Abstract
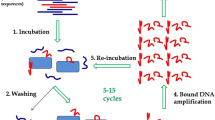
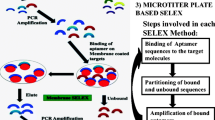
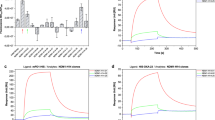
Protein E (PE) of Haemophilus influenzae is a highly conserved ubiquitous surface protein involved in adhesion to and activation of epithelial cells. The host proteins—vitronectin, laminin, and plasminogen are major targets for PE-dependent interactions with the host. To identify novel inhibitory molecules of PE, we used an in vitro selection method based on systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment known as SELEX in order to select 2′F-modified RNA aptamers that specifically bind to PE. Fourteen selection cycles were performed with decreasing concentrations of PE. Sequencing of clones from the 14th selection round revealed the presence of semiconserved sequence motifs in loop regions of the RNA aptamers. Among these, three aptamers showed the highest affinity to PE in electrophoretic mobility shift assays and in dot blots. These three aptamers also inhibited the interaction of PE with vitronectin as revealed by ELISA. Moreover, pre-treatment of H. influenzae with the aptamers significantly inhibited binding of vitronectin to the bacterial surface. Biacore experiments indicated that one of the aptamers had a higher binding affinity for PE as compared to the other aptamers. Our results show that it is possible to select RNA inhibitors against bacterial adhesins using SELEX in order to inhibit interactions with target proteins.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morris, S. K., Moss, W. J., & Halsey, N. (2008). Haemophilus influenzae type b conjugate vaccine use and effectiveness. The Lancet Infectious Diseases, 8, 435–443.
Yamanaka, N., Hotomi, M., & Billal, D. S. (2008). Clinical bacteriology and immunology in acute otitis media in children. Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 14, 180–187.
Murphy, T. F. (2009). Current and future prospects for a vaccine for nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae. Current Infectious Disease Reports, 11, 177–182.
Fink, D. L., Green, B. A., & St Geme, J. W., 3rd. (2002). The Haemophilus influenzae Hap autotransporter binds to fibronectin, laminin, and collagen IV. Infection and Immunity, 70, 4902–4907.
St Geme, J. W., 3rd. (1994). The HMW1 adhesin of nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae recognizes sialylated glycoprotein receptors on cultured human epithelial cells. Infection and Immunity, 62, 3881–3889.
Hallstrom, T., Trajkovska, E., Forsgren, A., & Riesbeck, K. (2006). Haemophilus influenzae surface fibrils contribute to serum resistance by interacting with vitronectin. Journal of Immunology, 177, 430–436.
Ronander, E., Brant, M., Eriksson, E., Morgelin, M., Hallgren, O., et al. (2009). Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae adhesin protein E: characterization and biological activity. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 199, 522–531.
Singh, B., Al-Jubair, T., Morgelin, M., Thunnissen, M. M., & Riesbeck, K. (2013). The unique structure of Haemophilus influenzae Protein E reveals multiple binding sites for host factors. Infection and Immunity, 81, 801–814.
Singh, B., Al Jubair, T., Fornvik, K., Thunnissen, M. M., & Riesbeck, K. (2012). Crystallization and X-ray diffraction analysis of a novel surface-adhesin protein: protein E from Haemophilus influenzae. Acta Crystallographica, Section F, 68, 222–226.
Singh, B., Blom, A. M., Unal, C., Nilson, B., Morgelin, M., et al. (2010). Vitronectin binds to the head region of Moraxella catarrhalis ubiquitous surface protein A2 and confers complement-inhibitory activity. Molecular Microbiology, 75, 1426–1444.
Singh, B., Jalalvand, F., Morgelin, M., Zipfel, P., Blom, A. M., et al. (2011). Haemophilus influenzae protein E recognizes the C-terminal domain of vitronectin and modulates the membrane attack complex. Molecular Microbiology, 81, 80–98.
Hallstrom, T., Blom, A. M., Zipfel, P. F., & Riesbeck, K. (2009). Nontypeable Haemophilus influenzae protein E binds vitronectin and is important for serum resistance. Journal of Immunology, 183, 2593–2601.
Singh, B., Su, Y. C., & Riesbeck, K. (2010). Vitronectin in bacterial pathogenesis: A host protein used in complement escape and cellular invasion. Molecular Microbiology, 78, 545–560.
Hallstrom, T., Singh, B., Resman, F., Blom, A. M., Morgelin, M., et al. (2011). Haemophilus influenzae protein E binds to the extracellular matrix by concurrently interacting with laminin and vitronectin. Journal of Infectious Diseases, 204, 1065–1074.
Bunka, D. H., & Stockley, P. G. (2006). Aptamers come of age—At last. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 4, 588–596.
Tuerk, C., & Gold, L. (1990). Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science, 249, 505–510.
Ellington, A. D., & Szostak, J. W. (1990). In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature, 346, 818–822.
Gopinath, S. C., Sakamaki, Y., Kawasaki, K., & Kumar, P. K. (2006). An efficient RNA aptamer against human influenza B virus hemagglutinin. Journal of Biochemistry, 139, 837–846.
Woo, H. M., Kim, K. S., Lee, J. M., Shim, H. S., Cho, S. J., et al. (2013). Single-stranded DNA aptamer that specifically binds to the influenza virus NS1 protein suppresses interferon antagonism. Antiviral Research, 100, 337–345.
Nimjee, S. M., Rusconi, C. P., & Sullenger, B. A. (2005). Aptamers: An emerging class of therapeutics. Annual Review of Medicine, 56, 555–583.
Grundy, W. N., Bailey, T. L., Elkan, C. P., & Baker, M. E. (1997). Meta-MEME: motif-based hidden Markov models of protein families. Computer Applications in the Biosciences, 13, 397–406.
Zuker, M. (2003). Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Research, 31, 3406–3415.
Hunter, R. (1970). Standardization of the chloramine-T method of protein iodination. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine, 133, 989–992.
Ronander, E., Brant, M., Janson, H., Sheldon, J., Forsgren, A., et al. (2008). Identification of a novel Haemophilus influenzae protein important for adhesion to epithelial cells. Microbes and Infection, 10, 87–96.
Eulberg, D., Buchner, K., Maasch, C., & Klussmann, S. (2005). Development of an automated in vitro selection protocol to obtain RNA-based aptamers: identification of a biostable substance P antagonist. Nucleic Acids Research, 33, e45.
Barfod, A., Persson, T., & Lindh, J. (2009). In vitro selection of RNA aptamers against a conserved region of the Plasmodium falciparum erythrocyte membrane protein 1. Parasitology Research, 105, 1557–1566.
Liang, O. D., Rosenblatt, S., Chhatwal, G. S., & Preissner, K. T. (1997). Identification of novel heparin-binding domains of vitronectin. FEBS Letters, 407, 169–172.
Ulrich, H., Magdesian, M. H., Alves, M. J., & Colli, W. (2002). In vitro selection of RNA aptamers that bind to cell adhesion receptors of Trypanosoma cruzi and inhibit cell invasion. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 277, 20756–20762.
Sayer, N., Ibrahim, J., Turner, K., Tahiri-Alaoui, A., & James, W. (2002). Structural characterization of a 2′F-RNA aptamer that binds a HIV-1 SU glycoprotein, gp120. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 293, 924–931.
Pan, Q., Zhang, X. L., Wu, H. Y., He, P. W., Wang, F., et al. (2005). Aptamers that preferentially bind type IVB pili and inhibit human monocytic-cell invasion by Salmonella enterica serovartyphi. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 49, 4052–4060.
Choi, J. S., Kim, S. G., Lahousse, M., Park, H. Y., Park, H. C., et al. (2011). Screening and characterization of high-affinity ssDNA aptamers against anthrax protective antigen. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 16, 266–271.
Hwang, J., & Nishikawa, S. (2006). Novel approach to analyzing RNA aptamer-protein interactions: toward further applications of aptamers. Journal of Biomolecular Screening, 11, 599–605.
Thiel, W. H., Bair, T., Wyatt Thiel, K., Dassie, J. P., Rockey, W. M., et al. (2011). Nucleotide bias observed with a short SELEX RNA aptamer library. Nucleic Acid Therapeutics, 21, 253–263.
Lee, J. H., Kim, H., Ko, J., & Lee, Y. (2002). Interaction of C5 protein with RNA aptamers selected by SELEX. Nucleic Acids Research, 30, 5360–5368.
Kim, M. Y., & Jeong, S. (2004). Inhibition of the functions of the nucleocapsid protein of human immunodeficiency virus-1 by an RNA aptamer. Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 320, 1181–1186.
Su, Y. C., Jalalvand, F., Morgelin, M., Blom, A. M., Singh, B., et al. (2013). Haemophilus influenzae acquires vitronectin via the ubiquitous Protein F to subvert host innate immunity. Molecular Microbiology, 87, 1245–1266.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Swedish Research Council (VR; grant number 521-2010-4221, www.vr.se), the Research Council Formas, the Research School in Pharmaceutical Sciences (FLÄK), the Swedish Medical Research Council, the Alfred Österlund, the Anna and Edwin Berger, Anna-Lisa and Sven-Erik Lundgren, Greta and Johan Kock, the Physiographical Society, the Cancer Foundation at the University Hospital in Malmö, and Skåne County Council′s research and development foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barfod, A., Singh, B., Johanson, U. et al. In Vitro Selection of RNA Aptamers Directed Against Protein E: A Haemophilus influenzae Adhesin. Mol Biotechnol 56, 714–725 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9749-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12033-014-9749-x