Abstract
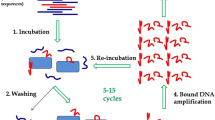
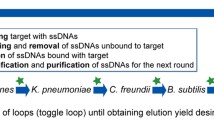
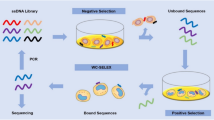
Haemophilus influenzae type b (Hib) causes acute bacterial meningitis (ABM) in children, with a mortality rate of about 3–6 % of the affected patients. ABM can lead to death during a period of hours to several days and, hence, rapid and early detection of the infection is crucial. Aptamers, the short single-stranded DNA or RNA with high affinity to target molecules, are selected by a high-flux screening technique known as in vitro screening and systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment technology (SELEX). In this study, whole-cell SELEX was applied for the selection of target-specific aptamers with high affinity to Hib. ssDNA aptamers prepared by lambda exonuclease were incubated with the target cells (Hib). The aptameric binding rate to Hib was characterized for binding affinity after seven SELEX rounds by flow cytometry. The aptamers with higher binding affinity were cloned. Four of 68 aptamer clones were selected for sequencing. The dissociation constant (Kd) of the high-affinity aptamer clones 45 and 63 were 47.10 and 28.46 pM, respectively. These aptamers did not bind to other bacterial species, including the seven meningitis-causing bacteria. They showed distinct affinity to various H. influenzae strains only. These aptamers showed the highest affinity to Hib and the lowest affinity to H. influenzae type c and to other meningitis-causing bacteria. Clone 63 could detect Hib in patients’ cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) samples at 60 colony-forming units (CFU)/mL. The results indicate applicability of the aptamers for rapid and early detection of infections brought about by Hib.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Murphy TF, Brauer AL, Sethi S, Kilian M, Cai X, Lesse AJ (2007) Haemophilus haemolyticus: a human respiratory tract commensal to be distinguished from Haemophilus influenzae. J Infect Dis 195:81–89
Cody AJ, Field D, Feil EJ, Stringer S, Deadman ME, Tsolaki AG, Gratz B, Bouchet V, Goldstein R, Hood DW, Moxon ER (2003) High rates of recombination in otitis media isolates of non-typeable Haemophilus influenzae. Infect Genet Evol 3:57–66
Pettigrew MM, Laufer AS, Gent JF, Kong Y, Fennie KP, Metlay JP (2012) Upper respiratory tract microbial communities, acute otitis media pathogens, and antibiotic use in healthy and sick children. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:6262–6270
Kroll JS, Loynds B, Brophy LN, Moxon ER (1990) The bex locus in encapsulated Haemophilus influenzae: a chromosomal region involved in capsule polysaccharide export. Mol Microbiol 4:1853–1862
Saeed-Kothe A, Yang W, Mills SD (2004) Use of the riboflavin synthase gene (ribC) as a model for development of an essential gene disruption and complementation system for Haemophilus influenzae. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:4136–4143
Tian GZ, Zhang LJ, Wang XL, Zhang L, Li SF, Gu CM, Sun J, Cui BY (2012) Rapid detection of Haemophilus influenzae and haemophilus parainfluenzae in nasopharyngeal swabs by multiplex PCR. Biomed Environ Sci 25:367–371
Morris SK, Moss WJ, Halsey N (2008) Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine use and effectiveness. Lancet Infect Dis 8:435–443
Rana R, Dalal J, Singh D, Kumar N, Hanif S, Joshi N, Chhikara MK (2015) Development and characterization of haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine prepared using different polysaccharide chain lengths. Vaccine 33:2646–2654
Brouwer MC, Tunkel AR, van de Beek D (2010) Epidemiology, diagnosis, and antimicrobial treatment of acute bacterial meningitis. Clin Microbiol Rev 23:467–492
Sneed BP, Scheld WM (2013) Acute bacterial meningitis. Hosp Med Clin 2:e358–e369
van de Beek D, Brouwer MC, Thwaites GE, Tunkel AR (2012) Advances in treatment of bacterial meningitis. Lancet 380:1693–1702
Thigpen MC, Whitney CG, Messonnier NE, Zell ER, Lynfield R, Hadler JL, Harrison LH, Farley MM, Reingold A, Bennett NM, Craig AS, Schaffner W, Thomas A, Lewis MM, Scallan E, Schuchat A; Emerging Infections Programs Network (2011) Bacterial meningitis in the United States, 1998–2007. N Engl J Med 364:2016–2025
Prasad K, Rai NK, Kumar A (2012) Use of corticosteroids and other adjunct therapies for acute bacterial meningitis in adults. Curr Infect Dis Rep 14:445–453
Yang L, Bashir R (2008) Electrical/electrochemical impedance for rapid detection of foodborne pathogenic bacteria. Biotechnol Adv 26:135–150
Hussein AS, Shafran SD (2000) Acute bacterial meningitis in adults. A 12-year review. Medicine (Baltimore) 79(6):360–368
Abdeldaim GM, Herrmann B (2013) PCR detection of Haemophilus influenzae from respiratory specimens. Methods Mol Biol 943:115–123
Arlett JL, Myers EB, Roukes ML (2011) Comparative advantages of mechanical biosensors. Nat Nanotechnol 6:203–215
Torres-Chavolla E, Alocilja EC (2009) Aptasensors for detection of microbial and viral pathogens. Biosens Bioelectron 24:3175–3182
Wang YX, Ye ZZ, Si CY, Ying YB (2012) Application of aptamer based biosensors for detection of pathogenic microorganisms. Chin J Analyt Chem 40:634–642
Yang Y, Yang D, Schluesener HJ, Zhang Z (2007) Advances in SELEX and application of aptamers in the central nervous system. Biomol Eng 24:583–592
Tombelli S, Minunni M, Mascini M (2005) Analytical applications of aptamers. Biosens Bioelectron 20:2424–2434
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Fan C, Zhao J (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 27:108–117
Van Dorst B, Mehta J, Bekaert K, Rouah-Martin E, De Coen W, Dubruel P, Blust R, Robbens J (2010) Recent advances in recognition elements of food and environmental biosensors: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1178–1194
Hamula CLA, Zhang H, Li F, Wang Z, Le Chris X, Li XF (2011) Selection and analytical applications of aptamers binding microbial pathogens. TrAC Trend Anal Chem 30:1587–1597
Kim YS, Song MY, Jurng J, Kim BC (2013) Isolation and characterization of DNA aptamers against Escherichia coli using a bacterial cell-systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment approach. Anal Biochem 436:22–28
Dwivedi HP, Smiley RD, Jaykus LA (2010) Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers with binding selectivity to Campylobacter jejuni using whole-cell SELEX. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 87:2323–2334
Cao X, Li S, Chen L, Ding H, Xu H, Huang Y, Li J, Liu N, Cao W, Zhu Y, Shen B, Shao N (2009) Combining use of a panel of ssDNA aptamers in the detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Nucleic Acids Res 37:4621–4628
Duan N, Ding X, He L, Wu S, Wei Y, Wang Z (2013) Selection, identification and application of a DNA aptamer against Listeria monocytogenes. Food Control 33:239–243
Dwivedi HP, Smiley RD, Jaykus LA (2013) Selection of DNA aptamers for capture and detection of Salmonella Typhimurium using a whole-cell SELEX approach in conjunction with cell sorting. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97:3677–3686
Vivekananda J, Kiel JL (2006) Anti-Francisella tularensis DNA aptamers detect tularemia antigen from different subspecies by Aptamer-Linked Immobilized Sorbent Assay. Lab Invest 86:610–618
Chen F, Zhou J, Luo F, Mohammed AB, Zhang XL (2007) Aptamer from whole-bacterium SELEX as new therapeutic reagent against virulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 357:743–748
Avci-Adali M, Paul A, Wilhelm N, Ziemer G, Wendel HP (2009) Upgrading SELEX technology by using lambda exonuclease digestion for single-stranded DNA generation. Molecules 15:1–11
Barfod A, Singh B, Johanson U, Riesbeck K, Kjellbom P (2014) In vitro selection of RNA aptamers directed against protein E: a Haemophilus influenzae adhesin. Mol Biotechnol 56:714–725
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the College of Basic Sciences, Shahed University for granting us permission to use its well-equipped laboratory. We thank Mr. Samani of Royan Institute for his assistance with the flow cytometry analysis. We appreciate Hazrat Rasool Hospital, Tehran for providing us with the CSF samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bitaraf, F.S., Rasooli, I. & Mousavi Gargari, S.L. DNA aptamers for the detection of Haemophilus influenzae type b by cell SELEX. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 35, 503–510 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2567-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10096-015-2567-7