Abstract
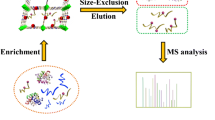
A zirconium(IV)-based metal organic framework (Zr-MOF) was deposited on polydopamine-coated silica microspheres to form microspheres of type SiO2@PDA@Zr-MOF. These were packed into capillary columns for enrichment of phosphopeptides. The column was off-line coupled to both matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time of flight mass spectrometry and LC-ESI-MS/MS. The method has a detection limit as low as 4 fmol of β-casein digest and a selectivity as high as 1:1000 (molar ratio of β-casein and BSA digest). It was applied to the analysis of human saliva. In total, 240 endogenous phosphopeptides were identified in only 25 μL human saliva.

A zirconium-based metal organic framework (Zr-MOF) was modified outside of polydopamine-coated silica microspheres to form microspheres named SiO2@PDA@Zr-MOF. Then they were packed in capillary columns for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides via interaction between Zr-O clusters and phosphate groups. The pre-concentration resulted in a better detection of phosphopeptides by mass spectrometry. Tris: Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane; DMF: Dimethyl Formamide; Zr-MOF: Zirconium(IV)-organic framework; MOAC: Metal oxide affinity chromatography.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lundby A, Secher A, Lage K, Nordsborg NB, Dmytriyev A, Lundby C, Olsen JV (2012) Quantitative maps of protein phosphorylation sites across 14 different rat organs and tissues. Nat Commun 3:876. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1871
Huttlin EL, Jedrychowski MP, Elias JE, Goswami T, Rad R, Beausoleil SA, Villen J, Haas W, Sowa ME, Gygi SP (2010) A tissue-specific atlas of mouse protein phosphorylation and expression. Cell 143(7):1174–1189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2010.12.001
Aebersold R, Mann M (2003) Mass spectrometry-based proteomics. Nature 422:198–207. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01511
Leitner A, Sturm M, Lindner W (2011) Tools for analyzing the phosphoproteome and other phosphorylated biomolecules: a review. Anal Chim Acta 703(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2011.07.012
Hortin GL (2006) The MALDI-TOF mass spectrometric view of the plasma proteome and peptidome. Clin Chem 52(7):1223–1237. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2006.069252
Wang ZG, Lv N, Bi WZ, Zhang JL, Ni JZ (2015) Development of the affinity materials for phosphorylated proteins/peptides enrichment in phosphoproteomics analysis. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(16):8377–8392. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b01254
Kailasa SK, Wu H-F (2014) Recent developments in nanoparticle-based MALDI mass spectrometric analysis of phosphoproteomes. Microchim Acta 181(9–10):853–864. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1191-z
Tan S, Wang J, Han Q, Liang Q, Ding M (2018) A porous graphene sorbent coated with titanium(IV)-functionalized polydopamine for selective lab-in-syringe extraction of phosphoproteins and phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(7):316. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2846-y
Jiang J, Sun X, She X, Li J, Li Y, Deng C, Duan G (2018) Magnetic microspheres modified with Ti(IV) and Nb(V) for enrichment of phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185(6):309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2837-z
Zhang L, Gan Y, Sun H, Yu B, Jin X, Zhang R, Zhang W, Zhang L (2016) Magnetic mesoporous carbon composites incorporating hydrophilic metallic nanoparticles for enrichment of phosphopeptides prior to their determination by MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry. Microchim Acta 184(2):547–555. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2046-6
Yan Y, Zheng Z, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X, Yang P (2013) Hydrophilic polydopamine-coated graphene for metal ion immobilization as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography platform for phosphoproteome analysis. Anal Chem 85(18):8483–8487. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401668e
Gu ZY, Chen YJ, Jiang JQ, Yan XP (2011) Metal-organic frameworks for efficient enrichment of peptides with simultaneous exclusion of proteins from complex biological samples. Chem Commun 47(16):4787–4789. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cc10579e
Zhu X, Gu J, Yang J, Wang Z, Li Y, Zhao L, Zhao W, Shi J (2015) Zr-based metal–organic frameworks for specific and size-selective enrichment of phosphopeptides with simultaneous exclusion of proteins. J Mater Chem B 3(20):4242–4248. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5tb00113g
Peng J, Zhang H, Li X, Liu S, Zhao X, Wu J, Kang X, Qin H, Pan Z, Wu R (2016) Dual-metal centered zirconium-organic framework: a metal-affinity probe for highly specific interaction with Phosphopeptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(51):35012–35020. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12630
Zhao M, Deng C, Zhang X (2014) The design and synthesis of a hydrophilic core-shell-shell structured magnetic metal-organic framework as a novel immobilized metal ion affinity platform for phosphoproteome research. Chem Commun 50(47):6228–6231. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cc01038h
Liu Q, Sun N, Gao M, Deng C (2018) Magnetic binary metal–organic framework as a novel affinity probe for highly selective capture of endogenous Phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(3):4382–4389. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b00023
Zhou J, Liang Y, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2017) Dual-functionalized magnetic metal–organic framework for highly specific enrichment of Phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 5(12):11413–11421. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b02521
Yang X, Xia Y (2016) Urea-modified metal-organic framework of type MIL-101(Cr) for the preconcentration of phosphorylated peptides. Microchim Acta 183(7):2235–2240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1860-1
Li D, Bie Z (2017) Metal–organic framework incorporated monolithic capillary for selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. RSC Adv 7(26):15894–15902. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra00263g
Li D, Yin D, Chen Y, Liu Z (2017) Coupling of metal-organic frameworks-containing monolithic capillary-based selective enrichment with matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time-of-flight mass spectrometry for efficient analysis of protein phosphorylation. J Chromatogr A 1498:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.10.054
Yang H, Deng C, Zhang X (2016) Preparation of Ti(4+)-immobilized modified silica capillary trapping column for on-line selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Talanta 153:285–294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.012
Choi H, Lee S, Jun CD, Park ZY (2011) Development of an off-line capillary column IMAC phosphopeptide enrichment method for label-free phosphorylation relative quantification. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 879(28):2991–2997. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2011.08.035
Richardson BM, Soderblom EJ, Thompson JW, Moseley MA (2013) Automated, reproducible, titania-based phosphopeptide enrichment strategy for label-free quantitative phosphoproteomics. J Biomol Tech 24(1):8–16. https://doi.org/10.7171/jbt.13-2401-002
Ruprecht B, Koch H, Medard G, Mundt M, Kuster B, Lemeer S (2015) Comprehensive and reproducible phosphopeptide enrichment using iron immobilized metal ion affinity chromatography (Fe-IMAC) columns. Mol Cell Proteomics 14(1):205–215. https://doi.org/10.1074/mcp.M114.043109
Xie Y, Deng C (2017) Designed synthesis of a "one for two" hydrophilic magnetic amino-functionalized metal-organic framework for highly efficient enrichment of glycopeptides and phosphopeptides. Sci Rep 7(1):1162. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01341-y
Lin H, Shao X, Lu Y, Deng C (2018) Preparation of iminodiacetic acid functionalized silica capillary trap column for on-column selective enrichment of N-linked glycopeptides. Talanta 188:499–506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.031
Vitorino R, Lobo MJ, Duarte JR, Ferrer-Correia AJ, Domingues PM, Amado FM (2005) The role of salivary peptides in dental caries. Biomed Chromatogr 19(3):214–222. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.438
Long X, Li J, Sheng D, Lian H (2016) Low-cost iron oxide magnetic nanoclusters affinity probe for the enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides in human saliva. RSC Adv 6(98):96210–96222. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra11125d
Su J, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2017) Adenosine phosphate functionalized magnetic mesoporous graphene oxide nanocomposite for highly selective enrichment of Phosphopeptides. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 6(2):2188–2196. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03607
Sun N, Deng C, Li Y, Zhang X (2014) Size-exclusive magnetic graphene/mesoporous silica composites with titanium(IV)-immobilized pore walls for selective enrichment of endogenous phosphorylated peptides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(14):11799–11804. https://doi.org/10.1021/am502529a
La Barbera G, Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Ferraris F, Montone CM, Piovesana S, Zenezini Chiozzi R, Lagana A (2018) Saliva as a source of new phosphopeptide biomarkers: development of a comprehensive analytical method based on shotgun peptidomics. Talanta 183:245–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.02.085
Lin H, Deng C (2016) Development of immobilized Sn(4+) affinity chromatography material for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. Proteomics 16(21):2733–2741. https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.201600187
Xiong Z, Zhang L, Fang C, Zhang Q, Ji Y, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Zou H (2014) Ti4+−immobilized multilayer polysaccharide coated magnetic nanoparticles for highly selective enrichment of phosphopeptides. J Mater Chem B 2(28):4473–4480. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4tb00479e
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2018YFA0507501) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21425518).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, H., Chen, H., Shao, X. et al. A capillary column packed with a zirconium(IV)-based organic framework for enrichment of endogenous phosphopeptides. Microchim Acta 185, 562 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3109-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3109-7