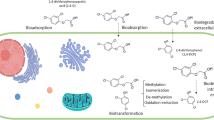
Abstract
The increasing use of toxic pesticides is a major environmental concern. Carbendazim is a systemic fungicide having wide applications for controlling fungal diseases in agriculture, forestry and veterinary medicines. Carbendazim is a major pollutant detectable in food, soil and water. Carbendazim extensive and repeated use induces acute and delayed toxic effects on humans, invertebrates, aquatic life forms and soil microorganisms. Here, we review the pollution, non-target toxicity and microbial degradation of carbendazim for crop and veterinary purposes. We found that carbendazim causes embryotoxicity, apoptosis, teratogenicity, infertility, hepatocellular dysfunction, endocrine-disrupting effects, disruption of haematological functions, mitotic spindle abnormalities, mutagenic and aneugenic effect. We also found that carbendazim disrupted the microbial community structure in various ecosystems. The detection of carbendazim in soil and reservoir sites is performed by spectroscopic, chromatographic, voltammetric, nanoparticles, carbon electrodes and mass spectrometry. A review of the degradation of carbendazim shows that carbendazim undergoes partial to complete biodegradation in the soil and water by Azospirillum, Aeromonas, Alternaria, Bacillus, Brevibacillus, Nocardioides, Pseudomonas, Ralstonia, Rhodococcus, Sphingomonas, Streptomyces and Trichoderma.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adedara IA, Vaithinathan S, Jubendradass R, Mathur PP, Farombi EO (2013) Kolaviron prevents carbendazim-induced steroidogenic dysfunction and apoptosis in testes of rats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 35:444–453. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2013.01.010
Aire TA (2005) Short-term effects of carbendazim on the gross and microscopic features of the testes of Japanese quails (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Anat Embryol 210:43–49. doi:10.1007/s00429-005-0001-0
Alvarez JLM, Calzón JAG, Fonseca JML (1997) Catalytic polarographic prewave of cobalt (II) induced by carbendazim. Application to the voltammetric determination of benomyl. Electroanal 9:500–502. doi:10.1002/elan.1140090614
Anastassiades M, Schwack W (1998) Analysis of carbendazim, benomyl, thiophanate methyl and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in fruits and vegetables after supercritical fluid extraction. J Chromatogr A 825:45–54. doi:10.1016/S0021-9673(98)00691-8
Andrade TS, Henriques JF, Almeida AR, Machado AL, Koba O, Giang PT, Soares AM, Domingues I (2016) Carbendazim exposure induces developmental, biochemical and behavioural disturbance in zebrafish embryos. Aquat Toxicol 170:390–399. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2015.11.017
Arya R, Sharma AK (2015) Bioremediation of carbendazim, a benzimidazole fungicide using Brevibacillus borstelensis and Streptomyces albogriseolus together. Curr Pharm Biotechnol 17:185–189. doi:10.2174/1389201016666150930115737
Bakirci GT, Acay DB, Bakirci F, Otles S (2014) Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the Aegean region, Turkey. Food Chem 160:379–392. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.02.051
Banyiova K, Necasova A, Kohoutek J, Justan I, Čupr P (2016) New experimental data on the human dermal absorption of simazine and carbendazim help to refine the assessment of human exposure. Chemosphere 145:148–156. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.11.018
Barnett RM, Carone CD, Groom DE, Trippe TG, Wohl CG, Armstrong B, Gee PS, Wagman GS, James F, Mangano M, Monig K (1996) Review of particle physics. Phys Rev D 54:1. doi:10.1103/PhysRevD.54.1
Bentley KS, Kirkland D, Murphy M, Marshall R (2000) Evaluation of thresholds for benomyl-and carbendazim-induced aneuploidy in cultured human lymphocytes using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Mutat Res 464:41–51. doi:10.1016/S1383-5718(99)00165-5
Bernard MB, Cole P, Kobelt A, Horne PA, Altmann J, Wratten SD, Yen AL (2010) Reducing the impact of pesticides on biological control in Australian vineyards: pesticide mortality and fecundity effects on an indicator species, the predatory mite Euseius victoriensis (Acari: Phytoseiidae). J Eco Entomol 103:2061–2071. doi:10.1603/EC09357
Bhushan C, Bhardwaj A, Misra SS (2013) State of pesticide regulations in India. Report of Centre for Science and Environment, New Delhi
Bicchi C, Belliardo F, Cantamessa L, Gasparini G, Icardi M, Sesia E (1989) Simultaneous determination of benzimidazole fungicides by HPLC on apples, pears and their pulps. Pest Sci 25:355–360. doi:10.1002/ps.2780250405
Canton JH (1976) The toxicity of benomyl, thiophanate-methyl, and BCM to four freshwater organisms. Environ Contam Toxicol 16:214–218. doi:10.1007/BF01685230
Carter SD, Hess RA, Laskey JW (1987) The fungicide methyl 2-benzimidazole carbamate causes infertility in male Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol Reprod 37:709–717. doi:10.1095/biolreprod37.3.709
Chatupote W, Panapitukkul N (2005) Regional assessment of nutrient and pesticide leaching in the vegetable production area of Rattaphum catchment, Thailand. Water Air Soil Pollut Focus 5:165–173. doi:10.1007/s11267-005-7411-0
Correa LM, Nakai M, Strandgaard CS, Hess RA, Miller MG (2002) Microtubules of the mouse testis exhibit differential sensitivity to the microtubule disruptors carbendazim and colchicine. Toxicol Sci 69:175–182. doi:10.1093/toxsci/69.1.175
Daam MA, Satapornvanit K, Van den BPJ, Nogueira AJ (2009) Sensitivity of macroinvertebrates to carbendazim under semi-field conditions in Thailand: implications for the use of temperate toxicity data in a tropical risk assessment of fungicides. Chemosphere 74:1187–1194. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2008.11.040
Dang Z, Smit CE (2008) Environmental risk limits for carbendazim. Bilthoven, The Netherlands: National Institute for Public Health and the Environment (RIVM). Letter Report (601716014)
EU Pesticide Database (2015) European Commission, (http://ec.europa.eu/food/plant/pesticides/eu-pesticides-database/public/?event=homepageandlanguage=EN)
Daundkar PS, Rampal S (2014) Evaluation of ameliorative potential of selenium on carbendazim induced oxidative stress in male goats. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 38:711–719. doi:10.1016/j.etap.2014.09.007
Davidse LC (1986) Benzimidazole fungicides: mechanism of action and biological impact. Ann Rev Phytopathol 24:43–65. doi:10.1146/annurev.py.24.090186.000355
De A, Bose R, Kumar A, Mozumdar S (2014) Worldwide pesticide use. In: Targeted Delivery of Pesticides Using Biodegradable Polymeric Nanoparticles; Springer: New Delhi, India, pp 5–6
Devi PA, Paramasivam M, Prakasam V (2015) Degradation pattern and risk assessment of carbendazim and mancozeb in mango fruits. Environ Monit Assess 187:1–6. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4142-6
Dikic D, Landeka I, Knežević F, Mojsović-Ćuić A, Benković V, Horvat-Knežević A, Rogić D (2012) Carbendazim impends hepatic necrosis when combined with imazalil or cypermethrin. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 110:433–440. doi:10.1111/j.1742-7843.2011.00831.x
Fang H, Wang Y, Gao C, Yan H, Dong B, Yu Y (2012) Isolation and characterization of Pseudomonas sp. CBW capable of degrading carbendazim. Biodegradation 21:939–946. doi:10.1007/s10532-010-9353-0
FAO (1998) Pesticides residues in food-1997 evaluations. Part I Residues, FAO Plant production and protection paper, Rome, p 146
Farag A, Ebrahim H, ElMazoudy R, Kadous E (2011) Developmental toxicity of fungicide carbendazim in female mice. Birth Defe Res B: Develop Reprod Toxicol 92:122–130. doi:10.1002/bdrb.20290
Fawole OB, Aluko M, Olowonihi TE (2010) Effects of a Carbendazim-Mancozeb fungicidal mixture on soil microbial populations and some enzyme activities in soil. Agrosearch 10:1–2. doi:10.4314/agrosh.v10i1-2.69831
Ferreira AL, Loureiro S, Soares AM (2008) Toxicity prediction of binary combinations of cadmium, carbendazim and low dissolved oxygen on Daphnia magna. Aqua Toxicol 89:28–39. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2008.05.012
Furini LN, Sanchez-Cortes S, López-Tocón I, Otero JC, Aroca RF, Constantino CJ (2015) Detection and quantitative analysis of carbendazim herbicide on Ag nanoparticles via surface-enhanced Raman scattering. J Raman Spectr 46:1095–1101. doi:10.1002/jrs.4737
Goodson WH, Lowe L, Carpenter DO, Gilbertson M, Ali AM, de Cerain Salsamendi AL et al (2015) Assessing the carcinogenic potential of low-dose exposures to chemical mixtures in the environment: the challenge ahead. Carcinogenesis 36:254–296. doi:10.1093/carcin/bgv039
Gray LE, Ostby J, Linder R, Goldman J, Rehnberg G, Cooper R (1990) Carbendazim-induced alterations of reproductive development and function in the rat and hamster. Fund Appl Toxicol 15:281–297. doi:10.1016/0272-0590(90)90055-O
Gupta RC, Aggarwal M (2007) Toxicity of fungicides. Veterinary Toxicology, New York
Hammond LA, Davidson K, Lawrence R, Camden JB, Von Hoff DD, Weitman S, Izbicka E (2001) Exploring the mechanisms of action of FB642 at the cellular level. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 127:301–313
Hao LQ (2002) Advances on the pesticide residue analysis of Chinese herbal medicine. J Huazhong Agric 2:20–24
Holtman MA, Kobayashi DY (1997) Identification of Rhodococcus erythropolis isolates capable of degrading the fungicide carbendazim. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 47:578–582. doi:10.1007/s002530050976
Hsu YH, Chang CW, Chen MC, Yuan CY (2011) Carbendazim-induced androgen receptor expression antagonized by flutamide in male rats. J Food Drug Anal 19:4
Huan Z, Luo J, Xu Z, Xie D (2016) Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of carbendazim, main impurities and metabolite to earthworms (Eisenia foetida). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 96:62–69. doi:10.1007/s00128-015-1653-y
Itak JA, Selisker MY, Jourdan SW, Fleeker JR, Herzog DP (1993) Determination of benomyl (as carbendazim) and carbendazim in water, soil, and fruit juice by a magnetic particle-based immunoassay. J Agric Food Chem 41:2329–2332. doi:10.1021/jf00036a021
Janardhan A, Rao AB, Sisodia P (1987) Sub-chronic toxicity of methyl benzimidazole carbamate in rats. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 38:890–898. doi:10.1007/BF01616717
Jansen JP (1999) Side effects of pesticides on adults of Aphidius rhopalosiphi De Stefani-Perez (Hym.: Aphidiidae) in the laboratory: results of the 8th Joint Pesticide Testing Programme. Versailles, France 27–29 October 23:65–72
Javorekova SN, Svrcbreve ekova I, Makova J (2010) Influence of benomyl and prometryn on the soil microbial activities and community structures in pasture grasslands of Slovakia. J Environ Sci Health B 45:702–709. doi:10.1080/03601234.2010.502463
Jiang J, Wu S, Wang Y, An X, Cai L, Zhao X, Wu C (2015) Carbendazim has the potential to induce oxidative stress, apoptosis, immunotoxicity and endocrine disruption during zebrafish larvae development. Toxicol In Vitro 29:1473–1481. doi:10.1016/j.tiv.2015.06.003
Jing-Liang X, Xiang-Yang G, Biao S, Zhi-Chun W, Kun W, Shun-Peng L (2006) Isolation and characterization of a carbendazim-degrading Rhodococcus sp. djl-6. Curr Microbiol 53:72–76. doi:10.1007/s00284-005-0474-3
John EM, Shaike JM (2015) Chlorpyrifos: pollution and remediation. Environ Chem Lett 13:269–291. doi:10.1007/s10311-015-0513-7
Jones SE, Williams DJ, Holliman PJ, Taylor N, Baumann J, Forster B, Van Gestel CAM, Rodrigues JML (2004) Ring-testing and field-validation of a terrestrial model ecosystem (TME)-an instrument for testing potentially harmful substances: fate of the model chemical carbendazim. Ecotoxicol 3:29–42. doi:10.1023/B:ECTX.0000012403.90709.c9
Kalwasińska A, Kęsy J, Donderski W, Lalke-Porczyk E (2008a) Biodegradation of carbendazim by planktonic and benthic bacteria of eutrophic lake Chełmżyńskie. Pol J Environ Stud 17:515–523
Kalwasińska A, Kęsy J, Donderski W (2008b) Biodegradation of carbendazim by epiphytic and neustonic bacteria of eutrophic chełmżyńskie lake. Pol J Microbiol 57:221–230
Karlsson I, Friberg H, Steinberg C, Persson P (2014) Fungicide effects on fungal community composition in the wheat phyllosphere. PLoS One 9:e111786. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0111786
Kaur T, Toor AP, Wanchoo RK (2015) Parametric study on degradation of fungicide carbendazim in dilute aqueous solutions using nano TiO2. Desalination Water Treat 54:122–131. doi:10.1080/19443994.2013.879081
Kaur T, Sraw A, Toor AP, Wanchoo RK (2016) Utilization of solar energy for the degradation of carbendazim and propiconazole by Fe doped TiO2. Sol Energy 125:65–66. doi:10.1016/j.solener.2015.12.001
Kosasa T, Kuriya Y, Matsui K, Yamanishi Y (1999) Effect of donepezil hydrochloride (E2020) on basal concentration of extracellular acetylcholine in the hippocampus of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 380:101–107. doi:10.1016/S0014-2999(99)00545-2
Kumar M (2001) Acute oral toxicity study with carbendazim technical 98% in Wistar rats. Toxicology Department, Rallis Research Centre, Bangalore, India. Report number: 3179/1. Report date: 16 August 2001
Lacey E, Watson TR (1985) Structure-activity relationships of benzimidazole carbamates as inhibitors of mammalian tubulin in vitro. Biochem Pharmacol 34:1073–1077. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(85)90611-2
Lin X, Za Hou, Zhao SF, Xie L, Li HJ, Li MZ (2011a) A high efficient carbendazim-degrading bacterial strain: its isolation and identification. Chin J Ecol 7:031
Lin X, Hou Z, Feng Y, Zhao S, Ye J (2011b) Isolation and characteristics of efficient carbendazim degradation bacterium. In: International Conference on Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering, Advances in Biomedical Engineering. 1:384–388
Liu K, Pan X, Han Y, Tang F, Yu Y (2012) Estimating the toxicity of the weak base carbendazim to the earthworm (Eisenia fetida) using in situ pore water concentrations in different soils. Sci Total Environ 438:26–32. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.068
Lopez A, Yusà V, Millet M, Coscollà C (2016) Retrospective screening of pesticide metabolites in ambient air using liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry. Talanta 150:27–36. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2015.11.068
Lu SY, Liao JW, Kuo ML, Wang SC, Hwang JS, Ueng TH (2004) Endocrine-disrupting activity in carbendazim-induced reproductive and developmental toxicity in rats. J Toxicol Env Heal A 67:1501–1515. doi:10.1080/15287390490486833
Ludwikowska A, Bojarski B, Socha M, Lutnicka H, Trzeciak KB (2013) The effect of carbendazim on embryonic Prussian carp (Carassius gibelio) development and hatching. Arch Polish Fisheries 21:367–371. doi:10.2478/aopf-2013-0038
Ma J, Zheng R, Xu L, Wang S (2002) Differential sensitivity of two green algae, Scenedesmus obliqnus and Chlorella pyrenoidosa to 12 pesticides. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 52:57–61. doi:10.1006/eesa.2002.2146
Manisankar P, Selvanathan G, Vedhi C (2005a) Utilisation of polypyrrole modified electrode for the determination of pesticides. Int J Environ Anal Chem 85:409–422. doi:10.1080/03067310500050726
Manisankar P, Selvanathan G, Vedhi C (2005b) Utilization of sodium montmorillonite clay-modified electrode for the determination of isoproturon and carbendazim in soil and water samples. Appl Clay Sci 29:249–257. doi:10.1016/j.clay.2005.01.006
Mantovani A, Maranghi F, Ricciardi C, Macrì C, Stazi AV, Attias L, Zapponi GA (1998) Developmental toxicity of carbendazim: comparison of no-observed-adverse-effect level and benchmark dose approach. Food Chem Toxicol 36:37–45. doi:10.1016/S0278-6915(97)00116-6
Mazellier P, Leroy E, De Laat J, Legube B (2003) Degradation of carbendazim by UV/H2O2 investigated by kinetic modelling. Environ Chem Lett 1:68–72. doi:10.1007/s10311-002-0010-7
Minta MA, Wilk IW, Żmudzki J (2004) Embryotoxicity of carbendazim in rat and hamster micromass cultures. Bull Vet Inst Pulawy 48:481–484
Morinaga H, Yanase T, Nomura M, Okabe T, Goto K, Harada N, Nawata H (2004) A benzimidazole fungicide, benomyl, and its metabolite, carbendazim, induce aromatase activity in a human ovarian granulose-like tumor cell line (KGN). Endocrinology 145:1860–1869. doi:10.1210/en.2003-1182
Mountfort KA, Reynolds SL, Thorpe SA, White SN (1994) Comparison of ELISA and HPLC techniques for the analysis of carbendazim and thiabendazole residues in fruit and vegetables. Food Agric Immunol 6:17–22. doi:10.1080/09540109409354808
Mullin CA, Frazier M, Frazier JL, Ashcraft S, Simonds R, Pettis JS (2010) High levels of miticides and agrochemicals in North American apiaries: implications for honey bee health. PLoS One 5(3):e9754. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0009754
Muthuviveganandavel V, Muthuraman P, Muthu S, Srikumar K (2008) Toxic effects of carbendazim at low dose levels in male rats. J Toxicol Sci 33:25–30. doi:10.2131/jts.33.25
Naidu PK, Niranjan T, Naidu NVS (2011) Spectrophotometric determination of carbendazim in its formulations and environmental samples. Int J Chem Tech Res 3:1728–1733
Niewiadomska A (2004) Effect of carbendazim, imazetapir and thiram on nitrogenase activity, the number of microorganisms in soil and yield of red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). Polish J Environ Studies 13:403–410
Olayemi OA (2015) Comparative toxicity of two different pesticides on the skin of Japanese quail (Cortunix japonica). World Vet J 5:13–18
Pacheco SE, Anderson LM, Sandrof MA, Vantangoli MM, Hall SJ, Boekelheide K (2012) Sperm mRNA transcripts are indicators of sub-chronic low dose testicular injury in the Fischer rat. PLoS One 7:e44280. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044280
Palanikumar L, Kumaraguru AK, Ramakritinan CM, Anand M (2014) Toxicity, biochemical and clastogenic response of chlorpyrifos and carbendazim in milkfish Chanos chanos. Int J Environ Sci Technol 11:765–774. doi:10.1007/s13762-013-0264-6
Pandey G, Dorrian SJ, Russell RJ, Brearley C, Kotsonis S, Oakeshott JG (2010) Cloning and biochemical characterization of a novel carbendazim (Methyl-1H-Benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate)-hydrolyzing esterase from the newly isolated Nocardioides sp. strain SG-4G and its potential for use in enzymatic bioremediation. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:2940–2945. doi:10.1128/AEM.02990-09
Parsons KC, Mineau P, Renfrew RB (2010) Effects of pesticide use in rice fields on birds. Waterbirds 33:193–218. doi:10.1675/063.033.s115
Patel GM, Rohit JV, Singhal RK, Kailasa SK (2015) Recognition of carbendazim fungicide in environmental samples by using 4-aminobenzenethiol functionalized silver nanoparticles as a colorimetric sensor. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 206:684–691. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.095
Petroni JM, Lucca BG, Fogliato DK, Ferreira VS (2016) Sensitive approach for voltammetric determination of carbendazim based on the use of an anionic surfactant. Electroanalysis [published online]. doi: 10.1002/elan.201501069
Pourreza N, Rastegarzadeh S, Larki A (2015) Determination of fungicide carbendazim in water and soil samples using dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction and microvolume UV-vis spectrophotometry. Talanta 134:24–29. doi:10.1016/j.talanta.2014.10.056
Prashantkumar W, Sethi RS, Pathak D, Rampal S, Saini SP (2012) Testicular damage after chronic exposure to carbendazim in male goats. Toxicol Environ Chem 94:1433–1442. doi:10.1080/02772248.2012.693493
Rajeswari R, Kanmani S (2009) TiO2-based heterogeneous photocatalytic treatment combined with ozonation for carbendazim degradation. Iran J Environ Health Sci Eng 6:61–66
Rama EM, Bortolan S, Vieira ML, Gerardin DC, Moreira EG (2014) Reproductive and possible hormonal effects of carbendazim. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 69:476–486. doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2014.05.016
Rico A, Sabater C, Castillo MÁ (2016) Lethal and sub-lethal effects of five pesticides used in rice farming on the earthworm Eisenia fetida. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 127:222–229. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2016.02.004
Sakr S, Shalaby SY (2014) Carbendazim-induced testicular damage and oxidative stress in albino rats: ameliorative effect of licorice aqueous extract. Toxicol Ind Health 230:259–267. doi:10.1177/0748233712456059
Salihu M, Ajayi BO, Adedara IA, Farombi EO (2015) 6-Gingerol-rich fraction from Zingiber officinale prevents hematotoxicity and oxidative damage in kidney and liver of rats exposed to carbendazim. J Diet Suppl 16:1–16. doi:10.3109/19390211.2015.1107802
Salunkhe VP, Sawant IS, Banerjee K, Wadkar PN, Sawant SD, Hingmire SA (2014) Kinetics of degradation of carbendazim by B. subtilis strains: possibility of in situ detoxification. Environ Monitor Assess 186:8599–8610. doi:10.1007/s10661-014-4027-8
Schaack S (2008) Daphnia comes of age: an ecological model in the genomic era. Mol Ecol 17:1634–1635. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2008.03698.x
Segner H (2009) Zebrafish (Danio rerio) as a model organism for investigating endocrine disruption. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C: Toxicol Pharmacol 149:187–195. doi:10.1016/j.cbpc.2008.10.099
Selmanoglu G, Barlas N, Songür S, KocSkaya EA (2001) Carbendazim-induced haematological, biochemical and histopathological changes to the liver and kidney of male rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 20:625–630. doi:10.1191/096032701718890603
Sharma KK (2007) Pesticide residue analysis manual. Directorate of Information and Publications of Agriculture. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
Silva AR, Cardoso DN, Cruz A, Lourenço J, Mendo S, Soares AM, Loureiro S (2015) Ecotoxicity and genotoxicity of a binary combination of triclosan and carbendazim to Daphnia magna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 115:279–290. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.02.022
Solomon KR, Brock TC, De Zwart D, Dyer SD, Posthuma L, Richards S, van den Brink PJ (2008) (eds). Extrapolation practice for ecotoxicological effect characterization of chemicals. CRC Press
Stollewerk A (2010) The water flea Daphnia—a ‘new’model system for ecology and evolution. J Biol 9:21. doi:10.1186/jbiol212
Strickland AD, Batt CA (2009) Detection of carbendazim by surface-enhanced Raman scattering using cyclodextrin inclusion complexes on gold nanorods. Anal Chem 81:2895–2903. doi:10.1021/ac801626x
Sun LN, Zhang J, Gong FF, Wang X, Hu G, Li SP, Hong Q (2014) Nocardioides soli sp. nov., a carbendazim-degrading bacterium isolated from soil under the long-term application of carbendazim. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:2047–2052. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.057935-0
Teadoum DN, Noumbo SK, Arnaud KT, Ranil TT, Zé ADM, Tonle IK (2016) Square wave voltammetric determination of residues of carbendazim using a Fullerene/Multiwalled carbon nanotubes/Nafion®/coated glassy carbon electrode. Int J Electrochem. doi:10.1155/2016/7839708
Tian L, Chen F (2009) Characterization of a carbendazim-degrading Trichoderma sp. T2-2 and its application in bioremediation. Wei Sheng Wu Xue Bao 49:925–930
Torstensson L, Wessen B (1984) Interactions between the fungicide benomyl and soil microorganisms. Soil Biol Biochem 16:445–452. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(84)90050-6
Tortella GR, Mella-Herrera RA, Sousa DZ, Rubilar O, Briceño G, Parra L, Diez MC (2013) Carbendazim dissipation in the biomixture of on-farm biopurification systems and its effect on microbial communities. Chemosphere 93:1084–1093
Van Wijngaarden RPA, Crum SJH, Decraene K, Hattink J, Van Kammen A (1998) Toxicicity of derosal (active ingredient carbendazim) to aquatic invertebrates. Chemosphere 37:673–683. doi:10.1016/S0045-6535(98)00083-6
Wang X, Song M, Gao C, Dong B, Zhang Q, Fang H, Yu Y (2009a) Carbendazim induces a temporary change in soil bacterial community structure. J Environ Sci (China) 21:1679–1683. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62473-0
Wang YS, Huang YJ, Chen WC, Yen JH (2009b) Effect of carbendazim and pencycuron on soil bacterial community. J Hazard Mat 172:84–91. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2009.06.142
Wang Z, Xu J, Li Y, Wang K, Wang Y, Hong Q, Li WJ, Li SP (2010a) Rhodococcus jialingiae sp. nov., an actinobacterium isolated from sludge of a carbendazim wastewater treatment facility. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 60:378–381. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.013219-0
Wang Z, Wang Y, Gong F, Zhang J, Hong Q, Li S (2010b) Biodegradation of carbendazim by a novel actinobacterium Rhodococcus jialingiae djl-6-2. Chemosphere 81:639–644. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.08.040
Wang X, Song M, Wang Y, Gao C, Zhang Q, Chu X, Fang H, Yu Y (2012) Response of soil bacterial community to repeated applications of carbendazim. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 75:33–39. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.08.014
Wang C, Wang F, Zhang Q, Liang W (2016) Individual and combined effects of tebuconazole and carbendazim on soil microbial activity. Eur J Soil Biol 72:6–13. doi:10.1016/j.ejsobi.2015.12.005
Wu YS, Lee HK, Li SFY (1997) Determination of carbendazim residues in grains by solid-phase extraction and micellar electrokinetic chromatography with ultraviolet detection. J Chromatogr Sci 35(11):513–518. doi:10.1093/chromsci/35.11.513
Xiao W, Wang H, Li T, Zhu Z, Zhang J, He Z, Yang X (2013) Bioremediation of Cd and carbendazim co-contaminated soil by Cd-hyperaccumulator Sedum alfredii associated with carbendazim-degrading bacterial strains. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20:380–389. doi:10.1007/s11356-012-0902-4
Xu JL, Wang ZC, Wang K, Li SP (2006) The isolation identification and degradation characters of an efficient carbendazim-degrading bacterium. China Environ Sci 26(3):307–310
Xu JL, He J, Wang ZC, Wang K, Li WJ, Tang SK, Li SP (2007) Rhodococcus qingshengii sp. nov., a carbendazim-degrading bacterium. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:2754–2757. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.65095-0
Yan H, Wang D, Dong B, Tang F, Wang B, Fang H, Yu Y (2011) Dissipation of carbendazim and chloramphenicol alone and in combination and their effects on soil fungal: bacterial ratios and soil enzyme activities. Chemosphere 84:634–641. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.03.038
Yarden O, Katan J, Aharonson N, Ben-Yephet Y (1985) Delayed and enhanced degradation of benomyl and carbendazim in disinfected and fungicide-treated soils. Phytopathol 75:763–777
Yarden O, Salomon R, Katan J, Aharonson N (1990) Involvement of fungi and bacteria in enhanced and nonenhanced biodegradation of carbendazim and other benzimidazole compounds in soil. Can J Microbiol 36:15–23. doi:10.1139/m90-004
Yenjerla M, Cox C, Wilson L, Jordan MA (2009) Carbendazim inhibits cancer cell proliferation by suppressing microtubule dynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:390–398. doi:10.1124/jpet.108.143537
Yoon CS, Jin JH, Park JH, Yeo CY, Kim SJ, Hwang YG, Hong SJ, Cheong SW (2008) Toxic effects of carbendazim and n-butyl isocyanate, metabolites of the fungicide benomyl, on early development in the African clawed frog, Xenopus laevis. Environ Toxicol 23:131–144. doi:10.1002/tox.20338
Yunlong YU, Xiaoqiang CHU, Guohui PANG, Xiang Y, Hua FANG (2009) Effects of repeated applications of fungicide carbendazim on its persistence and microbial community in soil. J Environ Sci 21(2):179–185. doi:10.1016/S1001-0742(08)62248-2
Zamora DP, Galera MM, Frenich AG, Vidal JM (2000) Trace determination of carbendazim, fuberidazole and thiabendazole in water by application of multivariate calibration to cross-sections of three-dimensional excitation–emission matrix fluorescence. Analyst 125(6):1167–1174. doi:10.1039/A909886K
Zhang GS, Jia XM, Cheng TF, Ma XH, Zhao YH (2005) Isolation and characterization of a new carbendazim-degrading Ralstonia sp. strain. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 21:265–269. doi:10.1007/s11274-004-3628-8
Zhang L, Qiao X, Ma L (2009) Influence of environmental factors on degradation of carbendazim by Bacillus pumilus strain NY97-1. Int J Environ Pollut 38:309–317. doi:10.1504/IJEP.2009.027231
Zhang X, Huang Y, Harvey PR, Li H, Ren Y (2013) Isolation and characterization of carbendazim-degrading Rhodococcus erythropolis djl-11. PLoS One 8:1–6. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074810
Zhu SH, Wu HL, Li BR, Xia AL, Han QJ, Zhang Y, Yu RQ (2008) Determination of pesticides in honey using excitation–emission matrix fluorescence coupled with second-order calibration and second-order standard addition methods. Anal Chim Acta 619:165–172. doi:10.1016/j.aca.2008.05.005
Zubrod JP, Baudy P, Schulz R, Bundschuh M (2014) Effects of current-use fungicides and their mixtures on the feeding and survival of the key shredder Gammarus fossarum. Aquatic Toxicol 150:133–143. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.03.002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
Authors declare that no conflicts of interest exist.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, S., Singh, N., Kumar, V. et al. Toxicity, monitoring and biodegradation of the fungicide carbendazim. Environ Chem Lett 14, 317–329 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0566-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-016-0566-2