Abstract
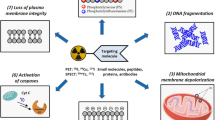
There is an increasing need to develop non-invasive molecular imaging strategies for visualizing and quantifying apoptosis status of diseases (especially for cancer) for diagnosis and monitoring treatment response. Since externalization of phosphatidylserine (PS) is one of the early molecular events during apoptosis, Annexin B1 (AnxB1), a member of Annexins family with high affinity toward the head group of PS, could be a potential positron emission tomography (PET) imaging probe for imaging cell death process after labeled by positron-emitting nuclides, such as 18F. In the present study, we investigated a novel PET probe, 18F-labeled Annexin B1 (18F-AnxB1), for apoptosis imaging. 18F-AnxB1 was prepared reliably by conjugating AnxB1 with a 18F-tag, N-succinimidyl 4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB), in a radiolabeling yield of about 20 % within 40 min. The in vitro binding of 18F-AnxB1 with apoptotic cells induced by anti-Fas antibody showed twofold increase compared to those without treatment, confirmed by flow cytometric analysis with AnxV-FITC/PI staining. Stability tests demonstrated 18F-AnxB1 was rather stable in vitro and in vivo without degradation. The serial 18F-AnxB1 PET/CT scans in healthy rats outlined its biodistribution and pharmacokinetics, indicating a rapid renal clearance and predominant accumulation into kidney and bladder at 2 h p.i. 18F-AnxB1 PET/CT imaging was successfully applied to visualize in vivo apoptosis sites in tumor induced by chemotherapy and in kidney simulated by ischemia–reperfusion injury. The high-contrast images were obtained at 2 h p.i. to delineate apoptotic tumor. Apoptotic region could be still identified by 18F-AnxB1 PET 4 h p.i., despite the high probe retention in kidneys. In summary, we have developed 18F-AnxB1 as a PS-specific PET probe for the apoptosis detection and quantification which could have broad applications from disease diagnosis to treatment monitoring, especially in the cases of cancer.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thompson CB (1995) Apoptosis in the pathogenesis and treatment of disease. Science 267:1456–1462
Kerr JF, Winterford CM, Harmon BV (1994) Apoptosis. Its significance in cancer and cancer therapy. Cancer 73:2013–2026
Evan GI, Vousden KH (2001) Proliferation, cell cycle and apoptosis in cancer. Nature 411:342–348
Kapty J, Murray D, Mercer J (2010) Radiotracers for noninvasive molecular imaging of tumor cell death. Cancer Biother Radiopharm 25:615–628
Niu G, Chen X (2010) Apoptosis imaging: beyond annexin V. J Nucl Med 51:1659–1662
Blankenberg FG, Strauss HW (2001) Will imaging of apoptosis play a role in clinical care? A tale of mice and men. Apoptosis 6:117–123
Blankenberg FG, Tait J, Ohtsuki K, Strauss HW (2000) Apoptosis: the importance of nuclear medicine. Nucl Med Commun 21:241–250
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Akselrod-Ballin A, Wall A, Ziv I (2010) Small-molecule biomarkers for clinical PET imaging of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 51:837–840
Kartachova MS, Verheij M, van Eck BL, Hoefnagel CA, Olmos RA (2008) Radionuclide imaging of apoptosis in malignancies: promise and pitfalls of 99mTc-Hynic-rh-Annexin V imaging. Clin Med Oncol 2:319–325
Hengartner MO (2000) The biochemistry of apoptosis. Nature 407:770–776
Schutters K, Reutelingsperger C (2010) Phosphatidylserine targeting for diagnosis and treatment of human diseases. Apoptosis 15:1072–1082
Burtea C, Laurent S, Lancelot E et al (2009) Peptidic targeting of phosphatidylserine for the MRI detection of apoptosis in atherosclerotic plaques. Mol Pharm 6:1903–1919
Lahorte CM, Vanderheyden JL, Steinmetz N, Van de Wiele C, Dierckx RA, Slegers G (2004) Apoptosis-detecting radioligands: current state of the art and future perspectives. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:887–919
Belhocine TZ, Tait JF, Vanderheyden JL, Li C, Blankenberg FG (2004) Nuclear medicine in the era of genomics and proteomics: lessons from annexin V. J Proteome Res 3:345–349
Boersma HH, Kietselaer BL, Stolk LM et al (2005) Past, present, and future of annexin A5: from protein discovery to clinical applications. J Nucl Med 46:2035–2050
Blankenberg FG, Katsikis PD, Tait JF et al (1998) In vivo detection and imaging of phosphatidylserine expression during programmed cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6349–6354
Yagle KJ, Eary JF, Tait JF et al (2005) Evaluation of 18F-annexin V as a PET imaging agent in an animal model of apoptosis. J Nucl Med 46:658–666
Toretsky J, Levenson A, Weinberg IN, Tait JF, Uren A, Mease RC (2004) Preparation of F-18 labeled annexin V: a potential PET radiopharmaceutical for imaging cell death. Nucl Med Biol 31:747–752
Keen HG, Dekker BA, Disley L et al (2005) Imaging apoptosis in vivo using 124I-annexin V and PET. Nucl Med Biol 32:395–402
Hu S, Kiesewetter DO, Zhu L et al (2012) Longitudinal PET imaging of doxorubicin-induced cell death with 18F-Annexin V. Mol Imaging Biol 14:762–770
Grierson JR, Yagle KJ, Eary JF et al (2004) Production of [F-18]fluoroannexin for imaging apoptosis with PET. Bioconjug Chem 15:373–379
Bauwens M, De Saint-Hubert M, Devos E et al (2011) Site-specific 68Ga-labeled Annexin A5 as a PET imaging agent for apoptosis. Nucl Med Biol 38:381–392
Zhang Y, Guo YJ, Sun SH, Yan HL, He Y (2004) Non-fusion expression in Escherichia coli, purification, and characterization of a novel Ca2+− and phospholipid-binding protein annexin B1. Protein Expr Purif 34:68–74
Wang F, Luo QY, He Y, Sun SH (2007) Screening, purification, and identification of annexin B1 mutants with high phosphatidylserine-binding activity and reduced immunogenicity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 75:539–548
Luo QY, Zhang ZY, Wang F, Lu HK, Guo YZ, Zhu RS (2005) Preparation, in vitro and in vivo evaluation of 99mTc-Annexin B1: a novel radioligand for apoptosis imaging. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 335:1102–1106
Luo QY, Wang F, Zhang ZY et al (2008) Preparation and bioevaluation of 99mTc-HYNIC-annexin B1 as a novel radioligand for apoptosis imaging. Apoptosis 13:600–608
Ding FX, Yan HL, Mei Q et al (2007) A novel, cheap and effective fusion expression system for the production of recombinant proteins. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:483–488
Hoglund J, Shirvan A, Antoni G et al (2011) 18F-ML-10, a PET tracer for apoptosis: first human study. J Nucl Med 52:720–725
Allen A, Ben-Ami M, Reshef A et al (2012) Assessment of response of brain metastases to radiotherapy by PET imaging of apoptosis with 18F-ML-10. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:1400–1408
Reshef A, Shirvan A, Waterhouse RN et al (2008) Molecular imaging of neurovascular cell death in experimental cerebral stroke by PET. J Nucl Med 49:1520–1528
Edgington LE, Berger AB, Blum G et al (2009) Noninvasive optical imaging of apoptosis by caspase-targeted activity-based probes. Nat Med 15:967–973
Murakami Y, Takamatsu H, Taki J et al (2004) 18F-labelled annexin V: a PET tracer for apoptosis imaging. EurJ Nucl Med Mol Imaging 31:469–474
Li X, Link JM, Stekhova S et al (2008) Site-specific labeling of annexin V with F-18 for apoptosis imaging. Bioconjug Chem 19:1684–1688
Kapty J, Kniess T, Wuest F, Mercer JR (2011) Radiolabeling of phosphatidylserine-binding peptides with prosthetic groups N-[6-(4-[18F]fluorobenzylidene)aminooxyhexyl]maleimide ([18F]FBAM) and N-succinimidyl-4-[18F]fluorobenzoate ([18F]SFB). Appl Radiat Isot 69:1218–1225
Wang M-W, Zhang Y-P, Zhang Y-J, Shen C (2011) Module-assisted one-pot synthesis of [18F]SFB for radiolabeling proteins. J Radioanal Nucl Chem 289:191–196
Vaidyanathan G, Zalutsky M (1992) Labeling proteins with fluorine-18 using N-succinimidyl 4-[18F]fluorobenzoate. Int J Rad Appl Instrum Part B Nucl Med Biol 19:275–281
Gottlieb RA, Nordberg J, Skowronski E, Babior BM (1996) Apoptosis induced in Jurkat cells by several agents is preceded by intracellular acidification. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:654–658
Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Wang F et al (2011) Evaluation of 18F-SFB-Annexin B1 in detecting apoptosis. Chin J Nucl Med 31:112–116
Gonzalez Trotter DE, Manjeshwar RM, Doss M et al (2004) Quantitation of small-animal 124I activity distributions using a clinical PET/CT scanner. J Nucl Med 45:1237–1244
Aide N, Desmonts C, Beauregard JM et al (2010) High throughput static and dynamic small animal imaging using clinical PET/CT: potential preclinical applications. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 37:991–1001
Gremse F, Schulz V (2011) Qualitative and quantitative data analysis. In: Kiessling F, Pichler BJ (eds) Small animal imaging. Springer, Berlin/Heidelberg, pp 363–378
Mingwei W, Yujia Z, Zhang Y, Yingjian Z (2012) Cancer apoptosis detection by 18F-Annexin B1 and 18F-Annexin V PET/CT imaging: a comparative study. J Nucl Med 53(S1):1700
Shreve PD, Anzai Y, Wahl RL. (1999) Pitfalls in oncologic diagnosis with FDG PET imaging: physiologic and benign variants. Radiographics 19:61–77; quiz 150–151
Sterin-Speziale N, Kahane V, Setton C, Fernandez M, Speziale E (1992) Compartmental study of rat renal phospholipid metabolism. Lipids 27:10–14
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30700188, No. 11275050).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ming-Wei Wang and Fang Wang contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, MW., Wang, F., Zheng, YJ. et al. An in vivo molecular imaging probe 18F-Annexin B1 for apoptosis detection by PET/CT: preparation and preliminary evaluation. Apoptosis 18, 238–247 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0788-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-012-0788-0