advances, Retreats Cambridge University Press, Cambridge: 1–20.
Komárek, J. & B. Fott, 1983. Chlorophyceae: Chlorococcales, Begründent von August Thienemann, Stuttgart.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 1986. Modern approach to the classification system of Cyanophytes, 2: Chroococcales. Algological Studies/archiv Für Hydrobiologie 73: 157–226.
Komárek, J. & K. Anagnostidis, 2005. Cyanoprokayota 2: Oscillatoriales. In Budel, B., L. Krienitz, G. Gartner & M. Schargerl (eds), Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa Elsevier, Müncher: 1–759.
Kosten, S., V. L. M. Huszar, N. Mazzeo, M. Scheffer, L. S. L. Sternberg & E. Jeppesen, 2009. Lake and watershed characteristics rather than climate influence nutrient limitation in shallow lakes. Ecological Applications 19: 1791–1804.
Krammer, K. & H. Lange-Bertalot, 1991. Bacillariophyceae: Achnanthaceae. Kritische Ergänzungen zu Navicula (Lineolatae) und Gomphonema. In Ettl, H., G. Gärtner, J. Gerloff, H. Heynig & D. Mollenhauer (eds), Süβwasserflora von Mitteleuropa Gustav Fischer Verlag, Stuttgart: 1–486.
Kruk, C. & A. M. Segura, 2012. The habitat template of phytoplankton morphology-based functional groups Phytoplankton responses to human impacts at different scales. Hydrobiologia 698: 191–202.
Kruk, C., M. Devercelli & V. L. Huszar, 2021. Reynolds Functional Groups: a trait-based pathway from patterns to predictions. Hydrobiologia 848: 113–129.
Kruk, C., M. Devercelli, V. L. M. Huszar, E. Hernández, G. Beamud, M. Diaz, L. H. S. Silva & A. M. Segura, 2017. Classification of Reynolds phytoplankton functional groups using individual traits and machine learning techniques. Freshwater Biology 62: 1681–1692.
Kruk, C., V. L. H. Huszar, E. T. H. M. Peeters, S. Bonilla, L. Costa, M. Lürling, C. S. Reynolds & M. Scheffer, 2010. A morphological classification capturing functional variation in phytoplankton. Freshwater Biology 55: 614–627.
Long, S., T. Zhang, J. Fan, C. Li & K. Xiong, 2020. Responses of phytoplankton functional groups to environmental factors in the Pearl River, South China. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 27: 42242–42253.
Lund, J. W. G., C. Kipling & E. D. Le Cren, 1958. The inverted microscope method of estimating algal numbers and the statistical basis of estimations by counting. Hydrobiologia 11: 143–170.
Mantzouki, E., P. M. Visser, M. Bormans & B. W. Ibelings, 2016. Understanding the key ecological traits of cyanobacteria as a basis for their management and control in changing lakes. Aquatic Ecology 50: 333–350.
Moura, A. N., N. K. C. Aragão-Tavares & C. A. Amorim, 2018. Cyanobacterial blooms in freshwaters bodies in a semiarid region, northeastern Brazil: a review. Journal of Limnology 77: 179–188.
Oksanen, J., F. G. Blanchet, M. Friendly, R. Kindt, P. Legendre, D. McGlinn, P. R. Minchin, R. B. O'Hara, G. L. Simpson, P. Solymos, M. H. H. Stevens, E. Szoecs, & H. Wagner, 2018. vegan: Community Ecology Package. R Package Version 2.5–2. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Padisák, J., G. Borics, I. Grigorszky & É. Soróczki-Pintér, 2006. Use of phytoplankton assemblages for monitoring ecological status of lakes within the water framework directive: The assemblage index. Hydrobiologia 553: 1–14.
Padisák, J., L. O. Crossetti & L. Naselli-Flores, 2009. Use and misuse in the application of the phytoplankton functional classification: a critical review with updates. Hydrobiologia 621: 1–19.
Prescott, G. W. & W. C. Vinyard, 1982. A Synopsis of North American Desmids, University of Nebraska Press, Nebraska.
R Core Team. 2021. R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. https://www.R-project.org/
Reid, A. J., A. K. Carlson, I. F. Creed, E. J. Eliason, P. A. Gell, P. T. J. Johnson, K. A. Kidd, T. J. MacCormack, J. D. Olden, S. J. Ormerod, J. P. Smol, W. W. Taylor, K. Tockner, J. C. Vermaire, D. Dudgeon & S. J. Cooke, 2019. Emerging threats and persistent conservation challenges for freshwater biodiversity. Biological Reviews 94: 849–873.
Reynolds, C. S., 1998. What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status? Hydrobiologia 369: 11–26.
Reynolds, C. S., 2006. Ecology of Phytoplankton, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Reynolds, C. S., 2012. Environmental requirements and habitat preferences of phytoplankton: chance and certainty in species selection. Botanica Marina 55: 1–17.
Reynolds, C. S., A. E. Irish & J. A. Elliott, 2001. The ecological basis for simulating phytoplankton responses to environmental change (PROTECH). Ecological Modelling 140: 271–291.
Reynolds, C. S., V. Huszar, C. Kruk, L. Naselli-Flores & S. Melo, 2002. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. Journal of Plankton Research 24: 417–428.
Rodrigues, L. C., B. M. Pivato, L. C. G. Vieira, V. M. Bovo-Scomparin, J. C. Bortolini, A. Pineda & S. Train, 2018. Use of phytoplankton functional groups as a model of spatial and temporal patterns in reservoirs: a case study in a reservoir of central Brazil. Hydrobiologia 805: 147–161.
Rojo, C., 2021. Community assembly: perspectives from phytoplankton’s studies. Hydrobiologia 848: 31–52.
Rojo, C. & M. Álvarez-Cobelas, 2003. Are there steady-state phytoplankton assemblages in the field? Hydrobiologia 502: 3–12.
Round, F. E., R. M. Crawford & D. G. Mann, 1990. Diatoms: Biology and Morphology of the Genera, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Rousso, B. Z., E. Bertone, R. Stewart & D. P. Hamilton, 2020. A systematic literature review of forecasting and predictive models for cyanobacteria blooms in freshwater lakes. Water Research 182: 115959.
Ruttner-Kolisko, A., 1977. Suggestions for biomass calculation of planktonic rotifers. Algological Studies/archiv Für Hydrobiologie 8: 71–76.
Salmaso, N. & J. Padisák, 2007. Morpho-Functional Groups and phytoplankton development in two deep lakes (Lake Garda, Italy and Lake Stechlin, Germany). Hydrobiologia 578: 97–112.
Salmaso, N., L. Naselli-Flores & J. Padisák, 2015. Functional classifications and their application in phytoplankton ecology. Freshwater Biology 60: 603–619.
Southwood, T. R. E., 1977. Habitat, the templet for ecological strategies? Journal of Animal Ecology 46: 336–365.
Strickland, J. D. H. & T. R. Parsons, 1965. A Manual of Sea Water Analysis, Fisheries Research Board of Canada Bulletin, Ottawa.
Townsend, C., S. Dolédec & M. Scarsbrook, 1997. Species traits in relation to temporal and spatial heterogeneity in streams: a test of habitat templet theory. Freshwater Biology 37: 367–387.
Utermöhl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton-Methodik. Internationalen Vereinigung Für Theoretische Und Angewandte Limnologie Mitteilungen 9: 1–38.
Valderrama, J. C., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 109–122.
Wehr, J. D., R. G. Sheath & J. P. Kociolek, 2015. Freshwater Algae of North America: Ecology and Classification, Elsevier, Academic Press, San Diego.
Wilson, A. E., O. Sarnelle & A. R. Tillmanns, 2006. Effects of cyanobacterial toxicity and morphology on the population growth of freshwater zooplankton: meta-analyses of laboratory experiments. Limnology and Oceanography 51: 1915–1924.
Wood, S. N., 2004. Stable and efficient multiple smoothing parameter estimation for generalized additive models. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society 99: 673–686.
Wood, S. N., 2011. Fast stable restricted maximum likelihood and marginal likelihood estimation of semiparametric generalized linear models. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology) 73: 3–36.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Limnology Laboratory and Professor William Severi, from the Department of Fisheries and Aquaculture of the Federal Rural University of Pernambuco, for supporting nutrient analysis.
Funding
This work was supported by the Brazilian National Council of Technological and Scientific Development—CNPq, Brazil (Grant Number 305829/2019–0), and Fundação de Amparo a Ciência e Tecnologia do Estado de Pernambuco—FACEPE, Brazil (Grant Number IBPG-0308–2.03/17).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CAA participated in the conceptualization, methodology development, validation, data curation, and formal analysis of all data, wrote the original draft, wrote, reviewed, and edited the final version of the manuscript. ANM participated in the conceptualization, supervision, funding acquisition, methodology of all data, wrote, reviewed, and edited the final version of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work in this paper.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Additional information
Handling editor: Luigi Naselli-Flores
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amorim, C.A., Moura, A.d.N. Habitat templates of phytoplankton functional groups in tropical reservoirs as a tool to understand environmental changes. Hydrobiologia 849, 1095–1113 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04750-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-021-04750-3