Abstract
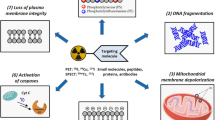
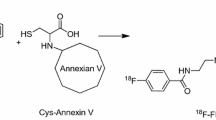
This review provides a critical and thorough overview of the radiopharmaceutical development and in vivo evaluation of all apoptosis-detecting radioligands that have emerged so far, along with their possible applications in nuclear medicine. The following SPECT and PET radioligands are discussed: all forms of halogenated Annexin V (i.e. 123I-labelled, 124I-labelled, 125I-labelled, 18F-labelled), 99mTc/94mTc-labelled Annexin V derivatives using different chelators and co-ligands (i.e. BTAP, Hynic, iminothiolane, MAG3, EDDA, EC, tricarbonyl, SDH) or direct 99mTc-labelling, 99mTc-labelled Annexin V mutants and 99mTc/18F-radiopeptide constructs (i.e. AFIM molecules), 111In-DTPA-PEG-Annexin V, 11C-Annexin V and 64Cu-, 67Ga- and 68Ga-DOTA-Annexin V. In addition, the potential role and clinical relevance of anti-PS monoclonal antibodies and other alternative apoptosis markers are reviewed, including: anti-Annexin V monoclonal antibodies, radiolabelled caspase inhibitors and substrates and mitochondrial membrane permeability targeting radioligands. Nevertheless, major emphasis is placed on the group of Annexin V-based radioligands, in particular 99mTc-Hynic-Annexin V, since this molecule is by far the most extensively investigated and best-characterised apoptosis marker at present. Furthermore, the newly emerging imaging modalities for in vivo detection of programmed cell death, such as MRI, MRS, optical, bioluminescent and ultrasound imaging, are briefly described. Finally, some future perspectives are presented with the aim of promoting the development of potential new strategies in pursuit of the ideal cell death-detecting radioligand.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
A detailed list of preclinical studies is available from the author.
References
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 1972;26:239–57
Proskuryakov SY, Konoplyannikov AG, Gabai VL. Necrosis: a specific form of programmed cell death? Exp Cell Res 2003;283:1–16
McConkey DJ. Biochemical determinants of apoptosis and necrosis. Toxicol Lett 1998;99:157–68
Majno G, Joris I. Apoptosis, oncosis and necrosis: an overview of cell death. Am J Pathol 1995;146:3–15
Honig LS, Rosenberg RN. Apoptosis and neurologic disease. Am J Med 2000;108:317–30
Allen RT, Hunter WJ, Agrawal DK. Morphological and biochemical characterization and analysis of apoptosis. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 1997;37:215–28
Saraste A, Pulkki K. Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:528–37
Wyllie AH, Kerr JFR, Currie AR. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. In: Bourne GH, Danielli JF, Jeon KW, eds. International review of cytology. London: Academic; 1980. pp. 251–306
Syeed SA, Vohra H, Gupta A, Ganguly NK. Apoptosis: molecular machinery. Curr Sci 2001;80:349–60
Böhm I, Schild H. Apoptosis: the complex scenario for a silent cell death. Mol Imaging Biol 2003;5:2–14
Bortner CD, Cidlowski A. A necessary role for cell shrinkage in apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 1998;56:1549–59
Denecker G, Vercammen D, Declercq W, Vandenabeele P. Apoptotic and necrotic cell death induced by death domain receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 2001;58:356–70
Bridgham JT, Wilder JA, Hollocher H, Johnson AL. All in the family: evolutionary and functional relationships among death receptors. Cell Death Differ 2003;10:19–25
French LE, Tschopp J. Protein-based therapeutic approaches targeting death receptors. Cell Death Differ 2003;10:117–23
Schmitz I, Kirchhoff S, Krammer PH. Regulation of death receptor-mediated apoptosis pathways. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2000;32:1132–6
Kaufmann SH. Activation of cell death pathways. Hematology 1999;476–82
Hengartner MO. The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 2000;407:770–7
Schimmer AD, Hedley DW, Penn LZ, Minden MD. Receptor- and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in acute leukemia: a translational view. Blood 2001;98:3541–53
Thompson CB. Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 1995;267:1456–62
Saikumar P, Dong Z, Mikhailov V, et al. Apoptosis: definition, mechanisms, and relevance to disease. Am J Med 1999;107:489–506
Yue T-L, Ohlstein EH, Ruffolo Jr RR. Apoptosis: a potential target for discovering novel therapies for cardiovascular diseases. Curr Opin Chem Biol 1999;3:474–80
Bosman FT, Visser BC, Van Oeveren J. Apoptosis: pathophysiology of programmed cell death. Pathol Res Pract 1996;192:676–83
Kam PCA, Ferch NI. Apoptosis: mechanisms and clinical implications. Anaesthesia 2000;55:1081–93
Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis 2000;21:485–95
Kerr JFR, Winterford CM, Harmon BV. Apoptosis: its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 1994;73:2013–26
Zörnig M, Hueber AO, Baum W, Evan G. Apoptosis regulators and their role in tumorigenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1551:1–37
Evan GI, Vousden KH. Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 2001;411:342–8
White E. Life, death and the pursuit of apoptosis. Gene Dev 1996;10:1–15
Ashkenazi A, Dixit VM. Death receptors: signalling and modulation. Science 1998;281:1305–8
Evan G, Littlewood T. Apoptosis: a matter of life and cell death. Science 1998;281:1317–21
Green DR, Reed JC. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 1998;281:1309–12
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science 1998;281:1312–6
Dive C, Hickman JA. Drug-target interactions: only the first step in the commitment to a programmed cell death? Br J Cancer 1991;64:192–6
Green AM, Steinmetz ND. Monitoring apoptosis in real time. Cancer J 2002;8:82–92
Belhocine T, Steinmetz N, Hustinx R, et al. Increased uptake of the apoptosis-imaging agent 99mTc recombinant human annexin V in human tumors after one course of chemotherapy as a predictor of tumor response and patient prognosis. Clin Cancer Res 2002;8:2766–74
Blankenberg FG, Narula J, Strauss HW. In vivo detection of apoptotic cell death: a necessary measurement for evaluating therapy for myocarditis, ischemia and heart failure. J Nucl Cardiol 1999;6:531–9
Gerke V, Moss SE. Annexins: from structure to function. Physiol Rev 2002;82:331–71
Benz J, Hofmann A. Annexins: from structure to function. Biol Chem 1997;378:177–83
Delmer DP, Potikha TS. Structures and functions of annexins in plants. Cell Mol Life Sci 1997;53:546–53
Tzima E, Walker JH. Platelet annexin V: the ins and outs. Platelets 2000;11:245–51
Swairjo MA, Seaton BA. Annexin structure and membrane interactions: a molecular perspective. Annu Rev Biophys Struct 1994;23:193–213
Van Heerde WL, de Groot PG. Reutelingsperger CPM. The complexity of the phospholipid binding protein annexin V. Thromb Haemost 1995;73:172–9
Weinman S. Calcium-binding proteins: an overview. J Biol Buccale 1991;19:90–8
Andree HAM, Reutelingsperger CPM, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC, Hermens WT, Willems GM. Binding of vascular anticoagulant α (VACα) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem 1990;265:4923–8
Römisch J, Schüler E, Bastian B, et al. Annexins I to VI: quantitative determination in different human cell types and in plasma after myocardial infarction. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 1992;3:11–7
Andree HAM, Stuart MCA, Hermens WT, Reutelingsperger CPM, Hemker HC, Frederik PM, Willems GM. Clustering of lipid-bound annexin V may explain its anticoagulant effect. J Biol Chem 1992;267:17907–12
Kirsch T, Harrison G, Golub EE, Nah H-D. The roles of annexins and types II and X collagen in matrix vesicle-mediated mineralization of growth plate cartilage. J Biol Chem 2000;275:35577–83
Matteo RG, Moravec CS. Immunolocalization of annexins IV, V and VI in the failing and non-failing human heart. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:961–70
Walker JH, Boustead CM, Brown R, Koster JJ, Middleton CA. Tissue and subcellular distribution of endonexin, a calcium-dependent phospholipid-binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans 1990;18:1235–6
Walker JH, Boustead CM, Koster JJ, Bewley M, Walker DA. Annexin V, a calcium-dependent phospholipid binding protein. Biochem Soc Trans 1992;20:828–33
Murphy CT, Peers SH, Forder RA, Flower RJ, Carey F, Westwick J. Evidence for the presence and location of annexins in human platelets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1992;189:1739–46
Huber R, Römisch J, Paques EP. The crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V, an anticoagulant protein that binds to calcium and membranes. EMBO J 1990;9:3867–74
Huber R, Berendes R, Burger A, et al. Crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V after refinement. Implications for structure, membrane binding and ion channel formation of the annexin family of proteins. J Mol Biol 1992;223:683–704
Gerke V, Moss SE. Annexins and membrane dynamics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1997;1357:129–54
Andree HAM, Reutelingsperger CPM, Hauptmann R, Hemker HC, Hermens WT, Willems GM. Binding of vascular anticoagulant (VAC) to planar phospholipid bilayers. J Biol Chem 1990;265:4923–8
Ahn NG, Teller DC, Bienkowski MJ, McMullen BA, Lipkin EW, de Haën C. Sedimentation equilibrium analysis of five lipocortin-related phospholipase A2 inhibitors from human placenta. J Biol Chem 1988;263:18657–63
Römisch J, Grote M, Weithmann KU, Heimburger N, Amann E. Annexin proteins PP4 and PP4-X: comparative characterization of biological activities of placental and recombinant proteins. Biochem J 1990;272:223–9
Tait JF, Gibson D, Fujikawa K. Phospholipid binding properties of human placental anticoagulant protein-I, a member of the lipocortin family. J Biol Chem 1989;264:7944–9
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C. A novel assay for apoptosis: flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using a fluorescein labelled annexin V. J Immunol Methods 1995;184:39–51
Tait JF, Smith C, Wood BL. Measurement of phosphatidylserine exposure in leukocytes and platelets by whole-blood flow cytometry with annexin V. Blood Cells Mol Dis 1999;25:271–8
Zhang G, Gurtu V, Kain SR, Yan G. Early detection of apoptosis using a fluorescent conjugate of annexin V. Biotechniques 1997;23:525-31
Ormerod MG, Sun X-M, Brown D, Snowden RT, Cohen GM. Quntification of apoptosis and necrosis by flow cytometry. Acta Oncol 1993;32:417–24
Van Heerde WL, Robert-Offerman S, Dumont E, Hofstra L, Doevendans PA, Smits JFM, Daemen MJAP, Reutelingsperger CPM. Markers of apoptosis in cardiovascular tissues: focus on annexin V. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:549–59
Sgonc R, Gruber J. Apoptosis detection: an overview. Exp Gerontol 1998;33:525–33
Kang PM, Izumo S. Apoptosis in heart failure: is there light at the end of the tunnel (TUNEL)? J Card Fail 2000;6:43–6
Darzynkiewicz Z, Bedner E, Traganos F. Difficulties and pitfalls in analysis of apoptosis. Methods in cell biology. London: Academic; 2001:527–46
Blankenberg FG, Tait JF, Strauss HW. Apoptotic cell death: its implications for imaging in the next millennium. Eur J Nucl Med 2000;27:359–67
Blankenberg FG, Ohtsuki K, Strauss HW. Dying a thousand deaths: radionuclide imaging of apoptosis. Q J Nucl Med 1999;43:170–6
Hofstra L, Liem IH, Dumont EA, et al. Visualisation of cell death in vivo in patients with acute myocardial infarction. Lancet 2000;356:209–12
Hofstra L, Dumont EA, Thimister PWL, et al. In vivo detection of apoptosis in an intracardiac tumor. J Am Med Assoc 2001;285:1841–2
Rao LVM, Tait JF, Hoang AD. Binding of annexin V to human ovarian carcinoma cell line (OC-2008). Contrasting effects on cell surface factor VIIa/tissue factor activity and prothrombinase activity. Thromb Res 1992;67:517–31
Funakoshi T, Heimark RL, Hendrickson LE, McMullen BA, Fujikawa K. Human placental anticoagulant protein: isolation and characterisation. Biochemistry 1987;26:5572–8
Tait JF, Sakata M, McMullen BA, Miao CH, Funakoshi T, Hendrickson LE, Fujikawa K. Placental anticoagulant proteins: isolation and comparative characterisation of four members of the lipocortin family. Biochemistry 1998;27:6268–76
Wood BL, Gibson DF, Tait JF. Increased erythrocyte phosphatidylserine exposure in sickle cell disease: flow-cytometric measurement and clinical associations. Blood 1996;88:1873–80
Tait JF, Engelhardt S, Smith C, Fujikawa K. Prourokinase-Annexin V chimeras. J Biol Chem 1995;270:21594–9
Thiagarajan P, Benedict CR. Inhibition of arterial thrombosis by recombinant annexin V in a rabbit carotid artery injury model. Circulation 1997;96:2339–47
Reutelingsperger CPM, van Heerde WL. Annexin V, the regulator of phosphatidylserine-catalyzed inflammation and coagulation during apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 1997;53:527–32
Williamson P, Schiegel RA. Back and forth: the regulation and function of transbilayer phospholipid movement in eukarotic cells. Mol Membr Biol 1994;11:199–216
Schroit AJ, Zwaal RFA. Transbilayer movement of phospholipids in red cell and platelet membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1991;1071:313–29
Zwaal RFA, Schroit AJ. Pathophysiologic implications of membrane phospholipid asymmetry in blood cells. Blood 1997;89:1121–32
Bevers EM, Comfurius P, Dekkers DWC, Zwaal RFA. Lipid translocation across the plasma membrane of mammalian cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1999;1439:317–30
Martin Brown J, Wouters BJ. Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Totowa: Humana; 1999:1–333
Hickman JA. Apoptosis induced by anticancer drugs. Cancer Metastasis Rev 1992;11:121–39
Hickman JA. Apoptosis and chemotherapy resistance. Eur J Cancer 1996;32A:921–6
Cohen-Jonathan E, Bernhard EJ, McKenna WG. How does radiation kill cells? Curr Opin Chem Biol 1999;3:77–83
Kessel D, Luo Y. Photodynamic therapy: a mitochondrial inducer of apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 1999;6:28–35
Dewey WC, Ling CC, Meyn RE. Radiation-induced apotosis: relevance to radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1995;33:781–96
Susin SA, Zamzami N, Kroemer G. Mitochondria as regulators of apoptosis: doubt no more. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1366:151–65
Martin SJ, Reutelingsperger CPM, McGahon AJ, et al. Early redistribution of plasma membrane phosphatidylserine is a general feature of apoptosis regardless of the initiating stimulus: inhibition by overexpression of Bcl-2 and Abl. J Exp Med 1995;182:1545–56
Van den Eijnde SM, Boshart L, Reutelingsperger CPM, De Zeeuw CI, Vermeij-Keers C. Phosphatidylserine plasma membrane asymetry in vivo: a pancellular phenomenon which alters during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 1997;4:311–6
Denecker G, Dooms H, Van Loo G, et al. Phosphatidyl serine exposure during apoptosis precedes release of cytohrome c and decrease in mitochondrial transmembrane potential. FEBS Lett 2000;465:47–52
Fadok VA, Savill JS, Haslett C, et al. Different populations of macrophages use either the vibronectin receptor or the phosphatidylserine receptor to recognize and remove apoptotic cells. J Immunol 1992;149:4029–35
Fadok VA, Voelker DR, Campbell PA, Cohen JJ, Bratton DL, Henson PM. Exposure of phosphatidylserine on the surface of apoptotic lymphocytes triggers specific recognition and removal by macrophages. J Immunol 1992;148:2207–16
Li MO, Sarkisian MR, Mehal WZ, Rakic P, Flavell RA. Phosphatidylserine receptor is required for clearance of apoptotic cells. Science 2003;302:1560–3
Sun J, Bird P, Salem HH. Interaction of annexin V and platelets: effects on platelet function and protein S binding. Thromb Res 1993;69:289–96
Thiagarajan P, Tait JF. Binding of annexin V/placental anticoagulant protein I to platelets. J Biol Chem 1990;265:17420–3
Tait JF, Gibson D. Measurement of membrane phospholipid asymmetry in normal and sickle-cell erythrocytes by means of annexin V binding. J Lab Clin Med 1994;123:741–8
Van Heerde WL, Poort S, Van’t Veer C, Reutelingsperger CPM, De Groot PG. Binding of recombinant annexin V to endothelial cells: effect of Annexin V binding on endothelial-cell-mediated thrombin formation. Biochem J 1994;302:305–12
Sugimura M, Donato R, Kakkar VV, Scully MF. Annexin V as a probe of the contribution of anionic phospholipids to the procoagulant activity of tumour cell surfaces. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis 1994;5:365–73
Meers P, Mealy T. Calcium-dependent annexin V binding to phospholipids: stoichiometry, specificity, and the role of negative charge. Biochemistry 1993;32:11711–21
Stratton JR, Dewhurst TA, Kasina S, Reno JM, Cerqueira MD, Baskin DG, Tait JF. Selective uptake of radiolabeled annexin V on acute porcine left atrial thrombi. Circulation 1995;92:3113–21
Bevers EM, Comfurius P, Zwaal RFA. Changes in membrane phospholipid distribution during platelet activation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1983;736:57–66
Stuart MCA, Bevers EM, Comfurius P, Zwaal RFA, Reutelingsperger CPM, Frederik PM. Ultrastructural detection of surface exposed phosphatidylserine on activated blood platelets. Thromb Haemost 1995;74:1145–51
Fraker P, Speck J. Protein and cell membrane iodinations with a sparingly soluble chloroamide, 1, 3, 4, 6-tetrachloro-3a, 6a-diphenylglycoluril. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1978;80:849–57
Tait JF, Gibson D. Measurement of membrane phospholipid asymmetry in normal and sickle-cell erythrocytes by means of annexin V binding. J Lab Clin Med 1994;123:741–8
Tait JF, Cerqueira MD, Dewhurst TA, Fujikawa K, Ritchie JL, Stratton JR. Evaluation of annexin V as a platelet-directed thrombus targeting agent. Thromb Res 1994;75:491–501
Goodwin CA, Wheeler-Jones C, Namiranian S, Bokkala S, Kakkar V, Authi KS, Scully MF. Increased expression of procoagulant activity on the surface of human platelets exposed to heavy-metal compounds. Biochem J 1991;308:15–21
Kinlough-Rathbone RL, Perry DW. Prolonged expression of procoagulant activity of human platelets degranulated by thrombin. Thromb Haemost 1995;74:958–61
Le DT, Rapaport SI, Rao LVM. Studies of the mechanism for enhanced cell surface factor VII/tissue factor activation of factor X on fibroblast monolayers after their exposure to N-ethylmaleimide. Thromb Haemost 1994;72:848–55
Rao LVM, Tait JF, Hoang AD. Binding of annexin V to human ovarian carcinoma cell line (OC-2008). Contrasting effects on cell surface factor VIIa/tissue factor activity and prothrombinase activity. Thromb Res 1992;67:517–31
Tait JF, Engelhardt S, Smith C, Fujikawa K. Prourokinase-Annexin V chimeras: construction, expression, and characterization of recombinant proteins. J Biol Chem 1995;270:21594–9
Lahorte C, Dumont F, Slegers G, Van De Wiele C, Dierckx RA, Philippé J. Synthesis and in vitro stability of 123I-labelled annexin V: a potential agent for SPECT imaging of apoptotic cells. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2000;43:739–51
Lahorte C, Slegers G, Philippé J, Van De Wiele C, Dierckx RA. Synthesis and in vitro evaluation of 123I-labelled human recombinant annexin V. Biomol Eng 2001;17:51–3
Lahorte C, Van de Wiele C, Bacher K, et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry study of 123I-rh-Annexin V in mice and humans. Nucl Med Commun 2003;24:871–80
Lahorte C, Pétillot P, Nevière R, Marchetti P, Slegers G. The myocardial uptake of 123I-annexin V is increased in septic rats [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2001;44(Suppl 1):S430–2
Pétillot P, Lahorte C, Nevière R, Slegers G, Vallet B, Formstecher P, Marchetti P. Myocardial protection is provided by the caspase inhibitor zVAD.fmk during septic shock [abstract]. Intensive Care Med 2001;27(43 Suppl 2):S146
Lahorte C, Pétillot P, Marchetti P, Bonanno E, Signore A, Slegers G. Ex vivo detection of myocardial cell death with 123I-annexin V in a rat model of septic shock [abstract]. Eur J Nucl 2002;29(Suppl 1):S91
World Health Organisation Technical Report Series 611. Use of ionizing radiation and radionuclides on human beings from medical research, training, and non-medical purposes. Report of a WHO Expert Committee, Geneva; 1977
Annals of the ICRP. Radiological protection in biomedical research. New York: Pergamon; 1991:12–3
Russell J, O’ Donoghue JA, Finn R, et al. Iodination of Annexin V for imaging apoptosis. J Nucl Med 2002;43:671–7
Glaser M, Collingridge DR, Aboagye E, et al. Preparation of [124I]IBA-annexin-V as a potential PET probe for apoptosis [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2001;44(Suppl 1):S336–8
Glaser M, Collingridge DR, Aboagye EO, et al. Iodine-124 labelled annexin-V as a potential radiotracer to study apoptosis using positron emission tomography. Appl Radiat Isot 2003;58:55–62
Keen H, Dekker B, Disley L, Hastings D, Lyons S, Smith N, Zweit J, Watson A. Iodine-124 labelled annexin V for PET imaging of in vivo cell death [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):180
Dekker B, Keen H, Zweit J, Lyons S, Smith N, Watson A, Williams G, Disley L. Detection of cell death using 124I-Annexin V [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):71P
Dekker B, Disley L, Hastings D, Keen H, Lyons S, Shaw D, Watson A, Zweit J. Use of [124I]-4-iodobenzylsuccinimide to radiolabel MBP-Annexin V [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2003;46(Suppl 1):S386
Wester HJ, Hammacher K, Stöcklin G. A comparative study of n.c.a. fluorine-18 labeling of proteins via acylation and photochemical conjugation. Nucl Med Biol 1996;23:365–72
Wester HJ. Zur praktisch trägerfreien 18F-fluorierung von Proteinen, Peptiden und Tyrosin. Berichte des Forschungszentrums Jülich [dissertation]. Germany: University of Cologne; 1996:3206
Zijlstra S, Gunawan J, Burchert W. Synthesis and evaluation of a 18F-labelled recombinant annexin-V derivative, for identification and quantification of apoptotic cells with PET. Appl Radiat Isot 2003;58:201–7
Zijlstra S, Gunawan J, Burchert W. Synthesis of fluorine-18 labeled recombinant annexin V derivative, for identification and quantification of apoptotic cells with PET [abstract]. Abstracts of the IXth Turku PET symposium, May 25–28, 2002, Turku, Finland; 2002
Mease RC, Weinberg IN, Toretsky JA, Tait JF. Preparation of F-18 labeled annexin V: a potential PET radiopharmaceutical for imaging cell death [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):295P–6P
Grierson JR, Yagle KJ, Eary JF, et al. Production of [F-18]fluoroannexin for imaging apoptosis with PET. Bioconjug Chem 2004; 15:373–9
Murakami Y, Takamatsu H, Tatsumi M, Noda A, Ichise R, Nishimura S. F-18 labeled annexin V: a PET tracer for apoptosis imaging [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):312P
Kasina S, Rao TN, Srinivasan A, et al. Development and biologic evaluation of a kit for preformed chelate technetium-99m radiolabeling of an antibody Fab fragment using a diamide dimercaptide chelating agent. J Nucl Med 1991;32:1445–51
Fritzberg AR, Abrams PG, Beaumier PL, et al. Specific and stable labeling of antibodies with technetium-99m with a diamide dithiolate chelating agent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1988;85:4025–9
Kown MH, Strauss HW, Blankenberg FG, et al. In vivo imaging of acute cardiac allograft rejection in human patients using 99mtechnetium labeled annexin V. Am J Transplant 2001;1:270–7
Narula J, Acio ER, Narula N, et al. Annexin-V imaging for noninvasive detection of cardiac allograft rejection. Nat Med 2001;7:1347–51
Kemerink GJ, Boersma HH, Thimister PWL, et al. Biodistribution and dosimetry of 99mTc-BTAP-annexin-V in humans. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:1373–8
Van den Heuvel IJ, Pool B, Valdés-Olmos R, Haas R. Labelling and imaging aspects of 99mTc-rh-Annexin V in tumour-apoptosis detection [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30(Suppl 2):S167
Haas RLM, Valdés-Olmos RA, De Jong D, Zerp SF, Van den Heuvel IJ, Hoefnagel CA, Bartelink H, Verheij M. Radiation induced apoptosis in follicular lymphoma patients assessed by 99mTc-Annexin V scintigraphy [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30(Suppl 2):S197
Abrams MJ, Juweid M, tenKate CI, et al. Technetium-99m-human polyclonal IgG radiolabeled via the hydrazino nicotinamide derivative for imaging focal sites of infection in rats. J Nucl Med 1990;31:2022–8
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, et al. In vivo detection and imaging of phosphatidylserine expression during programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998;95:6349–54
Blankenberg FG, Tait J, Ohtsuki K, Strauss HW. Apoptosis: the importance of nuclear medicine. Nucl Med Commun 2000;21:241–50
Narula J, Petrov A, Kolodgie FD, Acio ER, Snyder G, Tait JF, Blankenberg FG, Strauss HW. Transient sarcolemmal phosphatidyl serine expression as a marker of brief ischemia: an evaluation by 99mTc-Annexin V imaging [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2000;41(5):173P–4P
Kown MH, Van der Steenhoven T, Blankenberg FG, et al. Zinc-mediated reduction of apoptosis in cardiac allografts. Circulation 2000;102:III-228–32
Kown MH, Van der Steenhoven TJ, Jahncke CL, et al. Zinc chloride-mediated reduction of apoptosis as an adjunct immunosuppressive modality in cardiac transplantation. J Heart Lung Transplant 2002;21:360–5
Kemerink GJ, Liu X, Kieffer D, et al. Safety, biodistribution, and dosimetry of 99mTc-HYNIC-Annexin V, a novel human recombinant annexin V for human application. J Nucl Med 2003;44:947–52
Steinmetz N, Taillefer R, Hendel RC, et al. Simultaneous dual isotope 201TI/99mTc-Annexin (apomateTM) SPECT in detection of acute myocardial infarction: initial results of a phase II multicenter trial [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):4P
Taillefer R, Phaneuf DC, Duong DH, et al. 99mTc-Annexin V scintigraphy in detection of acute myocardial infarction (MI): repeat imaging after the onset of acute symptoms in order to evaluate the persistence of abnormal radiotracer uptake [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):5P
Thimister PWL, Pakbiers M, Janssen D, Heidendal GAK. Disappearance of apoptosis in the sub acute phase of acute myocardial infarction [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29(Suppl 1):S49
Kietselaer BL, Boersma HH, Heidendal GA, et al. The use of 99mTc labeled annexin-A5 imaging in the diagnostic work-up of intracardiac masses [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):156P
Van de Wiele C, Lahorte C, Vermeersch H, et al. Quantitative tumour apoptosis imaging using 99mTc-HYNIC-Annexin single photon emission computerized tomography. J Clin Oncol 2003;21:3483–7
Vermeersch H, Loose D, Lahorte C, et al. 99mTc-HYNIC Annexin-V imaging of primary head and neck carcinoma. Nucl Med Commun 2004;25:259-63
Kemerink GJ, Liem IH, Hofstra L, Boersma HH, Buijs WCAM, Reutelingsperger CPM, Heidendal GAK. Patient dosimetry of intravenously administered 99mTc-Annexin. J Nucl Med 2001;42:382–7
Goedemans WT, Panck KJ. A new simple method for labeling of proteins with 99mTc [abstract]. J Nucl Med Allied Sci 1989;33(3):286
Dumont EAW, Hofstra L, Van Heerde WL, et al. Cardiomyocyte death induced by myocardial ischemia and reperfusion: measurement with recombinant human annexin V in a mouse model. Circulation 2000;102:1564–8
Vanderheyden JL, Liu G, He J, Patel B, Hnatowich DJ. A comparison in normal mice of annexin V radiolabeled with 99mTc via hynic/tricine and MAG3 [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):311P
McQuade P, Jones LA, Vanderheyden JL, Welch MJ. 94mTc and 64Cu labeled annexin-V, positron emitting radiopharmaceuticals to study apoptosis [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2003;46(Suppl 1):S335
Decristoforo C, Mather SJ. The influence of chelator on the pharmacokinetics of 99mTc-labelled peptides. Q J Nucl Med 2002;46:195–205
Verbeke KA, Kieffer D, Vanderheyden JL, Steinmetz N, Green A, Verbruggen A. Influence of the co-ligand on the labelling and biodistribution of Tc-99m labelled Hynic-Annexin V [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29(Suppl 1):S369
Verbeke K, Kieffer D, Vanderheyden JL, et al. Optimization of the preparation of 99mTc-labeled Hynic-derivatized Annexin V for human use. Nucl Med Biol 2003;30:771–8
Yang DJ, Kim EE. Imaging of apoptosis and hypoxia. In: Kim EE, Yang DJ, editors. Targeted molecular imaging in oncology. New York: Springer-Verlag; 2001. p. 215–28
Yang DJ, Azhdarinia A, Wu P. In vivo and in vitro measurement of apoptosis in breast cancer cells using 99mTc-EC-annexin V. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2001;16:73–83
Kim EE, Yang DJ, Azhdarinia A, et al. Assessment of tumor growth using angiogenic and apoptotic agents [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30(Suppl 2):S316
Umezawa K, Nakazawa K Uchihata Y, Otsuka M. Screening for inducers of apoptosis in apoptosis-resistant human carcinoma cells. Adv Enzyme Regul 1999;39:145–56
Lennon SV, Martin SJ, Cotter TG. Dose-dependent induction of apoptosis in human tumour cell lines by widely diverging stimuli. Cell Prolif 1991;24:203–14
Haberkorn U, Bellemann ME, Brix G, et al. Apoptosis and changes in glucose transport early after treatment of Morris hepatoma with gemcitabine. Eur J Nucl Med 2001;28:418–25
Zhu L, Liu BL, Guo YZ. Tc-99m direct labeling of annexin V for potential apoptosis imaging in vivo [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2003;46(Suppl 1):S324
Garron JY, Pasqualini R, Saccavini JC. Radiomarquage des anticorps monoclonaux er des peptides par le technetium 99m–voie directe. In: Comet M, Vidal M, editors. Radiopharmaceutiques: chimie des radiotraceurs et applications biologiques. Grenoble: Universitaires de Grenoble; 1998:365–78
Subbarayan M, Häfeli UO, Feyes DK, Unnithan J, Emancipator SN, Mukhtar H. A simplified method for preparation of 99mTc-annexin V and its biologic evaluation for in vivo imaging of apoptosis after photodynamic therapy. J Nucl Med 2003;44:650–6
Reutelingsperger CPM, Hornstra G, Hemker HC. Isolation and partial purification of a novel anticoagulant from arteries of human umbilical cord. Eur J Biochem 1985;151:625–9
Subbarayan M, Hafeli U, Mukhtar H. Cellular imaging of apoptosis induced by photodynamic therapy (PDT) using Tc-99m-Annexin V made by a novel method [abstract]. Mol Imaging Biol 2002;4(4 Suppl 1);S41
Huber R, Schneider M, Mayr I, Romisch J, Paques EP. The calcium binding sites in human annexin V by crystal structure analysis at 2.0 Angström resolution. Implications for membrane binding and calcium channel activity. FEBS Lett 1990;275:15–21
Tait JF, Smith C. Site-specific mutagenesis of annexin V: role of residues from Arg-200 to Lys-207 in phospholipid binding. Arch Biochem Biophys 1991;288:141–4
Mira J-P, Dubois T, Oudinet J-P, Lukowski S, Russo-Marie F, Geny B. Inhibition of cytosolic phospholipase A2 by annexin V in differentiated permeabilized HL-60 cells. J Biol Chem 1997;272:10474–82
Montaville P, Neumann J-M, Russo-Marie F, Ochsenbein F, Sanson A. A new consensus sequence for phosphatidylserine recognition by annexins. J Biol Chem 2002;277:24684–93
Meers P. Location of tryptophans in membrane-bound annexins. Biochemistry 1990;29:3325–30
Meers P, Mealy T. Phospholipid determinants for annexin V binding sites and the role of tryptophan 187. Biochemistry 1994;33:5829–37
Dubois T, Mira J-P, Feliers D, Solito E, Russo-Marie F, Oudinet J-P. Annexin V inhibits protein kinase C activity via a mechanism of phospholipid sequestration. Biochem J 1998;330:1277–82
Tait JF, Brown DS, Gibson DF, Blankenberg FG, Strauss HW. Development and characterization of annexin V mutants with endogenous chelation sites for 99mTc. Bioconjug Chem 2000;11:918–25
Mariani G, Erba P, Pellegrino D, et al. Biodistribution patterns of native and mutant 99mTc-labeled annexin V in mice [abstract]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2003;18(2):290
Mariani G, Pellegrina D, Freer G, et al. Biodistribution of native and mutant annexin V in mice [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):138P
Mariani G, Pellegrino D, Freer G, Volterrani D, Bevilacqua G, Blankenberg F, Tait J, Strauss HW. Biodistribution patterns of native and mutant 99mTc-labeled annexin V in mice [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):153P–4P
Kuge Y, Sato M, Zhao S, et al. Does previous treatment with annexin V affect 99mTc-annexin V accumulation in the tumor before or after chemotherapy [abstract]? J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):180P–1P
Mochizuki T, Kuge Y, Zhao S, et al. Detection of apoptotic tumor response in vivo after a single dose of chemotherapy with 99mTc-annexin V. J Nucl Med 2003;44:92–7
Tait JF, Smith C, Gibson DF. Development of annexin V mutants suitable for labeling with Tc(I)-carbonyl complex. Bioconjug Chem 2002;13:1119–23
Alberto R, Schibli R, Egli A, Schubiger AP. A novel organometallic aqua complex of technetium for the labelling of biomolecules: synthesis of [99mTc(OH2)3(CO)3]+ from [99mTcO4]- in aqueous solution and its reaction with a bifunctional ligand. J Am Chem Soc 1998;120:7987–8
Han ES, Sato N, Wong KJ, Park LS, Yu S, Vanderheyden JL, Carrasquillo JA, Paik CH. Labeling annexin V with 99mTc-tricarbonyl PADA improved its organ clearance property [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):374P
Ohtsuki K, Akashi K, Aoka Y, Blankenberg FG, Kopiwoda S, Tait JF, Straus HW. Technetium-99m HYNIC-annexin V: a potential radiopharmaceutical for the in vivo detection of apoptosis. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26:1251–8
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF, et al. Imaging of apoptosis (programmed cell death) with 99mTc annexin V. J Nucl Med 1999;40:184–91
He J, Liu C, Vanderheyden JL, Liu G, Rusckowski M, Hnatowich DJ. Radiolabeling morpholinos with 188Re carbonyl provides improved in vitro and in vivo stability to re-oxidation. Nucl Med Commun 2004:in press
Chang SM, Lai PH, Cheng HW, Lo JM. 99mTc (I) tricarbonyl labeled hynic-annexin V as a potential apoptosis imaging agent [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):316P
Li C, Wen X, Wu Q, et al. Apoptosis induced by drug treatments correlates with uptake of 111In-labeled PEGylated annexin V in MDA-MB468 tumors [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):41P–2P
Ito M, Tomiyoshi K, Takahashi N, et al. Development of a new ligand, 11C-labeled annexin V, for PET imaging of apoptosis [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2002;43(5):362P
Smith-Jones PM, Afroze A, Zanzonico P, Tait J, Larson SM, Strauss HW. 68Ga labelling of annexin-V: comparison to 99mTc-annexin-V and 67Ga-annexin [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):49P–50P
Dollé F, Hinnen F, Lagnel B, Boisgard R, Sanson A, Russo-Marie F, Tavitian B. Radiosynthesis of a [18F]fluoropyridine-based maleimide reagent for protein labelling [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2003;46:S15
Boisgard R, Blondel A, Dolle F, et al. A new 18F tracer for apoptosis imaging in tumor bearing mice [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):49P
Boisgard R, Vuillemard C, Dollé F, et al. New 18F and 99mTc radiopeptides for apoptosis imaging in tumour-bearing mice [abstract]. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 2003;18(2):282
Boisgard R, Blondel A, Vuillemard C, et al. A new spect tracer for improved apoptosis imaging in tumor bearing mice [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):98P
Blondel A, Laurent D, Vuillemard C, et al. Apoptosis detection using a new tracer for SPECT and PET imaging [abstract]. Mol Imaging Biol 2003;5(3):170–1
Ran S, Thorpe PE. Phosphatidylserine is a marker of tumor vasculature and a potential target for cancer imaging and therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2002;54:1479–84
Hashizume DM, Baluk P, Morikawa S, et al. Openings between defective endothelial cells explain tumor vessel leakiness. Am J Pathol 2000;156:1363–80
Nakamura N, Kuragaki C, Shidara Y, Yamaji K, Wada Y. Antibody to annexin V has anti-phospholipid and lupus anticoagulant properties. Am J Hematol 1995;49:347–8
Nakamura N, Shidara Y, Kawaguchi N, Azuma C, Mitsuda N, Onishi S, Yamaji K, Wada Y. Lupus anticoagulant autoantibody induces apoptosis in umbilical vein endothelial cells: involvement of annexin V. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1994;205:1488–93
Arai T, Matsubayashi AT, Sugi T, et al. Anti-annexin A5 antibodies in reproductive failures in relation to antiphospholipid antibodies and phosphatidylserine. Am J Reprod Immunol 2003;50:202–8
Rodriguez-Garcia MI, Fernandez JA, Rodriguez A, Fernandez MP, Gutierrez C, Torre-Alonso JC. Annexin V autoantibodies in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 1996;55:895–900
Kobayashi H, Kusakabe K Kanaya K, Momose M, Nagamatsu H, Okawa T, Kaneko N. Myocardial ischemia memory imaging: time course of In-111-DTPA anti-annexin V antibody uptake in the ischemic area [abstract]. J Nucl Med 1999;40(5 Suppl S):P818
Kobayashi H, Kaneko N, Kanaya K, Momose M, Kusakabe K, Okawa T, Kasanuki H. Myocardial ischemia memory imaging using monoclonal antibodies for myocardial annexin V [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med 1999;26(9):OS341
Kobayashi H, Kaneko N, Kanaya K, Momose M, Kusakabe K, Okawa T, Sakomura Y, Horie T. Myocardial ischemia memory imaging using monoclonal antibodies for myocardial annexin V [abstract]. Circulation 1998;98(17 Suppl S):484
Benevolensky D, Belikova Y, Mohammadzadeh R, et al. Expression and localization of the annexins II, V, and VI in myocardium from patients with end-stage heart failure. Lab Invest 2000;80:123–33
Strauss HF, Narula J, Blankenberg F. Radioimaging to identify myocardial cell death and probably injury. Lancet 2000;356:180–1
Kaneko N, Matsuda R, Hosoda S, Kajita T, Ohta Y. Measurement of plasma annexin V by ELISA in the early detection of acute myocardial infarction. Clin Chim Acta 1996;251:65–80
Bleackley C, Heibein JA. Enzymatic control of apoptosis. Nat Prod Rep 2001;18:431–40
Talanian RV, Brady KD, Cryns VL. Caspases as targets for anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic drug discovery. J Med Chem 2000;43:1–21
Reed JC, Tomaselli KJ. Drug discovery opportunities from apoptosis research. Curr Opin Biotechnol 2000;11:586–92
Haberkorn U, Kinscherf R, Krammer PH, Mier W, Eisenhut M. Investigation of a potential scintigraphic marker of apoptosis: radioiodinated Z-Val-Ala-DL-Asp(O-methyl)-fluoromethylketone. Nucl Med Biol 2001;28:793–8
Fischer U, Jänicke RU, Schulze-Osthoff K. Many cuts to ruin: a comprehensive update of caspase substrates. Cell Death Differ 2003;10:76–100
Alauddin MM, Hu J, Prakash GKS, Conti PS, Olah GA. A general synthesis of [18F]-labeled α-trifluoromethyl ketones for PET imaging [abstract]. J Labelled Cpd Radiopharm 2003;46:S189
Halestrap AP, Kerr PM, Javadov S, Woodfield K-Y. Elucidating the molecular mechanism of the permeability transition pore and its role in reperfusion injury of the heart. Biochim Biophys Acta 1998;1366:79–94
Zoratti M, Szabò I. The mitochondrial permeability transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1995;1241:139–76
Zamzami N, Kroemer G. The mitochondrion in apoptosis: how Pandora’s box opens. Nat Rev: Mol Cell Biol 2001;2:67–71
Halestrap A, McStay GP. Clarke SJ. The permeability transition pore complex: another view. Biochimie 2002;84:153–66
Hirsch T, Susin SA, Marzo I, Marchetti P, Zamzami N, Kroemer G. Mitochondrial permeability transition in apoptosis and necrosis. Cell Biol Toxicol 1998;14:141–5
Desagher S, Martinou J-C. Mitochondria as the central control point of apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 2000;10:369–77
Decaudin D, Marzo I, Brenner C, Kroemer G. Mitochondria in chemotherapy-induced apoptosis: a prospective novel target of cancer therapy (review). Int J Oncol 1998;12:141–52
Bernardi P, Petronili V, Di Lisa F, Forte M. A mitochondrial perspective on cell death. Trends Biochem Sci 2001;26:112–7
Madar I, Ravert HT, Nelkin B, Scheffel U, Hilton J, Dannals RF, Frost JJ. Physicochemical characteristics and uptake kinetics of voltage indicator [F-18] phosphonium cations [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):50P
Madar I, Ravert HT, Hilton J, Dannals RF, Frost JJ., Hare JM. Quantitative imaging of cardiomyopathy in heart failure using the voltage indicator [F-18]p-fluorobenzyl triphenylphosphonium ([F-18]p-FBnTP) and PET [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):87P
Madar I, Nelkin B, Isaacs JT, Ravert HT, Scheffel U, Dannals RF, Frost JJ. In vitro and in vivo correlation of taxotere-induced apoptosis in malignant cells and accumulation of the voltage indicator [F-18]p-fluorobenzyltriphenyl phosphonium ([F-18]p-FBnTP) [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):179P–80P
Madar I, Isaacs TD, Ravert HT, Scheffel U, Dalrymple S, Dannals RF, Frost JJ. Detection of androgen depletion-induced apoptosis in prostate using the voltage indicator [F-18]p-fluorobenzyltriphenyl phosphonium ([F-18]p-FBnTP), in vivo [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):180P
Kothan S, Vergote J, Dechsupa S, Mankhetorn S, Hauet N, Moretti JL. Influence of flavanoid on the mitochondrial membrane potential, on Pgp efflux assessed by 99mTc-MIBI and on apoptosis assessed by 99mTc-Annexin V in multidrug resistant and sensitive cells [abstract]. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2003;30(Suppl 2):S316
Blankenberg FG, Storrs RW, Naumovski L, Goralski T, Spielman D. Detection of apoptotic cell death by proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Blood 1996;88:1951–6
Brisdelli F, Iorio E, Knijn A, et al. Two-step formation of 1H NMR visible mobile lipids during apoptosis of paclitaxel-treated K562 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 2003;65:1271–80
Valonen P, Griffin J, Vaisanen T, et al. Macromolecular and lipid resonances in apoptosing BT4C glioma cells in vitro and tumors in vivo [abstract]. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 2002;10:26
Goldberg A, Poptani H, Duvvure U, Wherli S, Leigh J, Glickson J, Delikatny E. Quantification of unsaturated lipid changes in cyclophosphamide treated tumors [abstract]. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 2002;10:2145
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Storrs RW, Beaulieu C, Spielman D, Chen JY, Naumovski L, Tait JF. Quantitative analysis of apoptotic cell death using proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Blood 1997;89:3778–86
Locke S, Brauer M. Response of the rat liver in situ to bromobenzene: in vivo proton MRI an 31P MRS studies. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1991;110:416–28
Henke J, Flogel U, Pfeuffer J, Leibfritz D. Multinuclear NMR studies of apoptotic changes in a human tumor cell line during miltefosin treatment [abstract]. Proc Int Soc Magn Reson Med 1999;7:1343
Hakumaki JM, Poptani H, Sandmair AM, Ylä-Herttuala S, Kauppinen RA. 1H MRS detects polyunsaturated fatty acid accumulation during gene therapy of glioma: implications for the in vivo detection of apoptosis. Nat Med 1999;5:1323–7
Brauer M. In vivo monitoring of apoptosis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 2003;27:323–31
Poptani H, Puumalainen AM, Grohn O, Loimas S, Kainulainen R, Kauppinen RA. Monitoring thymidine kinase and ganciclovir-induced changes in rat malignant gliomas in vivo by MRI. Cancer Gene Ther 1998;5:101–9
Zhao M, Pipe J, Bonnett J, Evelhoch J. Early detection of treatment response by diffusion-weighted 1H NMR spectroscopy in a murine tumour in vivo. Br J Cancer 1996;73:61–4
Davletov BA, Sudhof TC. A single C2 domain from synaptotagmin I is sufficient for high affinity Ca2+/phospholipid binding. J Biol Chem 1993;26:26386–90
Sutton BR, Davletov BA, Berghuis AM, Südhof TC, Sprang SR. Structure of the first C2 domain of synaptotagmin I: a novel Ca2+/phospholipid-binding fold. Cell 1995;80:929–38
Zhao M, Beauregard DA, Loizou L. Non-invasive detection of apoptosis using magnetic resonance imaging and a targeted contrast agent. Nat Med 2001;7:1241–3
Schellenberger EA, Bogdanov A, Högemann D, Weissleder R, Josephson L, Tait J. Annexin V-CLIO: a nanoparticle for detecting apoptosis by MRI. Mol Imaging 2002;1:1–6
Giorgetti AA, Pingitore A, Di Quirico S, Landi P, Lombardi M., Marzullo P. Non-invasive quantitative assessment of transmural extent of myocardial necrosis by means of contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance:comparison with post-nitrate 99mTc-tetrofosmin GSPECT [abstract]. J Nucl Cardiol 2003;10(1):S64
Pan D, Sun H, Rich TA, Berr SS. Evaluation of mouse tumor response to radiation therapy by near infrared fluorescence imaging using cyanine 5.5-Annexin V [abstract]. Mol Imaging Biol 2003;5(3):162
Mandl SJ, Mari C, Contag CH, Tait JF, Blankenberg FG. Increased annexin V uptake precedes tumor cell loss in mice with luciferase expressing BCL-1 lymphoma [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):179P
Hartung D, Petrov A, Kolodgie F, et al. Preventing apoptosis should constitute the basis of management of atherosclerosis: pan-caspase inhibitor simulate the effects of diet withdrawal and statin therapy [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):1P
Mari C, Yenari M, Tait JF, Zhu JH, Goris ML, Blankenberg FG. Application of dedicated small animal SPECT: radiolabeled annexin V tomographic imaging of ischemic reperfusion injury in the rat brain [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):215P
Dumont EA, Petrov A, Narula N, Haider N, Reutelingsperger CPM, Narula J, Hofstra L. Tc-99m Annexin-V imaging noninvasively detects ischemic memory as prolonged but reversible sarcolemmal phosphatidyl serine expression occurs in myocardial ischemia [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):104P
Van den Eijnde SM, Boshart L, Reutelingsperger CPM, De Zeeuw CI, Vermeij-Keers C. Phosphatidylserine plasma membrane asymmetry in vivo: a pancellular phenomenon which alters during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 1997;4:311–6
Sweeney TJ. Visualizing the kinetics of tumor-cell clearance in living animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1999;96:12044–9
Reynolds JS, Troy TL, Mayer RH, et al. Imaging of spontaneous canine mammary tumors using fluorescent contrast agents. Photochem Photobiol 1999;70:87–94
Dumont EA, Reutelingsperger CPM, Smits JFM, et al. Real-time imaging of apoptotic cell-membrane changes at the single cell level in the beating murine heart. Nat Med 2001;7:1352–5
Czarnota GJ, Kolios MC, Vaziri H, Benchimol S, Ottensmeyer FP, Sherar MD, Hunt JW. Ultrasonic biomicroscopy of viable, dead and apoptotic cells. Ultrasound Med Biol 1997;23:961–5
Czarnota GJ, Kolios MC, Abraham J, et al. Ultrasound imaging of apoptosis: high-resolution non-invasive monitoring of programmed cell death in vitro, in situ and in vivo. Br J Cancer 1999;81:520–7
Makin G, Hickman JA. Apoptosis and cancer chemotherapy. Cell Tissue Res 2000;301:143–52
Roman S, Petrusca D, Moldovan I, Paraoan M, Petrescu A, Damian D, Noica N, Sulica A. Evaluation of apoptosis of tumor and of apparently normal cells in human renal carcinoma. Immunol Lett 1999;67:15–22
Renehan AG, Bach SP, Potten CS. The relevance of apoptosis for cellular homeostasis and tumorigenesis in the intestine. Can J Gastroenterol 2001;15:166–76
Sheridan MT, Cooper RA, West CML. A high ratio of apoptosis to proliferation correlates with improved survival after radiotherapy for cervical adenocarcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1999;44:507–12
Dowsett M, Archer C, Assersohn L, et al. Clinical studies of apoptosis and proliferation in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 1999;6:25–8
Yaoita H, Ogawa K, Maehara K, Maruyama Y. Apoptosis in relevant clinical situations: contribution of apoptosis in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:630–41
Arola OJ, Saraste A, Pulkki K, Kallajoki M, Parvinen M, Voipio-Pulkki L-M. Acute doxorubicin cardiotoxicity involves cardiomyocyte apotosis. J Cancer Res 2000;60:1789–92
Diwakar J. Cardiotoxicity of doxorubicin and other anthracycline derivatives. J Nucl Cardiol 2000;7:53–62
Nakamura T, Ueda Y, Juan Y, Katsuda S, Takahashi H, Koh E. Fas-mediated apoptosis in adriamycin-induced cardiomyopathy in rats. Circulation 2000;102:572–8
Sandri M, Carraro U. Apoptosis of skeletal muscles during development and disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1999;31:1373–90
Narula J, Arbustini B, Chandrashekhar Y, Schwaiger M. Apoptosis and the systolic dysfunction in congestive heart failure. Cardiol Clin 2001;19:113–26
Haunstetter A, Izumo S. Future perspectives and potential implications of cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:795–801
Kockx MM, Herman AG. Apoptosis in atherosclerosis: beneficial or detrimental? Cardiovasc Res 2002;45:736–46
Rössig L, Dimmeler S, Zeiher AM. Apoptosis in the vascular wall and atherosclerosis. Basic Res Cardiol 2001;96:11–22
McCarthy NJ, Bennett MR. The regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:747–55
Sabbah HN. Apoptotic cell death in heart failure. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:704–12
Haunstetter A, Izumo S. Basic mechanisms and implications for cardiovascular disease. Circ Res 1998;82:1111–29
Elsässer A, Suzuki K, Lorenz-Meyer S, Bode C, Schaper J. The role of apoptosis in myocardial ischemia: a critical appraisal. Basic Res Cardiol 2001;96:219–26
Zhao Z-Q, Nakamura M, Wang N-P, et al. Reperfusion induces myocardial apoptotic cell death. Cardiovasc Res 2000;45:651–60
Ogura Y, Krams SM, Martinez OM, et al. Radiolabeled annexin V imaging: diagnosis of allograft rejection in an experimental rodent model of liver transplantation. Radiology 2000;214:795–800
Blankenberg FG, Robbins RC, Stoot JH, Vriens PW, Berry GJ, Tait JF, Strauss HW. Radionuclide imaging of acute lung transplant rejection with annexin V. Chest 2000;117:834–40
Blankenberg FG, Strauss HW. Non-invasive diagnosis of acute heart- or lung transplant rejection using radiolabeled annexin V. Pediatr Radiol 1999;29:299–305
Puig M, Ballester M, Matías-Guiu X, et al. Burden of myocardial damage in cardiac allograft rejection: scintigraphic evidence of myocardial injury and histologic evidence of myocyte necrosis and apoptosis. J Nucl Cardiol 2000;7:132–9
Skulachev VP. Phenoptosis: programmed cell death of an organism. Biochemistry 1999;64:1418–26
Charriaut-Marlangue C, Remolleau S, Aggoun-Zounaoui D, Ben-Ari Y. Apoptosis and programmed cell death: a role in cerebral ischemia. Biomed Pharmacother 1998;52:264–9
Li Y, Powers C, Jiang N, Chopp M. Intact, injured necrotic and apoptotic cells after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. J Neurol Sci 1998;156:119–32
Raina AK, Hochman A, Zhu X, et al. Abortive apoptosis in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 2001;101:305–10
Mattson MP. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev: Mol Cell Biol 2000;1:120–30
Martin LJ. Neuronal cell death in nervous system development, disease, and injury (review). Int J Mol Med 2001;7:455–78
Rand JH. The annexinopathies: a new category of diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 2000;1498:169–73
Grodzicky T, Elkon KB. Apoptosis in rheumatic diseases. Am J Med 2000;108:73–82
Vannier MW. Imaging apoptosis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Nucl Med 2002;43:1366–7
Andrade F, Casciola-Rosen L, Rosen A. Apoptosis in systemic lupus erythematosus: clinical implications. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 2000;26:215–27
Bastian BC. Annexins in cancer and autoimmune diseases. Cell Mol Life Sci 1997;53:554–36
Ueda N, Kaushal GP, Shah SV. Apoptotic mechanisms in acute renal failure. Am J Med 2000;108:403–15
Ortiz A, Cuadrado SG, Lorz C, Egido J. Apoptosis in renal diseases. Front Biosci 1996;1:30–47
Ramakers B, Oyen WJ, Smits P, Rongen GA. Tc-99m-Hynic-Annexin V in a human model for ischemic preconditioning [abstract]. J Nucl Med 2003;44(5):194P
Del Vecchio S, Zannetti A, Ciarmiello A, et al. Dynamic coupling of 99mTc-MIBI efflux and apoptotic pathway activation in untreated breast cancer patients. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2002;29:809–14
Thimister PW, Hofstra L, Liem IH, et al. In vivo detection of cell death in the area at risk in acute myocardial infarction. J Nucl Med 2003;44:391–6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lahorte, C.M.M., Vanderheyden, JL., Steinmetz, N. et al. Apoptosis-detecting radioligands: current state of the art and future perspectives. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31, 887–919 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-004-1555-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-004-1555-4