Abstract
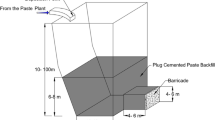
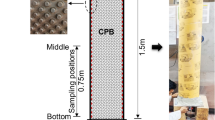
This paper presents and discusses the outcomes of an experimental study aimed at investigating changes in pore water pressure (PWP) in cemented paste backfill (CPB) materials incorporating polycarboxylate ether-based superplasticizer (PES). The research mimics real-world backfill field curing conditions, encompassing factors such as thermal (T; field curing temperatures), hydraulic (H; drainage conditions), mechanical (M; field vertical stress), and chemical (C; presence or absence of PES) factors. Utilizing a developed THMC backfill curing system, controlled THMC experiments were conducted to assess the impact of these factors and their interactions on pore water pressure (PWP) in CPB with or without PES. Results reveal that both individual THMC factors and their interactions significantly affect PWP development within CPB. The study also highlights the impact of PES on PWP in CPB, showing that adding 0.125% of PES can lead to a reduction in pore water pressure values by approximately 50% after 28 days of curing. Moreover, the results obtained demonstrated the effectiveness of the experimental THMC test techniques developed in this study in successfully mimicking field-like loading conditions, substantiating their usefulness for subjecting laboratory CPB samples to realistic loading scenarios in the field. These findings are of great importance for the mining industry and backfill designers, providing technical insights into complex THMC interactions affecting PWP in CPB-PES. Understanding these relationships is vital for optimizing CPB and barricade design, ensuring structural integrity, enhancing mine productivity, and guiding future research on numerical models for PWP prediction across all CPB structures.

















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data and materials or used during the study appear in the submitted article.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Alainachi I, Fall M, Majeed M (2022) Behaviour of backfill undergoing cementation under cyclic loading. Geotech Geol Eng 40:4735–4759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02181-y
Aldhafeeri Z, Fall M (2017) Sulphate induced changes in the reactivity of cemented tailings backfill. Int J Miner Process 166:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.06.007
Al-Moselly Z, Fall M (2022) Effect of thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical processes on the strength development of cemented paste backfill containing polycarboxylate ether-based superplasticizer. In: 75th Canadian geotechnical conference. Calgary, Canada
Al-Moselly Z, Fall M, Haruna S (2022) Further insight into the strength development of cemented paste backfill materials containing polycarboxylate ether-based superplasticizer. J Build Eng 47:103859. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103859
BASF (2015) MasterGlenium 7500 Full-range water-reducing admixture. https://www.master-builders-solutions.com/en-us/products/concrete-admixtures/water-reducers/water-reducers-high-range/masterglenium-7500
Belem T, Aatar OE, Bussière B et al (2006) Self-weight consolidation of column of cemented pastefill. In: 7th seminar on paste and thickened tailings. Irlande, p 13P
Bentz DP (2008) A review of early-age properties of cement-based materials. Cem Concr Res 38:196–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.09.005
Björnström J, Chandra S (2003) Effect of superplasticizers on the rheological properties of cements. Mater Struct Constr 36:685–692. https://doi.org/10.1617/13912
Cao S, Yilmaz E, Song W (2018) Evaluation of viscosity, strength and microstructural properties of cemented tailings backfill. Minerals 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3390/min8080352
Cavusoglu I, Fall M (2022) Engineering Properties of cemented paste backfill with full-range water-reducing admixture. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4156513
Chai S, Zheng J, Li L (2023) Kink Effect on the stress distribution in 2D backfilled Stopes. Geotech Geol Eng 41:3225–3238. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02434-4
Chen S, Wu A, Wang Y, Wang W (2021) Coupled effects of curing stress and curing temperature on mechanical and physical properties of cemented paste backfill. Constr Build Mater 273:121746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.121746
Cui L, Fall M (2016) Multiphysics model for consolidation behaviour of cemented paste backfill. ACSE Int J Geomech 17(3):23
Cui L, Fall M (2017) Multiphysics modeling of arching effects in fill mass. Comput Geotech 83:114–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2016.10.021
Cui L, Fall M (2017) Multiphysics model for consolidation behavior of cemented paste backfill. Int J Geomech. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gm.1943-5622.0000743
Cui L, Fall M (2017) Modeling of pressure on retaining structures for underground fill mass. Tunn Undergr Sp Technol 69:94–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2017.06.010
Cui L, Fall M (2018) Modeling of self-desiccation in a cemented backfill structure. Int J Numer Anal Methods Geomech 42:558–583. https://doi.org/10.1002/nag.2756
Cui L, Fall M (2018b) Multiphysics modeling and simulation of strength development and distribution in cemented tailings Backfill structures. Int J Concr Struct Mater. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40069-018-0250-y
Doherty JP, Hasan A, Suazo GH, Fourie A (2015) Investigation of some controllable factors that impact the stress state in cemented paste backfill. Can Geotech J 52:1901–1912. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2014-0321
Ercikdi B, Cihangir F, Kesimal A et al (2010) Utilization of water-reducing admixtures in cemented paste backfill of sulphide-rich mill tailings. J Hazard Mater 179:940–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.03.096
Fall M, Adrien D, Celestin JC, Pokharel M, Touré M (2009) Saturated hydraulic conductivity of cemented paste backfill. Miner Eng 22(15):1307–1317
Fall M, Célestin JC, Pokharel M, Touré M (2010) A contribution to understanding the effects of curing temperature on the mechanical properties of mine cemented tailings backfill. Eng Geol 114:397–413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2010.05.016
Fall M, Célestin J, Sen HF (2010) Potential use of densified polymer-pastefill mixture as waste containment barrier materials. Waste Manag 30:2570–2578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2010.07.016
Fang K, Fall M (2019) Chemically induced changes in the shear behaviour of interface between rock and tailings backfill undergoing cementation. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:3047–3062. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01757-0
Fang K, Fall M (2020) Shear behavior of the interface between rock and cemented backfill: effect of curing stress, drainage condition and backfilling rate. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:325–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01909-2
Fang K, Fall M (2021) Shear behaviour of rock–tailings backfill interface: effect of cementation, rock type, and rock surface roughness. Geotech Geol Eng 39:1753–1770. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-020-01586-x
Ghirian A, Fall M (2013) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical behaviour of cemented paste backfill in column experiments. Part I: physical, hydraulic and thermal processes and characteristics. Eng Geol 164:195–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2013.01.015
Ghirian A, Fall M (2013) Experimental investigations of the thermo-hydro-mechanical-chemical behavior of cemented paste backfill. 23rd world mining congress and expo. Montreal, Canada, pp 11–15
Ghirian A, Fall M (2014) Coupled thermo-hydro-mechanical—chemical behaviour of cemented paste backfill in column experiments part II: mechanical, chemical and microstructural processes and characteristics. Eng Geol 170:11–23
Ghirian A, Fall M (2015) Coupled behavior of cemented paste backfill at early ages. Geotech Geol Eng 33:1141–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-015-9892-6
Ghirian A, Fall M (2016) Strength evolution and deformation behaviour of cemented paste backfill at early ages: effect of curing stress, filling strategy and drainage. Int J Min Sci Technol 26:809–817. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmst.2016.05.039
Haruna S, Fall M (2020) Strength Development of cemented tailings materials containing polycarboxylate ether-based Superplasticizer: experimental results on the Effect of Time and temperature. Can J Civ Eng. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2019-0809
Haruna S, Fall M (2022) Reactivity of cemented paste backfill containing polycarboxylate-based superplasticizer. Min Eng 188:107856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2022.107856
Hasan A, Suazo G, Fourie AB (2013) Full scale experiments on the effectiveness of a drainage system for cemented paste backfill. In: Paste 2013. Jewell RJ, Fourie AB, Caldwell J, Pimenta J (eds), 2013 Australian centre for geomechanics, Perth, ISBN 978-0-9870937-6-9
Helinski M, Fourie A, Fahey M (2006) Mechanics of early age cemented Paste Backfill. In: Proceedings of ninth int semin paste thick tailings, pp 313–322. https://doi.org/10.36487/acg_repo/663_27
Helinski M, Fourie A, Fahey M, Ismail M (2007) Assessment of the self-desiccation process in cemented mine backfills. Can Geotech J 44:1148–1156. https://doi.org/10.1139/T07-051
Helinski M, Fahey M, Fourie A (2011) Behavior of cemented paste backfill in two mine stopes: measurements and modeling. J Geotech Geoenviron Eng 137:171–182. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)gt.1943-5606.0000418
Huang Z, Cao S, Qin S (2022) Research on the mechanical properties of 3D printing polymer reinforced cemented tailings Backfill under uniaxial compression. Geotech Geol Eng 40:3255–3266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02091-z
Hua C, Acker P, Ehrlacher A (1995) Analyses and models of the autogenous shrinkage of hardening cement paste. I. Modelling at macroscopic scale. Cem Concr Res 25:1457–1468. https://doi.org/10.1016/0008-8846(95)00140-8
Jiang H, Fall M, Li Y, Han J (2019) An experimental study on compressive behaviour of cemented rockfill. Constr Build Mater 213:10–19
Landriault D (2001) Backfill in underground mining. In: Hustrulid WA (ed) Underground mining methods engineering funda mentals and international case studies. SME, USA, pp 608–609
Lea F (1970) The chemistry of cement and concrete. Edward Arnold Ltd, London
Li W, Fall M (2016) Sulphate effect on the early age strength and self-desiccation of cemented paste backfill. Constr Build Mater 106:296–304. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.124
Li J, Yilmaz E, Cao S (2020) Influence of solid content, cement/tailings ratio, and curing time on rheology and strength of cemented tailings backfill. Minerals 10:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/min10100922
Lu G, Fall M (2018) Simulation of blast induced liquefaction susceptibility of subsurface fill mass. Geotech Geol Eng 36:1683–1706. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-017-0423-5
Mangane MBC, Argane R, Trauchessec R et al (2018) Influence of superplasticizers on mechanical properties and workability of cemented paste backfill. Min Eng 116:3–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2017.11.006
McCarter WJ, Chrisp TM, Starrs G, Blewett J (2003) Characterization and monitoring of cement-based systems using intrinsic electrical property measurements. Cem Concr Res 33:197–206. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(02)00824-4
Min C, Liu Z, Shi Y, Lu X (2023) Improving the strength performance of cemented phosphogypsum backfill with sulfate-resistant binders. Constr Build Mater 409:133974. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.133974
Morsy MS (1999) Effect of temperature on electrical conductivity of blended cement pastes. Cem Concr Res 29:603–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-8846(98)00198-7
Nasir O, Fall M (2009) Modeling the heat development in hydrating CPB structures. Comput Geotech 36:1207–1218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2009.05.008
Orejarena L, Fall M (2008) Mechanical response of a mine composite material to extreme heat. Bull Eng Geol Environ 67:387–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-008-0148-z
Ouattara D, Yahia A, Mbonimpa M, Belem T (2017) Effects of superplasticizer on rheological properties of cemented paste backfills. Int J Miner Process 161:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.minpro.2017.02.003
Ouattara D, Mbonimpa M, Yahia A, Belem T (2018) Assessment of rheological parameters of high density cemented paste backfill mixtures incorporating superplasticizers. Constr Build Mater 190:294–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.09.066
Papayianni I, Tsohos G, Oikonomou N, Mavria P (2005) Influence of superplasticizer type and mix design parameters on the performance of them in concrete mixtures. Cem Concr Compos 27:217–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2004.02.010
Roshani A, Fall M (2020) Rheological properties of cemented paste backfill with nano-silica: link to curing temperature. Cem Concr Compos 114:103785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103785
Sakai E, Kasuga T, Sugiyama T et al (2006) Influence of superplasticizers on the hydration of cement and the pore structure of hardened cement. Cem Concr Res 36:2049–2053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.08.003
Sari M, Yilmaz E, Kasap T, Guner NU (2022) Strength and microstructure evolution in cemented mine backfill with low and high pH pyritic tailings: Effect of mineral admixtures. Constr Build Mater 328:127109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.127109
Sari M, Yilmaz E, Kasap T (2023) Long-term ageing characteristics of cemented paste backfill: usability of sand as a partial substitute of hazardous tailings. J Clean Prod 401:136723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2023.136723
Shahsavari M, Grabinsky M (2015) Mine backfill porewater pressure dissipation: numerical predictions and field measurements. In: 68th proceedings Canadian geotechnical conference. Quebec City
Shahsavari M, Grabinsky M (2016) Pore Water pressure variations in cemented paste backfilled Stopes. Geo-Chicago. Chicago, Illinois, pp 331–342
Shahsavari M, Jafari M, Grabinsky M (2023) Simulation of cemented paste backfill (CPB) deposition through column experiments: comparisons of field measurements, laboratory measurements, and analytical solutions. Can Geotech J 60:1505–1514. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2020-0597
Simms P, Grabinsky M (2009) Direct measurement of matric suction in triaxial tests on early-age cemented paste backfill. Can Geotech J 46:93–101. https://doi.org/10.1139/T08-098
Thompson BD, Grabinsky MW, Bawden WF, Counter DB (2009) In-situ measurements of cemented paste backfill in long-hole stopes. RockEng09 proc 3. CANUS Rock Mech Symp 2009:1–10
Thottarath S (2010) Electromagnetic characterization of cemented paste backfill in the field and laboratory. University of Toronto
Wang H, Qiao L (2019) Coupled effect of cement-to-Tailings ratio and solid content on the early age strength of cemented Coarse tailings Backfill. Geotech Geol Eng 37:2425–2435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-018-00766-0
Wang Y, Fall M, Wu A (2016) Initial temperature-dependence of strength development and self-desiccation in cemented paste backfill that contains sodium silicate. Cem Concr Compos 67:101–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2016.01.005
Wang Y, Na Q, Yang J et al (2023) Monitoring of barricade pressure during the entire backfilling process for a high iron mine stope. Case Stud Constr Mater 19:e02456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2023.e02456
Wu D, Fall M, Cai S (2012) Coupled modeling of temperature distribution and evolution in cemented tailings Backfill structures that contain mineral admixtures. Geotech Geol Eng 30:935–961. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9518-1
Wu D, Fall M, Cai SJ (2013) Coupling temperature, cement hydration and rheological behaviour of fresh cemented paste backfill. Min Eng 42:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2012.11.011
Wu D, Fall M, Cai S (2014) Numerical modelling of thermally and hydraulically coupled processes in hydrating cemented tailings backfill columns. Int J Min Reclam Environ 28:173–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/17480930.2013.809194
Wu D, Zhao R, Qu C (2019) Effect of curing temperature on mechanical performance and acoustic emission properties of cemented coal gangue-fly Ash Backfill. Geotech Geol Eng 37:3241–3253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-019-00839-8
Yan R, Yin S, Zhang H et al (2023) Effect of superplasticizer on the setting behaviors and mechanical properties of tailings-waste rock cemented paste backfills. Case Stud Constr Mater 18:e01714. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2022.e01714
Yilmaz E, Kesimal A, Ercikdi B, Alp I (2003) Determination of the optimum cement content for paste backfill samples. In: 8th international mining congress and exhibition of Turkey IMCET. Antalya, Turkey, pp 119–126
Yilmaz E, Benzaazoua M, Belem T, Bussière B (2009) Effect of curing under pressure on compressive strength development of cemented paste backfill. Min Eng 22:772–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2009.02.002
Yilmaz E, Belem T, Benzaazoua M (2012) One-dimensional consolidation parameters of cemented paste backfills. Min Resour Manag 28:29–45. https://doi.org/10.2478/v10269-012-0030-2
Yilmaz E, Cao S (2022) Wu D (2022) Advances in the design and implementation of cementitious backfills. Frontiers in Materials 9:964111
Yoshioka K, Sakai E, Daimon M, Kitahara A (1997) Role of steric hindrance in the performance of superplasticizers for concrete. J Am Ceram Soc 80:2667–2671. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1151-2916.1997.tb03169.x
Zhang Z, Su H, Guan W (2022) Study on the geological environmental disturbance and reclamation technology of underground coal mines: a case study, Xinjiang, China. Geotech Geol Eng 41:1725–1739
Zhang D, Wang J, Guo S, Cao J (2022) Numerical simulation of crack evolution mechanism and subsidence characteristics effected by rock mass structure in block caving mining. Geotech Geol Eng 40:5377–5395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02220-8
Zhao X, Fourie A, Veenstra R, Qi C (2020) Safety of barricades in cemented paste-backfilled stopes. Int J Miner Metall Mater 27:1054–1064. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12613-020-2006-3
Zhou Q, Beaudoin JJ (2003) Effect of applied hydrostatic stress on the hydration of Portland cement and C3S. Adv Cem Res 15:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1680/adcr.2003.15.1.9
Funding
National Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no known conflicts of interests or competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Moselly, Z., Fall, M. Investigating Pore Water Pressure Development in Paste Backfill Under Conditions Mimicking Field Loading. Geotech Geol Eng (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02740-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-023-02740-x