Abstract
Background
Palmar hyperhidrosis involves excessive sweating of the palms, with no known etiology. Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) is a safe and effective treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis, but compensatory hyperhidrosis is a common complication after ETS, leading to reduced patient satisfaction and postoperative quality of life. However, the appropriate level of the sympathetic chain to target with ETS to achieve maximum efficacy and reduce the risk of compensatory hyperhidrosis (CH) is controversial. In this systemic review, we investigated the appropriate level of sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis.
Methods
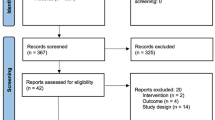
PRISMA guidelines were implemented to complete a systematic review. We performed a computerized systematic literature search using PubMed and EMBASE from January 1990 to July 2016. We chose the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool and the methodological index for non-randomized studies tool for examining study bias.
Results
A total of 4075 citations were identified, of which 91 were eligible for inclusion, including 68 observational studies and 23 comparative trials. In observational studies, sympathectomies showed similar efficacies for curing PH at different levels. However, T2-free groups (i.e., at levels T3, T4, or T3–T4 combined) could render a lower risk of Horner’s syndrome (0 vs. 1.21 ± 0.49%, p = 0.036) and CH (28.75 ± 7.25 vs. 57.46 ± 3.86, p = 0.002) compared with T2 involved. In comparative trials, there were 12 studies describing the comparison between T2-free ETS and T2 involved, and 9 of 12 (75%) showed T2-free ETS could reduce the incidence of CH. Overall, lowering the level and limiting the extent of sympathectomy could reduce the incidence of complications.
Conclusions
Cumulative data from more than 13,000 patients suggest that ETS is a safe, effective, and reproducible procedure with a high degree of patient satisfaction. Currently available evidence suggests that T2-free ETS may reduce the incidence of compensatory hyperhidrosis without compromising success rates and safety.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sato K (1991) Hyperhidrosis. JAMA 265(5):651
Sihoe AD, Liu RW, Lee AK, Lam CW, Cheng LC (2007) Is previous thoracic sympathectomy a risk factor for exertional heat stroke? Ann Thorac Surg 84(3):1025–1027
Nyamekye IK (2004) Current therapeutic options for treating primary hyperhidrosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 27(6):571–576
Gordon JR, Hill SE (2013) Update on pediatric hyperhidrosis. Dermatol Ther 26(6):452–461. doi:10.1111/dth.12104
Dogruk Kacar S, Ozuguz P, Eroglu S, Polat S, Karaca S (2014) Treatment of primary hyperhidrosis with tap water iontophoresis in paediatric patients: a retrospective analysis. Cutan Ocul Toxicol 33(4):313–316. doi:10.3109/15569527.2013.875559
Lakraj AA, Moghimi N, Jabbari B (2013) Hyperhidrosis: anatomy, pathophysiology and treatment with emphasis on the role of botulinum toxins. Toxins 5(4):821–840. doi:10.3390/toxins5040821
Grice K (1982) Special symposium on dermatological therapy: V. Diseases of the appendages. Treatment of hyperhidrosis. Clin Exp Dermatol 7(2):183–188
Naeini FF, Pourazizi M, Abtahi-Naeini B, Nilforoushzadeh MA, Najafian J (2015) A novel option for treatment of primary axillary hyperhidrosis: fractionated microneedle radiofrequency. J Postgrad Med 61(2):141–143. doi:10.4103/0022-3859.153111
Wang YC, Wei SH, Sun MH, Lin CW (2001) A new mode of percutaneous upper thoracic phenol sympathicolysis: report of 50 cases. Neurosurgery 49(3):628–634. (discussion 634–626)
Wong CW (1997) The second thoracic sympathetic ganglion determines palm skin temperature in patients with essential palmar hyperhidrosis. J Auton Nerv Syst 67(3):121–124
Kopelman D, Hashmonai M (2008) The correlation between the method of sympathetic ablation for palmar hyperhidrosis and the occurrence of compensatory hyperhidrosis: a review. World J Surg 32(11):2343–2356. doi:10.1007/s00268-008-9716-4
Deng B, Tan QY, Jiang YG, Zhao YP, Zhou JH, Ma Z, Wang RW (2011) Optimization of sympathectomy to treat palmar hyperhidrosis: the systematic review and meta-analysis of studies published during the past decade. Surg Endosc 25(6):1893–1901. doi:10.1007/s00464-010-1482-3
Moher D, Shamseer L, Clarke M, Ghersi D, Liberati A, Petticrew M, Shekelle P, Stewart LA (2015) Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 4:1. doi:10.1186/2046-4053-4-1
Higgins Jp T, Green S (2011) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Version 5.1.0. Wiley, Hoboken
Slim K, Nini E, Forestier D, Kwiatkowski F, Panis Y, Chipponi J (2003) Methodological index for non-randomized studies (minors): development and validation of a new instrument. ANZ J Surg 73(9):712–716
Chao C, Tsai CT, Hsiao HC, Wu WC, Lee CK (1993) Transaxillary endoscopic sympathectomy—a report of experience in 150 patients with palmar hyperhidrosis. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3(5):365–369
Chou SH, Lee SH, Kao EL (1993) Thoracic endoscopic T2-T3 sympathectomy in palmar hyperhidrosis: experience of 112 cases. Surg Today 23(2):105–107
Robertson DP, Simpson RK, Rose JE, Garza JS (1993) Video-assisted endoscopic thoracic ganglionectomy. J Neurosurg 79(2):238–240. doi:10.3171/jns.1993.79.2.0238
Wong CW (1997) Transthoracic video endoscopic electrocautery of sympathetic ganglia for hyperhidrosis palmaris: special reference to localization of the first and second ribs. Surg Neurol 47(3):224–229 discussion 229–230
Kopelman D, Hashmonai M, Ehrenreich M, Assalia A (1998) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: is there a learning curve? Surg Laparosc Endosc 8(5):370–375
Lin CL, Yen CP, Howng SL (1999) The long-term results of upper dorsal sympathetic ganglionectomy and endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Surg Today 29(3):209–213
Noppen M, D’Haese J, Dab I, Vincken W (1999) Thoracoscopic T2-T3 sympathicolysis for children with essential hyperhidrosis. J Bronchol 6(3):171–175
Goh PM, Cheah WK, De Costa M, Sim EK (2000) Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70(1):240–242
Yamamoto H, Kanehira A, Kawamura M, Okada M, Ohkita Y (2000) Needlescopic surgery for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 120(2):276–279. doi:10.1067/mtc.2000.107830
Johnson JP, Patel NP (2002) Uniportal and biportal endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. Neurosurgery 51(5 Suppl):S79–S83
Baumgartner FJ, Toh Y (2003) Severe hyperhidrosis: clinical features and current thoracoscopic surgical management. Ann Thorac Surg 76(6):1878–1883
Doblas M, Gutierrez R, Fontcuberta J, Orgaz A, Lopez P, Criado E (2003) Thoracodorsal sympathectomy for severe hyperhydrosis: posterior bilateral versus unilateral staged sympathectomy. Ann Vasc Surg 17(1):97–102. doi:10.1007/s10016-001-0343-x
Young O, Neary P, Keaveny TV, Mehigan D, Sheehan S (2003) Evaluation of the impact of transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy on patients with palmar hyperhydrosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 26(6):673–676. doi:10.1016/s1078
Georghiou GP, Berman M, Bobovnikov V, Vidne BA, Saute M (2004) Minimally invasive thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis via a transaxillary single-port approach. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 3(3):437–441. doi:10.1016/j.icvts.2004.03.003
Little AG (2004) Video-assisted thoracic surgery sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Arch Surg (Chicago, Ill:1960) 139(6):586–589. doi:10.1001/archsurg.139.6.586 (discussion 589)
Loscertales J, Arroyo Tristan A, Congregado Loscertales M, Jimenez Merchan R, Giron Arjona JC, Arenas Linares C, Ayarra Jarne J (2004) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Immediate results and postoperative quality of life. Arch Bronconeumol 40(2):67–71
de Campos JR, Wolosker N, Takeda FR, Kauffman P, Kuzniec S, Jatene FB, de Oliveira SA (2005) The body mass index and level of resection: predictive factors for compensatory sweating after sympathectomy. Clin Auton Res 15(2):116–120. doi:10.1007/s10286-005-0259-6
Elia S, Guggino G, Mineo D, Vanni G, Gatti A, Mineo TC (2005) Awake one stage bilateral thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a safe outpatient procedure. Eur J Cardio-thoracic Surg 28(2):312–317. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2005.03.046 (discussion 317)
Kumagai K, Kawase H, Kawanishi M (2005) Health-related quality of life after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 80(2):461–466. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.03.026
Licht PB, Pilegaard HK (2006) Gustatory side effects after thoracoscopic sympathectomy. Ann Thorac Surg 81(3):1043–1047. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.09.044
Assalia A, Bahouth H, Ilivitzki A, Assi Z, Hashmonai M, Krausz MM (2007) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: resection versus transection—a prospective trial. World J Surg 31(10):1976–1979. doi:10.1007/s00268-007-9160-x (discussion 1980–1971)
Libson S, Kirshtein B, Mizrahi S, Lantsberg L (2007) Evaluation of compensatory sweating after bilateral thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Tech 17(6):511–513. doi:10.1097/SLE.0b013e318136e3a1
Kwong KF, Hobbs JL, Cooper LB, Burrows W, Gamliel Z, Krasna MJ (2008) Stratified analysis of clinical outcomes in thoracoscopic sympathicotomy for hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 85 (2):390–393. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2007.08.001 (discussion 393–394)
Nakamura H, Haruki T, Adachi Y, Fujioka S, Miwa K, Taniguchi Y (2008) Patient satisfaction after endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Yonago Acta Medica 51(3):55–60
Rodriguez PM, Freixinet JL, Hussein M, Valencia JM, Gil RM, Herrero J, Caballero-Hidalgo A (2008) Side effects, complications and outcome of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis in 406 patients. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 34(3):514–519. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.05.036
Baumgartner FJ, Bertin S, Konecny J (2009) Superiority of thoracoscopic sympathectomy over medical management for the palmoplantar subset of severe hyperhidrosis. Ann Vasc Surg 23(1):1–7. doi:10.1016/j.avsg.2008.04.014
Fiorelli A, D’Aponte A, Canonico R, Palladino A, Vicidomini G, Limongelli F, Santini M (2012) T2-T3 sympathectomy versus sympathicotomy for essential palmar hyperhidrosis: comparison of effects on cardio-respiratory function. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 42(3):454–461. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezs071
Ibrahim M, Allam A (2014) Comparing two methods of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. JAAPA 27(9):1–4. doi:10.1097/01.JAA.0000453237.17130.6b
Vasseur Maurer S, De Buys Roessingh A, Reinberg O (2014) Thoracoscopic sympathectomies for primary palmar hyperhidrosis in children and adolescents. In: Swiss Medical Weekly, 26 May 2014, p 18S
Ravari H, Rajabnejad A (2015) Unilateral sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis. Available via Nlm
Youssef T, Soliman M (2015) Unilateral sequential endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a proposed technique to overcome compensatory hyperhidrosis and improve plantar hyperhidrosis. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 25(5):370–374. doi:10.1089/lap.2014.0620
Herbst F, Plas EG, Fugger R, Fritsch A (1994) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis of the upper limbs. A critical analysis and long-term results of 480 operations. Ann Surg 220(1):86–90
Shachor D, Jedeikin R, Olsfanger D, Bendahan J, Sivak G, Freund U (1994) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy in the treatment of primary hyperhidrosis. A review of 290 sympathectomies. Arch Surg (Chicago, Ill: 1960) 129(3):241–244
Al Dohayan A (1999) Transaxillary thoracoscopic sympathectomy experience in a hot climate: management of the dominant hand. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Tech 9(5):317–321
Vanaclocha V, Saiz-Sapena N, Panta F (2000) Uniportal endoscopic superior thoracic sympathectomy. Neurosurgery 46(4):924–928
Alric P, Branchereau P, Berthet JP, Leger P, Mary H, Mary-Ane C (2002) Video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: results in 102 cases. Ann Vasc Surg 16(6):708–713. doi:10.1007/s10016-001-0312-4
Dumont P, Denoyer A, Robin P (2004) Long-term results of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 78(5):1801–1807. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.03.012
Fujita T, Mano M, Nishi H, Shimizu N (2005) Intraoperative prediction of compensatory sweating for thoracic sympathectomy. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 53(9):481–485. doi:10.1007/s11748-005-0091-x
Sihoe AD, Cheung CS, Lai HK, Lee TW, Thung KH, Yim AP (2005) Incidence of chest wall paresthesia after needlescopic video-assisted thoracic surgery for palmar hyperhidrosis. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 27(2):313–319. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2004.10.038
Chen YB, Ye W, Yang WT, Shi L, Guo XF, Xu ZH, Qian YY (2009) Uniportal versus biportal video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Chin Med J 122(13):1525–1528
Flores LP (2012) Long-term outcomes associated to video-assisted thoracic sympathotomy for palmar-axillar subtype of the hyperhidrosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 70(6):398–403
Askari A, Kordzadeh A, Lee GH, Harvey M (2013) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis: a 16-year follow up in a single UK centre. Surg 11(3):130–133. doi:10.1016/j.surge.2012.09.002
Ibrahim M, Menna C, Andreetti C, Ciccone AM, D’Andrilli A, Maurizi G, Poggi C, Vanni C, Venuta F, Rendina EA (2013) Two-stage unilateral versus one-stage bilateral single-port sympathectomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 16(6):834–838. doi:10.1093/icvts/ivt039
Bell D, Jedynak J, Bell R (2014) Predictors of outcome following endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. ANZ J Surg 84(1–2):68–72. doi:10.1111/ans.12098
Bachmann K, Standl N, Kaifi J, Busch P, Winkler E, Mann O, Izbicki JR, Strate T (2009) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis: four-year outcome and quality of life after bilateral 5-mm dual port approach. Surg Endosc 23(7):1587–1593. doi:10.1007/s00464-009-0392-8
Duarte JB, Kux P (1998) Improvements in video-endoscopic sympathicotomy for the treatment of palmar, axillary, facial, and palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis. Eur J Surg Suppl 580:9–11
Lin CC (1992) Extended thoracoscopic T2-sympathectomy in treatment of hyperhidrosis: experience with 130 consecutive cases. J Laparoendosc Surg 2(1):1–6
Kao MC, Chern SH, Cheng LC, Hsiao YY, Lee YS, Tsai JC (1994) Video thoracoscopic laser sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Acad Med Singapore 23(1):38–42
Wu JJ, Hsu CC, Liao SY, Liu JC, Shih CJ (1996) Contralateral temperature changes of the finger surface during video endoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Auton Nerv Syst 59(3):98–102
Chu D, Shi PK, Wu CM (1997) Transthoracic endoscopic sympathectomy for treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 13(3):162–168
Fox AD, Hands L, Collin J (1999) The results of thoracoscopic sympathetic trunk transection for palmar hyperhidrosis and sympathetic ganglionectomy for axillary hyperhidrosis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 17(4):343–346. doi:10.1053/ejvs.1998.0783
Hsia JY, Chen CY, Hsu CP, Shai SE, Yang SS (1999) Outpatient thoracoscopic limited sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis palmaris. Ann Thorac Surg 67(1):258–259
Lu K, Liang CL, Cho CL, Cheng CH, Yen HL, Rau CS, Tsai YD, Chen HJ, Lee TC (2000) Patterns of palmar skin temperature alterations during transthoracic endoscopic T2 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Auton Neurosci 86(1–2):99–106. doi:10.1016/s1566-0702(00)00202-2
Lin TS, Kuo SJ, Chou MC (2002) Uniportal endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for treatment of palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis: analysis of 2000 cases. Neurosurgery 51(5 Suppl):S84–S87
Chiou TS (2005) Chronological changes of postsympathectomy compensatory hyperhidrosis and recurrent sweating in patients with palmar hyperhidrosis. J Neurosurg Spine 2(2):151–154. doi:10.3171/spi.2005.2.2.0151
Singh B, Moodley J, Allopi L, Cassimjee HM (2006) Horner syndrome after sympathectomy in the thoracoscopic era. Surgical Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Tech 16 (4):222–225
Atkinson JL, Fode-Thomas NC, Fealey RD, Eisenach JH, Goerss SJ (2011) Endoscopic transthoracic limited sympathotomy for palmar-plantar hyperhidrosis: outcomes and complications during a 10-year period. Mayo Clin Proc 86(8):721–729. doi:10.4065/mcp.2011.0199
Drott C (2003) Results of endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy (ETS) on hyperhidrosis, facial blushing, angina pectoris, vascular disorders and pain syndromes of the hand and arm. Clin Auton Res 13(Suppl 1):I26–I30
Schmidt J, Bechara FG, Altmeyer P, Zirngibl H (2006) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for severe hyperhidrosis: impact of restrictive denervation on compensatory sweating. Ann Thorac Surg 81(3):1048–1055
Yoon DH, Ha Y, Park YG, Chang JW (2003) Thoracoscopic limited T-3 sympathicotomy for primary hyperhidrosis: prevention for compensatory hyperhidrosis. J Neurosurg 99(1 Suppl):39–43
Dewey TM, Herbert MA, Hill SL, Prince SL, Mack MJ (2006) One-year follow-up after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: outcomes and consequences. Annals Thorac Surg 81(4):1227–1232. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2005.11.006 (discussion 1232–1223)
Prasad A, Ali M, Kaul S (2010) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperidrosis. Surg Endosc 24(8):1952–1957. doi:10.1007/s00464-010-0885-5
Zhu LH, Chen L, Yang S, Liu D, Zhang J, Cheng X, Chen W (2013) Embryonic NOTES thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: results of a novel technique and comparison with the conventional VATS procedure. Surg Endosc 27(11):4124–4129. doi:10.1007/s00464-013-3079-0
Apiliogullari B, Esme H, Yoldas B, Duran M, Duzgun N, Calik M (2012) Early and midterm results of single-port video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 60(4):285–289. doi:10.1055/s-0032-1304541
Chou SH, Kao EL, Li HP, Lin CC, Huang MF (2005) T4 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: an effective approach that simultaneously minimizes compensatory hyperhidrosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 21(7):310–313
Chou SH, Kao EL, Lin CC, Chang YT, Huang MF (2006) The importance of classification in sympathetic surgery and a proposed mechanism for compensatory hyperhidrosis: experience with 464 cases. Surg Endosc 20(11):1749–1753. doi:10.1007/s00464-005-0829-7
Wang FG, Chen YB, Yang WT, Shi L (2011) Comparison of compensatory sweating and quality of life following thoracic sympathetic block for palmar hyperhidrosis: electrocautery hook versus titanium clip. Chin Med J 124(21):3495–3498
Panhofer P, Gleiss A, Eilenberg WH, Jakesz R, Bischof G, Neumayer C (2013) Long-term outcomes after endothoracic sympathetic block at the T4 ganglion for upper limb hyperhidrosis. Br J Surg 100(11):1471–1477. doi:10.1002/bjs.9275
Purtuloglu T, Atim A, Deniz S, Kavakli K, Sapmaz E, Gurkok S, Kurt E, Turan A (2013) Effect of radiofrequency ablation and comparison with surgical sympathectomy in palmar hyperhidrosis. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 43(6):e151–e154. doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezt024
Chen JF, Lin JB, Tu YR, Lin M, Li X, Lai FC, Du Q, Dai YD (2015) Nonintubated transareolar single-port thoracic sympathicotomy with a needle scope in a series of 85 male patients. Surg Endosc. doi:10.1007/s00464-015-4628-5
Chen JF, Lin M, Chen P, Quan D, Li X, Lai FC, Tu YR (2016) Nonintubated needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized controlled trial. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Tech 26(4):328–333. doi:10.1097/sle.0000000000000287
Licht PB, Clausen A, Ladegaard L (2010) Resympathicotomy. Ann Thorac Surg 89(4):1087–1090
Yoon SH, Rim DC (2003) The selective T3 sympathicotomy in patients with essential palmar hyperhidrosis. Acta neurochirurgica 145 (6):467–471. doi:10.1007/s00701-003-0011-8 (discussion 471)
Yano M, Kiriyama M, Fukai I, Sasaki H, Kobayashi Y, Mizuno K, Haneda H, Suzuki E, Endo K, Fujii Y (2005) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: efficacy of T2 and T3 ganglion resection. Surgery 138(1):40–45. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2005.03.026
Reisfeld R (2006) Sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: should we place the clamps at T2-T3 or T3-T4? Clinical Auton Res 16(6):384–389. doi:10.1007/s10286-006-0374-z
Chang YT, Li HP, Lee JY, Lin PJ, Lin CC, Kao EL, Chou SH, Huang MF (2007) Treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis: T(4) level compared with T(3) and T(2). Ann Surg 246(2):330–336. doi:10.1097/SLA.0b013e3180caa466
Katara AN, Domino JP, Cheah WK, So JB, Ning C, Lomanto D (2007) Comparing T2 and T2-T3 ablation in thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial. Surg Endosc 21(10):1768–1771. doi:10.1007/s00464-007-9241-9
Yang J, Tan JJ, Ye GL, Gu WQ, Wang J, Liu YG (2007) T3/T4 thoracic sympathictomy and compensatory sweating in treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis. Chin Med J 120(18):1574–1577
Inan K, Goksel OS, Ucak A, Temizkan V, Karaca K, Ugur M, Arslan G, Us M, Yilmaz AT (2008) Thoracic endoscopic surgery for hyperhidrosis: comparison of different techniques. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 56(4):210–213. doi:10.1055/s-2007-989327
Li X, Tu YR, Lin M, Lai FC, Chen JF, Dai ZJ (2008) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial comparing T3 and T2-4 ablation. Ann Thorac Surg 85(5):1747–1751. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2008.01.060
Mahdy T, Youssef T, Elmonem HA, Omar W, Elateef AA (2008) T4 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: looking for the right operation. Surgery 143(6):784–789. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2008.01.007
Wolosker N, Yazbek G, Ishy A, de Campos JR, Kauffman P, Puech-Leao P (2008) Is sympathectomy at T4 level better than at T3 level for treating palmar hyperhidrosis? J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 18(1):102–106. doi:10.1089/lap.2007.0030
Liu Y, Yang J, Liu J, Yang F, Jiang G, Li J, Huang Y, Wang J (2009) Surgical treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized study comparing T3 and T4 sympathicotomy. Eur J Cardio Thorac Surg 35(3):398–402. doi:10.1016/j.ejcts.2008.10.048
Miller DL, Bryant AS, Force SD, Miller JI Jr (2009) Effect of sympathectomy level on the incidence of compensatory hyperhidrosis after sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 138(3):581–585. doi:10.1016/j.jtcvs.2009.03.059
Yazbek G, Wolosker N, Kauffman P, Campos JR, Puech-Leao P, Jatene FB (2009) Twenty months of evolution following sympathectomy on patients with palmar hyperhidrosis: sympathectomy at the T3 level is better than at the T2 level. Clinics 64(8):743–749. doi:10.1590/s1807-59322009000800006
Kim WO, Kil HK, Yoon KB, Yoon DM, Lee JS (2010) Influence of T3 or T4 sympathicotomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Am J Surg 199(2):166–169. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.12.024
Baumgartner FJ, Reyes M, Sarkisyan GG, Iglesias A, Reyes E (2011) Thoracoscopic sympathicotomy for disabling palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized comparison between two levels. Ann Thorac Surg 92(6):2015–2019. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.07.083
Ishy A, de Campos JR, Wolosker N, Kauffman P, Tedde ML, Chiavoni CR, Jatene FB (2011) Objective evaluation of patients with palmar hyperhidrosis submitted to two levels of sympathectomy: T3 and T4. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 12(4):545–548. doi:10.1510/icvts.2010.252015
Scognamillo F, Serventi F, Attene F, Torre C, Paliogiannis P, Pala C, Trignano E, Trignano M (2011) T2-T4 sympathectomy versus T3-T4 sympathicotomy for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis. Clin Auton Res 21(2):97–102. doi:10.1007/s10286-010-0110-6
Umezawa A, Seki Y, Kasama K, Negishi Y, Kurokawa Y (2011) Outcome comparing t3-t4 with t2-t4 sympathectomy for palmer hyperhidrosis. In: Surgical endoscopy and other interventional techniques, Springer, Berlin, p S51
Vicidomini G, Fiorelli A, Milione R, Napolitano F, Santini M (2011) Long-term outcomes after video-assisted thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: A prospective study comparing T3 and T2-T4 ablation. In: Interactive cardiovascular and thoracic surgery, p S48
Abd Ellatif ME, Hadidi AE, Musa AM, Askar W, Abbas A, Negm A, Moatamed A, Dawoud I (2014) Optimal level of sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: T3 versus T4 in a retrospective cohort study. Int J Surg 12(8):778–782. doi:10.1016/j.ijsu.2014.05.039
Cai S, Huang S, An J, Li Y, Weng Y, Liao H, Chen H, Liu L, He J, Zhang J (2014) Effect of lowering or restricting sympathectomy levels on compensatory sweating. Clin Auton Res 24(3):143–149. doi:10.1007/s10286-014-0242-1
Yang Y, Yan Z, Fu X, Dong L, Xu L, Wang J, Cheng G (2014) The clinical study of the optimalization of surgical treatment and the traditional Chinese medicine intervention on palmar hyperhidrosis. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(2):1401–1405. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-0070-x
Joo S, Lee GD, Haam S, Lee S (2016) Comparisons of the clinical outcomes of thoracoscopic sympathetic surgery for palmar hyperhidrosis: R4 sympathicotomy versus R4 sympathetic clipping versus R3 sympathetic clipping. J Thorac Dis 8(5):934–941. doi:10.21037/jtd.2016.03.57
Lin CC, Telaranta T (2001) Lin-Telaranta classification: the importance of different procedures for different indications in sympathetic surgery. Annales chirurgiae et gynaecologiae 90(3):161–166
Cerfolio RJ, De Campos JR, Bryant AS, Connery CP, Miller DL, DeCamp MM, McKenna RJ, Krasna MJ (2011) The Society of Thoracic Surgeons expert consensus for the surgical treatment of hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 91(5):1642–1648. doi:10.1016/j.athoracsur.2011.01.105
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81172786) and Youth Chenguang project of Science and Technology of Wuhan City (Grant No. 201050231077).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Hai-Wei Sang, Guo-Liang Li, Peng Xiong, Ming-Chuang Zhu and Min Zhu have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Additional information
Hai-Wei Sang and Guo-Liang Li have contributed equally to this work and should be regarded as co-first authors.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sang, HW., Li, GL., Xiong, P. et al. Optimal targeting of sympathetic chain levels for treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis: an updated systematic review. Surg Endosc 31, 4357–4369 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5508-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5508-y