Abstract
Objective
The systemic review and meta-analysis of the studies published during the past 10 years was designed to optimize the surgical procedures of video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy (VTS) to treat palmar hyperhidrosis (PH).
Methods
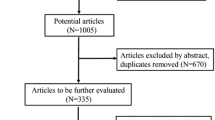
Citations from 2000 to 2010 were included regarding the following aspects: selection of ganglia level for VTS, comparison of different techniques for VTS, evaluating clinical efficacy of intraoperative intrapleural analgesia, and postoperative intrapleural drainage. Major clinical outcomes are defined as: cases with postoperative resolution of symptoms, total cases with postoperative compensatory hyperhidrosis (CH), cases with severe or moderate CH, satisfied cases, evaluation of postoperative pain, and postoperative pneumothorax.
Results
Systemic review indicates that T3 and T3–4 sympathectomy had the “best” clinical efficacy. Meta-analysis suggests that efficacious rates of PH are nearly similar compared with multiple and single ganglia sympathectomy (100 vs. 95.6%). However, single-ganglia sympathectomy can render a lower risk of total CH compared with multiple-ganglia block. Risk of moderate/severe CH has a similar trend. Additionally, single-ganglia sympathectomy is more potent to satisfy patients postoperatively. One randomized, controlled trial (RCT) that compared different techniques for VTS indicated that the overall success rate of the operation was 95% and the differences were not statistically significant. Two RCTs indicated that there were significant differences between trial group (intraoperative intercostal nerve blocks using bupivacaine) and control group regarding the attenuation of postoperative pain. One RCT suggested that there was no significant difference with or without pleural drainage regarding the incidence of postoperative residual pneumothorax.
Conclusions
T3 sympathectomy is supposed to be recommended for the treatment of PH regardless of using various techniques. Intraoperative intrapleural analgesia using bupivacaine or bupivacaine plus epinephrine is effective to prevent postoperative pain. Pleural drainage after VTS should be abandoned.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rajesh YS, Pratap CP, Woodyer AB (2002) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis and Raynaud’s phenomenon of the upper limb and excessive facial blushing: a 5-year experience. Postgrad Med J 78(925):682–684
Kux M (1978) Thoracic endoscopic sympathectomy in palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis. Arch Surg 113(3):264–266
Gossot D, Kabiri H, Caliandro R, Debrosse D, Girard P, Grunenwald D (2001) Early complications of thoracic endoscopic sympathectomy: a prospective study of 940 procedures. Ann Thorac Surg 71(4):1116–1119
Neumayer CH, Bischof G, Fugger R, Imhof M, Jakesz R, Plas EG, Herbst FR, Zacherl J (2001) Efficacy and safety of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis of the upper limb. Results of 734 sympathectomies. Ann Chir Gynaecol 90(3):195–199
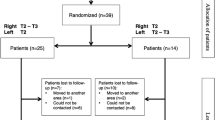
Katara AN, Domino JP, Cheah WK, So JB, Ning C, Lomanto D (2007) Comparing T2 and T2–T3 ablation in thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial. Surg Endosc 21(10):1768–1771
Lin M, Tu YR, Li X, Lai FC, Chen JF, Dai ZJ (2006) Comparison of curative effects of sympathectomy at different segments on palmar hyperhidrosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86(33):2315–2317
Yoon DH, Ha Y, Park YG, Chang JW (2003) Thoracoscopic limited T-3 sympathicotomy for primary hyperhidrosis: prevention for compensatory hyperhidrosis. J Neurosurg 99(1 Suppl):39–43
Liu Y, Yang J, Liu J, Yang F, Jiang G, Li J, Huang Y, Wang J (2009) Surgical treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective randomized study comparing T3 and T4 sympathicotomy. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 35(3):398–402
Li X, Tu YR, Lin M, Lai FC, Chen JF, Dai ZJ (2008) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a randomized control trial comparing T3 and T2–4 ablation. Ann Thorac Surg 85(5):1747–1751
Yang J, Tan JJ, Ye GL, Gu WQ, Wang J, Liu YG (2007) T3/T4 thoracic sympathictomy and compensatory sweating in treatment of palmar hyperhidrosis. Chin Med J (Engl) 120(18):1574–1577
Liu YG, Yang J, Wang J, Liu J, Li JF, Jiang GC, Huang YQ, Yang F, Zhao H (2006) A comparison of T3 sympathectomy versus T4 sympathectomy in the treatment of primary palmer hyperhidrosis. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 86(33):2318–2320
Drott C, Gothberg G, Claes G (1995) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy: an efficient and safe method for the treatment of hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 33(1):78–81
Byrne J, Walsh TN, Hederman WP (1990) Endoscopic transthoracic electrocautery of the sympathetic chain for palmar and axillary hyperhidrosis. Br J Surg 77(9):1046–1049
Lin CC, Mo LR, Lee LS, Ng SM, Hwang MH (1998) Thoracoscopic T2-sympathetic block by clipping: a better and reversible operation for treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris: experience with 326 cases. Eur J Surg 164(580):13–16
Kavanagh BP, Katz J, Sandler AN (1994) Pain control after thoracic surgery. A review of current techniques. Anesthesiology 81(3):737–759
Raffin L, Fletcher D, Sperandio M, Antoniotti C, Mazoit X, Bisson A, Fischler M (1994) Interpleural infusion of 2% lidocaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine for postthoracotomy analgesia. Anesth Analg 79(2):328–334.
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D, Jenkinson C, Reynolds DJM, Gavaghan DJ, McQuay HJ (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: Is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17(1):1–12
Inan K, Goksel OS, Ucak A, Temizkan V, Karaca K, Ugur M, Arslan G, Us M, Yilmaz AT (2008) Thoracic endoscopic surgery for hyperhidrosis: comparison of different techniques. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 56(4):210–213
Bolotin G, Lazarovici H, Uretzky G, Zlotnick AY, Tamir A, Saute M (2000) The efficacy of intraoperative internal intercostal nerve block during video-assisted thoracic surgery on postoperative pain. Ann Thorac Surg 70(6):1872–1875
Assalia A, Kopelman D, Markovits R, Hashmonai M (2003) Intrapleural analgesia following thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: a prospective, randomized trial. Surg Endosc 17(6):921–922
Lima AG, Marcondes GA, Teixeira AB, Toro IF, Campos JR, Jatene FB (2008) The incidence of residual pneumothorax after video-assisted sympathectomy with and without pleural drainage and its effect on postoperative pain. J Bras Pneumol 34(3):136–142
Schmidt J, Bechara FG, Altmeyer P, Zirngibl H (2006) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for severe hyperhidrosis: Impact of restrictive denervation on compensatory sweating. Ann Thorac Surg 81(3):1048–1055
de Campos JRM, Kauffman P, Werebe ED, Andrade LO, Kusniek S, Wolosker N, Jatene FB (2003) Quality of life, before and after thoracic sympathectomy: Report on 378 operated patients. Ann Thorac Surg 76(3):886–891
Ueyama T, Ueyama K, Ueyama K, Matsumoto Y (2004) Thoracoscopic sympathetic surgery for hand sweating. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 10(1):4–8
Goh PMY, Cheah WK, De Costa M, Sim EKW (2000) Needlescopic thoracic sympathectomy: treatment for palmar hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 70(1):240–242
Gossot D, Toledo L, Fritsch S, Celerier M (1997) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for upper limb hyperhidrosis: looking for the right operation. Ann Thorac Surg 64(4):975–978
Hsia JY, Chen CY, Hsu CP, Shai SE, Yang SS (1999) Outpatient thoracoscopic limited sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis palmaris. Ann Thorac Surg 67(1):258–259
Riegler FX, VadeBoncouer TR, Pelligrino DA (1989) Interpleural anesthetics in the dog: differential somatic neural blockade. Anesthesiology 71(5):744–750
McIlvaine WB (1996) Pro: intrapleural anesthesia is useful for thoracic analgesia. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth 10(3):425–428
Lu K, Liang CL, Cho CL, Cheng CH, Yen HL, Rau CS, Tsai YD, Chen HJ, Lee TC (2000) Patterns of palmar skin temperature alterations during transthoracic endoscopic T2 sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis. Auton Neurosci 86(1–2):99–106
Neumayer C, Zacherl J, Holak G, Jakesz R, Bischof G (2003) Experience with limited endoscopic thoracic sympathetic block for hyperhidrosis and facial blushing. Clin Auton Res 13(Suppl 1):I52–57
Schick CH, Fronek K, Held A, Birklein F, Hohenberger W, Schmelz M (2003) Differential effects of surgical sympathetic block on sudomotor and vasoconstrictor function. Neurology 60(11):1770–1776
Yazbek G, Wolosker N, de Campos JR, Kauffman P, Ishy A, Puech-Leao P (2005) Palmar hyperhidrosis–which is the best level of denervation using video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathectomy: T2 or T3 ganglion? J Vasc Surg 42(2):281–285
Eisenach JH, Pike TL, Wick DE, Dietz NM, Fealey RD, Atkinson JL, Charkoudian N (2005) A comparison of peripheral skin blood flow and temperature during endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy. Anesth Analg 100(1):269–276
Llado A, Leon L, Valls-Sole J, Mena P, Callejas MA, Peri JM (2005) Changes in the sympathetic skin response after thoracoscopic sympathectomy in patients with primary palmar hyperhidrosis. Clin Neurophysiol 116(6):1348–1354
Ting H, Lee SD, Chung AH, Chuang ML, Chen GD, Liao JM, Chang CL, Chiou TS, Lin TB (2005) Effects of bilateral T2-sympathectomy on static and dynamic heart rate responses to exercise in hyperhidrosis patients. Auton Neurosci 121(1–2):74–80
Yano M, Kiriyama M, Fukai I, Sasaki H, Kobayashi Y, Mizuno K, Haneda H, Suzuki E, Endo K, Fujii Y (2005) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: efficacy of T2 and T3 ganglion resection. Surgery 138(1):40–45
Leis S, Meyer N, Bickel A, Schick CH, Kruger S, Schmelz M, Birklein F (2010) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy at the T2 or T3 level facilitates bradykinin-induced protein extravasation in human forearm skin. Pain Med 11(5):774–780
Riet M, Smet AA, Kuiken H, Kazemier G, Bonjer HJ (2001) Prevention of compensatory hyperhidrosis after thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Surg Endosc 15(10):1159–1162
Yoon SH, Rim DC (2003) The selective T3 sympathicotomy in patients with essential palmar hyperhidrosis. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145(6):467–471 (discussion 471)
Gazelius B, Stange K, Lind G, Meyerson BA, Linderoth B (2002) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathicotomy and peripheral microcirculation: effects of electric sympathetic chain stimulation, thermocoagulation and anaesthetic agents. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 144(6):589–594
Baumgartner FJ, Toh Y (2003) Severe hyperhidrosis: clinical features and current thoracoscopic surgical management. Ann Thorac Surg 76(6):1878–1883
Kawamata YT, Kawamata T, Omote K, Homma E, Hanzawa T, Kaneko T, Namiki A (2004) Endoscopic thoracic sympathectomy suppresses baroreflex control of heart rate in patients with essential hyperhidrosis. Anesth Analg 98(1):37–39
de Campos JR, Wolosker N, Takeda FR, Kauffman P, Kuzniec S, Jatene FB, de Oliveira SA (2005) The body mass index and level of resection: predictive factors for compensatory sweating after sympathectomy. Clin Auton Res 15(2):116–120
Sihoe AD, Manlulu AV, Lee TW, Thung KH, Yim AP (2007) Pre-emptive local anesthesia for needlescopic video-assisted thoracic surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 31(1):103–108
Inbar O, Leviel D, Shwartz I, Paran H, Whipp BJ (2008) Thoracic sympathectomy and cardiopulmonary responses to exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 104(1):79–86
Wait SD, Killory BD, Lekovic GP, Dickman CA (2010) Biportal thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis in adolescents. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6(2):183–187
Kingma R, TenVoorde BJ, Scheffer GJ, Karemaker JM, Mackaay AJ, Wesseling KH, de Lange JJ (2002) Thoracic sympathectomy: effects on hemodynamics and baroreflex control. Clin Auton Res 12(1):35–42
Disclosures
Drs. Bo Deng, Qun-You Tan, Ru-Wen Wang, Yao-Guang Jiang, Yun-Ping Zhao, Jing-Hai Zhou and Zheng Ma have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The authors wish it to be known publicly that the first two authors (Bo Deng and Qun-You Tan) should be regarded as joint first authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, B., Tan, QY., Jiang, YG. et al. Optimization of sympathectomy to treat palmar hyperhidrosis: the systematic review and meta-analysis of studies published during the past decade. Surg Endosc 25, 1893–1901 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1482-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-010-1482-3