Abstract
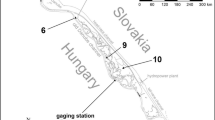
An analysis was made of the effect of dredging on the caddisfly fauna (Trichoptera) of the river Krąpiel (north-western Poland) a short time after the intervention. Pronounced changes were observed in the qualitative and quantitative structure and the biodiversity of Trichoptera. These changes should not, however, be characterized as unfavourable from an ecological perspective if we consider only the one group of insects analysed. Some species — Brachycentrus subnubilus and Lepidostoma hirtum — disappeared from the dredged parts of the river, but significantly more appeared, and these were typical river species. This replacement of species can be linked to habitat changes and the uncovering of larger patches of sandy bottom. The recolonizing species included accidental (eurytopic) species, which is typical in ecological succession for periods immediately following disturbances. On balance, despite the replacement of species, there was no decrease in species diversity, and typical river species appeared in larger numbers. In Trichoptera, recolonization following dredging first takes place as a result of drift of larvae, and then via dispersion of adults.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrikovics S, Kiss O, Nagy B (2005) Hosszú és rövid periódusú változásokról a Szalajka-patak gerinctelen macrofauna közösségeiben (Bükk hegység, Magyarország). Acta Biol Debr Oecol Hung 13:09–19
Brauer F (1857) Neuroptera Austriaca. Wien, pp XXIII + 80, 5 tt
Brock TCM, Arts GHP, Belgers JDM, van Rhenen-Kersten CH (2010) Ecological characterization of drainage ditches in the Netherlands to evaluate pesticide stress. In: Brock TCM, Alix A, Brown CD, Capri E, Gottesburen BFF, Heimbach F, Lythgo CM, Schulz R, Streloke E (eds) Linking aquatic exposure and effects in the risk assessment of plant products. SETAC Press and CRC Press, Taylor and Francis Group, Boca Raton, London, New York, pp 269–287
Chakona A, Phiri C, Day JA (2009) Potential for Trichoptera communities as biological indicators of morphological degradation in riverine systems. Hydrobiologia 621:155–167
Colwell RK (2012) Biodiversity: concepts, patterns and measurement. In: Levin SA (ed) The Princeton guide to ecology. Princeton University Press, Princeton, pp 257–263
Cortes RMV, Ferreira MT, Oliveira SV, Oliveira D (2002) Macroinvertebrate community structure in regulated river segment with different flow conditions. River Res Appl 18:367–382
Curtis J (1834) Description of hitherto some non-descript British species of May-Flies of Anglers. Phil Mag J Sci, London-Edinbyrg 4:212–218
Curtis J (1835) British entomology: being illustrations and descriptions of the genera of insects found in great Britain and Ireland, vol 12. Richard Taylor, London, pp 530–577
Czachorowski S (1989) Differentiation of the Hydropsychidae larvae (Insecta, Trichoptera) in the Pasłęka River as a result of avoidance of trophic competition. Pol Arch Hydrobiol 36:123–132
Dąbkowski P, Buczyński P, Zawal A, Stępień E, Buczyńska E, Stryjecki R, Czachorowski S, Śmietana P, Szenejko M (2015) The impact of dredging of a small lowland river on water beetle fauna (Coleoptera). Water Environ Res (in press)
De Jonge M, Belpaire C, Geeraerts C, De Cooman W, Blust R, Bervoets L (2012) Ecological impact assessment of sediments remediation in a metal-contaminated lowland river using translocated zebra mussels and resident macroinvertebrates. Environ Pollut 171:99–108
de Moor FC, Ivanov VD (2008) Global diversity of caddisflies (Trichoptera: Insecta) in freshwater. Hydrobiologia 595:393–407
Döhler W (1963) Liste der deutschen Trichopteren. Nachrichtenbl Bayer Ent 12:17–22
Downes BJ, Bellgrove A, Street JL (2005) Drifting or walking? Colonisation routes used by different instars and species of lotic, macroinvertebrate filter feeders. Mar Freshw Res 56:815–824
Fabricius JC (1775) Systema Entomologiae. Hafniae, XXVIII + pp 832
Fabricius JC (1781) Species Insectorum, exhibentes eorum differentias specificas, synonyma, auctorum, loca natalia, metamorphosin adiectis observationibus, descriptionibus. Impensis Carol. Ernest. Bohnii, Hamburgi & Kilonii, Kiel, vol 1, pp 388–392
Fabricius JC (1787) Mantissa Insectorum, sistens eorum species auper detectas, adiectis characteribus genericis, differentiis specificis, emendationibus, observationibus. Impensis Christ. Gottl. Proft, Hafniae, vol 1, pp 20 + 348
Giere O (2009) Meiobenthology: the microscopic motile fauna of aquatic sediments, 2nd edn. Springer Verlag, Berlin, p 527
Gordon ND, McMahon TA, Finlayson BL (1992) Stream hydrology: an introduction for ecologists. Wiley, Chichester, p 526
GUS (Główny Urząd Statystyczny) (2008) Mały Rocznik Statystyczny Polski 2008. Zakład Wydawnictw Statystycznych, Warszawa, p 712
Hawkins CP, Murphy ML, Anderson NH (1982) Effects of canopy, substrate composition, and gradient on the structure of macroinvertebrate communities in Cascade Range streams of Oregon. Ecology 63:1840–1856
Haynes JM, Makarewicz JC (1982) Comparison of benthic communities in dredged and undredged areas of the St. Lawrence River, Cape Vincent, NY. Ohio J Sci 82:165–170
Hill MO, Gauch HG (1980) Detrended correspondence analysis: an improved ordination technique. Vegetatio 42:47–58
Hussain QA, Pandit AK (2012) Macroinvertebrates in streams: a review of some ecological factors. Int J Fish Aquac 4:114–123
Hynes HBN (1970) The ecology of running waters. Liverpool University Press, Liverpool, p 555
Linnaeus C (1758) Systema Naturae. Regnum Animale, edn 10, vol I. Holmiae, p 824
Linnaeus C (1761) Fauna Suecica sistens animalia Suecica regni: Mammalia, Aves, Amphibia, Pisces, Insecta, Vermes. Distributa per classes & ordines, genera & species, cum differentiis specierum, synonymis auctorum, nominibus incolarum, locis natalium, descriptionibus insectorum. Stockholmiae, p 578
Lytle DA (2008) Life-history and behavioural adaptations to flow regime in aquatic insects. In: Lancaster J, Briers RA (eds) Aquatic insects: challenges to populations. Proceedings of the Royal Entomological Society’s 24th Symposium. CABI International, Wallingford, UK, pp 122–138
Lytle DA, Poff NL (2004) Adaptation to natural flow regimes. Trends Ecol Evol 19:94–100
Mackay RJ, Wiggins GB (1979) Ecological diversity in Trichoptera. Annu Rev Entomol 24:185–208
Malm T, Johanson KA, Wahlberg N (2013) The evolutionary history of Trichoptera (Insecta): a case of successful adaptation to life in freshwater. System Entomol 38:459–473
Malmqvist B, Rundle S, Brönmakr C (1991) Invertebrate colonization of a new, man-made stream in southern Sweden. Freshw Biol 26:307–324
Minshall GW (1984) Aquatic insect-substratum relationships. In: Resh VH, Rosenberg DM (eds) The ecology of aquatic insects. Praeger Publishers, New York, pp 358–400
Mushtaq B, Raina R, Yousuf AR, Wanganeo A, Rashid U (2013) Effect of dredging on the macrozoobenthos of Hazratbal Basin in the Dal Lake Srinagar. Kashmir, India. Jordan J Biol Sci 6:45–50
Niemi G, de Vore P, Detenbeck N, Taylor D, Lima A, Pastor J, Yount JD, Naiman JR (1990) Overview of case studies on recovery of aquatic systems from disturbance. Environ Manag 14:571–587
Obolewski K (2009) Zmiany struktury jakościowo-ilościowej makrozoobentosu rzeki Kwaczy pod wpływem zabiegów renaturyzacyjnych. In: Obolewski K (ed) Krótkoterminowe ekologiczne efekty renaturyzacji niewielkich rzek nizinnych na przykładzie rzeki Kwaczy. Park Krajobrazowy “Dolina Słupi”, Akademia Pomorska w Słupsku, Słupsk, pp 206–222
Parkyn SM, Smith BJ (2011) Dispersal constraints for stream invertebrates: setting realistic timescales for biodiversity restoration. Environ Manag 48:602–614
Pennak RW (1978) Fresh-water invertebrates of the United States (second edition). Wiley, New York, p 803
Pictet F (1834) Recherches pour server a I’historie et a l’anatimie des Phryganides. Geneve, p 239, 22 tt
Pirvu M, Pacioglu P (2012) The ecological requirements of caddisflies larvae (Insecta: Trichoptera) and their usefulness in water quality assessment of a river in south-west Romania. Knowl Manag Aquat Ecosyst 407:1–13
Pitsch T (1993) Zur Kenntnis der Hydropsyche pellucidula-Gruppe in Mitteleuropa (Trichoptera: Hydropsychidae). Braueria 20:27–32
Rambur P (1842) Histoire naturelle des Insectes Nevropteres. Paris, pp [3] + XVII+ 534, 12 tt
Rosenberg DM, Resh VH (1993) Freshwater biomonitoring and benthic macroinvertebrates. Chapman and Hall, New York, p 488
Rulkens WH (1998) Treatment of contaminated dredged sediments—the Dutch approach and experience. In: Buekens AG, Dragalov VV (eds) Environmentally devastated areas in river basins in Eastern Europe. Springer Verlag, Berlin, pp 199–219
Sanderson RA, Eyre MD, Rushton SP (2005) The influence of stream invertebrate composition at neighbouring sites on local assemblage composition. Freshw Biol 50:221–231
Schrank F (1781) Enumaratio Insectorum Austriae Indigenorum. Wien, pp XXII _ 548 + 2
Skuja A, Spungis V (2010) Influence of environmental factors on the distribution of caddisfly (Trichoptera) communities in medium-sized lowland stream in Latvia. Estonian J Ecol 59:197–215
Smith EP, Orvos DR, Cairns J Jr (1993) Impact assessment using the before-after-control-impact (BACI) model: concerns and comments. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 50:627–637
Stephens J (1836) Iluustrations of British entomology, vol 6. London, pp 146–234
Stępień E, Zawal A, Buczyńska E, Buczyński P (2015a) Effects of dredging on the vegetation in small lowland river. Limnetica (in press)
Stępień E, Zawal A, Buczyński P, Buczyńska E (2015b) Changes in plant communities in the regulated river on the example of Krąpiel river. Acta Biol 22 (in press)
Svendsen KM, Renshaw CE, Magilligan FJ, Nislow KH, Kaste JM (2009) Flow and sediment regimes and tributary junctions on a regulated river: impact on sediment residence time and benthic macroinvertebrate communities. Hydrol Process 23:284–296
Swales S (1989) The use of instream habitat improvement methodology in mitigating the adverse effects of river regulation in fisheries. In: Gore JA, Petts GE (eds) Alternatives in regulated river management. CRC Press Inc., Boca Raton, pp 185–208
Szlauer-Łukaszewska A, Zawal A (2014) The impact of river dredging on ostracod assemblages in the Krąpiel River (NW Poland). Fundam Appl Limnol 185:295–305
Szymelfenig M, Kotwicki L, Graca B (2006) Benthic recolonization in post-dredging pits in the Puck Bay (Southern Baltic Sea). Estuar Coast Shelf Sci 68:489–498
ter Braak CJF (1986) Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67:1167–1179
ter Braak CJF, Smilauer P (2002) CANOCO reference manual and CanoDraw for Windows user’s guide: software for canonical community ordination (version 4.5). Ithaca, Microcomputer Power, p 500
ter Braak CJF, Verdonschot PFM (1995) Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Sci 57:255–289
Thomas VG (1985) Experimentally determined impacts of a small suction dredge on a Montana stream. N Am J Fish Manag 5:480–488
Townsend CR, Hildrew AG (1994) Species traits in relation to a habitat templet for river systems. Freshw Biol 31:265–275
Twisk W, Noordervliet A, ter Keurs J (2000) Effects of ditch management on caddisfly, dragonfly and amphibian larvae in intensively farmed peat areas. Aquat Ecol 34:397–411
Urbanič G, Toman MJ, Krušnik C (2005) Microhabitat type selection of caddisfly larvae (Insecta: 872 Trichoptera) in a shallow lowland stream. Hydrobiologia 541:1–12
Van Dolah RF, Calder DR, Knott DM (1984) Effects of dredging and open-water disposal on benthic macroinvertebrates in a South-Carolina Estuary. Estuaries 7:28–37
Wallace JB (1990) Recovery of lotic macroinvertebrate communities from disturbance. Environ Manag 14:605–620
Whitaker GA, McCuen RH, Brush J (1979) Channel modification and macroinvertebrate community diversity in small streams. Water Resour Bull 15:874–879
Yount JD, Niemi GJ (1990) Recovery of lotic communities and ecosystems from disturbance. A narrative review of case studies. Environ Manag 14:547–569
Zawal A, Dzierzgowska K, Szlauer-Łukaszewska A, Michoński G, Kłosowska M, Bańkowska A, Stryjecki R (2014) A thermocline as an obstacle to the spread of water mites (Acari: Hydrachnidia) across the lake profile. Aquat Insects 35:47–61
Zawal A, Stępień E, Szlauer-Łukaszewska A, Michoński G, Kłosowska M, Bańkowska A, Myśliwy M, Stryjecki R, Buczyńska E, Buczyński P (2015a) The influence of a lowland river dredging (the Krąpiel in NW Poland) on water mite fauna (Acari: Hydrachnidia). Fundam Appl Limnol 186:217–232
Zawal A, Sulikowska-Drozd A, Stępień E, Szlauer-Łukaszewska A, Jankowiak Ł (2015) Regeneration of the molluscan fauna of a small lowland river after dredging. Fundam Appl Limnol (in press)
Acknowledgments
Financial support was provided by the Ministry of Science and Higher Education, no. N305 222537.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Kwang-Hyeon Chang.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zawal, A., Czachorowski, S., Stępień, E. et al. Early post-dredging recolonization of caddisflies (Insecta: Trichoptera) in a small lowland river (NW Poland). Limnology 17, 71–85 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-015-0466-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10201-015-0466-3