Abstract
Background
Thoracoscopic sympathectomy is a useful therapeutic option for palmar hyperhidrosis. Surgeons differ in the level of the sympathetic chain ablated. This study aimed to compare the blockade of the T2 with levels T2 and T3 to verify the effectiveness of different ablation levels in relieving hyperhidrosis symptoms.
Methods
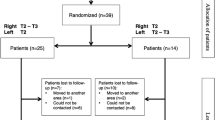
For patients undergoing bilateral thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis, T2–T3 ablation is performed bilaterally. In our series, 25 consecutive patients were blindly randomized to undergo unilateral T2 and T3 ablation followed by contralateral ablation of level T2 only. The patients were followed up and analyzed for comparison of symptoms bilaterally, compensatory hyperhidrosis, and levels of satisfaction postoperatively.
Results
The study group consisted of 25 patients with a male:female ratio of 3:2 and a mean age of 32 years (range, 19–50 years). The mean operative time was 35 min. The patients were followed up for a mean period of 23 months (range, 2–65 months). All 25 patients confirmed that their palmar sweating resolved postoperatively, with both palms equally dry. Of the 25 patients, 20 (80%) complained of compensatory hyperhidrosis, which also was bilaterally symmetric. The areas involved were trunk (80%), lower limbs (32%), and armpits (12%). Overall, 80% of the patients were very satisfied with the procedure. The remaining 20% experienced mild to moderate compensatory hyperhidrosis, which did not seem to affect their lifestyle.
Conclusion
The findings show that T2 ablation in thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis is as effective as T2–T3 ablation in terms of symptomatic relief, recurrence, compensatory hyperhidrosis, and patient satisfaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adar R, Kurchin A, Xzweig A, Moses M (1977) Palmar hyperhydrosis and its surgical connections. Ann Surg 186: 34–41
Aldohayan A (1999) Highly selective thoracoscopic sympathectomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 16(Suppl 1): s129
Andrews BT, Rennie JA (1997) Predicting changes in the distribution of sweating following thoracoscopic sympathectomy. Br J Surg 84: 1702–1704
Claes G, Drott C, Göthberg G (1993) Endoscopic electrocautery of the thoracic sympathetic chain: a minimally invasive way to treat palmar hyperhidrosis. Scand J Plast Reconstr Hand Surg 27: 29–33
Goh PM, Cheah WK, De Costa M, Sim EK (2000) Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70: 240–242
Gossot D, Kabiri H, Caliandro R, Debrosse D, Girard P, Grunenwald D (2001) Early complications of thoracic endoscopic sympathectomy: a prospective study of 940 procedures. Ann Thorac Surg 71: 1116–1119
Gossot D, Toledo L, Fritsch S, Célérier M (1997) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for upper limb hyperhidrosis: looking for the right operation. Ann Thorac Surg 64: 975–978
Herbst F, Plas EG, Fugger R, Fritsch A (1994) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for primary hyperhidrosis of the upper limbs: a critical analysis and long-term results of 480 operations. Ann Surg 220: 86–90
Hsia JY, Chen CY, Hsu CP, Shai SE, Yang SS (1999) Outpatient thoracoscopic limited sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis palmaris. Ann Thorac Surg 67: 258–259
Hughes J (1942) Endoscopic sympathectomy. Proc R Soc Med 35: 585–586
Hukkei I, Kuroiwa T (1958) Thoracic sympathetic ganglia cauterization (in Japanese). Kyobu Geka 11: 123–141
Kux E (1951) The endoscopic approach to the vegetative nerve system and its therapeutic possibilities. Dis Chest 20: 139–147
Leao LE, de Oliveira R, Szulc R, Mari Jde J, Crotti PL, Goncalves JJ (2003) Role of video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy in the treatment of primary hyperhidrosis. Sao Paulo Med J 121: 191–197
Lin CC, Mo LR, Lee LS, Ng SM, Hwang MH (1998) Thoracoscopic T2-sympathetic block by clipping a better and reversible operation for treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris: experience with 326 cases. Eur J Surg Suppl (580): 13–16
Ojimba TA, Cameron AEP (2004) Drawbacks of endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. Br J Surg 91: 264–269
Okura T, Suzuki T, Suzuki S, Kitami A, Hori G (1998) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy with a fine (2-mm) thoracoscope in palmar hyperhidrosis: a case report. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 8: 161–165
Reisfield R, Nguyen R, Pnini A (2002) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis: experience with both cauterization and clamming methods. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 12: 255–267
Robert A, Edmondson FRCS, Anjan K, et al (1991) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy in the treatment of hyperhydrosis. Ann Surg 215: 289–293
Telaranta T (1998) Treatment of social phobia by endoscopic thoracic sympathicotomy. Eur J Surg Suppl 580: 27–32
Ueyama T, Ueyama K, Ueyama K, Matsumoto Y (2004) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hand sweating. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 10: 4–8
Yano M, Kiriyama M, Fukai I, et al. (2005) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: efficacy of T2 and T3 ganglion resection. Surgery 138: 40–45
Yim AP, Liu HP, Lee TW, Wan S, Arifi AA (2000) “Needlescopic” video-assisted thoracic surgery for palmar hyperhidrosis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 17: 697–701
Zacherl J, Huber ER, Imhof M, Plas EG, Herbst F, Függer R (1998) Long-term results of 630 thoracoscopic sympathicotomies for primary hyperhidrosis: the Vienna experience. Eur J Surg Suppl 580: 43–46
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katara, A.N., Domino, J.P., Cheah, WK. et al. Comparing T2 and T2–T3 ablation in thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial. Surg Endosc 21, 1768–1771 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9241-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-007-9241-9