Abstract
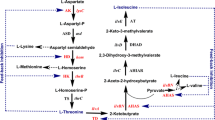
The peptidoglycan of the hyperthermophile Thermotoga maritima contains an unusual component, d-lysine (d-Lys), in addition to the typical d-alanine (d-Ala) and d-glutamate (d-Glu). In a previous study, we identified a Lys racemase that is presumably associated with d-Lys biosynthesis. However, our understanding of d-amino acid metabolism in T. maritima and other bacteria remains limited, although d-amino acids in the peptidoglycan are crucial for preserving bacterial cell structure and resistance to environmental threats. Herein, we characterized enzymatic and structural properties of TM0356 that shares a high amino acid sequence identity with serine (Ser) racemase. The results revealed that TM0356 forms a tetramer with each subunit containing a pyridoxal 5′-phosphate as a cofactor. The enzyme did not exhibit racemase activity toward various amino acids including Ser, and dehydratase activity was highest toward l-threonine (l-Thr). It also acted on l-Ser and l-allo-Thr, but not on the corresponding d-amino acids. The catalytic mechanism did not follow typical Michaelis–Menten kinetics; it displayed a sigmoidal dependence on substrate concentration, with highest catalytic efficiency (kcat/K0.5) toward l-Thr. Interestingly, dehydratase activity was insensitive to allosteric regulators l-valine and l-isoleucine (l-Ile) at low concentrations, while these l-amino acids are inhibitors at high concentrations. Thus, TM0356 is a biosynthetic Thr dehydratase responsible for the conversion of l-Thr to α-ketobutyrate and ammonia, which is presumably involved in the first step of the biosynthesis of l-Ile.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Dpm:
-
Diaminopimelate
- GlcNAc:
-
N-Acetylglucosamine
- MurNAc:
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid
- PLP:
-
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate
- OPA:
-
o-Phthalaldehyde
- NAC:
-
N-Acetyl-l-cysteine
- Boc-l-Cys:
-
N-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-l-cysteine
- Aba:
-
Aminobutyric acid
- Hse:
-
Homoserine
- Cit:
-
Citrulline
- Orn:
-
Ornithine
- SDS:
-
Sodium dodecyl sulfate
- AOAA:
-
Aminoxyacetic acid
- CHES:
-
N-Cyclohexyl-2-aminoethanesulfonic acid
- CAPS:
-
N-Cyclohexyl-3-aminopropanesulfonic acid
- BN-PAGE:
-
Blue native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- CBB:
-
Coomassie Brilliant Blue
References
Adachi M, Shimizu R, Kato S, Oikawa T (2019) The first identification and characterization of a histidine-specific amino acid racemase, histidine racemase from a lactic acid bacterium, Leuconostoc mesenteroides subsp. sake NBRC 102480. Amino Acids 51:331–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-018-2671-y
Amorim Franco TM, Blanchard JS (2017) Bacterial branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis: structures, mechanisms, and drugability. Biochemistry 56:5849–5865. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00849
Arias CA, Weisner J, Blackburn JM, Reynolds PE (2000) Serine and alanine racemase activities of VanT: a protein necessary for vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus gallinarum BM4174. Microbiology 146:1727–1734. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-146-7-1727
Arnold K, Bordoli L, Kopp J, Schwede T (2006) The SWISS-MODEL workspace: a web-based environment for protein structure homology modelling. Bioinformatics 22:195–201
Bellais S, Arthur M, Dubost L, Hugonnet JE, Gutmann L, van Heijenoort J, Legrand R, Brouard JP, Rice L, Mainardi JL (2006) Aslfm, the d-aspartate ligase responsible for the addition of d-aspartic acid onto the peptidoglycan precursor of Enterococcus faecium. J Biol Chem 281:11586–11594. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M600114200
Boniface A, Bouhss A, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D (2006) The MurE synthetase from Thermotoga maritima is endowed with an unusual d-lysine adding activity. J Biol Chem 281:15680–15686. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M506311200
Boniface A, Parquet C, Arthur M, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D (2009) The elucidation of the structure of Thermotoga maritima peptidoglycan reveals two novel types of cross-link. J Biol Chem 284:21856–21862. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M109.034363
Borchert AJ, Downs DM (2018) Analyses of variants of the Ser/Thr dehydratase IlvA provide insight into 2-aminoacrylate metabolism in Salmonella enterica. J Biol Chem 293:19240–19249. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.RA118.005626
Cava F, de Pedro MA, Lam H, Davis BM, Waldor MK (2011) Distinct pathways for modification of the bacterial cell wall by non-canonical d-amino acids. EMBO J 30:3442–3453. https://doi.org/10.1038/emboj.2011.246
Chen IC, Lin WD, Hsu SK, Thiruvengadam V, Hsu WH (2009) Isolation and characterization of a novel lysine racemase from a soil metagenomic library. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5161–5166. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00074-09
de Miranda J, Panizzutti R, Foltyn VN, Wolosker H (2002) Cofactors of serine racemase that physiologically stimulate the synthesis of the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor coagonist d-serine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14542–14547. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.222421299
Eisenstein E (1991) Cloning, expression, purification, and characterization of biosynthetic threonine deaminase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 266:5801–5807
Eisenstein E (1995) Allosteric regulation of biosynthetic threonine deaminase from Escherichia coli: effects of isoleucine and valine on active-site ligand binding and catalysis. Arch Biochem Biophys 316:311–318. https://doi.org/10.1006/abbi.1995.1042
Espaillat A, Carrasco-López C, Bernardo-García N, Pietrosemoli N, Otero LH, Álvarez L, de Pedro MA, Pazos F, Davis BM, Waldor MK, Hermoso JA, Cava F (2014) Structural basis for the broad specificity of a new family of amino-acid racemases. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70:79–90. https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004713024838
Favrot L, Amorim Franco TM, Blanchard JS (2018) Biochemical characterization of the Mycobacterium smegmatis threonine deaminase. Biochemistry 57:6003–6012. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00871
Gallagher DT, Gilliland GL, Xiao G, Zondlo J, Fisher KE, Chinchilla D, Eisenstein E (1998) Structure and control of pyridoxal phosphate dependent allosteric threonine deaminase. Structure 6:465–475. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0969-2126(98)00048-3
Goytia M, Chamond N, Cosson A, Coatnoan N, Hermant D, Berneman A, Minoprio P (2007) Molecular and structural discrimination of proline racemase and hydroxyproline-2-epimerase from nosocomial and bacterial pathogens. PLoS ONE 2:e885. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0000885
Grohs P, Gutmann L, Legrand R, Schoot B, Mainardi JL (2000) Vancomycin resistance is associated with serine-containing peptidoglycan in Enterococcus gallinarum. J Bacteriol 182:6228–6232. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.182.21.6228-6232.2000
Guinand M, Ghuysen JM, Schleifer KH, Kandler O (1969) The peptidoglycan in walls of Butyribacterium rettgeri. Biochemistry 8:200–207. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi00829a029
Hernández SB, Cava F (2016) Environmental roles of microbial amino acid racemases. Environ Microbiol 18:1673–1685. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.13072
Hochbaum AI, Kolodkin-Gal I, Foulston L, Kolter R, Aizenberg J, Losick R (2011) Inhibitory effects of d-amino acids on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm development. J Bacteriol 193:5616–5622. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.05534-11
Huber R, Langworthy TA, König H, Thomm M, Woese CR, Sleytr UB, Stetter KO (1986) Thermotoga maritima sp. nov. represents a new genus of unique extremely thermophilic eubacteria growing up to 90 °C. Arch Microbiol 144:324–333. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00409880
Jia R, Yang D, Xu D, Gu T (2017a) Mitigation of a nitrate reducing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm and anaerobic biocorrosion using ciprofloxacin enhanced by d-tyrosine. Sci Rep 7:6946. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-07312-7
Jia R, Li Y, Al-Mahamedh HH, Gu T (2017b) Enhanced biocide treatments with d-amino acid mixtures against a biofilm consortium from a water cooling tower. Front Microbiol 8:1538. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.01538
Kato S, Hemmi H, Yoshimura T (2012) Lysine racemase from a lactic acid bacterium, Oenococcus oeni: structural basis of substrate specificity. J Biochem 152:505–508. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvs120
Kolodkin-Gal I, Romero D, Cao S, Clardy J, Kolter R, Losick R (2010) d-Amino acids trigger biofilm disassembly. Science 328:627–629. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1188628
Kuan YC, Kao CH, Chen CH, Chen CC, Hu HY, Hsu WH (2011) Biochemical characterization of a novel lysine racemase from Proteus mirabilis BCRC10725. Process Biochem 46:1914–1920. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2011.06.019
Kubota T, Shimamura S, Kobayashi T, Nunoura T, Deguchi S (2016) Distribution of eukaryotic serine racemases in the bacterial domain and characterization of a representative protein in Roseobacter litoralis Och 149. Microbiology 162:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.000200
Lam H, Oh DC, Cava F, Takacs CN, Clardy J, de Pedro MA, Waldor MK (2009) d-Amino acids govern stationary phase cell wall remodeling in bacteria. Science 325:1552–1555. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1178123
Leiman SA, May JM, Lebar MD, Kahne D, Kolter R, Losick R (2013) d-Amino acids indirectly inhibit biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis by interfering with protein synthesis. J Bacteriol 195:5391–5395. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00975-13
Li E, Wang P, Zhang D (2016) d-Phenylalanine inhibits biofilm development of a marine microbe, Pseudoalteromonas sp. SC2014. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363:fnw198. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fnw198
Luginbuhl GH, Hofler JG, Decedue CJ, Burns RO (1974) Biodegradative l-threonine deaminase of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol 120:559–561. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.120.1.559-561.1974
Matsui D, Oikawa T, Arakawa N, Osumi S, Lausberg F, Stäbler N, Freudl R, Eggeling L (2009) A periplasmic, pyridoxal-5’-phosphate-dependent amino acid racemase in Pseudomonas taetrolens. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 83:1045–1054. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-009-1942-7
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2017) Identification and characterization of novel broad-spectrum amino acid racemases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Amino Acids 49:1885–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2486-2
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2018) Cystathionine β-lyase is involved in d-amino acid metabolism. Biochem J 475:1397–1410. https://doi.org/10.1042/BCJ20180039
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2019) Elucidation of the d-lysine biosynthetic pathway in the hyperthermophile Thermotoga maritima. FEBS J 286:601–614. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.14720
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2020a) Involvement of penicillin-binding proteins in the metabolism of a bacterial peptidoglycan containing a non-canonical d-amino acid. Amino Acids 52:487–497. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02830-7
Miyamoto T, Moriya T, Homma H, Oshima T (2020b) Enzymatic properties and physiological function of glutamate racemase from Thermus thermophilus. Biochim Biophys Acta Proteins Proteom 1868:140461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbapap.2020.140461
Mutaguchi Y, Ohmori T, Wakamatsu T, Doi K, Ohshima T (2013) Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel amino acid racemase, isoleucine 2-epimerase, from Lactobacillus species. J Bacteriol 195:5207–5215. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00709-13
Nakazawa A, Tokushige M, Hayaishi O, Ikehara M, Mizuno Y (1967) Studies on the interaction between regulatory enzymes and effectors. I. Effect of adenosine 5’-monophosphate analogues on threonine deaminase. J Biol Chem 242:3868–3872
Radkov AD, Moe LA (2013) Amino acid racemization in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Bacteriol 195:5016–5024. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.00761-13
Radkov AD, Moe LA (2014) Bacterial synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5363–5374. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5726-3
Ramón-Peréz ML, Diaz-Cedillo F, Ibarra JA, Torales-Cardeña A, Rodríguez-Martínez S, Jan-Roblero J, Cancino-Diaz ME, Cancino-Diaz JC (2014) d-Amino acids inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from ocular infections. J Med Microbiol 63:1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1099/jmm.0.075796-0
Rosen E, Tsesis I, Elbahary S, Storzi N, Kolodkin-Gal I (2016) Eradication of Enterococcus faecalis biofilms on human dentin. Front Microbiol 7:2055. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2016.02055
Sanchez Z, Tani A, Kimbara K (2013) Extensive reduction of cell viability and enhanced matrix production in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 flow biofilms treated with a d-amino acid mixture. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:1396–1399. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.02911-12
Sharma R, Keshari D, Singh KS, Singh SK (2017) Biochemical and functional characterization of MRA_1571 of Mycobacterium tuberculosis H37Ra and effect of its down-regulation on survival in macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 487:892–897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.04.149
Shulman A, Zalyapin E, Vyazmensky M, Yifrach O, Barak Z, Chipman DM (2008) Allosteric regulation of Bacillus subtilis threonine deaminase, a biosynthetic threonine deaminase with a single regulatory domain. Biochemistry 47:11783–11792. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi800901n
Simanshu DK, Savithri HS, Murthy MR (2006) Crystal structures of Salmonella typhimurium biodegradative threonine deaminase and its complex with CMP provide structural insights into ligand-induced oligomerization and enzyme activation. J Biol Chem 281:39630–39641. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M605721200
Simanshu DK, Chittori S, Savithri HS, Murthy MR (2007) Structure and function of enzymes involved in the anaerobic degradation of l-threonine to propionate. J Biosci 56:1195–1206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0121-1
Stadtman TC, Elliott P (1957) Studies on the enzymic reduction of amino acids. II. Purification and properties of d-proline reductase and a proline racemase from Clostridium sticklandii. J Biol Chem 228:983–997
Umbarger HE, Brown B (1957) Threonine deamination in Escherichia coli. II. Evidence for two l-threonine deaminases. J Bacteriol 73:105–112. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.73.1.105-112.1957
Wittig I, Braun HP, Schägger H (2006) Blue native PAGE. Nat Protoc 1:418–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2006.62
Yamashita T, Ashiuchi M, Ohnishi K, Kato S, Nagata S, Misono H (2004) Molecular identification of monomeric aspartate racemase from Bifidobacterium bifidum. Eur J Biochem 271:4798–4803. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04445.x
Yamauchi T, Choi SY, Okada H, Yohda M, Kumagai H, Esaki N, Soda K (1992) Properties of aspartate racemase, a pyridoxal 5’-phosphate-independent amino acid racemase. J Biol Chem 267:18361–18364
Yorifuji T, Ogata K (1971) Arginine racemase of Pseudomonas graveolens. I. Purification, crystallization, and properties. J Biol Chem 246:5085–5092
Yu X, Li Y, Wang X (2012) Molecular evolution of threonine dehydratase in bacteria. PLoS ONE 8:e80750. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0080750
Yu C, Li X, Zhang N, Wen D, Liu C, Li Q (2016) Inhibition of biofilm formation by d-tyrosine: effect of bacterial type and d-tyrosine concentration. Water Res 92:173–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2016.01.037
Zilm PS, Butnejski V, Rossi-Fedele G, Kidd SP, Edwards S, Vasilev K (2017) d-Amino acids reduce Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in vitro and in the presence of antimicrobials used for root canal treatment. PLoS ONE 12:e0170670. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170670
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TM designed the study, performed most of the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. HH and KS-K supervised and wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to data interpretation throughout the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: L. Chemes.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamoto, T., Katane, M., Saitoh, Y. et al. Identification and biochemical characterization of threonine dehydratase from the hyperthermophile Thermotoga maritima. Amino Acids 53, 903–915 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02993-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-021-02993-x