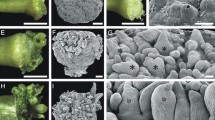
Abstract
The integration of cellular and molecular data is essential for understanding the mechanisms involved in the acquisition of competence by plant somatic cells and the cytological changes that underlie this process. In the present study, we investigated the dynamics and fate of Passiflora edulis Sims cotyledon explants that were committed to somatic embryogenesis by characterizing the associated ultrastructural events and analysing the expression of a putative P. edulis ortholog of the Somatic Embryogenesis Receptor-like Kinase (SERK) gene. Embryogenic calli were obtained from zygotic embryo explants cultured on Murashige and Skoog medium supplemented with 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 6-benzyladenine. Callus formation was initiated by the division of cells derived from the protodermal and subprotodermal cells on the abaxial side of the cotyledons. The isodiametric protodermal cells of the cotyledon explants adopted a columnar shape and became meristematic at the onset of PeSERK expression, which was not initially detected in explant cells. Therefore, we propose that these changes represent the first observable steps towards the acquisition of a competent state within this regeneration system. PeSERK expression was limited to the early stages of somatic embryogenesis; the expression of this gene was confined to proembryogenic zones and was absent in the embryos after the globular stage. Our data also demonstrated that the dynamics of the mobilization of reserve compounds correlated with the differentiation of the embryogenic callus.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SE:
-
Somatic embryogenesis
References
Albrecht C, Russinova E, Hecht V, Baaijens E, De Vries S (2005) The Arabidopsis thaliana SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASES1 and 2 control male sporogenesis. Plant Cell 17:3337–3349
Almeida M, Almeida CV, Graner EM, Brondani GE, Abreu-Tarazi MF (2012) Pre-procambial cells are niches for pluripotent and totipotent stem-like cells for organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in the peach palm: a histological study. Plant Cell Rep 31:1495–1515
Anthony P, Otoni WC, Power JB, Lowe KC, Davey MR (1999) Protoplast isolation, culture, and plant regeneration from Passiflora. In: Hall RD (ed) Plant cell culture protocols. Humana Press, Wageningen, pp 169–181
Barciela J, Vieitez AM (1993) Anatomical sequence and morphometric analysis during somatic embryogenesis on cultured cotyledon explants of Camellia japonica L. Ann Bot 71:395–404
Baudino S, Hansen S, Brettshneider R, Hecht VFG, Dresselhaus T, Lors H, Dumas C, Rogowsky PM (2001) Molecular characterization of two novel maiz LRR receptor-like kinase, which belong to the SERK gene family. Planta 213:1–10
Bhojwani SS, Dantu PK (2013) Somatic embryogenesis. Plant tissue culture: an introductory text. Springer, New Delhi, pp 75–92
Branca C, Torelli A, Fermi P, Altamura MM, Bassi M (1994) Early phases in in vitro culture of tomato cotyledons: starch accumulation and protein pattern in relation to the hormonal treatment. Protoplasma 182:59–64
Buckeridge MS, Aidar MPM, Santos HP, Tiné MAS (2004) Acúmulo de reservas. In: Ferreira AG, Borghetti F (eds) Germinação: do básico ao aplicado, 1st edn. ARTMED, Porto Alegre, pp 31–50
Cangahuala-Inocente GC, Steiner N, Santos M, Guerra MP (2004) Morphological analysis and histochemistry of Feijoa sellowiana somatic embryogenesis. Protoplasma 224:33–40
Cangahuala-Inocente GC, Silveira V, Caprestano CA, Floh EIS, Guerra MP (2014) Dynamics of physiological and biochemical changes during somatic embryogenesis of Acca sellowiana. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Plant 50:166–175
Canhoto JM, Cruz GS (1996) Histodifferentiation of somatic embryos in cotyledons of pineapple guava (Feijoa sellowiana Berg.). Protoplasma 19:34–45
Canhoto JM, Mesquita JF, Cruz GS (1996) Ultrastructural changes in cotyledons of pineapple guava (Myrtaceae) during somatic embryogenesis. Ann Bot 78:513–521
Chen X, Zuo S, Schwessinger B, Chern M, Canlas PE, Ruan D, Zhou X, Wang J, Daudi A, Petzold CJ, Heazlewood JL, Ronald PC (2014) An XA21-associated kinase (OsSERK2) regulates immunity mediated by the XA21 and XA3 immune receptors. Mol Plant 7:874–892
Corner EJH (1976) The seeds of dicotyledons, vol I. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Cutri L, Dornelas MC (2012) PASSIOMA: exploring expressed sequence tags during flower development in Passiflora spp. Comp Funct Genom 2012:510549
De Fillipis LF (2014) Crop improvement through tissue culture. In: Ahmad P, Wani MR, Azooz MM, Tran LSP (eds) Improvement of crops in the era of climate changes, vol 1. Springer, New York, pp 289–346
Dornelas MC, Van Lammeren AA, Kreis M (2000) Arabidopsis thaliana SHAGGY-related protein kinases (AtSK11 and 12) function in perianth and gynoecium development. Plant J 21:419–429
Elhiti M, Stasolla C (2011) The use of zygotic embryos as explants for in vitro propagation: an overview. In: Thorpe TA, Yeung EC (eds) Plant embryo culture: methods and protocols, vol 710. Humana Press, New York, pp 229–255
Fehér A (2005) Why somatic plant cells start to form embryos? In: Mujib A, Samaj J (eds) Somatic embryogenesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 85–101
Fehér A (2008) The initiation phase of somatic embryogenesis: what we know and what we don’t. Acta Biol Szeged 52:53–56
Fehér A (2015) Somatic embryogenesis—stress-induced remodeling of plant cell fate. Biochim Biophys Acta 1849:385–402
Fehér A, Pasternak TP, Dudits D (2003) Transition of somatic plant cells to an embryogenic state. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 74:201–228
Friml J (2003) Auxin transport—shaping the plant. Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:7–12
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima K (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Gordon SP, Heisler MG, Reddy GV, Ohno C, Das P, Meyerowitz EM (2007) Pattern formation during de novo assembly of the Arabidopsis shoot meristem. Development 134:3539–3548
Graham IA (2008) Seed storage oil mobilization. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:115–142
Hecht V, Vielle-Calzada JP, Hartog MV, Schmidt ED, Boutilier K, Grossniklaus U, de Vries SC (2001) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR KINASE 1 gene is expressed in developing ovules and embryos and enhances embryogenic competence in culture. Plant Physiol 127:803–816
Hu H, Xiong L, Yang Y (2005) Rice SERK1 gene positively regulates somatic embryogenesis of cultured cell and host defense response against fungal infection. Planta 222:107–117
Jamsheed S, Rasool S, Koul S, Azooz MM, Ahmad P (2013) Crop improvement through plant tissue culture. In: Hakeem KR, Ahmad P, Ozturk M (eds) Crop improvement: new approaches and modern techniques. Springer, New York, pp 123–148
Karami O, Aghavaisi B, Pour AM (2009) Molecular aspects of somatic-to-embryogenic transition in plants. J Chem Biol 2:177–190
Karlova R, Boeren S, Russinova E, Aker J, Vervoort J, de Vries S (2006) The Arabidopsis SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 protein complex includes BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE1. Plant Cell 18:626–638
Karnovsky MJ (1965) A formaldehyde-glutaraldehyde fixative of high osmolality for use in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 27:137–138
Krikorian AD, Simola LK (1999) Totipotency, somatic embryogenesis, and Harry Waris (1893-1973). Physiol Plant 105:348–355
Kurczyńska EU, Gaj MD, Ujczak A, Mazur E (2007) Histological analysis of direct somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. Planta 226:619–628
Kurczyńska EU, Potocka I, Dobrowolska I, Kulinska-Lukaszek K, Sala K, Wrobel J (2012) Cellular markers for somatic embryogenesis. In: Sato K-I (ed) Embryogenesis. InTech, Rijeka, pp 307–332
Kwaaitaal MACJ, de Vries SC (2007) The SERK1 gene is expressed in procambium and immature vascular cells. J Exp Bot 58:2887–2896
Lin Y, Lai Z (2013) Comparative analysis reveals dynamic changes in miRNAs and their targets and expression during somatic embryogenesis in Longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.). PLoS ONE 8:e60337
Ma J, He Y, Hu Z, Xu W, Xia J, Guo C, Lin S, Cao L, Chen C, Wu C, Zhang J (2012) Characterization and expression analysis of AcSERK2, a somatic embryogenesis and stress resistance related gene in pineapple. Gene 500:115–123
Ma J, He Y, Hu Z, Xu W, Xia J, Guo C, Lin S, Chen C, Wu C, Zhang J (2014) Characterization of the third SERK gene in pineapple (Ananas comosus) and analysis of its expression and autophosphorylation activity in vitro. Genet Mol Biol 37:530–539
Mahdavi-Darvari F, Noor NM, Ismanizan I (2015) Epigenetic regulation and gene markers as signals of early somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:407–422
Mansfield G, Briarty LG (1996) The dynamics of seedling and cotyledon cell development in Arabidopsis thaliana during reserve mobilization. Int J Plant Sci 157:280–295
Martin AB, Cuadrado Y, Guerra H, Gallego P, Hita O, Martin L, Dorado A, Villalobos N (2000) Differences in the contents of total sugars, starch and sucrose in embryogenic and nonembryogenic calli from Medicago arborea L. Plant Sci 154:143–151
Moura EF, Ventrella MC, Motoike SY, Sá Júnior AQ, Carvalho M, Manfio CE (2008) Histological study of somatic embryogenesis induction on zygotic embryos of macaw palm (Acrocomia aculeata (Jacq.) Lodd. ex Martius). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 95:175–184
Moura EF, Ventrella MC, Motoike SY (2010) Anatomy, histochemistry and ultrastructure of seed and somatic embryo of Acrocomia aculeata (Arecaceae). Sci Agric 67:399–407
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Murphy DJ (2001) Biogenesis and functions of lipid bodies in animals, plants and microorganisms. Prog Lipid Res 40:325–438
Namasivayam P (2007) Acquisition of embryogenic competence during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 90:1–8
Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Rose RJ (2003) Auxin up-regulates MtSERK1 expression in both Medicago truncatula root-forming and embryogenic cultures. Plant Physiol 133:218–230
Nolan KE, Kurdyukov S, Rose RJ (2009) Expression of the SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE1 (SERK1) gene is associated with developmental change in the life cycle of the model legume Medicago truncatula. J Exp Bot 60:1759–1771
O’Brien TP, McCully ME (1981) The study of plant structure principles and selected methods. Termarcarphi Pty, Melbourne
Otoni WC, Casali VWD, Power JB, Davey MR (1996) Particle bombardment-mediated transient expression of GUS in passionfruit (Passiflora giberti N.E. Brown). Rev Ceres 43:329–336 (In Portuguese)
Otoni WC, Paim Pinto DL, Rocha DI, Vieira LM, Dias LLC, Silva ML, Silva CV, Lani ERG, Silva LC, Tanaka FAO (2013) Organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis in passionfruit (Passiflora sps.). In: Aslam J, Srivastava OS, Sharma MP (eds) Somatic embryogenesis and gene expression. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 1–17
Paim Pinto DL, Almeida AMR, Rêgo MM, Silva ML, Oliveira EJ, Otoni WC (2011) Somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos of commercial passionfruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) genotypes. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 107:521–530
Pasternak TP, Ötvös K, Domoki M, Fehér A (2007) Linked activation of cell division and oxidative stress defense in alfalfa leaf protoplast-derived cells is dependent on exogenous auxin. Plant Growth Reg 51:109–117
Pérez-Nuñez MT, Souza R, Sáenz L, Chan JL, Zúñiga-Aguilar JJ, Oropeza C (2009) Detection of a SERK-like gene in coconut and analysis of its expression during the formation of embryogenic callus and somatic embryos. Plant Cell Rep 28:11–19
Pinto G, Silva S, Araújo C, Neves L, Santos C (2010) Histocytological changes and reserves accumulation during somatic embryogenesis in Eucalyptus globulus. Trees 24:763–769
Quiroz-Figueroa FR, Fuentes-Cerda CFJ, Rojas-Herrera R, Loyola-Vargas VM (2002) Histological studies on the developmental stages and differentiation of two different somatic embryogenesis systems of Coffea arabica. Plant Cell Rep 20:1141–1149
Quiroz-Figueroa FR, Rojas-Herrera R, Galaz-Avalos RM, Loyola-Vargas VM (2006) Embryo production through somatic embryogenesis can be used to study cell differentiation in plants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 86:285–301
Reis LB, Silva ML, Lima ABP, Oliveira MLP, Paim-Pinto DL, Lani ERG, Otoni WC (2007) Agrobacterium rhizogenes-mediated transformation of passionfruit species: Passiflora cincinnata and P. edulis f. flavicarpa. Acta Horticult 738:425–431
Reynolds ES (1963) The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17:208
Rocha DI, Dornelas MC (2013) Molecular overview on plant somatic embryogenesis. CAB Rev 8:1–17
Rocha DI, Vieira LM, Tanaka FA, Silva LC, Otoni WC (2012) Somatic embryogenesis of a wild passion fruit species Passiflora cincinnata Masters: histocytological and histochemical evidences. Protoplasma 249:747–758
Rocha DI, Monte-Bello CC, Dornelas MC (2015) Alternative induction of de novo shoot organogenesis or somatic embryogenesis from in vitro cultures of mature zygotic embryos of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis Sims) is modulated by the ratio between auxin and cytokinin in the medium. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:1087–1098
Rodriguez APM, Wetzstein HY (1998) A morphological and histological comparison of the initiation and development of pecan (Carya illinoinensis) somatic embryogenesis cultures induced with naphthaleneacetic acid or 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. Protoplasma 204:71–83
Rosa YBCJ, Monte Bello CC, Dornelas MC (2015) Species-dependent divergent responses to in vitro somatic embryo induction in Passiflora spp. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 120:69–77
Salaj J, von Recklinghausen I, Hecht V, de Vries S, Schel J, van Lammeren A (2008) AtSERK1 expression precedes and coincides with early somatic embryogenesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol Biochem 46:709–714
Salvo SAGD, Hirsch CN, Buell CR, Kaeppler SM, Kaeppler HF (2014) Whole transcriptome profiling of maize during early somatic embryogenesis reveals altered expression of stress factors and embryogenesis-related genes. PLoS ONE 9:e111407
Santa-Catarina C, Hanai LR, Dornelas MC, Viana AM, Floh EIS (2004) SERK gene homolog expression, polyamines and amino acids associated with somatic embryogenic competence of Ocotea catharinensis Mez. (Lauraceae). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 79:53–61
Santos MO, Romano E, Yotoko KSC, Tinoco MLP, Dias BBA, Aragão FJL (2005) Characterisation of the cacao somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase (SERK) gene expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Sci 168:723–729
Savona M, Mattioli R, Nigro S, Falasca G, Della Rovere F, Costantino P, De Vries S, Ruffoni B, Trovato M, Altamura MM (2012) Two SERK genes are markers of pluripotency in Cyclamen persicum Mill. J Exp Bot 63:471–488
Schellenbaum P, Jacques A, Maillot P, Bertsch C, Mazet F, Farine S, Walter B (2008) Characterization of VvSERK1, VvSERK2, VvSERK3 and VvL1L genes and their expression during somatic embryogenesis of grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.). Plant Cell Rep 27:1799–1809
Schmidt EDL, Guzzo F, Toonen MAJ, de Vries SC (1997) A leucine rich repeat containing receptor-like kinase marks somatic plant cells competent to form embryos. Development 124:2049–2062
Sharma SK, Millam S, Hein I, Bryan GJ (2008) Cloning and molecular characterisation of a potato SERK gene transcriptionally induced during initiation of somatic embryogenesis. Planta 228:319–330
Shimada T, Hirabayashi T, Endo T, Fujii H, Kita M, Omura M (2005) Isolation and characterization of the somatic embryogenesis receptor-like kinase gene homologue (CitSERK1) from Citrus unshui Marc. Sci Hortic 103:233–238
Silva ML, Paim Pinto DL, Guerra MP, Floh EIS, Bruckner CH, Otoni WC (2009) A novel regeneration system for wild passion fruit species (Passiflora cincinnata Mast.) based on somatic embryogenesis from mature zygotic embryos. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 99:47–54
Silva AT, Barduche D, Livramento KG, Ligterink W, Paiva LV (2014) Characterization of a putative Serk-Like ortholog in embryogenic cell suspension cultures of Coffea arabica L. Plant Mol Biol Rep 32:176–184
Singla B, Khurana JP, Khurana P (2008) Characterization of three somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase genes from wheat, Triticum aestivum. Plant Cell Rep 27:833–843
Smertenko A, Bozhkov PV (2014) Somatic embryogenesis: life and death processes during apical-basal patterning. J Exp Bot 65:1343–1460
Smith RS (2008) The role of auxin transport in plant patterning mechanisms. PLoS Biol 6:e323
Somleva MN, Schmidt EDL, De Vries SC (2000) Embryogenic cells in Dactylis glomerata L. (Poaceae) explants identified by cell tracking and by SERK expression. Plant Cell Rep 19:718–726
Spurr AR (1969) A low-viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J Ultrastruct Res 26:31–43
Steiner N, Santa-Catarina C, Guerra MP, Cutri L, Dornelas MC, Floh EIS (2012) A gymnosperm homolog of SOMATIC EMBRYOGENESIS RECEPTOR-LIKE KINASE-1 (SERK1) is expressed during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 109:41–50
Steward FC, Mapes MO, Mears K (1958) Growth and organized development of cultured cells. I. growth and division of freely suspended cells. Am J Bot 45:693–703
Talapatra S, Ghoshal N, Raychaudhuri SS (2014) Molecular characterization, modeling and expression analysis of a somatic embryogenesis receptor kinase (SERK) gene in Momordica charantia L. during somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 116:271–283
Thomas C, Meyer D, Himber C, Steinmetz A (2004) Spatial expression of a sunflower SERK gene during induction of somatic embryogenesis and shoot organogenesis. Plant Physiol Biochem 42:35–42
Tozzi HH, Takaki M (2011) Histochemical analysis of seed reserve mobilization in Passiflora edulis Sims fo. flavicarpa O. Deg. (yellow passion fruit) during germination. Braz J Biol 71:701–708
van Meer G, Voelker DR, Feigenson GW (2008) Membrane lipids: where they are and how they behave. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:112–124
Vasil IK (2008) A history of plant biotechnology: from the cell theory of Schleiden and Schwann to biotech crops. Plant Cell Rep 27:1423–1440
Verdeil JL, Hocher V, Huet C, Grosdemange F, Escoute J, Ferrière N, Nicole M (2001) Ultrastructural changes in coconut calli associated with the acquisition of embryogenic competence. Ann Bot 88:9–18
Verdeil JL, Alemanno L, Niemenak N, Trambarger TJ (2007) Pluripotent versus totipotent plant stem cells: dependence versus autonomy? Trends Plant Sci 12:245–252
Vieten A, Sauer M, Brewer PB, Friml J (2007) Molecular and cellular aspects of auxin-transport mediated development. Trends Plant Sci 12:160–168
Wang X, Nolan KE, Irwanto RR, Sheahan MB, Rose RJ (2011) Ontogeny of embryogenic callus in Medicago truncatula: the fate of the pluripotent and totipotent stem cells. Ann Bot 107:599–609
Wu X-M, Kou S-J, Liu Y-L, Fang Y-N, Xu Q, Guo W-W (2015) Genomewide analysis of small RNAs in nonembryogenic and embryogenic tissues of citrus: microRNA- and siRNA-mediated transcript cleavage involved in somatic embryogenesis. Plant Biotechnol J 13:383–394
Yang X, Zhang X (2010) Regulation of somatic embryogenesis in higher plants. Crit Rev Plant Sci 29:36–57
Zienkiewicz A, Jiménez-López JC, Zienkiewicz K, Alché JD, Rodríguez-García MI (2011) Development of the cotyledon cells during olive (Olea europaea L.) in vitro seed germination and seedling growth. Protoplasma 248:751–765
Zimmerman JL (1993) Somatic embryogenesis: a model for early development in higher plants. Plant Cell 5:1411–1423
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Viveiros Flora Brasil Ltda. (Araguari, MG, Brazil) for kindly providing Passiflora edulis seeds. This work was supported by the Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científicoa e Tecnológico (CNPq) (Brazil), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) (Brazil), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG) (Belo Horizonte, MG, Brazil) and Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP) (São Paulo, SP, Brazil).
Author contributions
MCD and WCO designed the research; DIR, LMV and DLPP established the embryogenic cultures; DIR and FAOT performed the light and transmission electron microscopy analyses; DLPP and MCD performed the in situ hybridization analysis; DIR, DLPP, MCD and WCO wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling Editor: Peter Nick
Diego Ismael Rocha and Daniela Lopes Paim Pinto contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rocha, D.I., Pinto, D.L.P., Vieira, L.M. et al. Cellular and molecular changes associated with competence acquisition during passion fruit somatic embryogenesis: ultrastructural characterization and analysis of SERK gene expression. Protoplasma 253, 595–609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0837-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0837-y