Abstract
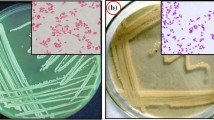
A metal-resistant and phosphate-solubilising bacterium, designated as strain D414T, was isolated from heavy metal (Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn)-polluted paddy soils at the surrounding area of Dabao Mountain Mine in Southeast China. The minimum inhibitory concentrations of heavy metals for strain D414T were 2000 mg L−1 (Cd), 800 mg L−1 (Pb), 150 mg L−1 (Cu) and 2500 mg L−1 (Zn). The strain possessed plant growth-promoting properties, such as 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate assimilation, indole production and phosphate solubilisation. Analysis of 16S rRNA gene sequence indicated that the isolate is a member of the genus Burkholderia where strain D414T formed a distinct phyletic line with validly described Burkholderia species. Strain D414T is closely related to Burkholderia tropica DSM 15359T, B. bannensis NBRC E25T and B. unamae DSM 17197T, with 98.5, 98.3 and 98.3 % sequence similarities, respectively. Furthermore, less than 34 % DNA–DNA relatedness was detected between strain D414T and the type strains of the phylogenetically closest species of Burkholderia. The dominant fatty acids of strain D414T were C14:0, C16:0, C17:0 cyclo and C18:1 ω7c. The DNA G+C content was 62.3 ± 0.5 mol%. On the basis of genotypic, phenotypic and phylogenetic data, strain D414T represents a novel species, for which the name Burkholderia metalliresistens sp. nov. is proposed, with D414T (=CICC 10561T = DSM 26823T) as the type strain


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIC:
-
Minimum inhibitory concentration
References
Aizawa T, Vijarnsorn P, Nakajima M, Sunairi M (2011) Burkholderia bannensis sp. nov., an acid-neutralizing bacterium isolated from torpedo grass (Panicum repens) growing in highly acidic swamps. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:1645–1650
Aleem A, Isar J, Malik A (2003) Impact of long term application of industrial wastewater on the emergence of resistance traits in Azotobacter chroococcum isolated from rhizosphere soil. Bioresour Technol 86:7–13
Angus AA, Lee A, Lum MR, Shehayeb M, Hessabi R, Fujishige NA, Yerrapragada S, Kano S, Song N, Yang P et al (2013) Nodulation and effective nitrogen fixation of Macroptilium atropurpureum (siratro) by Burkholderia tuberum a nodulating and plant growth promitng beta-proteobacterium, are influenced by environmental factors. Plant Soil 369:543–562
Blaha D, Pringet-Combaret C, Mirza MS, Moe¨nne-Loccoz Y (2006) Phylogeny of the 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase-encoding gene acdS in phytobeneficial and pathogenic proteobacteria and relation with strain biogeography. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 56:455–470
Caballero-Mellado J, Martinez-Aguilar L, Paredes-Valdez G, de Los Estrada, Santos P (2004) Burkholderia unamae sp. nov., an N2-fixing rhizospheric and endophytic species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:1165–1172
Caballero-Mellado J, Onofre-Lemus J, Estrada-de Los Santos P, Martinez-Aguilar L (2007) The tomato rhizosphere, an environment rich in nitrogen-fixing Burkholderia species with capabilities of interest for agriculture and bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5308–5319
Chen WM, James EK, Coenye T, Chou JH, Barrios E, de Faria SM, Elliott GN, Sheu SY, Sprent JI, Vandamme P (2006) Burkholderia mimosarum sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa spp. from Taiwan and South America. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:1847–1851
Chen WM, de Faria SM, James EK, Elliott GN, Lin KY, Chou JH, Sheu SY, Cnockaert M, Sprent JI, Vandamme P (2007) Burkholderia nodosa sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of the woody Brazilian legumes Mimosa bimucronata and Mimosa scabrella. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:1055–1059
Chen WM, de Faria SM, Chou J-H, James EK, Elliott GN, Sprent JI, Bontemps C, Young JPW, Vandamme P (2008) Burkholderia sabiae sp. nov., isolated from root nodules of Mimosa caesalpiniifolia. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:2174–2179
Chun J, Goodfellow M (1995) A phylogenetic analysis of the genus Nocardia with 16S rRNA gene sequences. Int J Syst Bacteriol 45:240–245
Coenye T, Vandamme P (2003) Diversity and significance of Burkholderia species occupying diverse ecological niches. Environ Microbiol 5:719–729
Coenye T, Gillis M, Vandamme P (2000) Pseudomonas antimicrobica Attafuah and Bradbury 1990 is a junior synonym of Burkholderia gladioli (Severini 1913) Yabuuchi et al. 1993. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:2135–2139
De Ley J, Cattoir H, Reynaerts A (1970) The quantitative measurement of DNA hybridization from renaturation rates. Eur J Biochem 12:133–142
Estrada-de los Santos P, Martı´nez-Aguilar L, Vinuesa P, Hirsch AM, Caballero-Mellado J (2013) Phylogenetic analysis of Burkholderia species by Multilocus sequence analysis. Curr Microbiol 67:51–60
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fitch WM (1971) Toward defining the course of evolution: minimum change for a specific tree topology. Syst Zool 20:406–416
Ghazi F, Henni DE, Benmechernene Z, Kihal M (2009) Phenotypic and whole cell protein analysis by SDS-PAGE for identification of dominants lactic acid bacteria isolated from algerian raw milk. World J Dairy Food Sci 4:78–87
Glick BR, Cheng Z, Czarny J, Duan J (2007) Promotion of plant growth by ACC deaminase-producing soil bacteria. Eur J Plant Pathol 119:329–339
Guo JK, Tang SR, Ju XH, Ding YZ, Liao SQ, Song NN (2011) Effects of inoculation of a plant growth promoting rhizobacterium Burkholderia sp. D54 on plant growth and metal uptake by a hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii Hance grown on multiple metal contaminated soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2835–2844
Hardy RW, Holsten RD, Jackson EK, Burns RC (1968) The acetylene-ethylene assay for N2 fixation: laboratory and field evaluation. Plant Physiol 43:1185–1207
Jiang CY, Sheng XF, Qian M, Wang QY (2008) Isolation and characterization of a heavy metal-resistant Burkholderia sp. from heavy metal-contaminated paddy field soil and its potential in promoting plant growth and heavy metal accumulation in metal-polluted soil. Chemosphere 72:157–164
Jones K (1970) Nitrogen fixation in the phyllosphere of the Douglas fir, Pseudotsuga douglasii. Ann Bot 34:239–244
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H et al (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (2004) MEGA3: integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinform 5:150–163
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Li WC, Ye ZH, Wong MH (2007) Effects of bacteria on enhanced metal uptake of the Cd/Zn-hyperaccumulating plant, Sedum alfredii. J Exp Bot 58:4173–4182
Lim JH, Baek SH, Lee ST (2008) Burkholderia sediminicola sp. nov., isolated from freshwater sediment. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:565–569
Lu P, Zheng LQ, Sun JJ, Liu HM, Li SP, Hong Q, Li WJ (2012) Burkholderia zhejiangensis sp. nov., a methyl-parathion-degrading bacterium isolated from a wastewater-treatment system. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:1337–1341
Martı´nez-Aguilar L, Salazar-Salazar C, Me´ndez RD, Caballero-Mellado J, Hirsch AM, Va´squez-Murrieta M, Estrada-de los SP (2013) Burkholderia caballeronis sp. nov., a nitrogen fixing species isolated from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) with the ability to effectively nodulate Phaseolus vulgaris. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek doi: 10.1007/s10482-013-0028-9
Mesbah M, Premachandran U, Whitman WB (1989) Precise measurement of the G+C content of deoxyribonucleic acid by high-performance liquid chromatography. Int J Syst Bacteriol 39:159–167
Onofre-Lemus J, Hernandez-Lucas I, Girard L, CaballeroMellado J (2009) ACC (1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate) deaminase activity, a widespread trait in Burkholderia species, and its growth-promoting effect on tomato plants. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6581–6590
Otsuka Y, Muramatsu Y, Nakagawa Y, Matsuda M, Nakamura M, Murata H (2011) Burkholderia oxyphila sp. nov., a bacterium isolated from acidic forest soil that catabolizes (+)-catechin and its putative aromatic derivatives. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 61:249–254
Pal A, Dutta S, Mukherjee PK, Paul AK (2005). Occurrence of heavy metal resistance in microflora from serpentine soil of Andaman. J Basic Microbiol 45:207–218
Palinska KA, Marquardt J (2008) Genotypic and phenotypic analysis of strains assigned to the widespread cyanobacterial morphospecies Phormidium autumnale (Oscillatoriales). Arch Microbiol 189:325–335
Reis VM, Estrada-de los Santos P, Tenorio-Salgado S, Vogel J, Stoffels M, Guyon S, Mavingui P, Baldani VLD, Schmid M et al (2004) Burkholderia tropica sp. nov., a novel nitrogen-fixing, plant-associated bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:2155–2162
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1993) Theoretical foundation of the minimum-evolution method of phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 10:1073–1095
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sasser M (1990) Identification of bacteria by gas chromatography of cellular fatty acids. USFCC Newsl 20:1–6
Suárez-Moreno ZR, Caballero-Mellado J, Coutinho BG, Mendonc¸a-Previato L, James EK, Venturi V (2012) Common features of environmetal and potentially beneficial plant associated Burkholderia. Microb Ecol 63:249–266
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL_X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Van de Peer Y, De Wachter R (1994) TREECON for Windows: a software package for the construction and drawing of evolutionary trees for the Microsoft Windows environment. Comput Appl Biosci 10:569–570
Vandamme P, Pot B, Gillis M, De Vos P, Kersters K, Swings J (1996) Polyphasic taxonomy, a consensus approach to bacterial systematics. Microbiol Rev 60:407–438
Vandamme P, Goris J, Chen WM, De Vos P, Willems A (2002) Burkholderia tuberum sp. nov. and Burkholderia phymatum sp. nov. nodulate the roots of tropical legumes. Syst Appl Microbiol 25:507–512
Watanabe FS, Olsen SR (1965) Test of an ascorbic acid method for determining phosphorous in water and NaHCO3 extracts from soil. Soil Sci Soc Am Proc 29:677–678
Wayne LG, Brenner DJ, Colwell RR, Grimont PAD, Kandler O, Krichevsky MI, Moore LH, Moore WEC, Murray RGE et al (1987) International committee on systematic bacteriology. Report of the ad hoc committee on reconciliation of approaches to bacterial systematics. Int J Syst Bacteriol 37:463–464
Wei GH, Wang ET, Tan ZY, Zhu ME, Chen WX (2002) Rhizobium indigoferae sp. nov. and Sinorhizobium kummerowiae sp. nov., respectively isolated from Indigofera spp. and Kummerowia stipulacea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:2231–2239
Yabuuchi E, Kosako Y, Oyaizu H, Yano I, Hotta H, Hashimoto Y, Ezaki T, Arakawa M (1992) Proposal of Burkholderia gen. nov. and transfer of seven species of the genus Pseudomonas homology group II to the new genus, with the type species Burkholderia cepacia (Palleroni and Holmes 1981) comb. nov. Microbiol Immunol 36:1251–1275
Zaidi S, Usmani S, Singh BR, Musarrat J (2006) Significance of Bacillus subtilis strain SJ-101 as a bioinoculant for concurrent plant growth promotion and nickel accumulation in Brassica juncea. Chemosphere 64:991–997
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank J.P. Euzéby for the helpful advice on etymology of bacterial names. We also acknowledge JinXia Li at the CICC and Dr. Sabine Gronow at the DSMZ for deposit of the isolates. This research was financially supported by the Central Public Research Institutes Basic Funds for Research and Development (Agro-Environmental Protection Institute, Ministry of Agriculture) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (41473115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
The GenBank/EMBL/DDBJ accession numbers for the 16S rRNA gene sequences of strain D414T is KF601211.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, J.K., Ding, Y.Z., Feng, R.W. et al. Burkholderia metalliresistens sp. nov., a multiple metal-resistant and phosphate-solubilising species isolated from heavy metal-polluted soil in Southeast China. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 107, 1591–1598 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0453-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-015-0453-z