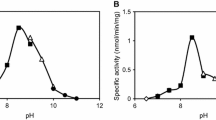
Abstract
Bacteria produce various d-amino acids, including non-canonical d-amino acids, to adapt to environmental changes and overcome a variety of threats. These d-amino acids are largely utilized as components of peptidoglycan, and they promote peptidoglycan remodeling and biofilm disassembly. The biosynthesis, maturation, and recycling of peptidoglycan are catalyzed by penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs). However, although non-canonical d-amino acids are known to be incorporated into peptidoglycan, the maturation and recycling of peptidoglycan containing such residues remain uncharacterized. Therefore, we investigated whether PBP4 and PBP5, low molecular mass (LMM) PBPs from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis, are involved in these events of peptidoglycan metabolism. Enzyme assays using p-nitroaniline (pNA)-derivatized d-amino acids and peptidoglycan-mimicking peptides revealed that PBP4 and PBP5 from both species have peptidase activity toward substrates containing d-Asn, d-His, or d-Trp. These d-amino acids slowed the growth of dacA- or dacB-deficient E. coli (∆dacA or ∆dacB) relative to the wild-type strain. Additionally, these d-amino acids affected biofilm formation by the ∆dacB strain. Collectively, PBP4 and PBP5 are involved in the cleavage of peptidoglycan containing non-canonical d-amino acids, and these properties affect growth and biofilm formation.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PBPs:
-
Penicillin-binding proteins
- GlcNAc:
-
N-Acetylglucosamine
- MurNAc:
-
N-Acetylmuramic acid
- Dpm:
-
Diaminopimelate
- PLP:
-
Pyridoxal 5′-phosphate
- HMM:
-
High molecular mass
- LMM:
-
Low molecular mass
- OPA:
-
o-Phthalaldehyde
- Ac:
-
Acetyl
- Ac2 :
-
Diacetyl
- pNA:
-
p-Nitroaniline
- Boc-l-Cys:
-
N-tert-Butoxycarbonyl-l-cysteine
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Aliashkevich A, Alvarez L, Cava F (2018) New insights into the mechanisms and biological roles of d-amino acids in complex eco-systems. Front Microbiol 9:683
Arias CA, Weisner J, Blackburn JM, Reynolds PE (2000) Serine and alanine racemase activities of VanT: a protein necessary for vancomycin resistance in Enterococcus gallinarum BM4174. Microbiology 146:1727–1734
Bellais S, Arthur M, Dubost L, Hugonnet JE, Gutmann L, van Heijenoort J, Legrand R, Brouard JP, Rice L, Mainardi JL (2006) Aslfm, the d-aspartate ligase responsible for the addition of d-aspartic acid onto the peptidoglycan precursor of Enterococcus faecium. J Biol Chem 281:11586–11594
Boniface A, Parquet C, Arthur M, Mengin-Lecreulx D, Blanot D (2009) The elucidation of the structure of Thermotoga maritima peptidoglycan reveals two novel types of cross-link. J Biol Chem 284:21856–21862
Caparrós M, Pisabarro AG, de Pedro MA (1992) Effect of d-amino acids on structure and synthesis of peptidoglycan in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 174:5549–5559
Cava F, de Pedro MA, Lam H, Davis BM, Waldor MK (2011a) Distinct pathways for modification of the bacterial cell wall by non-canonical d-amino acids. EMBO J 30:3442–3453
Cava F, Lam H, de Pedro MA, Waldor MK (2011b) Emerging knowledge of regulatory roles of d-amino acids in bacteria. Cell Mol Life Sci 68:817–831
Clarke TB, Kawai F, Park SY, Tame JR, Dowson CG, Roper DI (2009) Mutational analysis of the substrate specificity of Escherichia coli penicillin binding protein 4. Biochemistry 48:2675–2683
de Pedro MA, Quintela JC, Höltje JV, Schwarz H (1997) Murein segregation in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 179:2823–2834
Espaillat A, Carrasco-López C, Bernardo-García N, Pietrosemoli N, Otero LH, Álvarez L, de Pedro MA, Pazos F, Davis BM, Waldor MK, Hermoso JA, Cava F (2014) Structural basis for the broad specificity of a new family of amino-acid racemases. Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 70:79–90
González-Leiza SM, de Pedro MA, Ayala JA (2011) AmpH, a bifunctional dd-endopeptidase and dd-carboxypeptidase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 193:6887–6894
Grohs P, Gutmann L, Legrand R, Schoot B, Mainardi JL (2000) Vancomycin resistance is associated with serine-containing peptidoglycan in Enterococcus gallinarum. J Bacteriol 182:6228–6232
Hernández SB, Cava F (2016) Environmental roles of microbial amino acid racemases. Environ Microbiol 18:1673–1685
Hochbaum AI, Kolodkin-Gal I, Foulston L, Kolter R, Aizenberg J, Losick R (2011) Inhibitory effects of d-amino acids on Staphylococcus aureus biofilm development. J Bacteriol 193:5616–5622
Höltje JV (1998) Growth of the stress-bearing and shape-maintaining murein sacculus of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:181–203
Jia R, Li Y, Al-Mahamedh HH, Gu T (2017a) Enhanced biocide treatments with d-amino acid mixtures against a biofilm consortium from a water cooling tower. Front Microbiol 8:1538
Jia R, Yang D, Xu D, Gu T (2017b) Mitigation of a nitrate reducing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm and anaerobic biocorrosion using ciprofloxacin enhanced by d-tyrosine. Sci Rep 7:6946
Kato S, Oikawa T (2018) A novel bifunctional amino acid racemase with multiple substrate specificity, MalY from Lactobacillus sakei LT-13: genome-based identification and enzymological characterization. Front Microbiol 9:403
Kawarai T, Furukawa S, Narisawa N, Hagiwara C, Ogihara H, Yamasaki M (2009) Biofilm formation by Escherichia coli in hypertonic sucrose media. J Biosci Bioeng 107:630–635
Kolodkin-Gal I, Romero D, Cao S, Clardy J, Kolter R, Losick R (2010) d-Amino acids trigger biofilm disassembly. Science 328:627–629
Lam H, Oh DC, Cava F, Takacs CN, Clardy J, de Pedro MA, Waldor MK (2009) d-Amino acids govern stationary phase cell wall remodeling in bacteria. Science 325:1552–1555
Leiman SA, May JM, Lebar MD, Kahne D, Kolter R, Losick R (2013) d-Amino acids indirectly inhibit biofilm formation in Bacillus subtilis by interfering with protein synthesis. J Bacteriol 195:5391–5395
Li E, Wang P, Zhang D (2016) D-Phenylalanine inhibits biofilm development of a marine microbe, Pseudoalteromonas sp. SC2014. FEMS Microbiol Lett 363:fnw98
Meberg BM, Paulson AL, Priyadarshini R, Young KD (2004) Endopeptidase penicillin-binding proteins 4 and 7 play auxiliary roles in determining uniform morphology of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 186:8326–8336
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2017) Identification and characterization of novel broad-spectrum amino acid racemases from Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Amino Acids 49:1885–1894
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2018) Cystathionine β-lyase is involved in d-amino acid metabolism. Biochem J 475:1397–1410
Miyamoto T, Katane M, Saitoh Y, Sekine M, Homma H (2019) Elucidation of the d-lysine biosynthetic pathway in the hyperthermophile Thermotoga maritima. FEBS J 286:601–614
Mosteller RD, Goldstein RV (1975) Unusual sensitivity of Escherichia coli to adenine or adenine plus histidine. J Bacteriol 123:750–751
Mutaguchi Y, Ohmori T, Wakamatsu T, Doi K, Ohshima T (2013) Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel amino acid racemase, isoleucine 2-epimerase, from Lactobacillus species. J Bacteriol 195:5207–5215
Nelson DE, Young KD (2001) Contributions of PBP 5 and dd-carboxypeptidase penicillin binding proteins to maintenance of cell shape in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 183:3055–3064
Priyadarshini R, Popham DL, Young KD (2006) Daughter cell separation by penicillin-binding proteins and peptidoglycan amidases in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 188:5345–5355
Radkov AD, Moe LA (2013) Amino acid racemization in Pseudomonas putida KT2440. J Bacteriol 195:5016–5024
Radkov AD, Moe LA (2014) Bacterial synthesis of d-amino acids. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98:5363–5374
Ramón-Peréz ML, Diaz-Cedillo F, Ibarra JA, Torales-Cardeña A, Rodríguez-Martínez S, Jan-Roblero J, Cancino-Diaz ME, Cancino-Diaz JC (2014) d-Amino acids inhibit biofilm formation in Staphylococcus epidermidis strains from ocular infections. J Med Microbiol 63:1369–1376
Rosen E, Tsesis I, Elbahary S, Storzi N, Kolodkin-Gal I (2016) Eradication of Enterococcus faecalis biofilms on human dentin. Front Microbiol 7:2055
Sauvage E, Kerff F, Terrak M, Ayala JA, Charlier P (2008) The penicillin-binding proteins: structure and role in peptidoglycan biosynthesis. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:234–258
She P, Chen L, Liu H, Zou Y, Luo Z, Koronfel A, Wu Y (2015) The effects of d-tyrosine combined with amikacin on the biofilms of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Microb Pathog 86:38–44
Shimazaki J, Furukawa S, Ogihara H, Morinaga Y (2012) l-Tryptophan prevents Escherichia coli biofilm formation and triggers biofilm degradation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 419:715–718
Soutourina J, Plateau P, Blanquet S (2000) Metabolism of d-aminoacyl-tRNAs in Escherichia coli and Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells. J Biol Chem 275:32535–32542
Soutourina O, Soutourina J, Blanquet S, Plateau P (2004) Formation of d-tyrosyl-tRNATyr accounts for the toxicity of d-tyrosine toward Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 279:42560–42565
Typas A, Banzhaf M, Gross CA, Vollmer W (2012) From the regulation of peptidoglycan synthesis to bacterial growth and morphology. Nat Rev Microbiol 10:123–136
Vollmer W, Blanot D, de Pedro MA (2008) Peptidoglycan structure and architecture. FEMS Microbiol Rev 32:149–167
Yamashita T, Ashiuchi M, Ohnishi K, Kato S, Nagata S, Misono H (2004) Molecular identification of monomeric aspartate racemase from Bifidobacterium bifidum. Eur J Biochem 271:4798–4803
Yamauchi T, Choi SY, Okada H, Yohda M, Kumagai H, Esaki N, Soda K (1992) Properties of aspartate racemase, a pyridoxal 5'-phosphate-independent amino acid racemase. J Biol Chem 267:18361–18364
Yu C, Li X, Zhang N, Wen D, Liu C, Li Q (2016) Inhibition of biofilm formation by d-tyrosine: effect of bacterial type and d-tyrosine concentration. Water Res 92:173–179
Zilm PS, Butnejski V, Rossi-Fedele G, Kidd SP, Edwards S, Vasilev K (2017) d-Amino acids reduce Enterococcus faecalis biofilms in vitro and in the presence of antimicrobials used for root canal treatment. PLoS ONE 12:e0170670
Acknowledgements
We thank S. Kitamoto and R. Takasaki (School of Pharmacy, Kitasato University) for assistance with the experiments. This work was supported in part by Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) KAKENHI Grant number 17K18082 (to T.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TM designed the study, performed most of the experiments, and analyzed the data. HH supervised the study. TM and HH wrote the manuscript. All the authors contributed to the interpretation of the results throughout the study.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. Stuchlík.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miyamoto, T., Katane, M., Saitoh, Y. et al. Involvement of penicillin-binding proteins in the metabolism of a bacterial peptidoglycan containing a non-canonical d-amino acid. Amino Acids 52, 487–497 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02830-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-020-02830-7