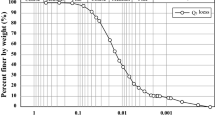
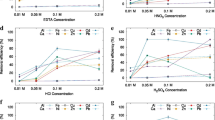
Abstract
The effect of the electrokinetic process on the extraction of trapped water was evaluated in the Miduk copper mine’s tailings slurry. The effect of the dewatering process on copper removal was also studied. The initial electroosmotic permeability was determined using a one-dimensional cell. In the next step, the effect of voltage and polarity reversal was evaluated for three scenarios: T1 (2 V/cm), T2 (2 V/cm), and T3 (1 V/cm). In addition, the polarity reversal method was applied to T2 and T3. To compare the amount of water extraction and energy consumption, three indices were considered and calculated: index of dry tone, water extraction, and normal water extraction. Moreover, the effect of electrokinetics on the final moisture content, physicochemical variation, and chemical composition were investigated. The results indicated that the calculated electroosmotic permeability ranged from 1.23 × 10–9 to 1.36 × 10–9 m2/V·S, which is acceptable for electrokinetic experiments. The water extraction experiments showed average flow rates of 1.68, 1.84, and 1.73 mL/h in T1, T2, and T3, respectively. The maximum amount of water extracted in T2 was ≈ 6% more than in T3. However, considering electric energy consumption, the highest efficiency of water extraction was achieved by applying a voltage gradient of 1 V/cm for 24 h. Consequently, polarity reversal affected the water extraction efficiency by reducing energy consumption. Furthermore, moisture reduction due to the dewatering process decreased the pH variation and copper release and transport. Roughly 35% of the extractable copper was removed on the anode side of T2, which was determined to be the most efficient for remediation.
Zusammenfassung
Die Auswirkungen des elektrokinetischen Prozesses auf die Extraktion von eingeschlossenem Wasser sowie Freisetzung und Transport von Kupfer wurde anhand von Tailings-Schlämmen aus der Miduk Kupfermine im Iran erprobt. Die anfängliche elektroosmotische Permeabilität wurde mittels eindimensionaler Zelle bestimmt. In einem Folgeschritt wurde der Effekt von Spannungs- und Polaritätswechsel für drei Szenarien untersucht: T1 (2 V/cm), Ts (2 V/cm) und T3 (1 V/cm), wobei für T2 und T3 auch die Polaritätsumkehr angewandt wurde. Um die Entwässerung und den Energieverbrauch der Szenarien zu verglichen, wurden drei Indizes berechnet und berücksichtigt: Energieeffizienz, Wasserextraktion und normalisierte Wasserextraktion. Zusätzlich wurde der Effekt der Elektrokinetik auf den finalen Wassergehalt, physikochemische Veränderungen und chemische Zusammensetzung untersucht. Die Ergebnisse zeigen eine (für elektrokinetische Experimente akzeptable) berechnete elektroosmotische Permeabilität im Bereich von 1,23 × 10–9 bis 1,36 × 10–9 m2/V∙S. Die Experimente zur Wasserextraktion zeigen mittlere Volumenströme von 1,68, 1,84 und 1,73 mL/h in T1, T2 und T3. Die höchste in T2 entzogene Wassermenge lag ≈6% über der in T3. Unter Berücksichtigung des Energieverbrauchs wurde allerdings die höchste Effizienz bei der Wasserextraktion bei einem Spannungsgradienten von 1 V/cm über 24 h erreicht. Insofern beeinflusste die Polaritätsumkehr die Effizienz der Entwässerung durch Verringerung des Energieverbrauchs. Zudem ging mit der Reduzierung der Feuchtigkeit auch eine Verringerung der pH-Schwankungen sowie Freisetzung und Transport von Kupfer einher. Rund 35% des extrahierbaren Kupfers wurden in T2 anodenseitig entfern, was für die Sanierung als am effizientesten angesehen wurde.
抽象的
评价了电动力学过程对提取Miduk铜矿尾浆束缚水的影响, 研究了脱水过程对去除铜的作用。用一维电导池确定了起始电渗透率。接着, 通过T1 (2 V/cm),T2 (2 V/cm) 和T3 (1 V/cm) 三种情形评价了电压和极性逆转的影响。T2和T3为极性逆转情形。为比较脱水量和能量消耗, 考虑并计算了三个指标: 干燥指数, 脱水量和正常脱水量。此外, 还研究了电动力学对最终含水量, 物理化学变化和化学成分的影响。结果表明, 计算电渗透率在1.23 × 10 −9到1.36 × 10 −9 m 2 /V∙S之间, 为电动力学实验可接受值。脱水实验显示, 情形T1、T2和T3的平均流量分别为1.68,1.84和1.73 mL/hr。情形T2的最大脱水量比情形T3多≈6%。然而, 从电能消耗角度, 24小时内1V/cm电压梯度的脱水效率最高。因此, 极性反转通过减少能源消耗影响脱水效率。此外, 脱水导致尾矿水分减少, 降低了pH值的变化, 减少了铜的释放与迁移。情形T2阳极去除了约35%的可萃取铜, 被认为是最有效的处理方案。
Resumen
Se evaluó el efecto del proceso electrocinético en la extracción de agua atrapada en los lodos de la mina de cobre de Miduk. También se estudió el efecto del proceso de desagote en la extracción de cobre. La permeabilidad electroosmótica inicial se determinó utilizando una celda unidimensional. A continuación, se evaluó el efecto del voltaje y la inversión de la polaridad para tres escenarios: T1 (2 V/cm), T2 (2 V/cm) y T3 (1 V/cm). Además, el método de inversión de polaridad se aplicó a T2 y T3. Para comparar la cantidad de agua extraída y el consumo de energía, se consideraron y calcularon tres índices: índice de tono seco, extracción de agua y extracción de agua normal. Además, se investigó el efecto de la electrocinética en el contenido final de humedad, la variación fisicoquímica y la composición química. Los resultados indicaron que la permeabilidad electroosmótica calculada oscilaba entre 1,23 × 10–9 y 1,36 × 10–9 m2/V∙S, lo cual es aceptable para los experimentos electrocinéticos. Los experimentos de extracción de agua mostraron caudales medios de 1,68, 1,84 y 1,73 mL/h en T1, T2 y T3, respectivamente. La cantidad máxima de agua extraída en T2 fue ≈ 6% más que en T3. Sin embargo, teniendo en cuenta el consumo de energía eléctrica, la mayor eficiencia de extracción de agua se logró aplicando un gradiente de voltaje de 1 V/cm durante 24 h. En consecuencia, la inversión de la polaridad afectó a la eficiencia de extracción de agua reduciendo el consumo de energía. Además, la reducción de la humedad debida al proceso de desagote disminuyó la variación del pH y la liberación y el transporte del cobre. Aproximadamente el 35% del cobre extraíble se eliminó en el lado del ánodo de T2, que se determinó como el más eficiente para la remediación.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah W, Al-Abadi A (2010) Cationic–electrokinetic improvement of an expansive soil. Appl Clay Sci 47:343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.11.046
Acar YB, Alshawabkeh AN (1993) Principles of electrokinetic remediation. Environ Sci Technol 27:2638–2647. https://doi.org/10.1021/es00049a002
Ammami M, Song Y, Benamar A, Portet-Koltalo F, Wang H (2020) Electro-dewatering of dredged sediments by combined effects of mechanical and electrical processes: Influence of operating conditions. Electrochim Acta. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2020.136462
Bourgès-Gastaud S, Dolez P, Blond E, Touze-Foltz N (2017) Dewatering of oil sands tailings with an electrokinetic geocomposite. Miner Eng 100:177–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2016.11.002
Cardenas-Peña AM, Ibanez JG, Vasquez-Medrano R (2012) Determination of the point of zero charge for electrocoagulation precipitates from an iron anode. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:6142–6153
Chapman DV (1996) Water quality assessments: a guide to the use of biota, sediments and water in environmental monitoring. CRC Press, New York
Chien S-C, Ou C-Y, Wang M-K (2009) Injection of saline solutions to improve the electro-osmotic pressure and consolidation of foundation soil. Appl Clay Sci 44:218–224. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.02.006
Conrardy J-B, Vaxelaire J, Olivier J (2016) Electro-dewatering of activated sludge: electrical resistance analysis. Water Res 100:194–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.05.033
Deng W, Lai Z, Hu M, Han X, Su Y (2020) Effects of frequency and duty cycle of pulsating direct current on the electro-dewatering performance of sewage sludge. Chemosphere 243:125372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125372
Dizon A, Orazem ME (2020) Advances and challenges of electrokinetic dewatering of clays and soils. Curr Opin Electrochem 22:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coelec.2020.03.002
Estabragh A, Naseh M, Javadi A (2014) Improvement of clay soil by electro-osmosis technique. Appl Clay Sci 95:32–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2014.03.019
Fourie A, Jones C (2010) Improved estimates of power consumption during dewatering of mine tailings using electrokinetic geosynthetics (EKGs). Geotext Geomembr 28:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2009.10.007
Fourie A, Johns D, Jones CF (2007) Dewatering of mine tailings using electrokinetic geosynthetics. Can Geotech J 44:160–172. https://doi.org/10.1139/t06-112
Guo Y, Shang JQ (2014) A study on electrokinetic dewatering of oil sands tailings. Environ Geotech 1:121–134. https://doi.org/10.1680/envgeo.13.00013
Hansen HK, Rojo A (2007) Testing pulsed electric fields in electroremediation of copper mine tailings. Electrochim Acta 52:3399–3405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2006.07.064
Huazhe J, Shufei W, Yixuan Y, Xinming C (2020) Water recovery improvement by shearing of gravity-thickened tailings for cemented paste backfill. J Cleaner Prod 245:118882. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118882
Karaca O, Cameselle C, Reddy KR (2017) Acid pond sediment and mine tailings contaminated with metals: physicochemical characterization and electrokinetic remediation. Environ Earth Sci 76:408. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-017-6736-0
Kargar M, Khorasani N, Karami M, Rafiee G, Naseh R (2012) Statistical source identification of major and trace elements in groundwater downward the tailings dam of Miduk Copper Complex, Kerman. Iran Environ Monit Assess 184:6173–6185. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2411-1
Kossoff D, Dubbin W, Alfredsson M, Edwards S, Macklin M, Hudson-Edwards KA (2014) Mine tailings dams: characteristics, failure, environmental impacts, and remediation. Appl Geochem 51:229–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2014.09.010
Lee JK, Shang JQ, Xu Y (2016) Electrokinetic dewatering of mine tailings using DSA electrodes. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:4149–4160. https://doi.org/10.20964/1009160
Lockhart N (1983) Electro-osmotic dewatering of fine tailings from mineral processing. Int J Miner Process 10:131–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/0301-7516(83)90038-8
López-Vizcaíno R, Yustres A, Sáez C, Cañizares P, Asensio L, Navarro V, Rodrigo M (2019) Techno-economic analysis of the scale-up process of electrochemically-assisted soil remediation. J Environ Manage 231:570–575. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.10.084
Maghsoudy S, Ardejani FD, Molson J, Amini M, Ebrahimi L (2019) Application of geo-electrical tomography in coupled hydro-mechanical–chemical investigations in heap leaching. Mine Water Environ 38:197–212. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-018-0557-6
Mahmoud A, Olivier J, Vaxelaire J, Hoadley AF (2010) Electrical field: a historical review of its application and contributions in wastewater sludge dewatering. Water Res 44:2381–2407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2010.01.033
Mahmoud A, Hoadley AF, Conrardy J-B, Olivier J, Vaxelaire J (2016) Influence of process operating parameters on dryness level and energy saving during wastewater sludge electro-dewatering. Water Res 103:109–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.07.016
Maiz I, Esnaola MV, Millan E (1997) Evaluation of heavy metal availability in contaminated soils by a short sequential extraction procedure. Sci Total Environ 206:107–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0048-9697(97)80002-2
Malekzadeh M, Lovisa J, Sivakugan N (2016) An overview of electrokinetic consolidation of soils. Geotech Geol Eng 34:759–776. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-016-0002-1
Masi M, Ceccarini A, Iannelli R (2017a) Model-based optimization of field-scale electrokinetic treatment of dredged sediments. Chem Eng J 328:87–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.07.004
Masi M, Ceccarini A, Iannelli R (2017b) Multispecies reactive transport modelling of electrokinetic remediation of harbour sediments. J Hazard Mater 326:187–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.12.032
Navab-Daneshmand T, Rl B, Hill RJ, Frigon D (2015) Impact of joule heating and pH on biosolids electro-dewatering. Environ Sci Technol 49:5417–5424. https://doi.org/10.1021/es5048254
Ortiz-Soto R, Leal D, Gutierrez C, Aracena A, Rojo A, Hansen HK (2019) Electrokinetic remediation of manganese and zinc in copper mine tailings. J Hazard Mater 365:905–911. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.11.048
Ou C-Y, Chien S-C, Wang Y-G (2009) On the enhancement of electroosmotic soil improvement by the injection of saline solutions. Appl Clay Sci 44:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2008.12.014
Reddy KR, Cameselle C (2009) Electrochemical remediation technologies for polluted soils, sediments and groundwater. Wiley, Hoboken
Rezaee M, Asadollahfardi G, Gomez-Lahoz C, Villen-Guzman M, Paz-Garcia JM (2019) Modeling of electrokinetic remediation of Cd- and Pb-contaminated kaolinite. J Hazard Mater 366:630–635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.12.034
Rosestolato D, Bagatin R, Ferro S (2015) Electrokinetic remediation of soils polluted by heavy metals (mercury in particular). Chem Eng J 264:16–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2014.11.074
Shang JQ, Xu Y (2019) Electrokinetic dewatering of mine tailings from hydrometallurgical processes. In: Proc, 22nd International Conf on Paste, Thickened and Filtered Tailings, Australian Centre for Geomechanics, pp 275–283. https://doi.org/10.36487/ACG_rep/1910_18_Shang
Siyar R, Ardejani FD, Farahbakhsh M, Norouzi P, Yavarzadeh M, Maghsoudy S (2020) Potential of Vetiver grass for the phytoremediation of a real multi-contaminated soil, assisted by electrokinetic. Chemosphere 246:125802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125802
Wang C, Harbottle D, Liu Q, Xu Z (2014) Current state of fine mineral tailings treatment: a critical review on theory and practice. Miner Eng 58:113–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2014.01.018
Wu P, Pi K, Shi Y, Li P, Wang Z, Zhang H, Liu D, Gerson AR (2020) Dewaterability and energy consumption model construction by comparison of electro-dewatering for industry sludges and river sediments. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109335
Xue Z, Tang X, Yang Q, Tian Z, Zhang Y (2019) Influence of salt content on clay electro-dewatering with copper and stainless steel anodes. Drying Technol 37:2005–2019. https://doi.org/10.1080/07373937.2018.1555709
Zhang L, Hu L (2019) Laboratory tests of electro-osmotic consolidation combined with vacuum preloading on kaolinite using electrokinetic geosynthetics. Geotext Geomembr 47:166–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2018.12.010
Zhang S, Yang Z, Lv X, Zhi S, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhang K (2017) Novel electro-dewatering system for activated sludge biosolids in bench-scale, pilot-scale and industrial-scale applications. Chem Eng Res Des 121:44–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2017.02.035
Zimmerman AJ, Weindorf DC (2010) Heavy metal and trace metal analysis in soil by sequential extraction: a review of procedures. Int J Anal Chem. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/387803
Acknowledgements
This article is part of a research project focused on monitoring and modelling of the electrokinetic process on the dewatering and remediation of mine tailings at the Miduk copper mine in Kerman, Iran. The authors are grateful to the R&D Division of the National Iranian Copper Company (NICICO) for their cooperation. The authors also thank Dr. S Maghsoudy, Mr. MJ. Khakpour, Mr. H. Mousavi, Mrs. R. Siyar, and Mrs. S.S. Saadaatmir for their technical and experimental support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shafaei, F., Doulati Ardejani, F., Bahroudi, A. et al. Electrokinetic Studies of Mine Tailings Considering Dewatering and Mass Transport at the Miduk Copper Mine, SE Iran. Mine Water Environ 40, 847–863 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-021-00806-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10230-021-00806-x