Abstract
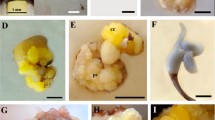
Large-scale propagation of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis, Jacq.) is difficult due to its single apical meristem. Thus, obtaining plants is mainly through seed germination, and a long growing period is required before oil production is possible. An alternative to large-scale seedling production is indirect somatic embryogenesis. The aim of this study was to analyze the somatic embryogenesis process in oil palm (E. guineensis Jacq.) with amino acids and low concentrations of auxins. The Tenera hybrid was analyzed by cytochemical and ultrastructural methods and was used to regenerate oil palm plants. First, calli were induced in MS culture media supplemented with 2,4-D and picloram. Two types of calli were obtained, characterized by beige or translucent color. Beige calli had embryogenic characteristics, such as large nuclei with prominent nucleoli, and they were multiplied for 8 months in MM culture (half strength MS, 1 mg L−1 2,4-D, 2 mg L−1 2iP, 1 mg L−1 IBA, 250 mg L−1 citric acid, 10 mg L−1 cysteine, 100 mg L−1 inositol, 1 mg L−1 thiamine, 1 mg L−1 pyridoxine, 1 mg L−1 nicotinic acid, 1 mg L−1 glycine, 200 mg L−1 malt extract, and 100 mg L−1 casein hydrolysate). After multiplication, the MCB culture medium (half strength MS, supplemented with 0.25 mg L−1 NAA, 2 mg L−1 BAP, MM vitamins and 200 mg L−1 malt extract, and 100 mg L−1 casein hydrolysate) was the most efficient for embryo formation, showing meristematic centers with totipotent cells in histochemical analyses. The somatic embryos were developed and germinated in MG medium (half strength MS, 0.45 mg L−1 IAA, 0.25 mg L−1 BAP, and MM vitamins), transplanted into polyethylene tubes containing pine bark substrates, and acclimatized in a greenhouse, achieving a 97% survival rate. The use of picloram for callus induction and somatic embryogenesis is advantageous and multiplication in MM medium is an important step for increasing cell mass. The calli with light beige color and nodular structures have meristematic cells with dense cytoplasm and totipotential features that later give rise to protoderm, procambium, and ground meristem during the globular, cordiform, and torpedo embryogenesis phases. In MCB medium, the concentration of vitamins and amino acids are crucial for somatic embryogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberlenc-Bertossi F, Chabrillange N, Duval Y, Tregear J (2008) Contrasting globulin and cysteine proteinase gene expression patterns reveal fundamental developmental differences between zygotic and somatic embryos of oil palm. Tree Physiol 28:1157–1167
Ahn IP, Kim S, Lee YH (2005) Vitamin B1 functions as an activator of plant disease resistance. Plant Physiol 138:1505–1515. doi:10.1104/pp.104.058693
Alberts B. (1998). The cell as a collection overview of protein machines: preparing the next generation of molecular biologists. Cell. 92:291-294. Doi: org/10.1016/S0092-8674(00)80922-8
Ammirato PV (1983) Embryogenesis. In: Evans DA, Sharp WR, Ammirato PV, Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of plant cell culture. Mac Millan, New York, pp 82–123
da Ângelo CS, Steinmacher DA, Lopes R, da Cunha RNV, Guerra MP (2013) Histological analysis and transcription profiles somatic embryogenesis in interspecific hybrids of Elaeis guineenses x Elaeis oleifera. Agric Sci 4:1–11. doi:10.4236/as.2013.411A001
da Angelo PCS, Lopes SR, Moraes LAC, da Cunha RNV (2009) Embryogenic calli induced in interspecific (Elaeis guineensis x E. oleifera) hybrid zygotic embryos. Crop Breed Appl Biotechnol 9:274–277. doi: org/10.4236/as.2013.411A001
Armstrong CL, Phillips RL (1988) Genetic and cytogenetic variation in plants regenerated from organogenic and friable, embryogenic tissue cultures of maize. Crop Sci 28:363–369. doi:10.2135/cropsci1988.0011183X002800020038x
Asad S, Arshad M, Mansoor S, Zafar Y (2009) Effect of various amino acids on shoot regeneration of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.). Afr J Biotechnol 8:1214–1218. doi: 10.5897/AJB
Aslam J, Khan SA, Cheruth AJ, Mujiba SMP, Srivastava PS (2011) Somatic embryogenesis, scanning electron microscopy, histology and biochemical analysis at different developing stages of embryogenesis in six date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) cultivars. Saudi J Biol Sci 18:369–380. doi:10.1016/j.sjbs.2011.06.002
Bairu MW, Aremu AO, Van Staden J (2011) Somaclonal variation in plants: causes and detection methods. Plant Growth Regul 63:147–173. doi:10.1007/s10725-010-9554-x
Balzon TA, Luis ZG, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2013) New approaches to improvethe efficiency of somatic embryogenesis in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) from mature zygotic embryos. In vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 49:41–50. doi:10.1007/s11627-012-9479-3
Bar OAE, Dawayat MME (2014) Histological changes on regeneration in vitro culture of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera) leaf explants. Aust J Crop Sci 8:848–855. doi:10.21475/ajcs.2016.10.12
Benelli C, Germana MA, Camino T, Beghe D, Fabbri A (2010) Morphological and anatomical observations of abnormal somatic embryos from anther cultures of Citrus reticulata. Biol Plant 54:224–230. doi:10.1007/s10535-010-0040-0
de Boari A J (2008) Estudos realizados sobre o amarelecimento fatal do dendezeiro (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). Belém: EMBRAPA Amazônia Oriental.59 p. (Documentos, 348)
Bossola JJ, Russell LD (1998) Electron microscopy, 2nd. edn. Jones and Bartlett, Boston, p 670
Boubakri H, Gargouri M, Mliki A, Brini F, Chong J, Jbara M (2016) Vitamins for enhancing plant resistance. Planta 244:529–543. doi:10.1007/s00425-016-2552-0
Brown DCW, Atanassov A (1985) Role of genetic background in somatic embryogenesis in Medicago. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 4:111–122. doi:10.1007/BF00042269
de Carvalho MA, Paiva R, Alves E, Nogueira RC, Stein VC, Castro EM (2013) Morphogenetic potential of native passion fruit (Passiflora gibertii N. E. Brown.) calli. Braz J Bot 36:141–151. doi:10.1007/s40415-013-0015-4
Chanprasert W, Myint T, Srikul S, Wongsri O (2012) Effects of neonicotinoid and method of breaking dormancy on seed germination and seedling vigour of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) J. Oil Palm Res 24:1227–1234
Corley RHV, Tinker PB (2003) The oil palm. Wiley, Oxford. doi:10.1002/9780470750971
Duval Y, Durand-Gasselin T, Konan KC (1988) In vitro vegetative propagation of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) Oleagineux 43:145–147
Feher A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 74:201–228. doi:10.1023/A:1024033216561
Filonova LH, Bozhkov PV, Brukhin VB, Daniel G, Zhivotovsky B, Von Arnold S (2000) Two waves of programmed cell death occur during formation and development of somatic embryos in the gymnosperm Norway spruce. J Cell Sci 113:4399–4411
Gomes HT, Bartos PMC, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2015) In vitro cell. Dev.Biol.-Plant 51:111. doi:10.1007/s11627-015-9669-x
Gomes HT, Bartos PMC, Silva CO, do Amaral LIV, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2014) Comparative biochemical profiling during the stages of acquisition and development of somatic embryogenesis in African oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) Plant Growth Regul 74:199. doi:10.1007/s10725-014-9901-4
Guerra PG, Torres AC, Teixeira JB (1999) Embriogênese somática e sementes sintéticas. In: Torres AC, Caldas LS, Buso IA (Ed.). Cultura de tecidos e transformação genética de plantas. Braília: EMBRAPA-CNPH 2:533–568
Halperin W (1995) In vitro embryogenesis: some historial issues and unresolved problems. In: In vitro embryogenesis in plants (Thorpe, T.A., ed.): 1–16, Kluwer Academic Publishers
Hanson AD, Gregory JF (2011) Folate biosynthesis, turnover, and transport in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 62:105–125. doi:10.1146/annurev-arplant-042110-103819
Havaux M, Ksas B, Szewczyk A, Rumeau D, Franck F, Caffarri S, Triantaphylides C (2009) Vitamin B6 deficient plants display increased sensitivity to high light and photooxidative stress. BMC Plant Biol 9:130. doi:10.1186/1471-2229- 9-130
Jayanthi M, Susanthi B, Mohan NMM, Manda PK (2015) In vitro somatic embryogenesis and plantlet regeneration from immature male inflorescence of adult Dura and Tenera palms of Elaeis guineensis (Jacq.) SpringerPlus 4:256. doi:10.1186/s40064-015-1025-4
Jiménez VM (2005) Involvement of plant hormones and plant growth regulators on in vitro somatic embryogenesis. J Plant Growth Reg 47:91–110. doi:10.1007/s10725-005-3478-x
Jouannic S, Lartaud M, Herve J, Collin M, Orieux Y, Verdeil J-L, Tregear JW (2011) The shoot apical meristem of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis; Arecaceae): developmental progression and dynamics. Ann Bot 108:1477–1487. doi:10.1093/aob/mcr019
Konan EE, Durand-Gasselin T, Kouadio JY, Flori A, Riva A (2006) A modeling approach of the in vitro conversion of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis) somatic embryos. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 84:99–112. doi:10.1007/s11240-005-9010-1
Lam E, Fukuda H, Greenberg J (2000) Programmed cell death of tracheary elements as a paradigm in plants. Plant Mol Biol 44:245–253. doi:10.1023/A:1026532223173
Luis ZG, Bezerra KMG, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2010) Adaptability and leaf anatomical features in oil palm seedlings produced by embryo rescue and pre-germinated seeds. Braz J Plant Physiol. 22:209-215. Doi: org/10.1590/s1677-04202010000300008
MAPA. Anuário Estatístico de Agroenergia 2014; Statistical Yearbook of Agroenergy 2014
Martine BM, Laurent KK, Pierre BJ, Eugene KK, Hilaire KT, Justin KY (2009) Effect of storage and heat treatments on the germination of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) seed. Afr JAgric Res 4:931–937. doi:10.1590/S2317-15372013000300004
Matsui A, Yin Y, Yamanaka K, Iwasaki M, Ashihara H (2007) Metabolic fate of nicotinamide in higher plants. Physiol Plant 131:191–200. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.2007.00959.x
Mgbeze GC, Iserhienrhien A (2014) Somaclonal variation associated with oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) clonal propagation: a review. Afr J Biotechnol 13:989–997. doi:10.5897/AJBX12.011
Miret JA, Munné-Bosch S (2014) Plant amino acid-derived vitamins: biosynthesis and function. Amino Acids 46:809. doi:10.1007/s00726-013-1653-3
Moura EF, Motoike SY (2009) Induction of somatic embryogenesis in immature seeds of guava tree cv. Paluma Rev Bras Frutic 31:507–511. doi:10.1590/S0100-29452009000200027
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3054.1962.tb08052.x
Murphy DJ (2014) The future of oil palm as a major global crop: opportunities and challenges. J Oil Palm Res 26:1–24
Myint T, Chanprasert W, Srikul S (2010) Germination of seed of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) as affected by different mechanical scarification methods. Seed Sci. Technol 38:635–645. doi:10.15258/sst.2010.38.3.11
Pádua MS, Paiva LV, Labory CRG, Alves E, Stein VC (2013) Induction and characterization of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) pro-embryogenic masses. An Acad Bras de Ciênc 85:1545–1556. doi:10.1590/0001-37652013107912
Pádua MS, Paiva LV, da Silva LC, do Livramento KG, Alves E, Castro AHF (2014a) Morphological characteristics and cell viability of coffee plants calli. Ciênc Rural 44:660–665. doi:10.1590/S0103-84782014000400014
Pádua MS, Paiva LV, da Silva LGT, Silva LC, Stein VC (2014b) In vitro development and acclimatization of dendezeiro (Elaeis guineenisis). Rev Árvore 38:1095–1102. doi:10.1590/S0100-67622014000600014
Pedroso CM, Pais MS (1995) Factors controlling somatic embryogenesis. Palnt Cell Tiss Org Cult 43:147–154. doi:10.1007/BF00052170
Perilli S, Moubayidin L, Sabatini S (2010) The molecular basis of cytokinin function. Curr Opin Plant Biol 13:21–26. doi:10.1016/ j.pbi.2009.09.018
Reddy ASN, Poovaiah BW (1987) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 147:885–891
Rival A (2000). Somatic embryogenesis in oil palm. In: somatic embryogenesis in woody plants. Jain, S.M., Guptal, T. K and Newton, R.I (eds). Kluwer Academic Publishers, Netherlands 6:249–290
Rival A, Beule T, Barre B, Hamon S, Duval Y, Noirot M (1997) Comparative flow cytometric estimation of nuclear DNA content in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq) tissue cultures and seed-derived plants. Plant Cell Rep 16:884–887. doi:10.1007/s002990050339
Rohani O, Zamzuri I, Tarmizi AH (2003) Oil palm cloning: MPOB protocol. MPOB Technology No. 26. MPOB, Bangi
Sachetto-Martins G, de Franco LODD (2000) Plant glycine-rich proteins: a family or just proteins with a common motif. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) 21:1–14
Sambanthamurthi R, Singh R, Kadir APG, Abdullah MO, Kushairi A (2009) Opportunities for the oil palm via breeding and biotechnology. In: Mohan Jain S, Priyadarshan PM (eds) Breeding Plantation Tree Crops: Tropical Species. Springer, New York, pp 377–421. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-71201-7
Scherwinski-Pereira JE, da Guedes RS, Fermino PCP Jr, Silva TL, Costa FHS (2010) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in oil palm using the thin cell layer technique. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 46:378–385. doi:10.1007/s11627-010-9279-6
Scherwinski-Pereira JE, da Guedes RS, da Silva RA, Fermino PCP Jr, Luis ZG, de Freitas EO (2012) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in açaí palm (Euterpe oleracea). Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 109:501–508. doi:10.1007/s11240-012-0115-z
de Silva RC, Carmo LS, Luis ZG, Silva LP, Scherwinsk-Pereira JE, Mehta A (2014a) Proteomic identification of differentially expressed proteins during the acquisition of somatic embryogenesis in oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) J Proteomics 104:112–127b. doi:10.1016/j.jprot.2014.03.013
de Silva RC, Luis ZG, Scherwinski-Pereira E (2014b) The histodifferentiation events involved during the acquisition and development of somatic embryogenesis in oil palm (Elaeis guineenses Jacq.) Plant Growth Regulation 72:67–80a. doi:10.1007/s10725-013-9837-0
de Silva RC, Luis ZG, Scherwinski-Pereira JE (2012) Differential responses to somatic embryogenesis of different genotypes of Brazilian oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 111:59–67. doi:10.1007/s11240-012-0170-5
Sogeke AK (1998) Stages in the vegetative propagation of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) through tissue culture. J Oil Palm Res 10:1–9
Steiner N, do Vieira FN, Maldonado S, Guerra MP (2005) Effect of charcoal source on morphology and histodiffentiation of Araucaria angustifolia embryogenic cultures. Braz Arch Biol Technol 48:895–903. doi:10.1590/S1516-89132005000800005
Steinmacher DA, Clement CR, Guerra MP (2007) Somatic embryogenesis from immature peach palm inflorescence explants: towards development of an efficient protocol. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 89:15–22. doi:10.1007/s11240-007-9207-6
Steinmacher DA, Guerra MP, Saaresurminsk K, Lieberei RA (2011) A temporary immersion system improves in vitro regeneration of peach palm through secondary somatic embryogenesis. Ann Bot 108:1463–1475. doi:10.1093/aob/mcr019
Sumaryono RI, Kasi PD, Ginting G (2008) Growth and differentiation of embryogenic callus and somatic embryos of oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) in temporary immersion system. Indones J Agric 1:109–114
Teixeira JB, Sondahl MR, Kirby EG (1993) Somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of oil palm. Plant Cell Tissue Org Cult 34:227–233. doi:10.1007/BF00029711
Thuzar M, Vanavichit A, Tragoonrung S, Jantasurivarat C (2011) Efficient and rapid plant regeneration of oil palm zygotic embryos cv. ‘Tenera’ through somatic embryogenesis. Acta Physiol Plant 33:123–128. doi:10.1007/s11738-010-0526-6
Verdeil J-L, Alemanno L, Niemenak N, Tranbarger TJ (2007) Pluripotent versus totipotent plant stem cells: dependence versus autonomy? Trends Plant Sci 12:245–252. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2007.04.002
Zouine J, Hadrami IEI (2007) Effect of 2, 4-D, glutamine and BAP on embryogenic suspension culture of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Sci Hortic 112:221–226. doi:10.1016/j.scienta.2006.12.041
Acknowledgements
Our thanks to the Laboratory of Electron Microscopy and Ultrastructural Analysis, the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), the Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG), and the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pádua, M.S., Santos, R.S., Labory, C.R.G. et al. Histodifferentiation of oil palm somatic embryo development at low auxin concentration. Protoplasma 255, 285–295 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1143-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-017-1143-7