Abstract
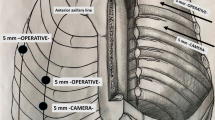
Upper dorsal sympathectomy is the only successful therapeutic method for idiopathic palmar hyperhidrosis (IPHH). However, the techniques for sympathetic ablation are still debated. The aim of this study was to compare prospectively two accepted methods for endoscopic sympathetic ablation: resection of T2-T3 ganglia versus transection of the chain over the second to fourth ribs. During the period September 2000 to June 2002, a total of 32 patients with IPHH were operated on. Operations were performed under general anesthesia through two 5-mm trocars using electrocautery. Resection was done on one side and transection on the other, with both sides being addressed during the same operation. The sides of resection/transection were alternated at each operation. There were 14 men and 18 women aged 18.8 ± 4.7 years. The mean operating times for sympathectomy were 12.0 ± 3.1 minutes for resection and 6.6 ± 1.9 minutes for transection (p = 1.38). All patients were examined at 2 weeks postoperatively and again at 1 month. During November–December 2005, patients were approached by telephone questionnaire, the mean follow-up period being 4.3 ± 0.9 years. Altogether, 26 of the 32 patients could be located (15 women, 11 men). There was no significant difference with regards to perioperative complications, immediate or long-term pain. All but two hands were warm and dry 1 month after operation and remained so at follow-up. The exceptions included one hand with recurrent hyperhidrosis after 1.5 years and one that became less dry and cold at 3 years. Both were on the transected sides. Our results suggest that sympathetic resection may achieve slightly better long-term results than transection in patients with IPHH. Large-scale prospective studies are needed to confirm these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dumont P, Denoyer A, Robin P (2004) Long-term results of thoracoscopic sympathectomy for hyperhidrosis. Ann Thorac Surg 78:1801–1807
Hashmonai M, Kopelman D, Assalia A (2000) The treatment of primary palmar hyperhidrosis: a review. Surg Today 30:211–218
Hashmonai M, Kopelman D, Schein M (1993) Thoracoscopic versus open supraclavicular upper dorsal sympathectomy: a prospective randomized trial. Eur J Surg Suppl 572:13–16
Hashmonai M, Assalia A, Kopelman D (2001) Thoracoscopic sympathectomy for palmar hyperhidrosis: ablate or resect? Surg Endosc 15:435–441
Chao C, Tsai CT, Hsiao HC, et al (1993) Transaxillary endoscopic sympathectomy: a report of experience in 150 patients with palmar hyperhidrosis. Surg Laparosc Endosc 3:365–369
Pillay PK, Thomas J, Mack P (1994) Thoracoscopic ganglionectomy for hyperhidrosis. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 63:198–202
Drott C, Gothberg G, Claes G (1995) Endoscopic transthoracic sympathectomy: an efficient and safe method for the treatment of hyperhidrosis. J Am Acad Dermatol 33:78–81
Hashmonai M, Kopelman D, Klein O, et al. (1992) Upper thoracic sympathectomy for primary palmar hyperhidrosis: long-term follow up. Br J Surg 79:268–271
Haxton HA (1970) Upper limb resympathectomy. Br J Surg 57:106–108
Linn CC, Mo LR, Lee LS, et al. (1998) Thoracoscopic T2 sympathetic block by clipping: a better and reversible operation for treatment of hyperhidrosis palmaris—experience with 326 patients. Eur J Surg 164:13–16
Linn TS (2001) Endoscopic clipping in video-assisted thoracoscopic sympathetic blockade for axillary hyperhidrosis: an analysis of 26 cases. Surg Endosc 15:126–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was presented as an oral presentation at the 14th International Congress of the European Association of Endoscopic Surgery, Berlin, September 2006.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Assalia, A., Bahouth, H., Ilivitzki, A. et al. Thoracoscopic Sympathectomy for Primary Palmar Hyperhidrosis: Resection Versus Transection—A Prospective Trial. World J Surg 31, 1976–1979 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9160-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-007-9160-x