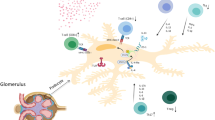
Abstract
The pathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome (INS) is as yet unknown, but several lines of evidence indicate that the immune system may play a crucial pathogenic role in non-genetic INS. The most important of these are, first, the effectiveness of therapy based on immunosuppression and, second, a vast body of data derived both from experimental models and from patient studies that implicate T cells and more recently B cells as major players in INS pathogenesis. However, recent findings also suggest a direct role of podocytes as drivers of the disease process, and the interplay between the glomerulus and the immune system is still being elucidated. In this review we provide an overview of current knowledge on the role of different components of the immune system in determining disease. Advances in our understanding of the pathogenesis of INS may help drive new, more tailored therapeutic approaches.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eddy AA, Symons JM (2003) Nephrotic syndrome in childhood. Lancet 362(9384):629–639
Vivarelli M, Moscaritolo E, Tsalkidis A, Massella L, Emma F (2010) Time for initial response to steroids is a major prognostic factor in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Pediatr 156(6):965–971
Vivarelli M, Massella L, Ruggiero B, Emma F (2016) Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. doi:10.2215/CJN.05000516
Fogo AB (2015) Causes and pathogenesis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Rev Nephrol 11(2):76–87
Maas RJ, Wetzels JF (2017) Glomerular disease in 2016: New advances in the treatment of glomerular disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(2):65–66
Lovric S, Ashraf S, Tan W, Hildebrandt F (2016) Genetic testing in steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome: when and how? Nephrol Dial Transplant 31(11):1802–1813
Davin JC (2016) The glomerular permeability factors in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 31(2):207–215
Konigshausen E, Sellin L (2016) Circulating permeability factors in primary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a review of proposed candidates. Biomed Res Int 2016:3765608
Hoyer JR, Vernier RL, Najarian JS, Raij L, Simmons RL, Michael AF (1972) Recurrence of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome after renal transplantation. Lancet 2(7773):343–348
Mauer SM, Hellerstein S, Cohn RA, Sibley RK, Vernier RL (1979) Recurrence of steroid-responsive nephrotic syndrome after renal transplantation. J Pediatr 95(2):261–264
Kemper MJ, Wolf G, Muller-Wiefel DE (2001) Transmission of glomerular permeability factor from a mother to her child. N Engl J Med 344(5):386–387
Gallon L, Leventhal J, Skaro A, Kanwar Y, Alvarado A (2012) Resolution of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis after retransplantation. N Engl J Med 366(17):1648–1649
Zimmerman SW (1984) Increased urinary protein excretion in the rat produced by serum from a patient with recurrent focal glomerular sclerosis after renal transplantation. Clin Nephrol 22(1):32–38
Goldwich A, Burkard M, Olke M, Daniel C, Amann K, Hugo C, Kurts C, Steinkasserer A, Gessner A (2013) Podocytes are nonhematopoietic professional antigen-presenting cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 24(6):906–916
Rabelink TJ, de Zeeuw D (2015) The glycocalyx—linking albuminuria with renal and cardiovascular disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 11(11):667–676
McDonald JC, Moore DL, Quennec P (1989) Clinical and epidemiologic features of mumps meningoencephalitis and possible vaccine-related disease. Pediatr Infect Dis J 8(11):751–755
Uwaezuoke SN (2015) Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome in children: triggers of relapse and evolving hypotheses on pathogenesis. Ital J Pediatr 41:19
Gulati A, Sinha A, Sreenivas V, Math A, Hari P, Bagga A (2011) Daily corticosteroids reduce infection-associated relapses in frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome: a randomized controlled trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(1):63–69
Yildiz N, Sever L, Kasapcopur O, Cullu F, Arisoy N, Caliskan S (2013) Hepatitis B virus vaccination in children with steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome: immunogenicity and safety? Vaccine 31(33):3309–3312
Abeyagunawardena AS, Goldblatt D, Andrews N, Trompeter RS (2003) Risk of relapse after meningococcal C conjugate vaccine in nephrotic syndrome. Lancet 362(9382):449–450
Salsano ME, Graziano L, Luongo I, Pilla P, Giordano M, Lama G (2007) Atopy in childhood idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Acta Paediatr 96(4):561–566
Shalhoub RJ (1974) Pathogenesis of lipoid nephrosis: a disorder of T-cell function. Lancet 2(7880):556–560
Pereira Wde F, Brito-Melo GE, Guimaraes FT, Carvalho TG, Mateo EC, Simoes e Silva AC (2014) The role of the immune system in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome: a review of clinical and experimental studies. Inflamm Res 63(1):1–12
Sahali D, Sendeyo K, Mangier M, Audard V, Zhang SY, Lang P, Ollero M, Pawlak A (2014) Immunopathogenesis of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome with relapse. Semin Immunopathol 36(4):421–429
Couser WG (2012) Basic and translational concepts of immune-mediated glomerular diseases. J Am Soc Nephrol 23(3):381–399
Lama G, Luongo I, Tirino G, Borriello A, Carangio C, Salsano ME (2002) T-lymphocyte populations and cytokines in childhood nephrotic syndrome. Am J Kidney Dis 39(5):958–965
Kemper MJ, Zepf K, Klaassen I, Link A, Muller-Wiefel DE (2005) Changes of lymphocyte populations in pediatric steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome are more pronounced in remission than in relapse. Am J Nephrol 25(2):132–137
Lapillonne H, Leclerc A, Ulinski T, Balu L, Garnier A, Dereuddre-Bosquet N, Watier H, Schlageter MH, Deschenes G (2008) Stem cell mobilization in idiopathic steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 23(8):1251–1256
Wang Y, Wang Y, Feng X, Bao S, Yi S, Kairaitis L, Tay YC, Rangan GK, Harris DC (2001) Depletion of CD4(+) T cells aggravates glomerular and interstitial injury in murine adriamycin nephropathy. Kidney Int 59(3):975–984
Yap HK, Cheung W, Murugasu B, Sim SK, Seah CC, Jordan SC (1999) Th1 and Th2 cytokine mRNA profiles in childhood nephrotic syndrome: evidence for increased IL-13 mRNA expression in relapse. J Am Soc Nephrol 10(3):529–537
Araya CE, Wasserfall CH, Brusko TM, Mu W, Segal MS, Johnson RJ, Garin EH (2006) A case of unfulfilled expectations. Cytokines in idiopathic minimal lesion nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 21(5):603–610
Shao XS, Yang XQ, Zhao XD, Li Q, Xie YY, Wang XG, Wang M, Zhang W (2009) The prevalence of Th17 cells and FOXP3 regulate T cells (Treg) in children with primary nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 24(9):1683–1690
Wang YM, Hu M, Wang Y, Polhill T, Zhang GY, Wang Y, Lee VW, Harris DC, Alexander SI (2008) Regulatory T cells in renal disease. Int J Clin Exp Med 1(4):294–304
Hashimura Y, Nozu K, Kanegane H, Miyawaki T, Hayakawa A, Yoshikawa N, Nakanishi K, Takemoto M, Iijima K, Matsuo M (2009) Minimal change nephrotic syndrome associated with immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 24(6):1181–1186
Bertelli R, Bonanni A, Di Donato A, Cioni M, Ravani P, Ghiggeri GM (2016) Regulatory T cells and minimal change nephropathy: in the midst of a complex network. Clin Exp Immunol 183(2):166–174
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Duval A, Riveron S, Macher MA, Deschenes G, Loirat C, Verpont MC, Peuchmaur M, Ronco P, Monteiro RC, Haddad E (2007) A humanized mouse model of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome suggests a pathogenic role for immature cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 18(10):2732–2739
Carsetti R, Rosado MM, Wardmann H (2004) Peripheral development of B cells in mouse and man. Immunol Rev 197:179–191
Hoffman W, Lakkis FG, Chalasani G (2016) B Cells, Antibodies, and more. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(1):137–154
Benz K, Dotsch J, Rascher W, Stachel D (2004) Change of the course of steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome after rituximab therapy. Pediatr Nephrol 19(7):794–797
Ravani P, Bonanni A, Rossi R, Caridi G, Ghiggeri GM (2016) Anti-CD20 antibodies for idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in children. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(4):710–720
Leandro MJ (2013) B-cell subpopulations in humans and their differential susceptibility to depletion with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Arthritis Res Ther 15[Suppl 1]:S3
Huang H, Benoist C, Mathis D (2010) Rituximab specifically depletes short-lived autoreactive plasma cells in a mouse model of inflammatory arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(10):4658–4663
Worch J, Makarova O, Burkhardt B (2015) Immunreconstitution and infectious complications after rituximab treatment in children and adolescents: what do we know and what can we learn from adults? Cancers (Basel) 7(1):305–328
Dantal J, Godfrin Y, Koll R, Perretto S, Naulet J, Bouhours JF, Soulillou JP (1998) Antihuman immunoglobulin affinity immunoadsorption strongly decreases proteinuria in patients with relapsing nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 9(9):1709–1715
Kemper MJ, Altrogge H, Ganschow R, Muller-Wiefel DE (2002) Serum levels of immunoglobulins and IgG subclasses in steroid sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 17(6):413–417
Delville M, Sigdel TK, Wei C, Li J, Hsieh SC, Fornoni A, Burke GW, Bruneval P, Naesens M, Jackson A, Alachkar N, Canaud G, Legendre C, Anglicheau D, Reiser J, Sarwal MM (2014) A circulating antibody panel for pretransplant prediction of FSGS recurrence after kidney transplantation. Sci Transl Med 6(256):256ra136
Kemper MJ, Meyer-Jark T, Lilova M, Muller-Wiefel DE (2003) Combined T- and B-cell activation in childhood steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Clin Nephrol 60(4):242–247
Dossier C, Sellier-Leclerc AL, Rousseau A, Michel Y, Gautheret-Dejean A, Englender M, Madhi F, Charbit M, Ulinski T, Simon T, Jacqz-Aigrain E, Deschenes G (2014) Prevalence of herpesviruses at onset of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 29(12):2325–2331
Gbadegesin RA, Adeyemo A, Webb NJ, Greenbaum LA, Abeyagunawardena A, Thalgahagoda S, Kale A, Gipson D, Srivastava T, Lin JJ, Chand D, Hunley TE, Brophy PD, Bagga A, Sinha A, Rheault MN, Ghali J, Nicholls K, Abraham E, Janjua HS, Omoloja A, Barletta GM, Cai Y, Milford DD, O’Brien C, Awan A, Belostotsky V, Smoyer WE, Homstad A, Hall G, Wu G, Nagaraj S, Wigfall D, Foreman J, Winn MP, Mid-West Pediatric Nephrology C (2015) HLA-DQA1 and PLCG2 are candidate risk loci for childhood-onset steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(7):1701–1710
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Macher MA, Loirat C, Guerin V, Watier H, Peuchmaur M, Baudouin V, Deschenes G (2010) Rituximab efficiency in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 25(6):1109–1115
Colucci M, Carsetti R, Cascioli S, Casiraghi F, Perna A, Rava L, Ruggiero B, Emma F, Vivarelli M (2016) B cell reconstitution after rituximab treatment in idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(6):1811–1822
Sellier-Leclerc AL, Baudouin V, Kwon T, Macher MA, Guerin V, Lapillonne H, Deschenes G, Ulinski T (2012) Rituximab in steroid-dependent idiopathic nephrotic syndrome in childhood—follow-up after CD19 recovery. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(3):1083–1089
Fornoni A, Sageshima J, Wei C, Merscher-Gomez S, Aguillon-Prada R, Jauregui AN, Li J, Mattiazzi A, Ciancio G, Chen L, Zilleruelo G, Abitbol C, Chandar J, Seeherunvong W, Ricordi C, Ikehata M, Rastaldi MP, Reiser J, Burke GW 3rd (2011) Rituximab targets podocytes in recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Sci Transl Med 3(85):85ra46
Tasaki M, Shimizu A, Hanekamp I, Torabi R, Villani V, Yamada K (2014) Rituximab treatment prevents the early development of proteinuria following pig-to-baboon xeno-kidney transplantation. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(4):737–744
Basu B (2014) Ofatumumab for rituximab-resistant nephrotic syndrome. N Engl J Med 370(13):1268–1270
Schuh A (2011) Anti-CD20: tales of identical twins? Blood 118(19):5066–5067
Barisoni L, Schnaper HW, Kopp JB (2007) A proposed taxonomy for the podocytopathies: a reassessment of the primary nephrotic diseases. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2(3):529–542
Banas MC, Banas B, Hudkins KL, Wietecha TA, Iyoda M, Bock E, Hauser P, Pippin JW, Shankland SJ, Smith KD, Stoelcker B, Liu G, Grone HJ, Kramer BK, Alpers CE (2008) TLR4 links podocytes with the innate immune system to mediate glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(4):704–713
Shimada M, Ishimoto T, Lee PY, Lanaspa MA, Rivard CJ, Roncal-Jimenez CA, Wymer DT, Yamabe H, Mathieson PW, Saleem MA, Garin EH, Johnson RJ (2012) Toll-like receptor 3 ligands induce CD80 expression in human podocytes via an NF-nB-dependent pathway. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27(1):81–89
Akilesh S, Huber TB, Wu H, Wang G, Hartleben B, Kopp JB, Miner JH, Roopenian DC, Unanue ER, Shaw AS (2008) Podocytes use FcRn to clear IgG from the glomerular basement membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(3):967–972
Reiser J, Mundel P (2004) Danger signaling by glomerular podocytes defines a novel function of inducible B7-1 in the pathogenesis of nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 15(9):2246–2248
Huber TB, Reinhardt HC, Exner M, Burger JA, Kerjaschki D, Saleem MA, Pavenstadt H (2002) Expression of functional CCR and CXCR chemokine receptors in podocytes. J Immunol 168(12):6244–6252
Lee HS (2012) Mechanisms and consequences of TGF-ss overexpression by podocytes in progressive podocyte disease. Cell Tissue Res 347(1):129–140
Xing CY, Saleem MA, Coward RJ, Ni L, Witherden IR, Mathieson PW (2006) Direct effects of dexamethasone on human podocytes. Kidney Int 70(6):1038–1045
Garin EH, Diaz LN, Mu W, Wasserfall C, Araya C, Segal M, Johnson RJ (2009) Urinary CD80 excretion increases in idiopathic minimal-change disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 20(2):260–266
Yu CC, Fornoni A, Weins A, Hakroush S, Maiguel D, Sageshima J, Chen L, Ciancio G, Faridi MH, Behr D, Campbell KN, Chang JM, Chen HC, Oh J, Faul C, Arnaout MA, Fiorina P, Gupta V, Greka A, Burke GW 3rd, Mundel P (2013) Abatacept in B7-1-positive proteinuric kidney disease. N Engl J Med 369(25):2416–2423
Novelli R, Gagliardini E, Ruggiero B, Benigni A, Remuzzi G (2016) Any value of podocyte B7-1 as a biomarker in human MCD and FSGS? Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 310(5):F335–F341
Chatzigeorgiou A, Lyberi M, Chatzilymperis G, Nezos A, Kamper E (2009) CD40/CD40L signaling and its implication in health and disease. Biofactors 35(6):474–483
Beaudreuil S, Lorenzo HK, Durrbach A (2015) The anti-CD40 auto-antibody: a biomarker or a factor for the permeability of recurrent focal segmental glomerulosclerosis? Ann Transl Med 3(9):115
Lennon R, Singh A, Welsh GI, Coward RJ, Satchell S, Ni L, Mathieson PW, Bakker WW, Saleem MA (2008) Hemopexin induces nephrin-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in podocytes. J Am Soc Nephrol 19(11):2140–2149
Bakker WW, van Dael CM, Pierik LJ, van Wijk JA, Nauta J, Borghuis T, Kapojos JJ (2005) Altered activity of plasma hemopexin in patients with minimal change disease in relapse. Pediatr Nephrol 20(10):1410–1415
Wei C, El Hindi S, Li J, Fornoni A, Goes N, Sageshima J, Maiguel D, Karumanchi SA, Yap HK, Saleem M, Zhang Q, Nikolic B, Chaudhuri A, Daftarian P, Salido E, Torres A, Salifu M, Sarwal MM, Schaefer F, Morath C, Schwenger V, Zeier M, Gupta V, Roth D, Rastaldi MP, Burke G, Ruiz P, Reiser J (2011) Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Med 17(8):952–960
Hahm E, Wei C, Fernandez I, Li J, Tardi NJ, Tracy M, Wadhwani S, Cao Y, Peev V, Zloza A, Lusciks J, Hayek SS, O’Connor C, Bitzer M, Gupta V, Sever S, Sykes DB, Scadden DT, Reiser J (2017) Bone marrow-derived immature myeloid cells are a main source of circulating suPAR contributing to proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med 23(1):100–106
Kronbichler A, Saleem MA, Meijers B, Shin JI (2016) Soluble urokinase receptors in focal segmental glomerulosclerosis: a review on the scientific point of view. J Immunol Res 2016:2068691
Savin VJ, Sharma M, Zhou J, Gennochi D, Fields T, Sharma R, McCarthy ET, Srivastava T, Domen J, Tormo A, Gauchat JF (2015) Renal and hematological effects of CLCF-1, a B-cell-stimulating cytokine of the IL-6 family. J Immunol Res 2015:714964
Clement LC, Avila-Casado C, Mace C, Soria E, Bakker WW, Kersten S, Chugh SS (2011) Podocyte-secreted angiopoietin-like-4 mediates proteinuria in glucocorticoid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome. Nat Med 17(1):117–122
Larkins N, Kim S, Craig J, Hodson E (2016) Steroid-sensitive nephrotic syndrome: an evidence-based update of immunosuppressive treatment in children. Arch Dis Child 101(4):404–408
Iijima K, Sako M, Nozu K, Mori R, Tuchida N, Kamei K, Miura K, Aya K, Nakanishi K, Ohtomo Y, Takahashi S, Tanaka R, Kaito H, Nakamura H, Ishikura K, Ito S, Ohashi Y, Rituximab for Childhood-onset Refractory Nephrotic Syndrome Study G (2014) Rituximab for childhood-onset, complicated, frequently relapsing nephrotic syndrome or steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicentre, double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 384(9950):1273–1281
Ravani P, Rossi R, Bonanni A, Quinn RR, Sica F, Bodria M, Pasini A, Montini G, Edefonti A, Belingheri M, De Giovanni D, Barbano G, Degl’Innocenti L, Scolari F, Murer L, Reiser J, Fornoni A, Ghiggeri GM (2015) Rituximab in children with steroid-dependent nephrotic syndrome: a multicenter, open-label, noninferiority, randomized controlled trial. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(9):2259–2266
Ruggenenti P, Ruggiero B, Cravedi P, Vivarelli M, Massella L, Marasa M, Chianca A, Rubis N, Ene-Iordache B, Rudnicki M, Pollastro RM, Capasso G, Pisani A, Pennesi M, Emma F, Remuzzi G, Rituximab in Nephrotic Syndrome of Steroid-Dependent or Frequently Relapsing Minimal Change Disease Or Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis Study (NEMO) Study Group (2014) Rituximab in steroid-dependent or frequently relapsing idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(4):850–863
Vivarelli M, Colucci M, Bonanni A, Verzani M, Serafinelli J, Emma F, Ghiggeri G (2017) Ofatumumab in two pediatric nephrotic syndrome patients allergic to rituximab. Pediatr Nephrol 32(1):181–184
Coutinho AE, Chapman KE (2011) The anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive effects of glucocorticoids, recent developments and mechanistic insights. Mol Cell Endocrinol 335(1):2–13
Boumpas DT, Chrousos GP, Wilder RL, Cupps TR, Balow JE (1993) Glucocorticoid therapy for immune-mediated diseases: basic and clinical correlates. Ann Intern Med 119(12):1198–1208
Herold MJ, McPherson KG, Reichardt HM (2006) Glucocorticoids in T cell apoptosis and function. Cell Mol Life Sci 63(1):60–72
Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M (1995) Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science 270(5234):286–290
Banuelos J, Lu NZ (2016) A gradient of glucocorticoid sensitivity among helper T cell cytokines. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 31:27–35
Luther C, Adamopoulou E, Stoeckle C, Brucklacher-Waldert V, Rosenkranz D, Stoltze L, Lauer S, Poeschel S, Melms A, Tolosa E (2009) Prednisolone treatment induces tolerogenic dendritic cells and a regulatory milieu in myasthenia gravis patients. J Immunol 183(2):841–848
Li L, Zhang T, Diao W, Jin F, Shi L, Meng J, Liu H, Zhang J, Zeng CH, Zhang MC, Liang S, Liu Y, Zhang CY, Liu Z, Zen K (2015) Role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in glucocorticoid-mediated amelioration of FSGS. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(9):2183–2197
Lill-Elghanian D, Schwartz K, King L, Fraker P (2002) Glucocorticoid-induced apoptosis in early B cells from human bone marrow. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 227(9):763–770
Thaunat O, Koenig A, Leibler C, Grimbert P (2016) Effect of immunosuppressive drugs on humoral allosensitization after kidney transplant. J Am Soc Nephrol 27(7):1890–1900
Cupps TR, Gerrard TL, Falkoff RJ, Whalen G, Fauci AS (1985) Effects of in vitro corticosteroids on B cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation. J Clin Invest 75(2):754–761
Schonenberger E, Ehrich JH, Haller H, Schiffer M (2011) The podocyte as a direct target of immunosuppressive agents. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(1):18–24
Ransom RF, Lam NG, Hallett MA, Atkinson SJ, Smoyer WE (2005) Glucocorticoids protect and enhance recovery of cultured murine podocytes via actin filament stabilization. Kidney Int 68(6):2473–2483
Yu S, Li Y (2013) Dexamethasone inhibits podocyte apoptosis by stabilizing the PI3K/Akt signal pathway. Biomed Res Int 2013:326986
Fassbinder T, Saunders U, Mickholz E, Jung E, Becker H, Schluter B, Jacobi AM (2015) Differential effects of cyclophosphamide and mycophenolate mofetil on cellular and serological parameters in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 17:92
Lutsiak ME, Semnani RT, De Pascalis R, Kashmiri SV, Schlom J, Sabzevari H (2005) Inhibition of CD4(+)25+ T regulatory cell function implicated in enhanced immune response by low-dose cyclophosphamide. Blood 105(7):2862–2868
Hoyer BF, Moser K, Hauser AE, Peddinghaus A, Voigt C, Eilat D, Radbruch A, Hiepe F, Manz RA (2004) Short-lived plasmablasts and long-lived plasma cells contribute to chronic humoral autoimmunity in NZB/W mice. J Exp Med 199(11):1577–1584
Moysiadis DK, Perysinaki GS, Bertsias G, Stratakis S, Kyriacou K, Nakopoulou L, Boumpas DT, Daphnis E (2012) Early treatment with glucocorticoids or cyclophosphamide retains the slit diaphragm proteins nephrin and podocin in experimental lupus nephritis. Lupus 21(11):1196–1207
Vafadari R, Kraaijeveld R, Weimar W, Baan CC (2013) Tacrolimus inhibits NF-kappaB activation in peripheral human T cells. PLoS One 8(4):e60784
Liu G, Fan G, Guo G, Kang W, Wang D, Xu B, Zhao J (2016) FK506 attenuates the inflammation in rat spinal cord injury by inhibiting the activation of NF-kappaB in microglia cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s10571-016-0422-8
Mattila PS (1996) The actions of cyclosporin A and FK506 on T-lymphocyte activation. Biochem Soc Trans 24(1):45–49
De Serres SA, Sayegh MH, Najafian N (2009) Immunosuppressive drugs and Tregs: a critical evaluation! Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4(10):1661–1669
De Bruyne R, Bogaert D, De Ruyck N, Lambrecht BN, Van Winckel M, Gevaert P, Dullaers M (2015) Calcineurin inhibitors dampen humoral immunity by acting directly on naive B cells. Clin Exp Immunol 180(3):542–550
Heidt S, Roelen DL, Eijsink C, Eikmans M, van Kooten C, Claas FH, Mulder A (2010) Calcineurin inhibitors affect B cell antibody responses indirectly by interfering with T cell help. Clin Exp Immunol 159(2):199–207
Struijk GH, Minnee RC, Koch SD, Zwinderman AH, van Donselaar-van der Pant KA, Idu MM, ten Berge IJ, Bemelman FJ (2010) Maintenance immunosuppressive therapy with everolimus preserves humoral immune responses. Kidney Int 78(9):934–940
Faul C, Donnelly M, Merscher-Gomez S, Chang YH, Franz S, Delfgaauw J, Chang JM, Choi HY, Campbell KN, Kim K, Reiser J, Mundel P (2008) The actin cytoskeleton of kidney podocytes is a direct target of the antiproteinuric effect of cyclosporine A. Nat Med 14(9):931–938
Shen X, Jiang H, Ying M, Xie Z, Li X, Wang H, Zhao J, Lin C, Wang Y, Feng S, Shen J, Weng C, Lin W, Wang H, Zhou Q, Bi Y, Li M, Wang L, Zhu T, Huang X, Lan HY, Zhou J, Chen J (2016) Calcineurin inhibitors cyclosporin A and tacrolimus protect against podocyte injury induced by puromycin aminonucleoside in rodent models. Sci Rep 6:32087
Shengyou Y, Li Y, Zhihong H, Yuanyuan M (2015) Influence of tacrolimus on podocyte injury inducted by angiotensin II. J Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Syst 16(2):260–266
Allison AC (2005) Mechanisms of action of mycophenolate mofetil. Lupus 14[Suppl 1]:s2–s8
Karnell JL, Karnell FG 3rd, Stephens GL, Rajan B, Morehouse C, Li Y, Swerdlow B, Wilson M, Goldbach-Mansky R, Groves C, Coyle AJ, Herbst R, Ettinger R (2011) Mycophenolic acid differentially impacts B cell function depending on the stage of differentiation. J Immunol 187(7):3603–3612
Lv W, Lou J, Zhang Y, Lian P, Qi D, Wang J (2015) Mycophenolate mofetil inhibits hypertrophy and apoptosis of podocyte in vivo and in vitro. Int J Clin Exp Med 8(10):19781–19790
Kemper MJ, Lehnhardt A, Zawischa A, Oh J (2014) Is rituximab effective in childhood nephrotic syndrome? Yes and no. Pediatr Nephrol 29(8):1305–1311
Chan CY, Liu ID, Resontoc LP, Ng KH, Chan YH, Lau PY, Than M, Jordan SC, Lam KP, Yeo WS, Yap HK (2016) T lymphocyte activation markers as predictors of responsiveness to rituximab among patients with FSGS. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(8):1360–1368
Melet J, Mulleman D, Goupille P, Ribourtout B, Watier H, Thibault G (2013) Rituximab-induced T cell depletion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: association with clinical response. Arthritis Rheum 65(11):2783–2790
van de Veerdonk FL, Lauwerys B, Marijnissen RJ, Timmermans K, Di Padova F, Koenders MI, Gutierrez-Roelens I, Durez P, Netea MG, van der Meer JW, van den Berg WB, Joosten LA (2011) The anti-CD20 antibody rituximab reduces the Th17 cell response. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1507–1516
Byng-Maddick R, Ehrenstein MR (2015) The impact of biological therapy on regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54(5):768–775
Weiner GJ (2010) Rituximab: mechanism of action. Semin Hematol 47(2):115–123
Pateinakis P, Pyrpasopoulou A (2014) CD20+ B cell depletion in systemic autoimmune diseases: common mechanism of inhibition or disease-specific effect on humoral immunity? Biomed Res Int 2014:973609
Crook TR, Souhami RL, McLean AE (1986) Cytotoxicity, DNA cross-linking, and single strand breaks induced by activated cyclophosphamide and acrolein in human leukemia cells. Cancer Res 46(10):5029–5034
Maltzman JS, Koretzky GA (2003) Azathioprine: old drug, new actions. J Clin Invest 111(8):1122–1124
Eggleton P, Bremer E (2014) Direct and indirect rituximab-induced T cell depletion: comment on the article by Melet et Al. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(4):1053
Peired AJ, Sisti A, Romagnani P (2016) Mesenchymal stem cell-based therapy for kidney disease: a review of clinical evidence. Stem Cells Int 2016:4798639
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colucci, M., Corpetti, G., Emma, F. et al. Immunology of idiopathic nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol 33, 573–584 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3677-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-017-3677-5