Abstract
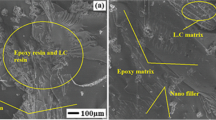
The objective of this investigation is to explore the influence of rice husk nano-particles (RHN) in determining the physical, mechanical, thermal, and morphological properties of Borassus leaf fiber (BLF) reinforced epoxy hybrid composites. The leaf of Borassus flabellifer L. was used to extract a novel genus of natural cellulosic fiber and treated with a sodium hydroxide solution to reduce the non-cellulosic contents. RHN obtained from rice husk was blended with epoxy resin to modify them with 0.25, 0.45, and 0.65 wt.%, respectively, using mechanical stirring and sonication processes. The hand lay-up method was used for the fabrication of composites. Among the developed composites, the superior performance was observed with 0.45 wt.% RHN blend composites for tensile strength, tensile modulus, flexural modulus (14 MPa, 489 MPa, and 15 GPa, respectively), reduced voids, and reduced water absorption capability (1.707% and 4.62%, respectively). From the obtained results, it could be concluded that as the RHN wt.% increased, the hardness of the composites increased (30.25 to 35.25 HB), while the flexural strength (43.10 to 31.42 MPa) and impact strength (43.32 to 38.02 kJ/m2) gradually decreased. TG and DTG analysis confirm that the improved thermal stability and maximum degradation temperature were 381 °C and 411 °C, respectively, for the 0.45 wt.% RHN blend composites. SEM analysis of the fractured surface of the composites shows that the RHN blend with epoxy improved the fiber-matrix adhesion properties. The fabricated composites are to be used for low-cost building materials, home appliances, automotive parts, and other suitable commercial applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data and materials used/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ASTM:
-
American standard testing methods
- BLF:
-
Borassus leaf fiber
- BLFs:
-
Borassus leaf fibers
- DTG:
-
Derivative thermogravimetry
- HCL:
-
Hydrochloric acid
- LC:
-
Least count
- RH:
-
Rice husk
- RHN:
-
Rice husk nanoparticles
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TGA:
-
Thermo gravimetric analysis
References
Abdullah HH, Zakaria S, Anuar NIS, Mohd Salleh K, Sayed Jaafar SN (2020) Effect of harvesting time and water retting fiber processing methods on the physico-mechanical properties of kenaf fiber. BioResources 15(3):7207–7222. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.3.7207-7222
Adeniyi AG, Onifade DV, Ighalo JO, Adeoye AS (2019) A review of coir fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos Part B Eng 176:107305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107305
Amjad A, Anjang Ab Rahman A, Awais H, Zainol Abidin MS, Khan J (2022) A review investigating the influence of nanofiller addition on the mechanical, thermal and water absorption properties of cellulosic fibre reinforced polymer composite. J Ind Text 51(1):65S-100S. https://doi.org/10.1177/15280837211057580
Arjmandi R, Hassan A, Majeed K, Zakaria Z (2015) Rice husk filled polymer composites. Int J Polym Sci 2015:1–32. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/501471
Ashok RB (2020) Study on morphology and mechanical behavior of areca leaf sheath reinforced epoxy composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3(3):365–374
Azlina Ramlee N, Jawaid M, Abdul Karim Yamani S, Syams Zainudin E, Alamery S (2021) ffect of surface treatment on mechanical, physical and morphological properties of oil palm/bagasse fiber reinforced phenolic hybrid composites for wall thermal insulation application. Constr Build Matr 276:122239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.122239
Balaji A, Karthikeyan B, Swaminathan J (2019) Comparative mechanical, thermal, and morphological study of untreated and NaOH-treated bagasse fiber-reinforced cardanol green composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2(2):125–132
Bhat R, Mohan N, Sharma S, Pratap A, Keni AP, Sodani D (2019) Mechanical testing and microstructure characterization of glass fiber reinforced isophthalic polyester composites. J Mater Res Technol 8(4):3653–3661. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.06.003
Biener J, Wittstock A, Baumann TF, Weissmüller J, Bäumer M, Hamza AV (2009) Surface chemistry in nanoscale materials. Materials 2(4):2404–2428. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma2042404
Chandgude S, Salunkhe S (2020) Biofiber-reinforced polymeric hybrid composites: An overview on mechanical and tribological performance. Polym Compos 41(10):3908–3939
Chatterjee A, Kumar S, Singh H (2020) Tensile strength and thermal behavior of jute fibre reinforced polypropylene laminate composite. Compos Commun 22:20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2020.100483
Chen RS, Ab Ghani MH, Salleh MN, Ahmad S, Tarawneh MA (2015) Mechanical, water absorption, and morphology of recycled polymer blend rice husk flour biocomposites. J Appl Polym Sci 132(8):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.41494
Chen Z, Xu Y, Shivkumar S (2018) Microstructure and tensile properties of various varieties of rice husk. J Sci Food Agric 98(3):1061–1070. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.8556
Da Silva TT, Mendonça Da Silveira PHP, Ribeiro MP, Lemos MF, Da Silva AP, Monteiro SN, Cassiano Nascimento LF (2021) Thermal and chemical characterization of kenaf fiber (Hibiscus cannabinus) reinforced epoxy matrix composites. Polymers (basel) 13(12):1–15. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym13122016
Fuqua MA, Huo S, Ulven CA (2012) Natural fiber reinforced composites. Polym Rev 52(3–4):259–320. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2012.705409
Gan L, Xiao Z, Wang A, Pan H, Hu J, Xu W, Wang Y, Wang X (2021) Efficient preparation of ultrafine powder from waste cellulose by physicochemical method. Powder Technol 379:478–484. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.10.092
Gokul K, Prabhu TR, Rajasekaran T (2017) Processing and evaluation of mechanical properties of sugarcane fiber reinforced natural composites. Trans Indian Inst Met 70(10):2537–2546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12666-017-1116-8
Guo G, Finkenstadt VL, Nimmagadda Y (2019) Mechanical properties and water absorption behavior of injection-molded wood fiber/carbon fiber high-density polyethylene hybrid composites. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 2(4):690–700
Guo J, Cao M, Ren W, Wang H, Yu Y (2021) Mechanical, dynamic mechanical and thermal properties of TiO2 nanoparticles treatment bamboo fiber-reinforced polypropylene composites. J Mater Sci 56(22):12643–12659. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-021-06100-z
Hossain T, Hossain S, Uddin MB, Khan RA (2020) Preparation and characterization of sodium silicate—treated jute-cotton blended polymer—reinforced UPR-based composite : effect of γ -radiation. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 4(2):257–264
Hsissou R, Seghiri R, Benzekri Z, Hilali M, Rafik M, Elharfi A (2021) Polymer composite materials: A comprehensive review. Compos Struct 262:113640. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2021.113640
Jagadeesh P, Puttegowda M, Mavinkere Rangappa S, Siengchin S (2021) Influence of nanofillers on biodegradable composites: A comprehensive review. Polym Compos 42(11):5691–5711
Kar J, Rout AK, Sutar AK (2018) Physical, mechanical, and erosion characterization of palm leaf stalk fiber reinforced epoxy composites filled with palm leaf stem stalk (PLSS) powder. BioResources 13(4):7212–7231. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.13.4.7212-7231
Kar J, Rout K, Sutar AK, Mohanty T (2020) Study on static and dynamic mechanical properties of hybrid palm stalk fiber reinforced epoxy composites. BioResources 15(2):4249–4270. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.15.2.4249-4270
Karimah A, Ridho MR, Munawar SS, Adi DS, Ismadi DR, Subiyanto B, Fatriasari W, Fudholi A (2021) A review on natural fibers for development of eco-friendly bio-composite: characteristics, and utilizations. J Mater Res Technol 13:2442–2458
Karimzadeh A, Yahya MY, Abdullah MN, Wong KJ (2020) Effect of stacking sequence on mechanical properties and moisture absorption characteristic of hybrid PALF / glass fiber composites. Fibers Polym 21(7):1583–1593
Khui PLN, Rahman MR, Ahmed AS, Kuok KK, Bakri MK, Tazeddinova D, Kazhmukanbetkyzy ZA, Torebek B (2021) Morphological and thermal properties of composites prepared with poly(lactic acid), poly(ethylene-alt-maleic anhydride), and biochar from microwave-pyrolyzed jatropha seeds. BioResources 16(2):3171–3185. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.16.2.3171-3185
Kumar N, Singh A, Debnath K, Kumar N (2020) Water absorption and mechanical behaviour of borassus fruit fibre-reinforced composites. Emerg Mater Res 9(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1680/jemmr.19.00044
Kumar R, Gunjal J, Chauhan S (2021) Effect of carbonization temperature on properties of natural fiber and charcoal filled hybrid polymer composite. Compos Part B 217:108846. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108846
Li S, Zheng T, Li Q, Hu Y, Wang B (2019) Flexural and energy absorption properties of natural-fiber reinforced composites with a novel fabrication technique. Compos Commun 16:124–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coco.2019.09.005
Lu W, Yu W, Zhang B, Dou X, Han X, Cai H (2021) Kevlar fibers reinforced straw wastes-polyethylene composites: Combining toughness, strength and self-extinguishing capabilities. Compos Part B Eng 223:109117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.109117
Moriana R, Vilaplana F, Karlsson S, Ribes A (2014) Correlation of chemical, structural and thermal properties of natural fibres for their sustainable exploitation. Carbohydr Polym 112:422–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2014.06.009
Narayanasamy P, Balasundar P, Senthil S, Sanjay MR, Siengchin S, Khan A, Asiri AM (2020) Characterization of a novel natural cellulosic fiber from Calotropis gigantea fruit bunch for ecofriendly polymer composites. Int J Biol Macromol 150:793–801. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.134
Nayak RK, Mahato KK, Ray BC (2016) Water absorption behavior, mechanical and thermal properties of nano TiO2 enhanced glass fiber reinforced polymer composites. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 90:736–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.09.003
Njoku CE, Omotoyinbo JA, Alaneme KK, Daramola MO (2020) Structural characterization and mechanical behaviour of sodium hydroxide-treated urena lobata fiber reinforced polypropylene matrix composites. Fibers Polym 21(12):2983–2992
Othman SH (2014) Bio-nanocomposite materials for food packaging applications: Types of biopolymer and nano-sized filler. Agric Agric Sci Procedia 2:296–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aaspro.2014.11.042
Panithasan MS, Gopalakichenin D, Venkadesan G, Veeraraagavan S (2019) Impact of rice husk nanoparticle on the performance and emission aspects of a diesel engine running on blends of pine oil-diesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(1):282–291
Panithasan MS, Gopalakichenin D, Venkadesan G, Malairajan M (2020) Evaluating the working characters of a diesel engine fueled with biodiesel blends added with rice husk Nano particles. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 1–19:1767726. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1767726
Prasad V, Joseph MA, Sekar K (2018) Investigation of mechanical, thermal and water absorption properties of flax fibre reinforced epoxy composite with nano TiO2 addition. Compos Part A Appl Sci Manuf 115:360–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.09.031
Raj S, Trivedi R, Soni V (2021) Biogenic synthesis of silver nanoparticles, characterization and their applications-A review. Surfaces 5(1):67–90
Ramamoorthy SK, Skrifvars M, Persson A (2015) A review of natural fibers used in biocomposites: Plant, animal and regenerated cellulose fibers. Polym Rev 55(1):107–162. https://doi.org/10.1080/15583724.2014.971124
Rashid S, Dutta H (2020) Characterization of nanocellulose extracted from short, medium and long grain rice husks. Ind Crops Prod 154:112627. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112627
Rojas FH, Daniel GP, Posidia RR (2019) Production and characterization of silica nanoparticles from rice husk. Adv Mater Lett 10(1):67–73. https://doi.org/10.5185/amlett.2019.2142
Rosamah E, Abdul Khalil HPS, Yap SW, Saurabh CK, Tahir PM, Dungani R, Owolabi AF (2018) The role of bamboo nanoparticles in kenaf fiber reinforced unsaturated polyester composites. J Renew Mater 6(1):75–86. https://doi.org/10.7569/JRM.2017.634152
Rout AK, Kar J, Jesthi DK, Sutar AK (2016) Effect of surface treatment on the physical, chemical, and mechanical properties of palm tree leaf stalk fibers. BioResources 11(2):4432–4445. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.2.4432-4445
Saba N, Tahir PM, Jawaid M (2014) A review on potentiality of nano filler/natural fiber filled polymer hybrid composites. Polymers 6(8):2247–2273
Sarasini F, Tirillò J, Puglia D, Dominici F, Santulli C, Boimau K, Valente T, Torre L (2017) Biodegradable polycaprolactone-based composites reinforced with ramie and borassus fibres. Compos Struct 167:20–29. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compstruct.2017.01.071
Sarr MM, Inoue H, Kosaka T (2021) Study on the improvement of interfacial strength between glass fiber and matrix resin by grafting cellulose nanofibers. Compos Sci Technol 211:108853. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compscitech.2021.108853
Sathees Kumar S (2020) Effect of natural fiber loading on mechanical properties and thermal characteristics of hybrid polyester composites for industrial and construction fields. Fibers Polym 21(7):1508–1514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12221-020-9853-4
Senthamaraikannan P, Kathiresan M (2018) Characterization of raw and alkali treated new natural cellulosic fiber from Coccinia grandis.L. Carbohydr Polym 186:332–343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.072
Senthamaraikannan P, Saravanakumar SS (2023) Evaluation of characteristic features of untreated and alkali-treated cellulosic plant fibers from Mucuna atropurpurea for polymer composite reinforcement. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03736-y
Sharma S, Poddar MK, Moholkar VS, Poddar MK, Moholkar VS (2017) Enhancement of thermal and mechanical properties of poly(MMA-co-BA)/Cloisite 30B nanocomposites by ultrasound-assisted in-situ emulsion polymerization. Ultrason Sonochem 36:212–225. https://doi.org/10.15376/biores.11.2.4432-4445
Singh JK, Rout AK (2022) Characterization of raw and alkali-treated cellulosic fibers extracted from Borassus flabellifer L. Biomass Conv Bioref. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-022-03238-x
Singh JK, Rout AK, Kumari K (2021) A review on Borassus flabellifer lignocellulose fiber reinforced polymer composites. Carbohydr Polym 262:117929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.117929
Sun J, Shen J, Chen S, Cooper MA, Fu H, Wu D, Yang Z (2018) Nanofiller reinforced biodegradable PLA/PHA composites: current status and future trends. Polymers 10(5):1–22. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym10050505
Thakur M, Chandel M, Rani A, Sharma A (2022) Introduction to biorenewable nanocomposite materials: methods of preparation, current developments, and future perspectives. ACS Symp Ser 1411:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1021/bk-2022-1411.ch001
Vijay R, Singaravelu DL, Vinod A, Sanjay MR, Siengchin S, Jawaid M, Khan A, Parameswaranpillai J (2019) Characterization of raw and alkali treated new natural cellulosic fibers from Tridax procumbens. Int J Biol Macromol 125:99–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.056
Vinod B, Suresh S, Sudhakara D (2020) Investigation of biodegradable hybrid composites: effect of fibers on tribo-mechanical characteristics. Adv Compos Hybrid Mater 3(3):194–204. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42114-020-00148-2
Wang H, Xian G, Li H (2015) Grafting of nano-TiO 2 onto flax fibers and the enhancement of the mechanical properties of the flax fiber and flax fiber/epoxy composite. Compos Part A 76:172–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesa.2015.05.027027
Webo W, Masu L, Maringa M (2018) The impact toughness and hardness of treated and untreated sisal fibre-epoxy resin composites. Adv Mater Sci Eng 8234106:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/8234106
Yadav M, Rengasamy RS, Gupta D (2019) Characterization of Pearl Millet (Pennisetum glaucum) waste. Carbohydr Polym 212:160–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.034
Yew MC, Yew MK, Saw LH, Ng TC, Durairaj R, Beh JH (2018) Influences of nano bio-filler on the fire-resistive and mechanical properties of water-based intumescent coatings. Prog Org Coatings 124:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.porgcoat.2018.07.022
Yussuf AA, Massoumi I, Hassan A (2010) Comparison of polylactic Acid/Kenaf and polylactic Acid/Rise husk composites: the influence of the natural fibers on the mechanical, thermal and biodegradability properties. J Polym Environ 18(3):422–429. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-010-0185-0
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to give special thanks to the Veer Surendra Sai University of Technology and OP Jindal University for providing the necessary resources and support for this research paper.
Funding
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JKS: Investigation, formal analysis, visualization, writing original draft and revision of the manuscript. AKR: Resources, methodology, manuscript editing and review and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
‘Not applicable’ for that section.
Consent for publication
I, on behalf of all co-authors, the undersigned, give my consent for publication of identifiable details, which can include photograph(s) and/or case history and/or details within the text (Materials) to be published in the above Journal.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, J.K., Rout, A.K. Study on the physical, mechanical, and thermal behaviour of RHN blend epoxy hybrid composites reinforced by Borassus flabellifer L. fibers. Cellulose 30, 5033–5049 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05191-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-023-05191-y