Abstract
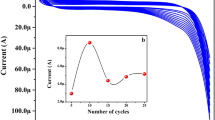
A cage-like PbS nanostructure was functionalized with platinum nanoparticles, and the resulting material (PtNP@PbS) was deposited on a glassy carbon electrode in order to study the direct electron transfer to FADH2 in glucose oxidase (GOx) and further to construct a glucose biosensor. The PtNP@PbS nanostructure and the biosensor were characterized using scanning electron microscopy, UV-vis and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy, and by cyclic voltammetry. Compared to the use of cage-like PbS alone, the PtNP@PbS nanostructure shows much higher electrochemical activity and an enhanced direct electron transfer rate. The GOx loaded onto the nanostructure displays good enzymatic activity and an apparent electron transfer rate constant of 3.0 s−1. The glucose biosensor is operated best at −0.4 V (vs. SCE) and then exhibits a linear range that extends from 4 μM to 1.1 mM, with a detection limit as low as 1 μM (at an S/N ratio of 3). The biosensor is selective, acceptably repeatable and stable. It was applied to the determination of glucose in human serum samples.

Platinum nanoparticles functionalized cage-like PbS (PtNP@PbS) nanostructured composite is fabricated, characterized, and employed to immobilize glucose oxidase (GOx) for direct-electron-transfer-based electrochemical glucose biosensing applications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Luong JHT, Glennon JD, Gedanken A, Vashist SK (2017) Achievement and assessment of direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase in electrochemical biosensing using carbon nanotubes, graphene, and their nanocomposites. Microchim Acta 25:901
Meng L, Jin J, Yang GX, TH L, Zhang H, Cai CX (2009) Nonenzymatic electrochemical detection of glucose based on palladium-single-walled carbon nanotube hybrid nanostructures. Anal Chem 81:7271
Liu Q, Lu XB, Li J, Yao L, H Li J (2007) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and electrochemical biosensing of glucose on quantum dots/carbon nanotubes electrodes. Biosens Bioelectron 22:3203
Vaddiraju S, Tomazos I, Burgess DJ, Jain FC, Papadimitrakopoulos F (2010) Emerging synergy between nanotechnology and implantable biosensors: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 25:1553
Li XJ, Yu SQ, Yan T, Zhang Y, Du B, Wu D, Wei Q (2017) A sensitive electrochemiluminescence immunosensor based on Ru(bpy)3 2+ in 3D CuNi oxalate as luminophores and graphene oxide–polyethylenimine as released Ru(bpy)3 2+ initiator. Biosens Bioelectron 89:1020
Wu D, Liu YX, Wang YG, Hu LH, Ma HM, Wang GQ, Wei Q (2016) Label-free electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for detection of prostate specific antigen based on aminated graphene quantum dots and carboxyl graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 6:20511
Yang ZJ, Huang XC, Zhang YC, Li J, Xu Q, Hu XY Novel urchin-like In2O3-chitosan modified electrode for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing. Electrochim Acta 70:325
Dai ZH, Shao GJ, Hong JM, Bao JC, Shen J (2009) Immobilization and direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase on a tetragonal Pyramid-shaped porous ZnO nanostructure for a glucose biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:1286
Bao SJ, Li C, Zang JF, Cui XQ, Qiao Y, Guo J (2008) New nanostructured TiO2 for direct electrochemistry and glucose sensor applications. Adv Funct Mater 18:591
Yang ZJ, Ren YY, Zhang YC, Li J, Li HB, Huang XC, XY H, Xu Q (2011) Nanoflake-like SnS2 matrix for glucose biosensing based on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4337
Huang QL, Chen H, Wu CL, Zhang YC (2010) Hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of PbS cage-like structures. Mater Lett 64:1891
Zhang YC, Qiao T, XY H, Wang GY, Wu X (2005) Shape-controlled synthesis of PbS microcrystallites by mild solvothermal decomposition of a single-source molecular precursor. J Cryst Growth 277:518
Patel AA, Wu F, Zhang JZ, Torres-Martinez CL, Mehra RK, Yang Y, Risbud SH (2000) Synthesis, optical spectroscopy and ultrafast electron dynamics of PbS nanoparticles with different surface capping. J Phys Chem B 104:11598
Li J, Tang Y, Yang J, Yang ZJ, Zhang YC, Hu XY (2014) Cage-like PbS nanostructure for the construction of novel glucose electrochemical biosensor. Sensors Actuators B 190:549
Wu H, Wang J, Kang XH, Wang CM, Wang DH, Liu J, Aksay IA, Lin Y (2009) Glucose biosensor based on immobilization of glucose oxidase in platinum nanoparticles/graphene/chitosan nanocomposite film. Talanta 80:403
Tang S, Wang XZ, Lei JP, Hu Z, Deng SY, Ju HX (2010) Pt-dispersed flower-like carbon nanosheet aggregation for low-overpotential electrochemical biosensing. Biosens Bioelectron 26:432
Zhou DL, Feng JJ, Cai LY, Fang QX, Chen JR, Wang AJ (2014) Facile synthesis of monodisperse porous Cu2O nanospheres on reduced graphene oxide for non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensing. Electrochim Acta 115:103
Mei LP, Song P, Feng JJ, Shen JH, Wang W, Wang AJ, Weng XX (2015) Nonenzymatic amperometric sensing of glucose using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of reduced graphene oxide decorated with Cu2O nanoclusters. Microchim Acta 282:1701
Chen XM, GH W, Cai ZX, Oyama M, Chen X (2014) Advances in enzyme-free electrochemical sensors for hydrogen peroxide, glucose, and uric acid. Microchim Acta 181:689
Ding CP, Yan YH, Xiang DS, Zhang CL, Xian YZ (2016) Magnetic Fe3S4 nanoparticles with peroxidase-like activity, and their use in a photometric enzymatic glucose assay. Microchim Acta 183:625
Zhang YC, Du ZN, Li SY, Zhang M (2010) Novel synthesis and high visible light photocatalytic activity of SnS2 nanoflakes from SnCl2. 2H2O and S powders. Appl Catal B Environ 95:153
Han X, Zhu YH, Yang XL, Li CZ (2010) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on platinum nanoparticle encapsulated with a clay. Microchim Acta 171:233
Wang XP, Xu R, Sun X, Wang YG, Ren X, Du B, Wu D, Wei Q, Wei Q (2017) Using reduced graphene oxide-Ca:CdSe nanocomposite to enhance photoelectrochemical activity of gold nanoparticles functionalized tungsten oxide for highly sensitive prostate specific antigen detection. Biosens Bioelectron 96:239
Liu YX, Ma HM, Zhang Y, Pang XH, Fan DW, Wu D, Wei Q (2016) Visible light photoelectrochemical aptasensor for adenosine detection based on CdS/PPy/g-C3N4 nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 86:439
Liu HY, NF H (2007) Study on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase stabilized by cross-linking and immobilized in silica nanoparticle films. Electroanalysis 19:884
Deng CY, Chen JH, Chen XL, Xiao CH, Nie LH, Yao SZ (2008) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on boron-doped carbon nanotubes modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1272
Hui JN, Cui JW, Xu GQ, Adeloju SB, Wu YC (2013) Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase based on Nafion-graphene-GOD modified gold electrode and application to glucose detection. Mater Lett 108:88
Bard J, Faulkner LR (2001) Electrochemistry methods, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Deng SY, Jian GQ, Lei JP, Hu Z, Ju HX (2009) A glucose biosensor based on direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on nitrogen-doped carbon nanotubes. Biosens Bioelectron 25:373
Wen D, Liu Y, Yang GC, Dong SJ (2007) Electrochemistry of glucose oxidase immobilized on the carbon nanotube wrapped by polyelectrolyte. Electrochim Acta 52:5312
Liu SQ, Ju HX (2003) Reagentless glucose biosensor based on direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase immobilized on colloidal gold modified carbon paste electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 19:177
Li ZJ, Sheng LY, Meng AL, Xie CC, Zhao K (2016) A glassy carbon electrode modified with a composite consisting of reduced graphene oxide, zinc oxide and silver nanoparticles in a chitosan matrix for studying the direct electron transfer of glucose oxidase and for enzymatic sensing of glucose. Microchim Acta 183:1625
Ren XL, Chen D, Meng XW, Tang FQ, Du AM, Zhang L (2009) Amperometric glucose biosensor based on a gold nanorods/cellulose acetate composite film as immobilization matrix. Colloids Surf B 72:188
Wang YL, Liu L, Li MG, Xu SD, Gao F (2011) Multifunctional carbon nanotubes for direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and glucose bioassay. Biosens Bioelectron 30:107
Ye Y, Ding S, Ye Y, Xu H, Cao X, Liu S, Sun H (2015) Enzyme-based sensing of glucose using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a one-pot synthesized nanocomposite consisting of chitosan, reduced graphene oxide and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182:1783
Acknowledgments
The financial support for this work was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 21475116, 21575125, and 21575124), Qinglan Project of Jiangsu Province and High-end talent support program of Yangzhou University for Zhanjun Yang, Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institution (PAPD), and the Six Talent Peaks Project of Jiangsu Province for Juan Li. In addition, many thanks are given to the Testing Center of Yangzhou University for all of the characterizations that were performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Highlights
• PtNP@cage-like PbS nanostructure was prepared for the immobilization of enzymes.
• Direct electron transfer of GOx at PtNP@cage-like PbS nanostructure was studied.
• The glucose biosensor showed high assay capability.
• PtNP@cage-like PbS nanostructure provides a potential matrix for biosensing applications.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 271 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, J., Huang, Y., Chen, Y. et al. A glassy carbon electrode modified with a platinum nanoparticle/cage-like PbS nanostructure for direct electron transfer to enzymes and for use in biosensing. Microchim Acta 184, 4845–4852 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2528-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2528-1