Abstract
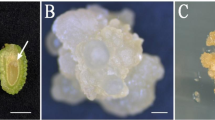
Immature zygotic embryos at different developmental stages were used for callus induction and regeneration studies. Immature embryos excised from fruits 77, 91, 100, 114, 128, 140 and 193 days after pollination and mature embryos were cultured on modified Y3 medium containing 500 mgl−1 cysteine, 0.5% (w/v) PVP-40, 500 μM 2,4-d and 0.3% (w/v) charcoal. Compact embryogenic tissue began differentiating directly from embryo explants after 2 weeks of culture. The percentage of embryos forming compact embryogenic tissue ranged from 28.6% for 91-day-old embryos to 0% for 140-day-old and older embryos. Friable embryogenic tissue was observed in callus cultures derived from 100-day-old embryos. Although both compact and friable embryogenic tissues were successfully isolated, normal embryo and plantlet development was observed only from friable embryogenic tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
- 2,4-d :
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- NAA:
-
naphthaleneacetic acid
- PVP:
-
polyvinylpyrollidone
References
Ahee J, Arthuis P, Cas G, Duval Y Guenin G, Janower J, Hanower P, Lievoux D, Lioret C, Malaurie B, Pannetier C, Raillot D, Varechon C & Zuckerman L (1981) La multiplication végétative in vitro du palmier à huile per embryogénèse somatique. Oléagineaux 36: 113–115
Ammar S & Benbadis A (1977) Multiplication végétative du palmierdattier (Phoenix dactylifera L.) par la culture de tissus de jeunes plantes issues de semis. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris 284: 1789–1792
Armstrong CL & Green CE (1985) Establishment and maintenance of friable, embryogenic maize callus and the involvement of l-proline. Planta 164: 207–214
Eeuwens CJ (1976) Mineral requirements for growth and callus inhibition of tissue explants excised from mature coconut palms (Cocos nucifera L.) and culture in vitro. Physiol. Plant. 36: 23–28
Eeuwens CJ (1978) Effect of organic nutrients and hormones on growth and development of tissue explants from coconut (Cocos nucifera L.) and date (Phoenix dactylifera L.) palms cultured in vitro. Physiol. Plant. 42: 173–178
Eeuwens CJ & Blake J (1977) Culture of coconut and date palm tissue with a view to vegetative propagation. Acta Hort. 78: 277–286
Green CE (1982) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from the friable callus of Zea mays In: Fujiwara A (Ed) Plant Tissue Culture (pp 107–108). Maruzen Co., Tokyo
Green CE & Phillips RL (1975) Plant regeneration from tissue cultures of maize. Crop Sci. 15: 417–421
Guerra PM & Handro W (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in embryo cultures of Euterpe edulis Mart. (Palmae). Plant Cell Rep. 7: 550–552
Hanower J & Pannetier C (1982) In vitro vegetative propagation of the oil palm (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.). In: Fujiwara A (Ed) Plant Tissue Culture (pp 745–746). Maruzen Co., Tokyo
Jones L H (1974) Propagation of clonal oil palms by tissue culture. Oil Palm News 17: 1–8
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Nwankwo BA & Krikorian AD (1983) Morphogenetic potential of embryo and seedling-derived callus of Elaeis guineensis Jacq. var. Pisifera Becc. Ann. Bot. 51: 65–76
Pannetier C, Arthuis P & Lievoux D (1981) Néoformatin de jeunes plantes d'Elaeis guineensis à partir de cals primaires obtenus sur fragments foliaries cultivés in vitro. Oléagineux 36: 119–120
Prioli L & Söndahl MR (1989) Plant regeneration and recovery of fertile plants from protoplasts of maize (Zea mays L.). BioTechnology 7: 589–594
Rabechault H & Martin JP (1976) Multiplication végétative du palmier à huile (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) à l'aide de culture de tissus foliaires. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris 283: 1735–1737
Rabechault H, Ahee J & Guenin G (1970) Colonies cellulaires et formes embryoides obentues in vitro à partir de cultures d'embryons de Palmier à huile (Elaeis guineensis Jacq. var. dura Becc.). C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris 270: 3067–3070
Rabechault H, Martin JP Cas S (1972) Recherches sur la culture de palmier à huile (Elaeis guineensis Jacq.) Oléagineux 27: 531–534
Reuveni O & Lilien-Kipnis H (1974) Studies on the in vitro culture of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) Pamphlet No. 145, Volcani Inst. Agr. Res. Israel
Reynolds JF & Murashige T (1979) Asexual embryogenesis in callus cultures of palms. In Vitro 5: 383–387
Sharp WR, Söndahl MR, Caldas LS & Maraffa SB (1980) The physiology of in vitro a sexual embryogenesis. Hort. Rev. 2: 268–310
Shillito RD, Carswell GK, Johnson CM, Dimaio JJ & Harms CT (1989) Regeneration of fertile plants from protoplasts of elite inbred maize. BioTechnology 7: 581–588
Singer SR (1986) Analyzing growth in cell cultures. I. Calculating growth rates. Can. J. Bot. 64: 233–241
Smith WK & Thomas JA (1973) The isolation and in vitro cultivation of cells of Elaeis guineensis. Oléagineux 28: 123–127
Söndahl MR, Spahlinger DA & Sharp WR (1979) A histological study of high frequency and low frequency induction of somatic embryos in cultured leaf explants of Coffea arabica L. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 94: 101–108
Street HE (1979) Embryogenesis and chemically induced organogenesis. In: Sharp WR, Jansen PO, Paddock EF & Raghavan V (Eds) Plant Cell and Tissue Culture. Principles and Applications (pp 123–153). Ohio State University Press. Columbus
Tisserat B (1979) Propagation of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.) J. Exp. Bot. 30: 1275–1283
Turnham J & Northcote DH (1982) The use of acetyl-CoA carboxylase activity and changes in wall composition as measures of embryogenesis in tissue cultures of oil palm (Elaeis guineenis). Biochem. J. 208: 323–332
Ziv M & Halevy AH (1983) Control of oxidative browning and in vitro propagation of Strelitzia reginae. HortScience 18: 434–436
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Teixeira, J.B., Söndahl, M.R. & Kirby, E.G. Somatic embryogenesis from immature zygotic embryos of oil palm. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 34, 227–233 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029711
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029711