Abstract
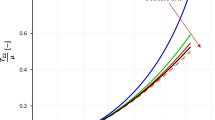
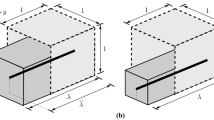
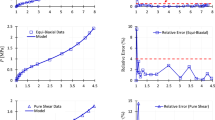
A direct approach is proposed to obtain new multi-axial elastic potentials for incompressible soft solids. Results are presented with novelties in three respects, namely (i) any given benchmark test data for three deformation modes may be exactly fitted, including uniaxial, equi-biaxial, and plane-strain extension; (ii) model parameters of direct physical meanings may be provided to represent both the strain-stiffening effect and failure behavior; and (iii) error estimation may be established for all possible deformation modes. Numerical examples are in good agreement with Treloar’s classic data for rubbers and with extensive data for gellan gels up to failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, L.: On H. Hencky’s approximate strain-energy function for moderate deformations. J. Appl. Mech. 46, 78–82 (1979)
Anand, L.: Moderate deformations in extension-torsion of incompressible isotropic elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 34, 293–304 (1986)
Aron, M.: On certain deformation classes of compressible Hencky materials. Math. Mech. Solids 19, 467–478 (2006)
Arruda, E.M., Boyce, M.C.: A three-dimensional constitutive model for the large stretch behaviour of rubber elastic materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41, 389–412 (1993)
Beatty, M.F.: Topic in finite elasticity: hyperelasticity of rubber, elastomers, and biological tissues-with examples. Appl. Mech. Rev. 40, 1699–1733 (1987)
Beatty, M.F.: An average-stretch full-network model for rubber elasticity. J. Elast. 70, 65–86 (2003)
Beatty, M.F.: On constitutive models for limited elastic, molecular based materials. Math. Mech. Solids 13, 375–387 (2008)
Boyce, M.C.: Direct comparison of the Gent and the Arruda-Boyce constitutive models of rubber elasticity. Rubber Chem. Techn. 69, 781–785 (1996)
Boyce, M.C., Arruda, E.M.: Constitutive models of rubber elasticity: a review. Rubber Chem. Techn. 73, 504–523 (2000)
Bruhns, O.T., Xiao, H., Meyers, A.: Self-consistent Eulerian rate type elastoplasticity models based upon the logarithmic stress rate. Int. J. Plast. 15, 479–520 (1999)
Criscione, J.C., Humphrey, J.D., Douglas, A.S., Hunter, W.C.: An invariant basis for natural strain which yields orthogonal stress response terms in isotropic hyperelasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 48, 2445–2465 (2000)
Diani, J., Gilormini, P.: Combining the logarithmic strain and the full-network model for a better understanding of the hyperelastic behaviour of rubber-like materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids. 53, 2579–2596 (2005)
Drozdov, A.D., Gottlieb, M.: Ogden-type constitutive equations in finite elasticity of elastomers. Acta Mech. 183, 231–252 (2006)
Fitzjerald, S.: A tensorial Hencky measure of strain and strain rate for finite deformation. J. Appl. Phys. 51, 5111–5115 (1980)
Fried, E.: An elementary molecular-statistical basis for the Mooney and Rivlin–Saunders theories of rubber elasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 50, 571–582 (2002)
Gent, A.N.: A new constitutive relation for rubber. Rubber Chem. Techn. 69, 59–61 (1996)
Gent, A.N.: Extensibility of rubber under different types of deformation. J. Rheol. 49, 271–275 (2005)
Gu, Z.X., Yuan, L., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: A multiaxial elastic potential with error-minimizing approximation to rubberlike elasticity. Acta Mech. Sin. 31, 637–646 (2015)
Hencky, H.: Über die Form des Elastizitätsgesetzes bei ideal elastischen Stoffen. Z. Techn. Phys. 9, 215–220; ibid, 457 (1928)
Hill, R.: Constitutive inequalities for simple materials. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 16, 229–242 (1968)
Hill, R.: Constitutive inequalities for isotropic elastic solids under finite strain. Proc. R. Soc. London A 326, 131–147 (1970)
Horgan, C.O., Murphy, J.G.: Limiting chain extensibility constitutive models of Valanis-Landel type. J. Elast. 86, 101–111 (2007)
Horgan, C.O., Murphy, J.G.: A generalization of Hencky’s strain-energy density to model the large deformation of slightly compressible solid rubber. Mech. Mater. 41, 943–950 (2009)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: A molecular-statistical basis for the Gent constitutive model of rubber elasticity. J. Elast. 68, 167–176 (2002)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Finite thermoelasticity with limiting chain extensibility. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 51, 1127–1146 (2003)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Constitutive models for compressible nonlinearly elastic materials with limiting chain extensibility. J. Elast. 77, 123–138 (2004)
Horgan, C.O., Saccomandi, G.: Phenomenological hyperelastic strain-stiffening constitutive models for rubber. Rubber Chem. Techn. 79, 1–18 (2006)
Jin, T.F., Yu, L.D., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: Bounded elastic potentials for rubberlike materials with strain-stiffening effects. ZAMM J. Appl. Math. Mech. 95, 1230–1242 (2015)
Jones, D.F., Treloar, L.R.G.: The properties of rubber in pure homogeneous strain. J. Phys. D 8, 1285–1304 (1975)
Li, H., Zhang, Y.Y., Wang, X.M., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: Obtaining multi-axial elastic potentials for rubber-like materials via an explicit, exact approach based on spline interpolation. Acta Mech. Sol. Sin. 27, 441–453 (2014)
Miehe, C., Göktepe, S., Lulei, F.: A micro-macro approach to rubberlike materials—part I: the non-affine microsphere model of rubber elasticity. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 52, 2617–2660 (2004)
Murphy, J.G.: Some remarks on kinematic modeling of limiting chain extensibility. Math. Mech. Solids 11, 629–641 (2006)
Ogden, R.W.: Large deformation isotropic elasticity-on the correlation of theory and experiment for incompressible rubberlike materials. Proc. R. Soc. London A 326, 565–584 (1972)
Ogden, R.W.: Large deformation isotropic elasticity-on the correlation of theory and experiment for compressible rubber-like materials. Proc. R. Soc. London A 328, 567–583 (1972)
Ogden, R.W.: Volume changes associated with the deformation of rubber-like solids. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 24, 323–338 (1976)
Ogden, R.W., Saccomandi, G., Sgura, I.: On worm-like chain models within the three-dimensional continuum mechanics framework. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. A 462, 749–768 (2006)
Rivlin, R.S.: Large elastic deformations of isotropic materials. IV. Further developments of the general theory. Philos. Trans. Roy. Soc. London A 241, 379–397 (1948)
Tang, J.M., Tung, M.A., Lelievre, J., Zeng, Y.Y.: Stress-strain relationships for gellan gels in tension, compression and Torsion. Int. J. Food Eng. 31, 511–529 (1997)
Treloar, L.R.G.: The Physics of Rubber Elasticity. Oxford University Press, Oxford (1975)
Wang, X.M., Li, H., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: Multiaxial strain energy functions of rubberlike materials: an explicit approach based on polynomial interpolation. Rubber Chem. Technol. 87, 168–183 (2014)
Wu, P.D., van der Giessen, E.: On improved network models for rubber elasticity and their application to orientation hardening in glassy polymers. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 41, 427–456 (1993)
Xiao, H.: Hencky strain and Hencky model: extending history and ongoing tradition. Multidiscip. Model. Mater. Struct. 1, 1–52 (2005)
Xiao, H.: An explicit, direct approach to obtaining multi-axial elastic potentials that exactly match data of four benchmark tests for rubberlike materials-part 1: incompressible deformations. Acta. Mech. 223, 2039–2063 (2012)
Xiao, H.: Elastic potentials with best approximation to rubberlike elasticity. Acta Mech. 226, 331–350 (2015)
Xiao, H., Bruhns, O.T., Meyers, A.: Logarithmic strain, logarithmic spin and logarithmic rate. Acta Mech. 124, 89–105 (1997)
Xiao, H., Bruhns, O.T., Meyers, A.: The choice of objective rates in finite elastoplasticity: general results on the uniqueness of the logarithmic rate. Proc. R. Soc. London A 456, 1865–1882 (2000)
Xiao, H., Bruhns, O.T., Meyers, A.: Explicit dual stress-strain and strain-stress relations of incompressible isotropic hyperelastic solids via deviatoric Hencky strain and Cauchy stress. Acta Mech. 168, 21–33 (2004)
Xiao, H., Bruhns, O.T., Meyers, A.: Elastoplasticity beyond small deformations. Acta Mech. 182, 31–111 (2006)
Xiao, H., Bruhns, O.T., Meyers, A.: Thermodynamic laws and consistent Eulerian formulation of finite elastoplasticity with thermal effects. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 55, 338–365 (2007)
Yeoh, O.H., Fleming, P.D.: A new attempt to reconcile the statistical and phenomenological theories of rubber elasticity. J. Polym. Sci. B 35, 1919–1931 (1997)
Yu, L.D., Jin, T.F., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: A model for rubberlike elasticity up to failure. Acta Mech. 226, 1445–1456 (2015)
Yu, L.D., Jin, T.F., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: Multi-axial strain-stiffening elastic potentials with energy bounds: explicit approach based on uniaxial data. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 36, 883–894 (2015)
Yuan, L., Gu, Z.X., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: New compressible hyperelastic models for rubberlike matereials. Acta Mech. 226, 4059–4072 (2015)
Zhang, Y.Y., Li, H., Wang, X.M., Yin, Z.N., Xiao, H.: Direct determination of multi-axial elastic potentials for incompressible elastomeric solids: an accurate, explicit approach based on rational interpolation. Cont. Mech. Thermodyn. 26, 207–220 (2013)
Zhang, Y.Y., Li, H., Xiao, H.: Further study of rubber-like elasticity: elastic potentials matching biaxial data. Appl. Math. Mech. (English Edition) 35, 13–24 (2014)
Zuniga, A.E.: A non-Gaussian network model for rubber elasticity. Polymer 47, 907–914 (2006)
Zuniga, A.E., Beatty, M.F.: Constitutive equations for amended non-Gaussian network models of rubber elasticity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 40, 2265–2294 (2003)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, J., Ding, XF., Yin, ZN. et al. Large elastic deformations of soft solids up to failure: new hyperelastic models with error estimation. Acta Mech 228, 1165–1175 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1753-8
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00707-016-1753-8