Abstract
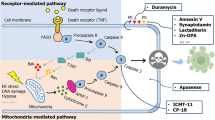
One major characteristic of programmed cell death (apoptosis) results in the increased expression of phosphatidylserine (PS) on the outer membrane of dying cells. Consequently, PS represents an excellent target for non-invasive imaging of apoptosis by single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) and positron emission tomography (PET). Annexin V is a 36 kDa protein which binds with high affinity to PS in the presence of Ca2+ ions. This makes radiolabeled annexins valuable apoptosis imaging agents for clinical and biomedical research applications for monitoring apoptosis in vivo. However, the use of radiolabeled annexin V for in vivo imaging of cell death has been met with a variety of challenges which have prevented its translation into the clinic. These difficulties include: complicated and time-consuming radiolabeling procedures, sub-optimal biodistribution, inadequate pharmacokinetics leading to poor tumour-to-blood contrast ratios, reliance upon Ca2+ concentrations in vivo, low tumor tissue penetration, and an incomplete understanding of what constitutes the best imaging protocol following induction of apoptosis. Therefore, new concepts and improved strategies for the development of PS-binding radiotracers are needed. Radiolabeled PS-binding peptides and various Zn(II) complexes as phosphate chemosensors offer an innovative strategy for radionuclide-based molecular imaging of apoptosis with PET and SPECT. Radiolabeled peptides and Zn(II) complexes provide several advantages over annexin V including better pharmacokinetics due to their smaller size, better availability, simpler synthesis and radiolabeling strategies as well as facilitated tissue penetration due to their smaller size and faster blood clearance profile allowing for optimized image contrast. In addition, peptides can be structurally modified to improve metabolic stability along with other pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic properties. The present review will summarize the current status of radiolabeled annexins, peptides and Zn(II) complexes developed as radiotracers for imaging apoptosis through targeting PS utilizing PET and SPECT imaging.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kerr JF, Wylie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: the basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Fulda S, Debatin KM (2006) Extrinsic versus intrinsic apoptosis pathways in anticancer chemotherapy. Oncogene 25:4798–4811
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–777
Syeed SA, Vohra H, Gupta A, Ganguly NK (2001) Apoptosis: molecular machinery. Curr Sci 80:349–360
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CP, McGahon AJ, Rader JA, van Schie RC, La Face DM, Green DR (1995) Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med 182:1545–1556
Schutters K, Reutelingsperger C (2010) Phosphatidylserine targeting for diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Apoptosis 15:1072–1082
Zwaal RF, Comfurius P, Bevers EM (2005) Surface exposure of phosphatidylserine in pathological cells. Cell Mol Life Sci 62:971–988
Saikumar P, Dong Z, Mikhailov V, Denton M, Weinberg JM, Venkatachalam MA (1999) Apoptosis: definition, mechanisms, and relevance to disease. Am J Med 107:489–506
Green AM, Steinmetz ND (2002) Monitoring apoptosis in real time. Cancer J 8:82–92
Boersma HH, Kietselaer BL, Stolk LM, Bennaghmouch A, Hofstra L, Narula J, Heidendal GA, Reutelingsperger CP (2005) Past, present, and future of annexin A5: from protein discovery to clinical applications. J Nucl Med 46:2035–2050
Gerke V, Moss SE (2002) Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 82:331–371
Lahorte CM, Vanderheyden JL, Steinmetz N, Van de Wiele C, Dierckx RA, Slegers G (2004) Apoptosis-detecting radioligands: current state of the art and future perspectives. Eur J Nucl Med 31:887–910
Bazzi MD, Nelsestuen GL (1991) Highly sequential binding of protein kinase C and related proteins to membranes. Biochemistry 30:7970–7977
Koopman G, Reutelingsperger CP, Kuijten GA, Keehnen RM, Pals ST, van Oers MH (1994) Annexin V for flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on B cells undergoing apoptosis. Blood 84:1415–1420
Thiagarajan P, Tait JF (1990) Binding of annexin V/placental anticoagulant protein I to platelets. Evidence for phosphatidylserine exposure in the procoagulant response of activated platelets. J Biol Chem 265:17420–17423
Lahorte C, Dumont F, Slegers G, Van De Wiele C, Dierckx RA, Philippe J (2000) Synthesis and in vitro stability of 123I-labelled annexin V: a potential agent for spect imaging of apoptotic cells. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 43:739–751
Lahorte C, Slegers G, Philippé J, Van de Wiele C, Dierckx RA (2001) Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 123I-labelled human recombinant annexin V. Biomol Eng 17:51–53
Rao LV, Tait JF, Hoang AD (1992) Binding of annexin V to a human ovarian carcinoma cell line (OC-2008). Contrasting effects on cell surface factor VIIa/tissue factor activity and prothrombinase activity. Thromb Res 67:517–531
Lahorte CM, van de Wiele C, Bacher K, van den Bossche B, Thierens H, van Belle S, Slegers G, Dierckx RA (2003) Biodistribution and dosimetry study of 123I-rh-annexin V in mice and humans. Nucl Med Commun 24:871–880
Russell J, O’Donoghue JA, Finn R, Koziorowski J, Ruan S, Humm JL, Ling CC (2002) Iodination of annexin V for imaging apoptosis. J Nucl Med 43:671–677
Eisenhut M (2006) Molecular position of radiolabels and its impact on functional integrity of proteins. J Nucl Med 47:1400–1402
Stratton JR, Dewhurst TA, Kasina S, Reno JM, Cerqueira MD, Baskin DG, Tait JF (1995) Selective uptake of radiolabeled annexin V on acute porcine left atrial thrombi. Circulation 92:3113–3121
Tait JF, Cerqueira MD, Dewhurst TA, Fujikawa K, Ritchie JL, Stratton JR (1994) Evaluation of annexin V as a platelet-directed thrombus targeting agent. Thromb Res 75:491–501
Kown MH, Strauss HW, Blankenberg FG, Berry GJ, Stafford-Cecil S, Tait JF, Goris ML, Robbins RC (2001) In vivo imaging of acute cardiac rejection in human patients using (99 m)technetium labeled annexin V. Am J Transplant 1:270–277
Narula J, Acio ER, Narula N, Samuels LE, Fyfe B, Wood D, Fitzpatrick JM, Raghunath PN, Tomaszewski JE, Kelly C, Steinmetz N, Green A, Tait JF, Leppo J, Blankenberg FG, Jain D, Strauss HW (2001) Annexin-V imaging for noninvasive detection of cardiac allograft rejection. Nat Med 7:1347–1352
Belhocine T, Steinmetz N, Hustinx R, Bartsch P, Jerusalem G, Seidel L, Rigo P, Green A (2002) Increased uptake of the apoptosis-imaging agent (99 m)Tc recombinant human Annexin V in human tumors after one course of chemotherapy as a predictor of tumor response and patient prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 8:2766–2774
Kemerink GJ, Boersma HH, Thimister PW, Hofstra L, Liem IH, Pakbiers MT, Janssen D, Reutelingsperger CP, Heidendal GA (2001) Biodistribution and dosimetry of 99mTc-BTAP-annexin-V in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 28:1373–1378
Boersma HH, Liem IH, Kemerink GJ, Thimister PW, Hofstra L, Stolk LM, van Heerde WL, Pakbiers MT, Janssen D, Beysens AJ, Reutelingsperger CP, Heidendal GA (2003) Comparison between human pharmacokinetics and imaging properties of two conjugation methods for 99mTc-annexin A5. Br J Radiol 76:553–560
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, Davis RE, Naumovski L, Ohtsuki K, Kopiwoda S, Abrams MJ, Darkes M, Robbins RC, Maecker HT, Strauss HW (1998) In vivo detection and imaging of phosphatidylserine expression during programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6349–6354
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, Davis RE, Naumovski L, Ohtsuki K, Kopiwoda S, Abrams MJ, Strauss HW (1999) Imaging of apoptosis (programmed cell death) with 99mTc annexin V. J Nucl Med 40:184–191
Vriens PW, Blankenberg FG, Stoot JH, Ohtsuki K, Berry GJ, Tait JF, Strauss HW, Robbins RC (1998) The use of technetium Tc 99 m annexin V for in vivo imaging of apoptosis during cardiac allograft rejection. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 116:844–853
Ohtsuki K, Akashi K, Aoka Y, Blankenberg FG, Kopiwoda S, Tait JF, Strauss HW (1999) Technetium-99m HYNIC-annexin V: a potential radiopharmaceutical for the in-vivo detection of apoptosis. Eur J Nucl Med 26:1251–1258
Blankenberg FG, Robbins RC, Stoot JH, Vriens PW, Berry GJ, Tait JF, Strauss HW (2000) Radionuclide imaging of acute lung transplant rejection with annexin V. Chest 117:834–840
Ogura Y, Krams SM, Martinez OM, Kopiwoda S, Higgins JP, Esquivel CO, Strauss HW, Tait JF, Blankenberg FG (2000) Radiolabeled annexin V imaging: diagnosis of allograft rejection in an experimental rodent model of liver transplantation. Radiology 214:795–800
Blankenberg FG, Tait JF, Blankenberg TA, Post AM, Strauss HW (2001) Imaging macrophages and the apoptosis of granulocytes in a rodent model of subacute and chronic abscesses with radiolabeled monocyte chemotactic peptide-1 and annexin V. Eur J Nucl Med 28:1384–1393
Blankenberg FG, Naumovski L, Tait JF, Post AM, Strauss HW (2001) Imaging cyclophosphamide-induced intramedullary apoptosis in rats using 99mTc-radiolabeled annexin V. J Nucl Med 42:309–316
Tokita N, Hasegawa S, Maruyama K, Izumi T, Blankenberg FG, Tait JF, Strauss HW, Nishimura T (2003) 99mTc-Hynic-annexin V imaging to evaluate inflammation and apoptosis in rats with autoimmune myocarditis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 30:232–238
Post AM, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, Geaghan SM, Strauss HW, Blankenberg FG (2002) Imaging cell death with radiolabeled annexin V in an experimental model of rheumatoid arthritis. J Nucl Med 43:1359–1365
Taki J, Higuchi T, Kawashima A, Tait JF, Kinuya S, Muramori A, Matsunari I, Nakajima K, Tonami N, Strauss HW (2004) Detection of cardiomyocyte death in a rat model of ischemia and reperfusion using 99mTc-labeled annexin V. J Nucl Med 45:1536–1541
Peker C, Sarda-Mantel L, Loiseau P, Rouzet F, Nazneen L, Martet G, Vrigneaud JM, Meulemans A, Saumon G, Michel JB, Le Guludec D (2004) Imaging apoptosis with (99 m)Tc-annexin-V in experimental subacute myocarditis. J Nucl Med 45:1081–1086
Tang XN, Wang Q, Koike MA, Cheng D, Goris ML, Blankenberg FG, Yenari MA (2007) Monitoring the protective effects of minocycline treatment with radiolabeled annexin V in an experimental model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Nucl Med 48:1822–1828
Mochizuki T, Kuge Y, Zhao S, Tsukamoto E, Hosokawa M, Strauss HW, Blankenberg FG, Tait JF, Tamaki N (2003) Detection of apoptotic tumor response in vivo after a single dose of chemotherapy with 99mTc-annexin V. J Nucl Med 44:92–97
Wong E, Kumar V, Howman-Giles RB, Vanderheyden JL (2008) Imaging of therapy-induced apoptosis using (99 m)Tc-HYNIC-annexin V in thymoma tumor-bearing mice. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 23:715–726
Lan XL, Zhang YX, He Y, Sun X, An R, Gao ZR, Cao GX (2008) Feasibility of apoptosis-imaging agent 99mTc-HYNIC-annexin V in early assessment of chemotherapeutic effect on tumor models. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi 30:737–740
Guo MF, Zhao Y, Tian R, Li L, Guo L, Xu F, Liu YM, He YB, Bai S, Wang J (2009) In vivo 99mTc-HYNIC-annexin V imaging of early tumor apoptosis in mice after single dose irradiation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:136
Erba PA, Manfredi C, Lazzeri E, Minichilli F, Pauwels EK, Sbrana A, Strauss HW, Mariani G (2010) Time course of Paclitaxel-induced apoptosis in an experimental model of virus-induced breast cancer. J Nucl Med 51:775–781
Kemerink GJ, Liu X, Kieffer D, Ceyssens S, Mortelmans L, Verbruggen AM, Steinmetz ND, Vanderheyden JL, Green AM, Verbeke K (2003) Safety, biodistribution, and dosimetry of 99mTc-HYNIC-annexin V, a novel human recombinant annexin V for human application. J Nucl Med 44:947–952
Thimister PW, Hofstra L, Liem IH, Boersma HH, Kemerink G, Reutelingsperger CP, Heidendal GA (2003) In vivo detection of cell death in the area at risk in acute myocardial infarction. J Nucl Med 44:391–396
Kiestelaer BLJH, Reutelingsperger CPM, Heidendal GAK, Daemen MJAP, Mess WH, Hofstra L (2004) Noninvasive detection of plaque instability with use of radiolabeled annexin A5 in patients with carotid-artery atherosclerosis. N Engl J Med 350:1472–1473
Blankenberg FG, Kalinyak J, Liu L, Koike M, Cheng D, Goris ML, Green A, Vanderheyden JL, Tong DC, Yenari MA (2006) 99mTc-HYNIC-annexin V SPECT imaging of acute stroke and its response to neuroprotective therapy with antiFas ligand antibody. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 33:566–574
Lorberboym M, Blankenberg FG, Sadeh M, Lampl Y (2006) In vivo imaging of apoptosis in patients with acute stroke: correlation with blood-brain barrier permeability. Brain Res 1103:13–19
Lampl Y, Lorberboym M, Blankenberg FG, Sadeh M, Gilad R (2006) Annexin V SPECT imaging of phosphatidylserine expression in patients with dementia. Neurology 66:1253–1254
van de Wiele C, Lahorte C, Vermeersch H, Loose D, Mervillie K, Steinmetz ND, Vanderheyden JL, Cuvelier CA, Slegers G, Dierck RA (2003) Quantitative tumor apoptosis imaging using technetium-99m-HYNIC annexin V single photon emission computed tomography. J Clin Oncol 21:3483–3487
Vermeersch H, Loose D, Lahorte C, Mervillie K, Dierckx R, Steinmetz N, Vanderheyden JL, Cuvelier C, Slegers G, Van de Wiele C (2004) 99mTc-HYNIC Annexin-V imaging of primary head and neck carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun 25:259–263
Rongen GA, Oyen WJ, Ramakers BP, Riksen NP, Boerman OC, Steinmetz N, Smits P (2005) Annexin A5 scintigraphy of forearm as a novel in vivo model of skeletal muscle preconditioning in humans. Circulation 111:173–178
Riksen NP, Oyen WJ, Ramakers BP, Van den Broek PH, Engbersen R, Boerman OC, Smits P, Rongen GA (2005) Oral therapy with dipyridamole limits ischemia-reperfusion injury in humans. Clin Pharmacol Ther 78:52–59
Riksen NP, Zhou Z, Oyen WJ, Jaspers R, Ramakers BP, Brouwer RM, Boerman OC, Steinmetz N, Smits P, Rongen GA (2006) Caffeine prevents protection in two human models of ischemic preconditioning. J Am Coll Cardiol 48:700–707
Haas RL, de Jong D, Olmos RAV, Hoefnagel CA, van den Heuvel I, Zerp SF, Bartelink H (2004) Verheij, M. In vivo imaging of radiation induced apoptosis in follicular lymphoma patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 59:782–787
Kartachova M, Haas RL, Olmos RA, Hoebers FJ, van Zandwijk N, Verheij M (2004) In vivo imaging of apoptosis by 99mTc-Annexin V scintigraphy: visual analysis in relation to treatment response. Radiother Oncol 72:333–339
Rottey S, Slegers G, Van Belle S, Goethals I, Van de Wiele C (2006) Sequential 99mTc-hydrazinonicotinamide-annexin V imaging for predicting response to chemotherapy. J Nucl Med 47:1813–1818
Rottey S, Loose D, Vakaet L, Lahorte C, Vermeersch H, Van Belle S, Van de Wiele C (2007) 99mTc-HYNIC Annexin-V imaging of tumors and its relationship to response to radiotherapy and/or chemotherapy. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 51:182–188
Hoebers FJ, Kartachova M, de Bois J, van den Brekel MW, van Tinteren H, van Herk M, Rasch CR, Valdés Olmos RA, Verheij M (2008) 99mTc Hynic-rh-Annexin V scintigraphy for in vivo imaging of apoptosis in patients with head and neck cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 35:509–518
Decristoforo C, Mather SJ (1999) Technetium-99m somatostatin analogues: effect of labelling methods and peptide sequence. Eur J Nucl Med 26:869–876
Verbeke K, Kieffer D, Vanderheyden JL, Reutelingsperger C, Steinmetz N, Green A, Verbruggen A (2003) Optimization of the preparation of 99mTc-labeled Hynic-derivatized Annexin V for human use. Nucl Med Biol 30:771–778
Vanderheyden JL, Liu G, He J, Patel B, Tait JF, Hnatowich DJ (2006) Evaluation of 99mTc-MAG3-annexin V: influence of the chelate on in vitro and in vivo properties in mice. Nucl Med Biol 33:135–144
Yang DJ, Azhdarinia A, Wu P, Yu DF, Tansey W, Kalimi SK, Kim EE, Podoloff DA (2001) In vivo and in vitro measurement of apoptosis in breast cancer cells using 99mTc-EC-annexin V. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 16:73–83
Blankenberg F (2002) To scan or not to scan, it is a question of timing: technetium-99m-annexin V radionuclide imaging assessment of treatment efficacy after one course of chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 8:2757–2758
Kurihara H, Yang DJ, Cristofanilli M, Erwin WD, Yu DF, Kohanim S, Mendez R, Kim EE (2008) Imaging and dosimetry of 99mTc EC annexin V: preliminary clinical study targeting apoptosis in breast tumors. Appl Radiat Isot 66:1175–1182
Tait JF, Brown DS, Gibson DF, Blankenberg FG, Strauss HW (2000) Development and characterization of annexin V mutants with endogenous chelation sites for (99 m)Tc. Bioconjug Chem 11:918–925
Tait JF, Smith C, Levashova Z, Patel B, Blankenberg FG, Vanderheyden JL (2006) Improved detection of cell death in vivo with annexin V radiolabeled by site-specific methods. J Nucl Med 47:1546–1553
Tait JF, Smith C, Blankenberg FG (2005) Structural requirements for in vivo detection of cell death with 99mTc-annexin V. J Nucl Med 46:807–815
Luo QY, Wang F, Zhang ZY, Zhang Y, Lu HK, Sun SH, Zhu RS (2008) Preparation and bioevaluation of (99 m)Tc-HYNIC-annexin B1 as a novel radioligand for apoptosis imaging. Apoptosis 13:600–608
Fonge H, de Saint Hubert M, Vunckx K, Rattat D, Nuyts J, Bormans G, Ni Y, Reutelingsperger C, Verbruggen A (2008) Preliminary in vivo evaluation of a novel 99mTc-labeled HYNIC-cys-annexin A5 as an apoptosis imaging agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18:3794–3798
Greupink R, Sio CF, Ederveen A, Orsel J (2009) Evaluation of a 99mTc-labeled AnnexinA5 variant for non-invasive SPECT imaging of cell death in liver, spleen and prostate. Pharm Res 26:2647–2656
Biechlin ML, Bonmartin A, Gilly FN, Fraysse M, du Moulinet d’Hardemare A (2008) Radiolabeling of annexin A5 with (99 m)Tc: comparison of HYNIC-Tc vs. iminothiolane-Tc-tricarbonyl conjugates. Nucl Med Biol 35:679–687
Vangestel C, Peeters M, Oltenfreiter R, D’Asseler Y, Staelens S, Van Steenkiste M, Philippé J, Kusters D, Reutelingsperger C, Van Damme N, Van de Wiele C (2010) In vitro and in vivo evaluation of [99mTc]-labeled tricarbonyl His-annexin A5 as an imaging agent for the detection of phosphatidylserine-expressing cells. Nucl Med Biol 37:965–975
De Saint-Hubert M, Mottaghy FM, Vunckx K, Nuyts J, Fonge H, Prinsen K, Stroobants S, Mortelmans L, Deckers N, Hofstra L, Reutelingsperger CP, Verbruggen A, Rattat D (2010) Site-specific labeling of ‘second generation’ annexin V with 99mTc(CO)3 for improved imaging of apoptosis in vivo. Bioorg Med Chem 18:1356–1363
Wen X, Wu QP, Ke S, Wallace S, Charnsangavej C, Huang P, Liang D, Chow D, Li C (2003) Improved radiolabeling of PEGylated protein: PEGylated annexin V for noninvasive imaging of tumor apoptosis. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 18:819–827
Glaser M, Collingridge DR, Aboagye EO, Bouchier-Hayes L, Hutchinson OC, Martin SJ, Price P, Brady F, Luthra SK (2003) Iodine-124 labelled annexin-V as a potential radiotracer to study apoptosis using positron emission tomography. Appl Radiat Isot 58:55–62
Collingridge DR, Glaser M, Osman S, Barthel H, Hutchinson OC, Luthra SK, Brady F, Bouchier-Hayes L, Martin SJ, Workman P, Price P, Aboagye EO (2003) In vitro selectivity, in vivo biodistribution and tumour uptake of annexin V radiolabelled with a positron emitting radioisotope. Br J Cancer 89:1327–1333
Dekker B, Keen H, Shaw D, Disley L, Hastings D, Hadfield J, Reader A, Allan D, Julyan P, Watson A, Zweit J (2005) Functional comparison of annexin V analogues labeled indirectly and directly with iodine-124. Nucl Med Biol 32:403–413
Keen HG, Dekker BA, Disley L, Hastings D, Lyons S, Reader AJ, Ottewell P, Watson A, Zweit J (2005) Imaging apoptosis in vivo using 124I-annexin V and PET. Nucl Med Biol 32:395–402
Dekker B, Keen H, Lyons S, Disley L, Hastings D, Reader A, Ottewell P, Watson A, Zweit (2005) J. MBP-annexin V radiolabeled directly with iodine-124 can be used to image apoptosis in vivo using PET. Nucl Med Biol 32:241–252
Zijlstra S, Gunawan J, Burchert W (2003) Synthesis and evaluation of a 18F-labelled recombinant annexin-V derivative, for identification and quantification of apoptotic cells with PET. Appl Radiat Isot 58:201–207
Toretsky J, Levenson A, Weinberg IN, Tait JF, Uren A, Mease RC (2004) Preparation of F-18 labeled annexin V: a potential PET radiopharmaceutical for imaging cell death. Nucl Med Biol 31:747–752
Grierson JR, Yagle KJ, Eary JF, Tait JF, Gibson DF, Lewellen B, Link JM, Krohn KA (2004) Production of [F-18]fluoroannexin for imaging apoptosis with PET. Bioconjug Chem 15:373–379
Murakami Y, Takamatsu H, Taki J, Tatsumi M, Noda A, Ichise R, Tait JF, Nishimura S (2004) 18F-labelled annexin V: a PET tracer for apoptosis imaging. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:469–474
Yagle KJ, Eary JF, Tait JF, Grierson JR, Link JM, Lewellen B, Gibson DF, Krohn KA (2005) Evaluation of 18F-annexin V as a PET imaging agent in an animal model of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 46:658–666
Hu S, Kiesewetter DO, Zhu L, Guo N, Gao H, Liu G, Hida N, Lang L, Niu G, Chen X (2012) Longitudinal PET imaging of doxorubicin-induced cell death with 18F-Annexin V. Mol Imaging Biol 14:762–770
Perreault A, Knight JC, Wang M, Way J, Wuest F (2016) 18F-Labeled wild-type annexin V: comparison of random and site-selective radiolabeling methods. Amino Acids 48:65–74
Li X, Link JM, Stekhova S, Yagle KJ, Smith C, Krohn KA, Tait JF (2008) Site-specific labeling of annexin V with F-18 for apoptosis imaging. Bioconjug Chem 19:1684–1688
Wuest F, Berndt M, Bergmann R, van den Hoff J, Pietzsch J (2008) Synthesis and application of [18F]FDG-maleimidehexyloxime ([18F]FDG-MHO): a [18F]FDG-based prosthetic group for the chemoselective 18F-labeling of peptides and proteins. Bioconjug Chem 19:1202–1210
Wang MW, Wang F, Zheng YJ, Zhang YJ, Zhang YP, Zhao Q, Shen CK, Wang Y, Sun SH (2013) An in vivo molecular imaging probe (18)F-Annexin B1 for apoptosis detection by PET/CT: preparation and preliminary evaluation. Apoptosis 18:238–247
Cauchon N, Langlois R, Rousseau JA, Tessier G, Cadorette J, Lecomte R, Hunting DJ, Pavan RA, Zeisler SK, van Lier JE (2007) PET imaging of apoptosis with (64)Cu-labeled streptavidin following pretargeting of phosphatidylserine with biotinylated annexin-V. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 34:247–258
Bauwens M, De Saint-Hubert M, Devos E, Deckers N, Reutelingsperger C, Mortelmans L, Himmelreich U, Mottaghy FM, Verbruggen A (2011) Site-specific 68 Ga-labeled Annexin A5 as a PET imaging agent for apoptosis. Nucl Med Biol 38:381–392
Davletov BA, Sudhof TC (1993) A single C2 domain from synaptotagmin I is sufficient for high affinity Ca2+/ phospholipid binding. J Biol Chem 268:26386–26390
Zhao M, Zhu X, Ji S, Zhou J, Ozker KS, Fang W, Molthen RC, Hellman RS (2006) 99mTc-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I as a target-specific molecular probe for noninvasive imaging of acute myocardial infarction. J Nucl Med 47:1367–1374
Alam IS, Neves AA, Witney TH, Boren J, Brindle KM (2010) Comparison of the C2A domain of synaptotagmin-I and annexin-V as probes for detecting cell death. Bioconjug Chem 21:884–891
Tavaré R, De Rosales TM, Blower PJ, Mullen GE (2009) Efficient site-specific radiolabeling of a modified C2A domain of synaptotagmin I with [99mTc(CO)3]+: a new radiopharmaceutical for imaging cell death. Bioconjug Chem 20:2071–2081
Hueting R, Tavaré R, Dilworth JR, Mullen GE (2013) Copper-64 radiolabelling of the C2A domain of synaptotagmin I using a functionalised bis(thiosemicarbazone): a pre- and post-labelling comparison. J Inorg Biochem 128:108–111
Wang F, Fang W, Zhang MR, Zhao M, Liu B, Wang Z, Hua Z, Yang M, Kumata K, Hatori A, Yamasaki T, Yanamoto K, Suzuki K (2011) Evaluation of chemotherapy response in VX2 rabbit lung cancer with 18F-labeled C2A domain of synaptotagmin I. J Nucl Med 52:592–599
Neves AA, Xie B, Fawcett S, Alam IS, Witney TH, de Backer MM, Summers J, Hughes W, McGuire S, Soloviev D, Miller J, Howat WJ, Hu DE, Rodrigues TB, Lewis DY, Brindle KM (2017) Rapid imaging of tumor cell death in vivo using the C2A domain of synaptotagmin-I. J Nucl Med 58:881–887
Reubi JC, Maecke HR (2008) Peptide-based probes for cancer imaging. J Nucl Med 49:1735–1738
Burtea C, Laurent S, Lancelot E, Ballet S, Murariu O, Rousseaux O, Port M, Elst LV, Corot C, Mueller RN (2009) Peptidic targeting of phosphatidylserine for the MRI detection of apoptosis in atherosclerotic plaques. Mol Pharm 6:1903–1919
Desai TJ, Toombs JE, Minna JD, Brekken RA, Udugamasooriya DG (2016) Identification of lipid-phosphatidylserine (PS) as the target of unbiasedly selected cancer specific peptide-peptoid hybrid PPS1. Oncotarget 7:30678–30690
Shao R, Xiong C, Wen X, Gelovani JG, Li C (2007) Targeting phosphatidylserine on apoptotic cells with phages and peptides selected from a bacteriophage display library. Mol Imaging 6:417–426
Richter S, Wuest F (2014) 18F-Labeled peptides: the future is bright. Molecules 19:20536–20556
Kapty J, Kniess T, Wuest F, Mercer JR (2011) Radiolabeling of phosphatidylserine-binding peptides with prosthetic groups N-[6-(4-[18F] fluorobenzylidene)-aminooxyhexyl]maleimide ([18F]FBAM) and N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB). Appl Radiat Isot 69:1218–1225
Wuest M, Perreault A, Kapty J, Richter S, Foerster C, Bergman C, Way J, Mercer J, Wuest F (2015) Radiopharmacological evaluation of (18)F-labeled phosphatidylserine-binding peptides for molecular imaging of apoptosis. Nucl Med Biol 42:864–874
Kapty J, Banman S, Goping IS, Mercer JR (2012) Evaluation of phosphatidylserine-binding peptides targeting apoptotic cells. J Biomol Screen 17:1293–1301
Khoshbakht S, Beiki D, Geramifar B, Kobarfard F, Sabzevari O, Amini M, Shahhosseini S (2016) 18FDG-labeled LIKKPF: a PET tracer for apoptosis imaging. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 310:413–421
Ben Azzouna R, Guez A, Benali K, Al-Shoukr F, Gonzalez W, Karoyan P, Rouzet F, Le Guludec D (2017) Synthesis, gallium labelling and characterization of P04087, a functionalized phosphatidylserine-binding peptide. EJNMMI Radiopharm Chem 2:3
Xiong C, Brewer K, Song S, Zhang R, Lu W, Wen X, Li C (2011) Peptide-based imaging agents targeting phosphatidylserine for the detection of apoptosis. J Med Chem 54:1825–1835
Igarashi K, Kaneda M, Yamaji A, Saido TC, Kikkawa U, Ono Y, Inoue K, Umeda M (1995) A novel phosphatidylserine-binding peptide motif defined by an anti-idiotypic monoclonal antibody. Localization of phosphatidylserine-specific binding sites on protein kinase C and phosphatidylserine decarboxylase. J Biol Chem 270:29075–29078
Song S, Xiong C, Lu W, Ku G, Huang G, Li C (2013) Apoptosis imaging probe predicts early chemotherapy response in preclinical models: a comparative study with 18F-FDG PET. J Nucl Med 54:104–110
Perreault A, Richter S, Bergman C, Wuest M, Wuest F (2016) Targeting phosphatidylserine with a 64Cu-labeled peptide for molecular imaging of apoptosis. Mol Pharm 13:3564–3577
Nock BA, Maina T, Krenning EP, de Jong M (2014) To serve and protect’: enzyme inhibitors as radiopeptide escorts promote tumor targeting. J Nucl Med 55:121–127
Langer M, Beck-Sickinger AG (2001) Peptides as carrier for tumor diagnosis and treatment. Curr Med Chem Anticancer Agents 1:71–93
Thapa N, Kim S, So IS, Lee BH, Kwon IC, Choi K, Kim IS (2008) Discovery of a phosphatidylserine-recognizing peptide and its utility in molecular imaging of tumour apoptosis. J Cell Mol Med 12:1649–1660
Kim S, Bae SM, Seo J, Cha K, Piao M, Kim SJ, Son HN, Park RW, Lee BH, Kim IS (2015) Advantages of the phosphatidylserine-recognizing peptide PSP1 for molecular imaging of tumor apoptosis compared with annexin V. PLoS ONE 10:e0121171
Shukla SP, Udugamasooriya DG (2017) A mini-library system to investigate non-essential residues of lipid-phosphatidylserine (PS) binding peptide-peptoid hybrid PPS1. Medchemcomm 8:2208–2215
Singh J, Shukla SP, Desai TJ, Udugamasooriya DG (2016) Identification of the minimum pharmacophore of lipid-phosphatidylserine (PS) binding peptide-peptoid hybrid PPS1D1. Bioorg Med Chem 24:4470–4477
Shukla SP, Manarang JC, Udugamasooriya DG (2017) A unique mid-sequence linker used to multimerize the lipid-phosphatidylserine (PS) binding peptide-peptoid hybrid PPS1. Eur J Med Chem 137:1–10
Zheng H, Wang F, Wang Q, Gao J (2011) Cofactor-free detection of phosphatidylserine with cyclic peptides mimicking lactadherin. J Am Chem Soc 133:15280–15283
Hosseini AS, Zheng H, Gao J (2014) Understanding lipid recognition by protein-mimicking cyclic peptides. Tetrahedron 70:7632–7638
Stafford JH, Hao G, Best AM, Sun X, Thorpe PE (2013) Highly specific PET imaging of prostate tumors in mice with an iodine-124-labeled antibody fragment that targets phosphatidylserine. PLoS ONE 8:e84864
Zhang L, Zhou H, Belzile O, Thorpe P, Zhao D (2014) Phosphatidylserine-targeted bimodal liposomal nanoparticles for in vivo imaging of breast cancer in mice. J Control Release 183:114–123
Koulov AV, Stucker KA, Lakshmi C, Robinson JP, Smith BD (2003) Detection of apoptotic cells using a synthetic fluorescent sensor for membrane surfaces that contain phosphatidylserine. Cell Death Differ 10:1357–1359
Ngo HT, Liu X, Jolliffe KA (2012) Anion recognition and sensing with Zn(II)-dipicolylamine complexes. Chem Soc Rev 41:4928–4965
Plaunt AJ, Harmatys KM, Wolter WR, Suckow MA, Smith BD (2014) Library synthesis, screening, and discovery of modified Zinc(II)-Bis(dipicolylamine) probe for enhanced molecular imaging of cell death. Bioconjug Chem 25:724–737
Oltmanns D, Zitzmann-Kolbe S, Mueller A, Bauder-Wuest U, Schaefer M, Eder M, Haberkorn U, Eisenhut M. Zn (2011) (II)-bis(cyclen) complexes and the imaging of apoptosis/necrosis. Bioconjug Chem 22:2611–2624
Wang H, Wu Z, Li S, Hu K, Tang G (2017) Synthesis and evaluation of a radiolabeled bis-zinc(II)-cyclen complex as a potential probe for in vivo imaging of cell death. Apoptosis 22:585–595
Wyffels L, Gray BD, Barber C, Moore SK, Woolfenden JM, Pak KY, Liu Z (2011) Synthesis and preliminary evaluation of radiolabeled bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine) coordination complexes as cell death imaging agents. Bioorg Med Chem 19:3425–3433
Sun T, Tang G, Tian H, Hu K, Yao S, Su Y, Wang C (2015) Positron emission tomography imaging of cardiomyocyte apoptosis with a novel molecule probe [18F]FP-DPAZn2. Oncotarget 6:30579–30591
Wang H, Tang X, Tang G, Huang T, Liang X, Hu K, Deng H, Yi C, Shi X, Wu K (2013) Noninvasive positron emission tomography imaging of cell death using a novel small-molecule probe, (18)F labeled bis(zinc(II)-dipicolylamine) complex. Apoptosis 18:1017–10927
Wen F, Nie D, Hu K, Tang G, Yao S, Tang C (2017) Semi-automatic synthesis and biodistribution of N-(2-(18)F-fluoropropionyl)-bis(zinc (II)-dipicolylamine) ((18)F-FP-DPAZn2) for AD model imaging. BMC Med Imaging 17:27
Wang X, Feng H, Zhao S, Xu J, Wu X, Cui J, Zhang Y, Qin Y, Liu Z, Gao T, Gao Y, Zeng W (2017) SPECT and PET radiopharmaceuticals for molecular imaging of apoptosis: from bench to clinic. Oncotarget 8:20476–20495
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the support of this research by the Dianne and Irving Kipnes Foundation, the Alberta Cancer Foundation (ACF) and the Canadian Foundation for Innovation (CFI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wuest, M., Perreault, A., Richter, S. et al. Targeting phosphatidylserine for radionuclide-based molecular imaging of apoptosis. Apoptosis 24, 221–244 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01523-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01523-1