Abstract
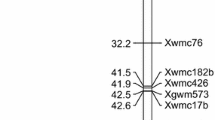
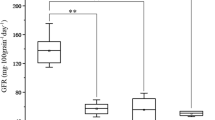
Markers linked to quantitative trait loci (QTL) must be validated in diverse genetic materials before they can be reliably used in molecular breeding programs. Here, 30 simple sequence repeat markers linked to QTL for grain iron content (GFeC), grain zinc content (GZnC), and grain protein content (GPC) were analyzed in 56 diverse dicoccum wheat genotypes. Seven markers were validated, including four (Xwmc617, Xbarc67, Xwmc283, Xgwm361) for grain iron content, one (Xbarc146) for both grain iron and protein contents; one more for grain protein (Xgwm408) and one for grain zinc content (Xgwm271). The segregating F2 population developed from the high-quality local landrace GPM DIC 87, and the high-yielding low-quality commercial cultivar (HW 1098) was used to revalidate the identified QTL-linked markers. As a result, Xgwm271 and Xbarc67 were re-validated in the F2 population, with values for phenotypic variation explained (PVE) of 56.50% and 72.78%, respectively. These two markers may serve as ideal candidates for molecular breeding programs to improve grain micronutrient contents. Additionally, the evaluation of the F2 population for agro-morphological, physiological, and quality traits, revealed large variability that can be useful for trait improvement. This population generated rare transgressive segregants with desirable allelic combinations that may be ideal for improving grain yield, grain quality, and physiological efficiency.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avivi L (1979) High grain protein content in wild tetraploid wheat triticum dicoccoides Korn. in proceedings of the fifth international wheat genetics symposium, New Delhi, India, 23–28 pp. 372–380
Biradar SS, Fyroj U, Desai SA, Patil MK, Krishnappa G, Chethan CK, Sudha T (2023) GGE biplot analysis of biofortification traits in relation to grain yield in landraces of tetraploid wheat (Triticum turgidum ssp. dicoccum). Genet Resour Crop Evol 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-023-01766-7
Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, De Onis M, Ezzati M, Grantham-McGregor S, Katz J, Martorell R, Uauy R (2013) Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. The Lancet 382(9890):427–451
Burton GW, Dewane EH (1953) Estimating heritability in tall fescues (Festuca allamidiaceae) from replicated clonal material. Agron J 45:1476–1481
Cakmak I, Ozkan H, Braun HJ, Welch RM, Romheld V (2000) Zinc and Iron concentrations in seeds of wild, primitive and modern Wheat. Food Nutr Bull 21(4):401–403
Chhuneja P, Dhaliwal HS, Bains NS, Singh K (2006) Aegilops kotschyi and aegilops tauschii are the sources for high grain iron and zinc. Plant Breed 125:529–531
Crain J, Ortiz-Monasterio I, Raun B (2012) Evaluation of a reduced cost active NDVI sensor for crop nutrient management. J Sens 2012:582028
Darnton-Hill I, Webb P, Harvey PW, Hunt JM, Dalmiya N, Chopra M, Ball MJ, Bloem MW, de Benoist B (2005) Micronutrient deficiencies and gender: social and economic costs. Am J Clin Nutr 81(5):1198S-1205S
Distelfeld A, Cakmak I, Peleg Z, Ozturk I, Yazici AM, Budak H et al (2007) Multiple QTL-effects of wheat GpcB1 locus on grain protein and micronutrient concentrations. Plant Physiol 129:635–643
Fyroj U, Biradar SS, Desai SA, Rudra Naik V, Patil MK, Lakkanagoudar S, Ram S, (2020) Triticum dicoccum schubler wheat: a potential source for wheat bio-fortification program. Inter J Chem Stud 8(5):1417–1422
Fyroj U (2017) Genetic variability studies for grain nutrients, yield and yield attributes in tetraploid wheat. M. Sc. (Agri) Thesis, Univ. Agric. Sci., Dharwad, Karnataka (India)
Genc Y, Verbyla A, Torun A, Cakmak I, Willsmore K, Wallwork H, McDonald GK (2009) Quantitative trait loci analysis of zinc efficiency and grain zinc concentration in wheat using whole genome average interval mapping. Plant Soil 314:49–66
Gopalareddy K, Singh AM, Ahlawat AK, Singh GP, Jaiswal JP (2015) Genotype-environment interaction for grain iron and zinc concentration in recombinant inbred lines of a bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cross. Indian J Genet Plant Breed 75:307–313
Von Grebmer K, Saltzman A, Birol E, Wiesman D, Prasai N, Yin S, Yohannes Y, Menon P, Thompson J, Sonntag A (2014) Synopsis: 2014 global hunger index: the challenge of hidden hunger Intl Food Policy Res Inst 83
Gupta PK, Balyan HS, Sharma S, Kumar R (2021) Biofortification and bioavailability of Zn, Fe and Se in wheat: present status and future prospects. Theor Appl Genet 134:1–35
Haley CS, Knott SA (1992) A simple regression method for mapping quantitative trait loci in line crosses using flanking markers. Heredity 6(4):315–324
Hammed AM, Simsek S (2014) Hulled wheat: a review of nutritional properties and processing methods. Cereal Chem 91:97–104
Hanson CH, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1956) Biometrical studies on yield in segregating population of Korean lespedesa. Agron J 48:268–272
Johnson HW, Robinson HF, Comstock RE (1955) Estimation of genetic and environmental variability in soybeans. Agron J 47:314–318
Krebs NF, Miller LV, Michael Hambidge K (2014) Zinc deficiency in infants and children: a review of its complex and synergistic interactions. Paediatr Int Child Health 34(4):279–288
Krishnappa G, Singh AM, Chaudhary S, Ahlawat AK, Singh SK, Shukla RB, Jaiswal JP, Singh GP, Solanki IS (2017) Molecular mapping of the grain iron and zinc concentration, protein content and thousand kernel weight in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). PLoS ONE 12:e0174972
Krishnappa G, Singh AM, Ahlawat AK, Singh SK, Sharma P, Shukla RB, Singh GP (2018) Validation of QTLs for grain iron and zinc concentration in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Indian J. Genet. Plant Breed. 78(03):378–381
Krishnappa G, Ahlawat AK, Shukla RB, Singh SK, Singh SK, Singh AM, Singh GP (2019) Multi-environment analysis of grain quality traits in recombinant inbred lines of a biparental cross in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Cereal Res Commun 47(2):334–344
Krishnappa G, Savadi S, Tyagi BS, Singh SK, Mamrutha HM, Kumar S, Mishra CN, Khan H, Singh G, Singh GP (2021) Integrated genomic selection for rapid improvement of crops. Genomics 113:1070–1086
Krishnappa G, Khan H, Krishna H, Kumar S, Mishra CN, Parkash O, Devate NB, Nepolean T, Rathan ND, Mamrutha HM, Srivastava P, Biradar S, Uday G, Kumar M, Singh G, Singh GP (2022) Genetic dissection of grain iron and zinc, and thousand kernel weight in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) using genome-wide association study. Sci Rep 12:12444
Krishnappa G, Khan H, Krishna H, Devate NB, Kumar S, Mishra CN, Parkash O, Kumar S, Kumar M, Mamrutha HM, Singh GP (2023) Genome-wide association study for grain protein, thousand kernel weight, and normalized difference vegetation index in bread wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genes 14(3):637
Krishnappa G, Mamrutha HM, Rathan ND, Khan H, Mishra CN, Kumar V, Reddy KV, Pandey V, Khobra R, Singh C, Yashavanthakumar KJ (2024) Micronutrient biofortification in wheat: status and opportunities. In wheat science (pp. 285–301). CRC Press
Lachman J, Orsak M, Pivec V, Jiru K (2012) Antioxidant activity of grain of einkorn (Triticum monococcum L.), emmer (Triticum dicoccum schuebl [Schrank]) and spring wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) varieties. Plant Soil Environ 58:15–21
Lephuthing MC, Tolmay VL, Baloyi TA, Hlongoane T, Oliphant TA, Tsilo TJ (2021) Relationship of grain micronutrient concentrations and grain yield components in a doubled haploid bread wheat (Triticum aestivum) population. Crop Pasture Sci 73:116–126
Listman M, Ordonez R (2019) Ten things you should know about maize and wheat. CIMMYT Batan, Mexico
Liu J, Bihua W, Ravi PS, Govindan V (2019) QTL mapping for micronutrients concentration and yield component traits in a hexaploid wheat mapping population. J Cereal Sci 88:55–64
Lobell DB, Schlenker W, Costa-Roberts J (2011) Climate trends and global crop production. Science 333(6042):616–620
Manish K, Mishra VK, Gupta PK, Yadav PS, Kumar H, Joshi Arun AK (2014) Introgression of the high grain protein gene Gpc-B1 in an elite wheat variety of Indo-gangetic plains through marker assisted backcross breeding. Curr Plant Biol 1:60–67
Monasterio I, Graham R (2000) Breeding for trace minerals in wheat. Food Nutr Bull 21:392–396
Moradi N, Badakhshan H, Mohammadzadeh H, Zakeri MR, Mirzaghaderi, (2014) Assessment of genetic diversity and identification of SSR markers associated with grain iron content in Iranian prevalent wheat genotypes. J Plant Mol Bred 2:64–73
Morgounov A, Gomez-Becerra HF, Abugalieva A, Dzhunusova M, Yessimbekova M, Muminjanov H, Zelenskiy Y, Cakmak OL, I, (2007) Iron and zinc grain density in common wheat grown in central asia. Euphytica 155(2):193–203
Paul AK, Islam MA, Hasan MJ, Chowdhury MMH (2006) Genetic variation of some morpho-physiological characters in Triticum durum wheat. Int J Sust Agril Tech 2(8):11–14
Quarrie S, Quarrie PS, Radosevic R, Rancic D, Kaminska A (2006) Dissecting a wheat QTL for yield present in a range of environments: from the QTL to candidate genes. J Exp Bot 57:2627–2637
Rathan ND, Krishna H, Ellur RK, Sehgal D, Velu G, Ahlawat AK, Krishnappa G, Jaiswal JP, Singh JB, Saiprasad SV, Ambati D, Singh SK, Bajpai K, Mahendru-Singh A (2022) Genome-wide association study identifies loci and candidate genes for grain micronutrients and quality traits in wheat (Triticum aestivum L). Sci Rep 12:7037
Rieseberg LH, Archer MA, Wayne RK (1999) Transgressive segregation, adaptation and speciation. Heredity 83(4):363–372
Sharp PJ, Johnston S, Brown G, Mcintosh RA, Pallotta M, Carter M, Bariana HS, Khatkar S, Lagudah ES, Singh RP, Khairallah M, Potter R, Jones MGK (2001) Validation of molecular markers for wheat breeding. Aust J Agri Res 52:1357–1366
Singh K, Ghai M, Garg M, Chhuneja P, Kaur P, Schnurbusch T, Keller B, Dhaliwal HS (2007) An integrated molecular linkage map of diploid wheat based on a T. boeoticum × T. monococcum RIL population. Theor Appl Genet 115:301–312
Singh P, Narayanan SS (2013) Biometrical techniques in plant breeding. In. Kalyani publishers, India
Spielmeyer W, Sharp PJ, Lagudah ES (2003) Identification and validation of markers linked to broad-spectrum stem rust resistance gene Sr2 in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Crop Sci 43:333–336
Stevens GA, Beal T, Mbuya MNN, Luo H, Neufeld LM (2022) Global micronutrient deficiencies research group micronutrient deficiencies among preschool-aged children and women of reproductive age worldwide: a pooled analysis of individual level data from population-representative surveys. Lancet Glob Health 10(11):1590–1599
Tazeen M, Nadia K, Farzana NN (2009) Heritability, phenotypic correlation and path co-efficient studies for some agronomic characters in synthetic elite lines of wheat. J Food Aric Environ 7(3):278–282
Uauy C, Distelfeld A, Fahima T, Blechl A, Dubcovsky J (2006) A NAC gene regulating senescence improves grain protein, zinc and iron content in wheat. Science 314:1298–1301
Xu Y, Diaoguo A, Dongcheng L, Aimin Z, Hongxing X, Bin L (2012) Molecular mapping of QTLs for grain zinc, iron and protein concentration of wheat across two environments. Field Crops Res 38:57–62
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SSB, RK, RRH and SAD conceptualized the research plan. GK and RK carried out data analysis. MKP, LJ, UF, and KKM carried out the experimentation. GK and SR analysed grain iron, zinc and protein content. GK wrote the original draft and all authors reviewed and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical statement
This investigation does not involve any research with animals at any stage of experimentation.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, R., Biradar, S.S., Patil, M.K. et al. Validation of quantitative trait loci for biofortification traits and variability research on agro-morphological, physiological, and quality traits in dicoccum wheat (Triticum dicoccum Schrank.). Genet Resour Crop Evol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-024-01973-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10722-024-01973-w