Abstract
Ovarian cancer (OC) is a fatal gynecological disease that is often diagnosed at later stages due to its asymptomatic nature and the absence of efficient early-stage biomarkers. Previous studies have identified genes with abnormal expression in OC that couldn’t be explained by methylation or mutation, indicating alternative mechanisms of gene regulation. Recent advances in human transcriptome studies have led to research on non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) as regulators of cancer gene expression. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), a class of ncRNAs with a length greater than 200 nucleotides, have been identified as crucial regulators of physiological processes and human diseases, including cancer. Dysregulated lncRNA expression has also been found to play a crucial role in ovarian carcinogenesis, indicating their potential as novel and non-invasive biomarkers for improving OC management. However, despite the discovery of several thousand lncRNAs, only one has been approved for clinical use as a biomarker in cancer, highlighting the importance of further research in this field. In addition to their potential as biomarkers, lncRNAs have been implicated in modulating chemoresistance, a major problem in OC. Several studies have identified altered lncRNA expression upon drug treatment, further emphasizing their potential to modulate chemoresistance. In this review, we highlight the characteristics of lncRNAs, their function, and their potential to serve as tumor markers in OC. We also discuss a few databases providing detailed information on lncRNAs in various cancer types. Despite the promising potential of lncRNAs, further research is necessary to fully understand their role in cancer and develop effective strategies to combat this devastating disease.


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
References
Abildgaard C, Canto LM, Rainho CA et al (2022) The long non-coding RNA SNHG 12 as a mediator of carboplatin resistance in ovarian cancer via epigenetic mechanisms. Cancers 14:1664. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers14071664
Ahadi A (2021) Functional roles of lncRNAs in the pathogenesis and progression of cancer. Genes Dis 8:424–437. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gendis.2020.04.009
Al Saqri A, Malgundkar SH, Al Kindi F et al (2022) SOCS3 gene silencing does not occur through methylation and mutations in gastric cancer. Hum Cell 35:1114–1125. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00715-3
Aliperti V, Skonieczna J, Cerase A (2021) Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) roles in cell biology, neurodevelopment and neurological disorders. Noncoding RNA 7:36. https://doi.org/10.3390/ncrna7020036
Aluloski I, Tanturovski M, Jovanovic R et al (2017) Survival of advanced stage high-grade serous ovarian cancer patients in the Republic of Macedonia. Open Access Maced J Med Sci 5:904–908. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2017.215
An J, Lv W, Zhang Y (2017) LncRNA NEAT1 contributes to paclitaxel resistance of ovarian cancer cells by regulating ZEB1 expression via miR-194. Onco Targets Ther 10:5377–5390. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S147586
Arun G, Diermeier SD, Spector DL (2018) Therapeutic targeting of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Trends Mol Med 24:257–277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2018.01.001
Awwad DA (2019) Beyond classic editing: innovative CRISPR approaches for functional studies of long non-coding RNA. Biol Methods Protocols. https://doi.org/10.1093/biomethods/bpz017
Baek J, Lee B, Kwon S, Yoon S (2018) LncRNAnet: long non-coding RNA identification using deep learning. Bioinformatics 34:3889–3897. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty418
Bai Z, Wu Y, Bai S et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA SNGH7 Is activated by SP1 and exerts oncogenic properties by interacting with EZH2 in ovarian cancer. J Cell Mol Med 24:7479–7489. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15373
Bao Z, Yang Z, Huang Z et al (2019) LncRNADisease 2.0: an updated database of long non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D1034–D1037. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky905
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS (2017) Long non-coding RNA (LncRNA) and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res 77:3965–3981. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2634
Bonetti A, Carninci P (2017) From bench to bedside: The long journey of long non-coding RNAs. Curr Opin Syst Biol 3:119–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coisb.2017.04.016
Brannan CI, Dees EC, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM (1990) The product of the H19 gene may function as an RNA. Mol Cell Biol 10:28–36. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.10.1.28-36.1990
Brown CJ, Ballabio A, Rupert JL et al (1991) A gene from the region of the human X inactivation centre is expressed exclusively from the inactive X chromosome. Nature 349:38–44. https://doi.org/10.1038/349038a0
Budiana ING, Angelina M, Pemayun TGA (2019) Ovarian cancer: Pathogenesis and current recommendations for prophylactic surgery. J Turk Ger Gynecol Assoc 20:47–54. https://doi.org/10.4274/jtgga.galenos.2018.2018.0119
Cabianca DS, Casa V, Bodega B et al (2012) A long ncRNA links copy number variation to a polycomb/trithorax epigenetic switch in FSHD muscular dystrophy. Cell 149:819–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.035
Cabili MN, Trapnell C, Goff L et al (2011) Integrative annotation of human large intergenic noncoding RNAs reveals global properties and specific subclasses. Genes Dev 25:1915–1927. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.17446611
Cancer today. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/home. Accessed 12 Sep 2021
Cancer Tomorrow. https://gco.iarc.fr/tomorrow/en/dataviz/trends?cancers=25. Accessed 2 Dec 2022
Cao M, Zhao J, Hu G (2019) Genome-wide methods for investigating long noncoding RNAs. Biomed Pharmacother 111:395–401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.078
Castellanos-Rubio A, Fernandez-Jimenez N, Kratchmarov R et al (2016) A long noncoding RNA associated with susceptibility to celiac disease. Science 352:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aad0467
Chan JJ, Tay Y (2018) Noncoding RNA:RNA regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19:1310. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051310
Chandra A, Pius C, Nabeel M et al (2019) Ovarian cancer: current status and strategies for improving therapeutic outcomes. Cancer Med 8:7018–7031. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2560
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK et al (2022) UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 25:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001
Chang L, Guo R, Yuan Z et al (2018) LncRNA HOTAIR regulates CCND1 and CCND2 expression by sponging miR-206 in ovarian cancer. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:1289–1303. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493408
Chen X-J, An N (2021) Long noncoding RNA ATB promotes ovarian cancer tumorigenesis by mediating histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation through binding to EZH2. J Cell Mol Med 25:37–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15329
Chen M, Jin Y, Bi Y et al (2014) A survival analysis comparing women with ovarian low-grade serous carcinoma to those with high-grade histology. Onco Targets Ther 7:1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S67812
Chen Q, Shen H, Zhu X et al (2020) A nuclear lncRNA Linc00839 as a Myc target to promote breast cancer chemoresistance via PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Cancer Sci 111:3279–3291. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14555
Chowdhary A, Satagopam V, Schneider R (2021) Long non-coding RNAs: mechanisms, experimental, and computational approaches in identification, characterization, and their biomarker potential in cancer. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.649619
Chu C, Chang HY (2016) Understanding RNA-Chromatin Interactions Using Chromatin Isolation by RNA Purification (ChIRP). In: Lanzuolo C, Bodega B (eds) Polycomb Group Proteins: Methods and Protocols. Springer, New York, NY, pp 115–123
Coleman RL, Monk BJ, Sood AK, Herzog TJ (2013) Latest research and treatment of advanced-stage epithelial ovarian cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 10:211–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2013.5
Coticchia CM, Yang J, Moses MA (2008) Ovarian cancer biomarkers: current options and future promise. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 6:795–802
Cuykendall TN, Rubin MA, Khurana E (2017) Non-coding genetic variation in cancer. Curr Opin Syst Biol 1:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coisb.2016.12.017
de Gonzalo-Calvo D, Sopić M, Devaux Y (2022) Methodological considerations for circulating long noncoding RNA quantification. Trends Mol Med 28:616–618. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmed.2022.05.011
de Hoon M, Shin JW, Carninci P (2015) Paradigm shifts in genomics through the FANTOM projects. Mamm Genome 26:391–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00335-015-9593-8
Derrien T, Johnson R, Bussotti G et al (2012) The GENCODE v7 catalog of human long noncoding RNAs: Analysis of their gene structure, evolution, and expression. Genome Res 22:1775–1789. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.132159.111
Ding Y, Yang D-Z, Zhai Y-N et al (2017) Microarray expression profiling of long non-coding RNAs in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncol Lett 14:2523–2530. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.6448
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A et al (2012) Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature 489:101–108. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11233
Dragomir M, Chen B, Calin GA (2018) Exosomal lncRNAs as new players in cell-to-cell communication. Transl Cancer Res 7:S243–S252. https://doi.org/10.21037/tcr.2017.10.46
Du Y-L, Liang Y, Shi G-Q et al (2020) LINC00689 participates in proliferation, chemoresistance and metastasis via miR-31-5p/YAP/β-catenin axis in colorectal cancer. Exp Cell Res 395:112176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112176
El Bairi K, Kandhro AH, Gouri A et al (2017) Emerging diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic biomarkers for ovarian cancer. Cell Oncol 40:105–118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-016-0309-1
Elsayed AM, Amero P, Salama SA et al (2020) Back to the future: rethinking the great potential of lncRNAS for optimizing chemotherapeutic response in ovarian cancer. Cancers (Basel) 12:2406. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12092406
Erickson BK, Conner MG, Landen CN (2013) The role of the fallopian tube in the origin of ovarian cancer. Am J Obstet Gynecol 209:409–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2013.04.019
Fang Y, Fullwood MJ (2016) Roles, functions, and mechanisms of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Genom Proteom Bioinform 14:42–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2015.09.006
Fang S, Zhang L, Guo J et al (2018) NONCODEV5: a comprehensive annotation database for long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D308–D314. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1107
Fathi Dizaji B (2020) Strategies to target long non-coding RNAs in cancer treatment: progress and challenges. Egypt J Med Hum Genet 21:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43042-020-00074-4
Fatica A, Bozzoni I (2014) Long non-coding RNAs: new players in cell differentiation and development. Nat Rev Genet 15:7–21. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3606
Flippot R, Malouf GG, Su X, et al (2016) Cancer subtypes classification using long non-coding RNA. Oncotarget 7:54082–54093. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10213
Fort A, Hashimoto K, Yamada D et al (2014) Deep transcriptome profiling of mammalian stem cells supports a regulatory role for retrotransposons in pluripotency maintenance. Nat Genet 46:558–566. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2965
Friedman RC, Farh KK-H, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.082701.108
Galea M, Gauci G, Calleja-Agius J, Schembri-Wismayer P (2017) Peritoneal biomarkers in the early detection of ovarian cancer. Minerva Ginecol 69:84–99. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4784.16.03943-5
Gao J, Liu M, Zou Y et al (2015) Long non-coding RNA growth arrest-specific transcript 5 is involved in ovarian cancer cell apoptosis through the mitochondria-mediated apoptosis pathway. Oncol Rep 34:3212–3221. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.4318
Gao C, Zhao D, Zhao Q et al (2019a) Microarray profiling and co-expression network analysis of lncRNAs and mRNAs in ovarian cancer. Cell Death Discov 5:93. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-019-0173-7
Gao Y, Li X, Zhi H et al (2019b) Comprehensive characterization of somatic mutations impacting lncRNA expression for pan-cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 18:66–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2019.08.004
Gao Y, Wang P, Wang Y et al (2019c) Lnc2Cancer v2.0: updated database of experimentally supported long non-coding RNAs in human cancers. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D1028–D1033. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1096
Gibb EA, Brown CJ, Lam WL (2011) The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol Cancer 10:38. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-10-38
Gong J, Liu W, Zhang J et al (2015) lncRNASNP: a database of SNPs in lncRNAs and their potential functions in human and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D181–D186. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1000
Gong Y, Zhu W, Sun M, Shi L (2021) Bioinformatics analysis of long non-coding RNA and related diseases: an overview. Front Genet 12:2575. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2021.813873
Gov E, Kori M, Arga KY (2017) RNA-based ovarian cancer research from ‘a gene to systems biomedicine’ perspective. Syst Biol Reprod Med 63:219–238. https://doi.org/10.1080/19396368.2017.1330368
Groskopf J, Aubin SMJ, Deras IL et al (2006) APTIMA PCA3 molecular urine test: development of a method to aid in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. Clin Chem 52:1089–1095. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2005.063289
Gross AL, Kurman RJ, Vang R et al (2010) Precursor lesions of high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma: morphological and molecular characteristics. J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/126295
Gu L, Li Q, Liu H et al (2020) Long noncoding RNA TUG1 promotes autophagy-associated paclitaxel resistance by sponging miR-29b-3p in ovarian cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 13:2007–2019. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S240434
Guan R, Wang W, Fu B et al (2019) Increased lncRNA HOTAIR expression promotes the chemoresistance of multiple myeloma to dexamethasone by regulating cell viability and apoptosis by mediating the JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 20:3917–3923. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.10603
Guo Q, Wu Y, Guo X et al (2020) The RNA-binding protein CELF2 inhibits ovarian cancer progression by stabilizing FAM198B. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 23:169–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.10.011
Gutschner T, Diederichs S (2012) The hallmarks of cancer. RNA Biol 9:703–719. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.20481
Guttman M, Amit I, Garber M et al (2009) Chromatin signature reveals over a thousand highly conserved large non-coding RNAs in mammals. Nature 458:223–227. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07672
Ha M, Kim VN (2014) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15:509–524. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3838
Hafner M, Katsantoni M, Köster T et al (2021) CLIP and complementary methods. Nat Rev Methods Primers 1:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1038/s43586-021-00018-1
Hanly DJ, Esteller M, Berdasco M (2018) Interplay between long non-coding RNAs and epigenetic machinery: emerging targets in cancer? Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society b: Biological Sciences 373:20170074. https://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2017.0074
Harrow J, Frankish A, Gonzalez JM et al (2012) GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE Project. Genome Res 22:1760–1774. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.135350.111
He S-L, Chen Y-L, Chen Q-H et al (2022) LncRNA KCNQ1OT1 promotes the metastasis of ovarian cancer by increasing the methylation of EIF2B5 promoter. Mol Med 28:112. https://doi.org/10.1186/s10020-022-00521-5
Heery R, Finn SP, Cuffe S, Gray SG (2017) Long non-coding RNAs: key regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition, tumour drug resistance and cancer stem cells. Cancers (Basel) 9:38. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers9040038
Helleman J, Jansen MPHM, Span PN et al (2006) Molecular profiling of platinum resistant ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer 118:1963–1971. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.21599
Heydarnezhad Asl M, Pasban Khelejani F, Bahojb Mahdavi SZ et al (2022) The various regulatory functions of long noncoding RNAs in apoptosis, cell cycle, and cellular senescence. J Cell Biochem 123:995–1024. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.30221
Holoch D, Moazed D (2015) RNA-mediated epigenetic regulation of gene expression. Nat Rev Genet 16:71–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3863
Hu W, Alvarez-Dominguez JR, Lodish HF (2012) Regulation of mammalian cell differentiation by long non-coding RNAs. EMBO Rep 13:971–983. https://doi.org/10.1038/embor.2012.145
Huang X, Yuan T, Tschannen M et al (2013) Characterization of human plasma-derived exosomal RNAs by deep sequencing. BMC Genom 14:319. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-319
Hui B, Lu C, Wang J et al (2022) Engineered exosomes for co-delivery of PGM5-AS1 and oxaliplatin to reverse drug resistance in colon cancer. J Cell Physiol 237:911–933. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.30566
Iyer MK, Niknafs YS, Malik R et al (2015) The landscape of long noncoding RNAs in the human transcriptome. Nat Genet 47:199–208. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3192
Jiang N, Zhang X, Gu X et al (2021) Progress in understanding the role of lncRNA in programmed cell death. Cell Death Discov 7:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41420-021-00407-1
Jin H, Du W, Huang W et al (2021) lncRNA and breast cancer: Progress from identifying mechanisms to challenges and opportunities of clinical treatment. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 25:613–637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2021.08.005
Kamps R, Brandão RD, van den Bosch BJ et al (2017) Next-generation sequencing in oncology: genetic diagnosis, risk prediction and cancer classification. Int J Mol Sci 18:308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020308
Kapranov P, St Laurent G, Raz T et al (2010) The majority of total nuclear-encoded non-ribosomal RNA in a human cell is “dark matter” un-annotated RNA. BMC Biol 8:149. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-8-149
Karagkouni D, Paraskevopoulou MD, Tastsoglou S et al (2020) DIANA-LncBase v3: indexing experimentally supported miRNA targets on non-coding transcripts. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D101–D110. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1036
Karreth FA, Pandolfi PP (2013) ceRNA cross-talk in cancer: when ce-bling rivalries go awry. Cancer Discov 3:1113–1121. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0202
Kitagawa M, Kitagawa K, Kotake Y et al (2013) Cell cycle regulation by long non-coding RNAs. Cell Mol Life Sci 70:4785–4794. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-013-1423-0
Konstantinopoulos PA, Spentzos D, Cannistra SA (2008) Gene-expression profiling in epithelial ovarian cancer. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 5:577–587. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncponc1178
Kornienko AE, Guenzl PM, Barlow DP, Pauler FM (2013) Gene regulation by the act of long non-coding RNA transcription. BMC Biol 11:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/1741-7007-11-59
Koshiyama M, Matsumura N, Konishi I (2014) Recent concepts of ovarian carcinogenesis: Type I and Type II. Biomed Res Int 2014:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/934261
Kurman RJ, Shih I-M (2010) The origin and pathogenesis of epithelial ovarian cancer- a proposed unifying theory. Am J Surg Pathol 34:433–443. https://doi.org/10.1097/PAS.0b013e3181cf3d79
Kurman RJ, Shih I-M (2016) The dualistic model of ovarian carcinogenesis. Am J Pathol 186:733–747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2015.11.011
Lai Y, Dong L, Jin H, et al (2021) Exosome long non-coding RNA SOX2-OT contributes to ovarian cancer malignant progression by miR-181b-5p/SCD1 signaling. Aging (Albany NY) 13:23726–23738. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203645
Ledermann JA, Raja FA, Fotopoulou C et al (2013) Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 24:vi24–vi22. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdt333
Lee C, Kikyo N (2012) Strategies to identify long noncoding RNAs involved in gene regulation. Cell Biosci 2:37. https://doi.org/10.1186/2045-3701-2-37
Lee TI, Young RA (2013) Transcriptional regulation and its misregulation in disease. Cell 152:1237–1251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.02.014
Li J-H, Liu S, Zhou H et al (2014) starBase v2.0: decoding miRNA-ceRNA, miRNA-ncRNA and protein-RNA interaction networks from large-scale CLIP-Seq data. Nucleic Acids Res 42:D92–D97. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt1248
Li J, Han L, Roebuck P et al (2015a) TANRIC: An interactive open platform to explore the function of lncRNAs in cancer. Cancer Res 75:3728–3737. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-0273
Li Q, Shao Y, Zhang X et al (2015b) Plasma long noncoding RNA protected by exosomes as a potential stable biomarker for gastric cancer. Tumour Biol 36:2007–2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2807-y
Li J, Huang H, Li Y et al (2016a) Decreased expression of long non-coding RNA GAS5 promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion, and indicates a poor prognosis in ovarian cancer. Oncol Rep 36:3241–3250. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2016.5200
Li R, Zhu H, Luo Y (2016b) Understanding the functions of long non-coding RNAs through their higher-order structures. Int J Mol Sci 17:702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050702
Li S, Li Y, Chen B et al (2018) exoRBase: a database of circRNA, lncRNA and mRNA in human blood exosomes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D106–D112. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx891
Li Y, Ma H-Y, Hu X-W et al (2020) LncRNA H19 promotes triple-negative breast cancer cells invasion and metastasis through the p53/TNFAIP8 pathway. Cancer Cell Int 20:200. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01261-4
Li G, Gong J, Cao S et al (2021a) The non-coding RNAs inducing drug resistance in ovarian cancer: a new perspective for understanding drug resistance. Front Oncol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.742149
Li L, Wei H, Zhang YW, et al (2021b) Differential expression of long non-coding RNAs as diagnostic markers for lung cancer and other malignant tumors. Aging (Albany NY) 13:23842–23867. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203523
Li X, Zhang Y, Wang X et al (2022) Long non-coding RNA CTSLP8 mediates ovarian cancer progression and chemotherapy resistance by modulating cellular glycolysis and regulating c-Myc expression through PKM2. Cell Biol Toxicol 38:1027–1045. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10565-021-09650-9
Lin A, Li C, Xing Z et al (2016) The LINK-A lncRNA activates normoxic HIF1α signalling in triple-negative breast cancer. Nat Cell Biol 18:213–224. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3295
Lin X, Yang F, Qi X et al (2019) LncRNA DANCR promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis in ovarian cancer through direct targeting of miR-145. Mol Carcinog 58:2286–2296. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.23117
Lin H, Shen L, Lin Q et al (2020) SNHG5 enhances Paclitaxel sensitivity of ovarian cancer cells through sponging miR-23a. Biomed Pharmacother 123:109711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109711
Lin C, Zheng M, Yang Y et al (2022) Knockdown of lncRNA ACTA2-AS1 reverses cisplatin resistance of ovarian cancer cells via inhibition of miR-378a-3p-regulated Wnt5a. Bioengineered 13:9829–9838. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2022.2061181
Liu S-P, Yang J-X, Cao D-Y, Shen K (2013) Identification of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs in human ovarian cancer cells with different metastatic potentials. Cancer Biol Med 10:138–141. https://doi.org/10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2013.03.003
Liu J, Wang G, Zhao J et al (2021) LncRNA H19 promoted the epithelial to mesenchymal transition and metastasis in gastric cancer via activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Dig Dis 40:436–447. https://doi.org/10.1159/000518627
Lou Y, Jiang H, Cui Z et al (2017) Linc-ROR induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in ovarian cancer by increasing Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Oncotarget 8:69983–69994. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.19545
Lou Y, Jiang H, Cui Z et al (2018) Gene microarray analysis of lncRNA and mRNA expression profiles in patients with high-grade ovarian serous cancer. Int J Mol Med 42:91–104. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3588
Lu C, Wei Y, Wang X et al (2020) DNA-methylation-mediated activating of lncRNA SNHG12 promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Mol Cancer 19:28. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1137-5
Ma L, Bajic VB, Zhang Z (2013) On the classification of long non-coding RNAs. RNA Biol 10:925–933. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.24604
Magri F, Vanoli F, Corti S (2018) miRNA in spinal muscular atrophy pathogenesis and therapy. J Cell Mol Med 22:755–767. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.13450
Mahdian-Shakib A, Dorostkar R, Tat M et al (2016) Differential role of microRNAs in prognosis, diagnosis, and therapy of ovarian cancer. Biomed Pharmacother 84:592–600. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.09.087
Malgundkar SH, Hassan NA, Al Badi H et al (2022) Identification and validation of a novel long non-coding RNA (LINC01465) in ovarian cancer. Hum Cell. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13577-022-00842-x
Martini P, Paracchini L, Caratti G et al (2017) lncRNAs as novel indicators of patients’ prognosis in stage I epithelial ovarian cancer: a retrospective and multicentric study. Clin Cancer Res 23:2356–2366
Maruyama R, Yokota T (2020) Knocking Down Long Noncoding RNAs Using Antisense Oligonucleotide Gapmers. In: Yokota T, Maruyama R (eds) Gapmers: Methods and Protocols. Springer, US, New York, pp 49–56
Mattick JS, Rinn JL (2015) Discovery and annotation of long noncoding RNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 22:5–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.2942
McColl H, Zagozewski JL, Eisenstat DD (2019) Chromatin Immunoprecipitation (ChIP) protocols for the cancer and developmental biology laboratory. Methods Mol Biol 1869:143–153. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-8805-1_13
Miao J-T, Gao J-H, Chen Y-Q et al (2019) LncRNA ANRIL affects the sensitivity of ovarian cancer to cisplatin via regulation of let-7a/HMGA2 axis. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20182101
Miller JL, Grant PA (2013) The role of DNA methylation and histone modifications in transcriptional regulation in humans. Subcell Biochem 61:289–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-94-007-4525-4_13
Miller KD, Nogueira L, Mariotto AB et al (2019) Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin 69:363–385. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565
Mitra S, Das S, Chakrabarti J (2013) Systems biology of cancer biomarker detection. Cancer Biomark 13:201–213. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-130363
Mundade R, Ozer HG, Wei H et al (2014) Role of ChIP-seq in the discovery of transcription factor binding sites, differential gene regulation mechanism, epigenetic marks and beyond. Cell Cycle 13:2847–2852. https://doi.org/10.4161/15384101.2014.949201
Nagano T, Fraser P (2011) No-nonsense functions for long noncoding RNAs. Cell 145:178–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.014
Nasioudis D, Sisti G, Kanninen TT et al (2016) Epidemiology and outcomes of squamous ovarian carcinoma; a population-based study. Gynecol Oncol 141:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2016.02.004
Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(19)31561-3/fulltext. Accessed 17 Jun 2023d
Norouzi-Barough L, Sarookhani MR, Sharifi M et al (2018) Molecular mechanisms of drug resistance in ovarian cancer. J Cell Physiol 233:4546–4562. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26289
Nukala SB, Jousma J, Cho Y et al (2022) Long non-coding RNAs and microRNAs as crucial regulators in cardio-oncology. Cell Biosci 12:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-022-00757-y
Otmani K, Lewalle P (2021) Tumor suppressor miRNA in cancer cells and the tumor microenvironment: mechanism of deregulation and clinical implications. Front Oncol 11:708765. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.708765
Ovarian Cancer Stages, Survival Rate and Prognosis. In: OCRA. https://ocrahope.org/get-the-facts/staging/. Accessed 18 Feb 2023
Özeş AR, Miller DF, Özeş ON et al (2016) NF-κB-HOTAIR axis links DNA damage response, chemoresistance and cellular senescence in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 35:5350–5361. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.75
Pronina IV, Uroshlev LA, Moskovtsev AA, Zaichenko DM, Filippova EA, Fridman MV et al (2022) Dysregulation of lncRNA– miRNA–mRNA interactome as a marker of metastatic process in ovarian cancer. Biomedicines 10(4):824
Pal MK, Jaiswar SP, Dwivedi VN et al (2015) MicroRNA: a new and promising potential biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Med 12:328–341. https://doi.org/10.7497/j.issn.2095-3941.2015.0024
Peng Y, Tang D, Zhao M et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA: a recently accentuated molecule in chemoresistance in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev 39:825–835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-020-09910-w
Ponting CP, Oliver PL, Reik W (2009) Evolution and functions of long noncoding RNAs. Cell 136:629–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.02.006
Prensner JR, Chinnaiyan AM (2011) The emergence of lncRNAs in cancer biology. Cancer Discov 1:391–407. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-11-0209
Qian Y, Shi L, Luo Z (2020) Long non-coding RNAs in cancer: implications for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapy. Front Med (Lausanne) 7:612393. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.612393
Quek XC, Thomson DW, Maag JLV et al (2015) lncRNAdb v2.0: expanding the reference database for functional long noncoding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 43:D168–D173. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku988
Quinn JJ, Chang HY (2016) Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet 17:47–62. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg.2015.10
Rao AKDM, Rajkumar T, Mani S (2017) Perspectives of long non-coding RNAs in cancer. Mol Biol Rep 44:203–218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-017-4103-6
Rao MS, Van Vleet TR, Ciurlionis R et al (2019) Comparison of RNA-Seq and microarray gene expression platforms for the toxicogenomic evaluation of liver from short-term rat toxicity studies. Front Genet. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2018.00636
Renganathan A, Felley-Bosco E (2017) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer and therapeutic potential. In: Rao MRS (ed) Long Non Coding RNA Biology. Springer, Singapore, pp 199–222
Ricciardi E, Baert T, Ataseven B et al (2018) Low-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 78:972–976. https://doi.org/10.1055/a-0717-5411
Rishabh K, Khadilkar S, Kumar A et al (2021) MicroRNAs as modulators of oral tumorigenesis—a focused review. Int J Mol Sci 22:2561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22052561
Salamini-Montemurri M, Lamas-Maceiras M, Barreiro-Alonso A et al (2020) The challenges and opportunities of LncRNAs in ovarian cancer research and clinical use. Cancers (Basel) 12:1020. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12041020
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y et al (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Schmitt AM, Chang HY (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell 29:452–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2016.03.010
Shan L, Song P, Zhao Y, An N, Xia Y, Qi Y et al (2022) miR-600 promotes ovarian cancer cells stemness, proliferation and metastasis via targeting KLF9. J Ovarian Res 15:52
Shen H, Laird PW (2013) Interplay between the cancer genome and epigenome. Cell 153:38–55. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.03.008
Shi T, Gao G, Cao Y (2016) Long noncoding RNAs as novel biomarkers have a promising future in cancer diagnostics. Dis Markers. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/9085195
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2016) Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin 66:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21332
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A (2017) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 67:7–30. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21387
Slack FJ, Chinnaiyan AM (2019) The role of non-coding RNAs in oncology. Cell 179:1033–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2019.10.017
Spentzos D, Levine DA, Ramoni MF et al (2004) Gene expression signature with independent prognostic significance in epithelial ovarian cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:4700–4710. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2004.04.070
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL et al (2021) Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J Clin. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Svoronos AA, Engelman DM, Slack FJ (2016) OncomiR or tumor suppressor? The duplicity of MicroRNAs in cancer. Can Res 76:3666–3670. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0359
Tao Z, Shi A, Li R et al (2017) Microarray bioinformatics in cancer- a review. J BUON 22:838–843
Tian J, Wang Y, Zhang X et al (2017) Calycosin inhibits the in vitro and in vivo growth of breast cancer cells through WDR7-7-GPR30 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:153. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0625-y
Torre LA, Trabert B, DeSantis CE et al (2018) Ovarian cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 68:284–296. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21456
Treiber T, Treiber N, Meister G (2019) Regulation of microRNA biogenesis and its crosstalk with other cellular pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20:5–20. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0059-1
Trinidad CV, Tetlow AL, Bantis LE, Godwin AK (2020) Reducing ovarian cancer mortality through early detection: approaches using circulating biomarkers. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 13:241–252. https://doi.org/10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-19-0184
van Solingen C, Cyr Y, Scacalossi KR et al (2022) Long noncoding RNA CHROMR regulates antiviral immunity in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci 119:e2210321119. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2210321119
Volders P-J, Anckaert J, Verheggen K et al (2019) LNCipedia 5: towards a reference set of human long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 47:D135–D139. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1031
Wambecke A, Ahmad M, Morice P et al (2021) The lncRNA ‘UCA1’ modulates the response to chemotherapy of ovarian cancer through direct binding to miR-27a-5p and control of UBE2N levels. Mol Oncol 15:3659–3678. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.13045
Wang KC, Chang HY (2011) Molecular mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs. Mol Cell 43:904–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.08.018
Wang F, Zhou J, Xie X et al (2015) Involvement of SRPK1 in cisplatin resistance related to long non-coding RNA UCA1 in human ovarian cancer cells. Neoplasma 62:432–438
Wang H, Fu Z, Dai C et al (2016) LncRNAs expression profiling in normal ovary, benign ovarian cyst and malignant epithelial ovarian cancer. Sci Rep 6:38983. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep38983
Wang J, Ye C, Liu J, Hu Y (2018) UCA1 confers paclitaxel resistance to ovarian cancer through miR-129/ABCB1 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 501:1034–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.05.104
Wang J, Dean DC, Hornicek FJ et al (2019a) RNA sequencing (RNA-Seq) and its application in ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 152:194–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ygyno.2018.10.002
Wang W-T, Han C, Sun Y-M et al (2019b) Noncoding RNAs in cancer therapy resistance and targeted drug development. J Hematol Oncol 12:55. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-019-0748-z
Wang H, Su H, Tan Y (2020a) UNC5B-AS1 promoted ovarian cancer progression by regulating the H3K27me on NDRG2 via EZH2. Cell Biol Int 44:1028–1036. https://doi.org/10.1002/cbin.11300
Wang P, Li X, Gao Y et al (2020b) LnCeVar: a comprehensive database of genomic variations that disturb ceRNA network regulation. Nucleic Acids Res 48:D111–D117. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz887
Wang Z, Wang Q, Xu G et al (2020c) The long noncoding RNA CRAL reverses cisplatin resistance via the miR-505/CYLD/AKT axis in human gastric cancer cells. RNA Biol 17:1576–1589. https://doi.org/10.1080/15476286.2019.1709296
Wang Y, Shao F, Chen L (2022) miR-425 regulates ovarian cancer proliferation, metastasis, and apoptosis by repressing PAK4 expression. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol 18(1):76–83
Wang J, Liu L (2021) MiR-149-3p promotes the cisplatin resistance and EMT in ovarian cancer through downregulating TIMP2 and CDKN1A. J Ovarian Res 14:165
Wen S, Wei Y, Zen C et al (2020) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 promotes bone metastasis of prostate cancer through N6-methyladenosine. Mol Cancer 19:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01293-4
Wiehle L, Breiling A (2016) Chromatin Immunoprecipitation. In: Lanzuolo C, Bodega B (eds) Polycomb group proteins: methods and protocols. Springer, New York, pp 7–21
Xiu Y, Sun K, Chen X, et al (2017) Upregulation of the lncRNA Meg3 induces autophagy to inhibit tumorigenesis and progression of epithelial ovarian carcinoma by regulating activity of ATG3. Oncotarget 8:31714–31725. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.15955
Xu H, Ding Y, Yang X (2021) Overexpression of long noncoding RNA H19 downregulates miR-140-5p and activates PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to promote invasion, migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition of ovarian cancer cells. Biomed Res Int. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6619730
Xue Y, Ma G, Gu D et al (2015) Genome-wide analysis of long noncoding RNA signature in human colorectal cancer. Gene 556:227–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2014.11.060
Yan X, Hu Z, Feng Y et al (2015) Comprehensive genomic characterization of long non-coding RNAs across human cancers. Cancer Cell 28:529–540. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.006
Yang Y, Jiang Y, Wan Y et al (2016) UCA1 functions as a competing endogenous RNA to suppress epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis. Tumour Biol 37:10633–10641. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-4917-1
Yang F, Ning Z, Ma L et al (2017) Exosomal miRNAs and miRNA dysregulation in cancer-associated fibroblasts. Mol Cancer 16:148. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-017-0718-4
Yang Z, Xu F, Teschendorff AE et al (2022) Insights into the role of long non-coding RNAs in DNA methylation mediated transcriptional regulation. Front Mol Biosci. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmolb.2022.1067406
Ye Y, Li S-L, Wang S-Y (2018) Construction and analysis of mRNA, miRNA, lncRNA, and TF regulatory networks reveal the key genes associated with prostate cancer. PLoS One. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198055
Yuan D, Guo T, Zhu D et al (2022) Exosomal lncRNA ATB derived from ovarian cancer cells promotes angiogenesis via regulating miR-204-3p/TGFβR2 axis. Cancer Manag Res 14:327–337. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S330368
Zaman MS, Maher DM, Khan S et al (2012) Current status and implications of microRNAs in ovarian cancer diagnosis and therapy. J Ovarian Res 5:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/1757-2215-5-44
Zhan L, Li J, Wei B (2018) Long non-coding RNAs in ovarian cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0793-4
Zhang B, Cai FF, Zhong XY (2011) An overview of biomarkers for the ovarian cancer diagnosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 158:119–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2011.04.023
Zhang Y, Feng Y, Hu Z et al (2016a) Characterization of long non-coding RNA associated proteins by RNA-immunoprecipitation. Methods Mol Biol 1402:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3378-5_3
Zhang Z, Cheng J, Wu Y et al (2016b) LncRNA HOTAIR controls the expression of Rab22a by sponging miR-373 in ovarian cancer. Mol Med Rep 14:2465–2472. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5572
Zhang Z, Liu T, Cheng C et al (2022) LncRNA GAS5 regulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through the miR-18a-5p/AXIN2/GSK3β axis to inhibit the proliferation and migration of bladder cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 43:1176–1189. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgac087
Zhao Y, Li H, Fang S et al (2016) NONCODE 2016: an informative and valuable data source of long non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 44:D203–D208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1252
Zheng M-J, Li X, Hu Y-X et al (2019a) Identification of molecular marker associated with ovarian cancer prognosis using bioinformatics analysis and experiments. J Cell Physiol 234:11023–11036. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27926
Zheng Y, Xu Q, Liu M et al (2019b) lnCAR: a comprehensive resource for lncRNAs from cancer arrays. Cancer Res 79:2076–2083. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2169
Zhou Y, Xu X, Lv H et al (2016) The long noncoding RNA MALAT-1 is highly expressed in ovarian cancer and induces cell growth and migration. PLoS One 11:e0155250. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0155250
Zhou R-S, Zhang E-X, Sun Q-F et al (2019) Integrated analysis of lncRNA-miRNA-mRNA ceRNA network in squamous cell carcinoma of tongue. BMC Cancer 19:779. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-019-5983-8
Zhu Y, Chen J, Zhou L et al (2022) A platinum resistance-related lncRNA signature for risk classification and prognosis prediction in patients with serous ovarian cancer. J Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7625138
Acknowledgements
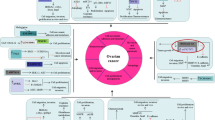
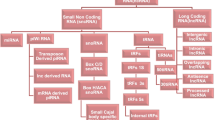
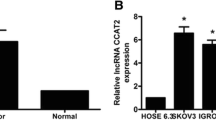
We would like to acknowledge Biorender, through which we created Fig. 2.
Funding
SQU internal Grant: Grant number: IG/MED/BIOC/22/01.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SH drafted the review article. YT contributed to the concept and reviewing of the article. All the authors approved the final version of this manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent to publish
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Malgundkar, S.H., Tamimi, Y. The pivotal role of long non-coding RNAs as potential biomarkers and modulators of chemoresistance in ovarian cancer (OC). Hum. Genet. 143, 107–124 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-023-02635-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-023-02635-0