Abstract
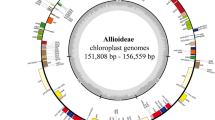
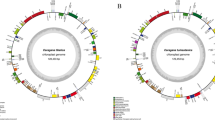
Atalantia plants are small trees in the family Rutaceae that have great potential for use in agriculture, medicine, and carving. However, the phylogenetic relationships of Atalantia species have not been systematically studied due to the lack of available molecular resources and highly variable molecular markers. In this study, the complete chloroplast genomes of four Atalantia species were newly sequenced and characterized. The length of the chloroplast genomes in Atalantia species ranged from 159,557 to 160,341 bp, which was more similar to Fortunella and Citrus species in the Rutaceae. The rpl22 genes were pseudogenized at the SSC/IRa boundary. Certain mechanisms have been evolved to compensate for the pseudogenization of the accD and infA genes in Atalantia chloroplast genomes. Some highly divergent intergenic regions (trnH-GUG–psbA, rps16–trnQ-UUG, trnS-GCU–trnG-UCC, atpF–atpI, petN–psbM, psbM–trnD-GUC, ndhC–trnV-UAC, atpB–rbcL, accD–psaI, and ycf4–cemA) and genes (psbM, trnD-GUC, rpl32, ndhF, and ycf1) were detected, which serve as potential phylogenetic markers. The phylogenetic relationships and divergence times of Atalantia species were explored based on the complete chloroplast genome. Based on the phylogenetic trees, Atalantia species were grouped into two sub-branches. Atalantia monophylla and A. buxifolia were found to be more closely related, whereas A. ceylanica and A. roxburghiana exhibited a closer relationship. The divergence time estimation indicated that the common ancestor of the Atalantia species diverged approximately 14.26 million years ago. These findings will help with the identification, categorization, and utilization of Atalantia species.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
In the GenBank database, the data supporting the findings of this study can be found at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/, under accession numbers NC_065396–NC_065399.
References
Alves MN, Lopes SA, Raiol-Junior LL et al (2021) Resistance to ‘Candidatus Liberibacter asiaticus’, the Huanglongbing Associated Bacterium, in sexually and/or graft-compatible citrus relatives. Frontiers Pl Sci 11:617664. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.617664
Appelhans MS, Keßler PJA, Smets E et al (2012) Age and historical biogeography of the pantropically distributed Spathelioideae (Rutaceae, Sapindales). J Biogeogr 39:1235–1250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2699.2012.02686.x
Bacher M, Brader G, Hofer O, Greger H (1999) Oximes from seeds of Atalantia ceylanica. Phytochemistry 50:991–994. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00638-4
Baskar K, Sudha V, Nattudurai G et al (2018) Larvicidal and repellent activity of the essential oil from Atalantia monophylla on three mosquito vectors of public health importance, with limited impact on non-target zebra fish. Physiol Molec Pl Pathol 101:197–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2017.03.002
Bausher MG, Singh ND, Lee SB et al (2006) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Citrus sinensis (L.) Osbeck var “Ridge Pineapple”: Organization and phylogenetic relationships to other angiosperms. BMC Pl Biol 6:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-6-21
Bayer RJ, Mabberley DJ, Morton C et al (2009) A molecular phylogeny of the orange subfamily (Rutaceae: Aurantioideae) using nine cpDNA sequences. Amer J Bot 96:668–685. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.0800341
Beier S, Thiel T, Münch T et al (2017) MISA-web: a web server for microsatellite prediction. Bioinformatics 33:2583–2585. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx198
Bilder P, Lightle S, Bainbridge G et al (2006) The structure of the carboxyltransferase component of acetyl-CoA carboxylase reveals a zinc-binding motif unique to the bacterial enzyme. Biochemistry 45:1712–1722. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi0520479
Bolger AM, Lohse M, Usadel B (2014) Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30:2114–2120. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btu170
Brown J, Pirrung M, Mccue LA (2017) FQC Dashboard: integrates FastQC results into a web-based, interactive, and extensible FASTQ quality control tool. Bioinformatics 33:3137–3139. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx373
Brudno M, Do CB, Cooper GM et al (2003) LAGAN and Multi-LAGAN: efficient tools for large-scale multiple alignment of genomic DNA. Genome Res 13:721–731. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.926603
Carbonell-Caballero J, Alonso R, Ibañez V et al (2015) A phylogenetic analysis of 34 chloroplast genomes elucidates the relationships between wild and domestic species within the genus Citrus. Molec Biol Evol 32:2015–2035. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msv082
Chat J, Jáuregui B, Petit RJ, Nadot S (2004) Reticulate evolution in kiwifruit (Actinidia, Actinidiaceae) identified by comparing their maternal and paternal phylogenies. Amer J Bot 91:736–747. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.91.5.736
Chen C, Chen H, Zhang Y et al (2020) TBtools: an integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Molec Pl 13:1194–1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
Chukaew A, Ponglimanont C, Karalai C, Tewtrakul S (2008) Potential anti-allergic acridone alkaloids from the roots of Atalantia monophylla. Phytochemistry 69:2616–2620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.08.007
Curk F, Ancillo G, Garcia-Lor A et al (2014) Next generation haplotyping to decipher nuclear genomic interspecific admixture in Citrus species: analysis of chromosome 2. BMC Genet 15:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12863-014-0152-1
Darriba D, Taboada GL, Doallo R, Posada D (2012) JModelTest 2: more models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nature Meth 9:772. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.2109
Das AK, Swamy S (2016) Antioxidant activity and determination of bioactive compounds by GC-MS in fruit methanol extracts—a comparative analysis of three Atalantia species from south India. J Appl Pharm Sci 6:130–134. https://doi.org/10.7324/JAPS.2016.60220
de Araújo EF, de Queiroz LP, Machado MA (2003) What is Citrus? Taxonomic implications from a study of cp-DNA evolution in the tribe Citreae (Rutaceae subfamily Aurantioideae). Organisms Diversity Evol 3:55–62. https://doi.org/10.1078/1439-6092-00058
Dierckxsens N, Mardulyn P, Smits G (2017) NOVOPlasty: de novo assembly of organelle genomes from whole genome data. Nucl Acids Res 45:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw955
Dobrogojski J, Adamiec M, Luciński R (2020) The chloroplast genome: a review National Center for Biotechnology Information. Acta Physiol Pl 42:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11738-020-03089-x
Esser H-J (2021) Taxonomic notes on the Rutaceae of Thailand. Thai Forest Bull 49:27–31. https://doi.org/10.20531/TFB2021.49.1.02
Fernando CD, Soysa P (2014) Total phenolic, flavonoid contents, in-vitro antioxidant activities and hepatoprotective effect of aqueous leaf extract of Atalantia ceylanica. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:395. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-395
Fischer TC, Butzmann R (1998) Citrus meletensis (Rutaceae), a new species from the Pliocene of Valdarno (Italy). Pl Syst Evol 210:51–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00984727
Frazer KA, Pachter L, Poliakov A et al (2004) VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res 32:273–279. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkh458
Green MR, Sambrook J (1972) Agarose gel electrophoresis. Cold Spring Harbor Protoc 124:7–19. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot100404
Gregor HJ (1989) Aspects of the fossil record and phylogeny of the family Rutaceae (Zanthoxyleae, Toddalioideae). Pl Syst Evol 162:251–265. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00936920
Greiner S, Lehwark P, Bock R (2019) OrganellarGenomeDRAW (OGDRAW) version 1.3.1: expanded toolkit for the graphical visualization of organellar genomes. Nucl Acids Res 47:W59–W64. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz238
Grosser JW, Mourao-Fo FAA, Gmitter FG et al (1996) Allotetraploid hybrids between citrus and seven related genera produced by somatic hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 92:577–582. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224561
Guo X, Fang D, Sahu SK et al (2021) Chloranthus genome provides insights into the early diversification of angiosperms. Nat Commun 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26922-4
Guo C, Luo Y, Gao L et al (2022) Phylogenomics and the flowering plant tree of life. J Integr Plant Biol 65:299–323. https://doi.org/10.1111/jipb.13415
Herrero R, Asíns MJ, Carbonell EA, Navarro L (1996) Genetic diversity in the orange subfamily Aurantioideae. I. intraspecies and intragenus genetic variability. Theor Appl Genet 92:599–609. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224564
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 17:754–755. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/17.8.754
Jin JJ, Bin YuW, Yang JB et al (2020) GetOrganelle: a fast and versatile toolkit for accurate de novo assembly of organelle genomes. Genome Biol 21:1–31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-020-02154-5
Katoh K, Standley DM (2013) MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: improvements in performance and usability. Molec Biol Evol 30:772–780. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/mst010
Kearse M, Moir R, Wilson A et al (2012) Geneious basic: an integrated and extendable desktop software platform for the organization and analysis of sequence data. Bioinformatics 28:1647–1649. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts199
Koenen EJM, Clarkson JJ, Pennington TD, Chatrou LW (2015) Recently evolved diversity and convergent radiations of rainforest mahoganies (Meliaceae) shed new light on the origins of rainforest hyperdiversity. New Phytol 207:327–339. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.13490
Konishi T, Shinohara K, Yamada K, Sasaki Y (1996) Acetyl-CoA carboxylase in higher plants: most plants other than gramineae have both the prokaryotic and the eukaryotic forms of this enzyme. Pl Cell Physiol 37:117–122. https://doi.org/10.1093/oxfordjournals.pcp.a028920
Kurtz S, Choudhuri JV, Ohlebusch E et al (2001) REPuter: the manifold applications of repeat analysis on a genomic scale. Nucl Acids Res 29:4633–4642. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/29.22.4633
Lehwark P, Greiner S (2018) GB2sequin—a file converter preparing custom GenBank files for database submission. Genomics 111:759–761. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygeno.2018.05.003
Leister D (2003) Chloroplast research in the genomic age. Trends Genet 19:47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0168-9525(02)00003-3
Li H (2018) Minimap2: pairwise alignment for nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics 34:3094–3100. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty191/4994778
Li D, Xing F (2016) Ethnobotanical study on medicinal plants used by local Hoklos people on Hainan Island, China. J Ethnopharmacol 194:358–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2016.07.050
Li H, Handsaker B, Wysoker A et al (2009) The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics 25:2078–2079. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352
Liu TJ, Zhang CY, Yan HF et al (2016) Complete plastid genome sequence of Primula sinensis (Primulaceae): structure comparison, sequence variation and evidence for accD transfer to nucleus. PeerJ 4:e2101. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.2101
Liu Y, Li D, Zhang Q et al (2017) Rapid radiations of both kiwifruit hybrid lineages and their parents shed light on a two-layer mode of species diversification. New Phytol 215:877–890. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14607
Liu Y, Tahir Ul Qamar M, Feng JW et al (2019) Comparative analysis of miniature inverted-repeat transposable elements (MITEs) and long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons in six Citrus species. BMC Pl Biol 19:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-019-1757-3
Liu X, Chang E, Liu J (2021) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genomes of six white oaks with high ecological amplitude in China. J Forest Res 32:2203–2218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-020-01288-3
Liu Q, Gao Y, Dong W, Zhao L (2023) Plastome evolution and phylogeny of the tribe Ruteae (Rutaceae). Ecol Evol 13:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.9821
Manafzadeh S, Salvo G, Conti E (2014) A tale of migrations from east to west: the Irano-Turanian floristic region as a source of Mediterranean xerophytes. J Biogeogr 41:366–379. https://doi.org/10.1111/jbi.12185
Millen RS, Olmstead RG, Adams KL et al (2001) Many parallel losses of infA from chloroplast DNA during angiosperm evolution with multiple independent transfers to the nucleus. Pl Cell 13:645–658. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.13.3.645
Nagano Y, Mimura T, Kotoda N et al (2018) Phylogenetic relationships of Aurantioideae (Rutaceae) based on RAD-Seq. Tree Genet Genomes 14:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-017-1223-z
Pang X, Almaz B, Qi XJ et al (2020) Bioactivity of essential oil from Atalantia buxifolia leaves and its major sesquiterpenes against three stored-product insects. J Essent Oil-Bearing Pl 23:38–50. https://doi.org/10.1080/0972060X.2020.1729245
Penjor T, Anai T, Nagano Y et al (2010) Phylogenetic relationships of Citrus and its relatives based on rbcL gene sequences. Tree Genet Genomes 6:931–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-010-0302-1
Penjor T, Yamamoto M, Uehara M et al (2013) Phylogenetic relationships of Citrus and Its relatives based on matK gene sequences. PLoS ONE 8:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0062574
Pfeil BE, Crisp MD (2008) The age and biogeography of Citrus and the orange subfamily (Rutaceae: Aurantioideae) in Australasia and New Caledonia. Amer J Bot 95:1621–1631. https://doi.org/10.3732/ajb.0800214
Prasad PRC, Kumari JA (2019) Structure, composition and diversity of trees within the dry evergreen reserve forest of Kondapalli (Eastern Ghats, southern India). Biodivers Res Conserv 54:23–36. https://doi.org/10.2478/biorc-2019-0009
Puttick MN (2019) MCMCtreeR: functions to prepare MCMCtree analyses and visualize posterior ages on trees. Bioinformatics 35:5321–5322. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz554
Qu XJ, Moore MJ, Li DZ, Yi TS (2019) PGA: a software package for rapid, accurate, and flexible batch annotation of plastomes. Pl Meth 15:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13007-019-0435-7
Ranade SA, Nair KN, Srivastava AP, Pushpangadan P (2009) Analysis of diversity amongst widely distributed and endemic Atalantia (family Rutaceae) species from Western Ghats of India. Physiol Molec Biol Pl 15:211–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12298-009-0025-7
Ranwez V, Douzery EJP, Cambon C et al (2018) MACSE v2: toolkit for the alignment of coding sequences accounting for frameshifts and stop codons. Molec Biol Evol 35:2582–2584. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msy159
Rousseau-Gueutin M, Huang X, Higginson E et al (2013) Potential functional replacement of the plastidic acetyl-CoA carboxylase subunit (accD) gene by recent transfers to the nucleus in some angiosperm lineages. Plant Physiol 161:1918–1929. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.214528
Rozas J, Ferrer-Mata A, Sanchez-DelBarrio JC et al (2017) DnaSP 6: DNA sequence polymorphism analysis of large data sets. Mol Biol Evol 34:3299–3302. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msx248
Salvo G, Ho SYW, Rosenbaum G et al (2010) Tracing the temporal and spatial origins of island endemics in the Mediterranean region: a case study from the Citrus family (Ruta L., Rutaceae). Syst Biol 59:705–722. https://doi.org/10.1093/sysbio/syq046
Sasaki Y, Nagano Y (2004) Plant acetyl-CoA carboxylase: structure, biosynthesis, regulation, and gene manipulation for plant breeding. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 68:1175–1184. https://doi.org/10.1271/bbb.68.1175
Sasaki Y, Hakamada K, Suama Y et al (1993) Chloroplast-encoded protein as a subunit of acetyl-CoA carboxylase in pea plant. J Biol Chem 268:25118–25123. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0021-9258(19)74577-3
Sayers EW, Beck J, Bolton EE et al (2021) Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information. Nucleic Acids Res 49:D10–D17. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa892
Schwartz T, Nylinder S, Ramadugu C et al (2015) The origin of oranges: a multi-locus phylogeny of Rutaceae subfamily aurantioideae. Syst Bot 40:1053–1062. https://doi.org/10.1600/036364415X690067
Scora RW, Duesch G, England AB (1969) Essential leaf oils in representatives of the aurantioideae (Rutaceae). Amer J Bot 56:1094–1102. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1537-2197.1969.tb09764.x
Shi C, Hu N, Huang H et al (2012) An improved chloroplast DNA extraction procedure for whole plastid genome sequencing. PLoS ONE 7:e31468. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0031468
Shi M, Guo X, Chen Y et al (2014) Isolation and characterization of 19 polymorphic microsatellite loci for Atalantia buxifolia (Rutaceae), a traditional medicinal plant. Conservation Genet Resources 6:857–859. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12686-014-0224-6
Shi W, Song W, Chen Z et al (2023a) Comparative chloroplast genome analyses of diverse Phoebe (Lauraceae) species endemic to China provide insight into their phylogeographical origin. PeerJ 11:e14573. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.14573
Shi W, Song W, Liu J et al (2023b) Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of Citrus (Rutaceae) species : insights into genomic characterization, phylogenetic relationships, and discrimination of subgenera. Sci Hortic (Amsterdam) 313:111909. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scienta.2023.111909
Shimada H, Sugiura M (1991) Fine structural features of the chloroplast genome: comparison of the sequenced chloroplast genomes. Nucl Acids Res 19:983–995. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/19.5.983
Song W, Chen Z, He L et al (2022a) Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of wax gourd (Benincasa hispida) with three benincaseae species, revealing evolutionary dynamic patterns and phylogenetic implications. Genes (Basel) 13:461. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13030461
Song W, Chen Z, Shi W et al (2022b) Comparative analysis of complete chloroplast genomes of nine species of Litsea (Lauraceae): hypervariable regions, positive selection, and phylogenetic relationships. Genes (Basel) 13:1550. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes13091550
Song W, Ji C, Chen Z et al (2022c) Comparative analysis the complete chloroplast genomes of nine Musa species: genomic features, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic implications. Frontiers Pl Sci 13:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.832884
Soomro N, Mangi JU, Panhwer M et al (2021) Anatomical characteristics of fossil wood collected from the Manchar Formation (Miocene), Thano Bula Khan, Sindh, Pakistan. Ital Bot 11:1–8. https://doi.org/10.3897/ITALIANBOTANIST.11.60344
Su HJ, Hogenhout SA, Al-Sadi AM, Kuo CH (2014) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of omani lime (Citrus aurantiifolia) and comparative analysis within the rosids. PLoS ONE 9:e113049. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0113049
Sun K, Liu QY, Wang A et al (2021) Comparative analysis and phylogenetic implications of plastomes of five genera in subfamily Amyridoideae (Rutaceae). Forests 12:1–14. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12030277
Swingle W, Reece P (1967) The botany of Citrus and its wild relatives. Citrus Ind 1:190–430
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Molec Biol Evol 38:3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Tillich M, Lehwark P, Pellizzer T et al (2017) GeSeq—versatile and accurate annotation of organelle genomes. Nucl Acids Res 45:W6–W11. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx391
Trifinopoulos J, Nguyen LT, von Haeseler A, Minh BQ (2016) W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucl Acids Res 44:W232–W235. https://doi.org/10.1093/NAR/GKW256
Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z et al (2010) KaKs_Calculator 2.0: A toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genom Proteom Bioinform 8:77–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3
Wang X, Xu Y, Zhang S et al (2017) Genomic analyses of primitive, wild and cultivated Citrus provide insights into asexual reproduction. Nat Genet 49:765–772. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3839
Wang T, Kuang RP, Wang XH et al (2021) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Fortunella venosa (Champ. ex benth.) C.C.Huang (Rutaceae): comparative analysis, phylogenetic relationships, and robust support for its status as an independent species. Forests 12:996. https://doi.org/10.3390/f12080996
Wang T, Chen LL, Shu HJ et al (2022) Fortunella venosa (Champ. ex Benth.) C. C. Huang and F. hindsii (Champ. ex Benth.) swingle as independent species: evidence from morphology and molecular systematics and taxonomic revision of Fortunella (Rutaceae). Frontiers Pl Sci 13:867659. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.867659
Wu GA, Terol J, Ibanez V et al (2018) Genomics of the origin and evolution of Citrus. Nature 554:311–316. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25447
Xia X, Yu X, Fu Q et al (2022) Comparison of chloroplast genomes of compound—leaved maples and phylogenetic inference with other Acer species. Tree Genet Genomes 18:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11295-022-01541-2
Xie S, Manchester SR, Liu K et al (2013) Citrus linczangensis sp. n., a leaf fossil of Rutaceae from the late Miocene of Yunnan. China Int J Pl Sci 174:1201–1207. https://doi.org/10.1086/671796
Xu X, Wang D (2021) Comparative chloroplast genomics of Corydalis species (Papaveraceae): evolutionary perspectives on their unusual large scale rearrangements. Frontiers Pl Sci 11:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.600354
Yang Z (2007) PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Molec Biol Evol 24:1586–1591. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm088
Yang M, Zhang X, Liu G et al (2010) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). PLoS ONE 5:e12762. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012762
Yang K, You CX, Wang CF et al (2015) Chemical composition and bioactivity of essential oil of Atalantia guillauminii against three species stored product insects. J Oleo Sci 64:1101–1109. https://doi.org/10.5650/jos.ess15135
Yang X, Zhou T, Su X et al (2021) Structural characterization and comparative analysis of the chloroplast genome of Ginkgo biloba and other gymnosperms. J Forest Res 32:765–778. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11676-019-01088-4
Zhang YM, Han LJ, Yang CW et al (2022) Comparative chloroplast genome analysis of medicinally important Veratrum (Melanthiaceae) in China: insights into genomic characterization and phylogenetic relationships. Pl Diversity 44:70–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pld.2021.05.004
Zhao K, Li L, Quan H et al (2021) Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes from 14 Zanthoxylum species: identification of variable DNA markers and phylogenetic relationships within the genus. Frontiers Pl Sci 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.605793
Zhou T, Zhu H, Wang J et al (2020) Complete chloroplast genome sequence determination of Rheum species and comparative chloroplast genomics for the members of Rumiceae. Pl Cell Rep 39:811–824. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00299-020-02532-0
Zhou W, Harris AJ, Xiang QY (2022) Phylogenomics and biogeography of Torreya (Taxaceae)—integrating data from three organelle genomes, morphology, and fossils and a practical method for reducing missing data from RAD-seq. J Syst Evol 60:1241–1262. https://doi.org/10.1111/jse.12838
Zhu Z, Wang J, Sun X et al (2018) Complete plastome sequence of Atalantia kwangtungensis (Rutaceae): an endemic “near threatened” shrub in South China. Mitochondrial DNA Part B 3:730–731. https://doi.org/10.1080/23802359.2018.1483764
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Palaeobiology and Stratigraphy (Nos. 223123 and 213119), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31801022), and Shandong Province Natural Science Foundation of China (No. ZR2019BC094).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WBS helped in conceptualization, data curation, investigation, methodology, project administration, software, visualization, writing—review & editing, writing—original draft. WCS contributed to conceptualization, data curation, formal analysis, investigation, project administration. YZ was involved in data curation, formal analysis, validation. CS performed conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, writing—original draft. SW helped in data curation, funding acquisition, project administration. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that the work reported in this manuscript does not present any conflicts of interest for them.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Julien Boutte.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Information on Electronic Supplementary Material
Online Resource 1. Taxonomic position, species name and NCBI accession numbers of Aurantioideae species in the phylogenetic trees.
Online Resource 2. The results of mapping the reads to the assembled Atalantia complete cp genome sequences.
Online Resource 3. The individual chloroplast genome maps for each Atalantia species.
Online Resource 4. Statistics on the relative synonymous codon usage (RSCU) values of different Atalantia species.
Online Resource 5. Statistics of Ka/Ks values obtained from selection pressure analysis of other Atalantia species, using Atalantia roxburghiana as a reference.
Online Resource 6. Statistics regarding the number, type, region, and location of simple sequence repeats (SSRs) in diverse Atalantia chloroplast genomes.
Online Resource 7. Statistics regarding the type, number, region, and location of long repeats in diverse Atalantia chloroplast genomes.
Online Resource 8. Statistics on the nucleotide diversity (Pi) values of the Atalantia chloroplast genome, as well as the corresponding gene regions and their locations.
Online Resource 9. The pseudogenization of the accD gene in A. kwangtungensis.
Online Resource 10. Information on heterozygous variants present in Atalantia species, including Phred-scaled quality scores, genotypes, and likelihood statistics for each genotype.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, W., Song, W., Zhao, Y. et al. Complete chloroplast genomes of four Atalantia (Rutaceae) species: insights into comparative analysis, phylogenetic relationships, and divergence time estimation. Plant Syst Evol 309, 31 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-023-01868-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-023-01868-w