Abstract
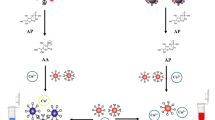
Staphylococcus aureus causes numerous illnesses and national loss in many countries. Therefore, to prevent food poisoning outbreaks, a rapid and straightforward on-site detection method is required without special skills or equipment. Here, we used aptamer-immobilized gold nanoparticles (aiGNPs) for the on-site colorimetric S. aureus detection. For the rapid and facile detection of S. aureus, the SA61 aptamer hybridized with thiol-modified adaptors conjugated onto the GNP surface of approximately 13 nm diameter. The synthesis of GNPs was confirmed using a transmission electron microscopy and energy dispersive spectroscopy. Images using a scanning electron microscope showed attachment of aiGNPs to S. aureus. After 30-min incubation and 20-min centrifugation, the red pellet was specifically observed with the sensitivity of OD600 0.050 equivalent to 7.5 × 106 cells/mL. Besides, aiGNPs could accurately detect S. aureus with a detection limit of OD600 0.10 equivalent to 1.5 × 107 cells/mL even in the mixed sample with Escherichia coli. Quantitative analysis was performed between relative area and cell concentration. Because this method enables fast and specific S. aureus detection without special skills or expensive equipment, aiGNPs could enable a rapid and effective on-site detection of S. aureus to prevent pathogenic outbreaks.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reddy, P. N., K. Srirama, and V. R. Dirisala (2017) An update on clinical burden, diagnostic tools, and therapeutic options of Staphylococcus aureus. Infect. Dis. (Auckl). 10: 1179916117703999.
Scallan, E., R. M. Hoekstra, F. J. Angulo, R. V. Tauxe, M. A. Widdowson, S. L. Roy, J. L. Jones, and P. M. Griffin (2011) Foodborne illness acquired in the United States—major pathogens. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 17: 7–15.
Kadariya, J., T. C. Smith, and D. Thapaliya (2014) Staphylococcus aureus and staphylococcal food-borne disease: an ongoing challenge in public health. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014: 827965.
Kourtis, A. P., K. Hatfield, J. Baggs, Y. Mu, I. See, E. Epson, J. Nadle, M. A. Kainer, G. Dumyati, S. Petit, S. M. Ray, D. Ham, C. Capers, H. Ewing, N. Coffin, L. C. McDonald, J. Jernigan, and D. Cardo (2019) Vital signs: Epidemiology and recent trends in methicillin-resistant and in methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus bloodstream infections — United States. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 68: 214–219.
Hewitt, J. H., A. W. Coe, and M. T. Parker (1969) The detection of methicillin resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Microbiol. 2: 443–456.
Eom, H. S., B. H. Hwang, D. H. Kim, I. B. Lee, Y. H. Kim, and H. J. Cha (2007) Multiple detection of food-borne pathogenic bacteria using a novel 16S rDNA-based oligonucleotide signature chip. Biosens. Bioelectron. 22: 845–853.
Shin, H. H., B. H. Hwang, and H. J. Cha (2016) Multiplex 16S rRNA-derived geno-biochip for detection of 16 bacterial pathogens from contaminated foods. Biotechnol. J. 11: 1405–1414.
Hwang, B. H., H. H. Shin, and H. J. Cha (2017) Optimization of DNA microarray biosensors enables rapid and sensitive detection. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 22: 469–473.
Park, C. R., S. J. Park, W. G. Lee, and B. H. Hwang (2018) Biosensors using hybridization chain reaction — design and signal amplification strategies of hybridization chain reaction. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 23: 355–370.
Park, C. R., W. J. Rhee, K. W. Kim, and B. H. Hwang (2019) Colorimetric biosensor using dual-amplification of enzyme-free reaction through universal hybridization chain reaction system. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 116: 1567–1574.
Chang, Y. C., C. Y. Yang, R. L. Sun, Y. F. Cheng, W. C. Kao, and P. C. Yang (2013) Rapid single cell detection of Staphylococcus aureus by aptamer-conjugated gold nanoparticles. Sci. Rep. 3: 1863.
Hakkinen, H. (2012) The gold-sulfur interface at the nanoscale. Nat. Chem. 4: 443–455.
Chhatre, A., P. Solasa, S. Sakle, R. Thaokar, and A. Mehra (2012) Color and surface plasmon effects in nanoparticle systems: Case of silver nanoparticles prepared by microemulsion route. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 404: 83–92.
Zagorovsky, K. and W. C. W. Chan (2013) A plasmonic DNAzyme strategy for point-of-care genetic detection of infectious pathogens. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 52: 3168–3171.
Hurst, S. J., A. K. R. Lytton-Jean, and C. A. Mirkin (2006) Maximizing DNA loading on a range of gold nanoparticle sizes. Anal. Chem. 78: 8313–8318.
Park, J. Y., H. Y. Jeong, M. I. Kim, and T. J. Park (2015) Colorimetric detection system for Salmonella typhimurium based on peroxidase-like activity of magnetic nanoparticles with DNA aptamers. J. Nanomater. 2015: 527126.
Bayrac, C., F. Eyidogan, and H. A. Oktem (2017) DNA aptamer-based colorimetric detection platform for Salmonella enteritidis. Biosens. Bioelectron. 98: 22–28.
Kim, T. Y., J. W. Lim, M. C. Lim, N. E. Song, and M. A. Woo (2020) Aptamer-based fluorescent assay for simple and sensitive detection of fipronil in liquid eggs. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 246–254.
Hidayat, M. A., D. A. Maharani, D. A. Purwanto, B. Kuswandi, and M. Yuwono (2020) Simple and sensitive paper-based colorimetric biosensor for determining total polyphenol content of the green tea beverages. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 25: 255–263.
Acknowledgments
An Incheon National University Research Grant supported this research in 2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical Statement Neither ethical approval nor informed consent was required for this study.
Conflict of Interest The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, S.H., Ryu, Y.C. & Hwang, B.H. Aptamer-immobilized Gold Nanoparticles Enable Facile and On-site Detection of Staphylococcus aureus. Biotechnol Bioproc E 26, 107–113 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0161-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0161-z