Abstract
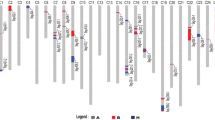
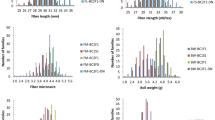
Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) race stocks may possess desirable traits for the genetic improvement of cotton. Quantitative trait locus (QTL) analysis can assist in uncovering new alleles from unadapted race stocks. In this study, three sets of chromosome segment introgression lines (ILs) were developed from three backcrosses (BC3) between three race stocks, G. hirsutum races latifolium accs. TX-34 and TX-48 and punctatum acc. TX-114, as donor parents and Texas Marker-1 (TM-1) as the recurrent parent. Based on a total of 452 polymorphic simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers in BC3F2 genotyping, 149, 150 and 184 ILs were obtained from TM-1 × TX-34, TM-1 × TX-48 and TM-1 × TX-114, respectively. The average introgressed chromosomal segment length was 12.7 cM, and the total genetic distance was 3268 cM covering approximately 73.4% of the Upland cotton genome. The BC3F2, BC3F2:3 and BC3F2:4 progeny, which produced the ILs, were evaluated for yield and fibre quality traits. A total of 128 QTLs were detected, each of which explained 1.6–13.0% of the phenotypic variation. Thirty-five common QTLs related to eight traits were detected. Six QTL clusters were found on five chromosomes. Thirty-eight QTLs were previously unreported, and they may be footprints of cotton domestication. Domestication or artificial selection by humans successfully eliminated most unfavourable QTLs (21/38); however, some favourable QTLs (17/38) are not present in modern cultivars, demonstrating the importance of race stocks for improving cotton cultivars. The 26 elite ILs developed could be used to improve the yield and fibre quality components simultaneously. These results provide information on desirable QTLs for cotton improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brubaker CL (1999) The origin and domestication of cotton. In: Smith C, Cothren J (eds) Cotton: origin, history, technology and production. Wiley, New York pp 3–31
Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1994) Reevaluating the origin of domesticated cotton (Gossypium hirsutum; Malvaceae) using nuclear restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs). Am J Bot 81:1309–1326
Byers RL, Harker DB, Yourstone SM, Maughan PJ, Udall JA (2012) Development and mapping of SNP assays in allotetraploid cotton. Theor Appl Genet 124:1201–1214
Cao Z, Wang P, Zhu X, Chen H, Zhang T (2014) SSR marker-assisted improvement of fiber qualities in Gossypium hirsutum using G. barbadense introgression lines. Theor Appl Genet 127:587–594
Cao Z, Zhu X, Chen H, Zhang T (2015) Fine mapping of clustered quantitative trait loci for fiber quality on chromosome 7 using a Gossypium barbadense introgressed line. Mol Breed 35:215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-015-0393-3
Chen ZJ, Scheffler BE, Dennis E, Triplett BA, Zhang T et al (2007) Toward sequencing cotton (Gossypium) genomes. Plant Physiol 145:1303–1310
Culp TW, Harrell DC (1973) Breeding methods for improving yield and fiber quality of Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Crop Sci 13:686–689
Culp TW, Harrell DC, Kerr T (1979) Some genetic implications in the transfer of high fiber strength genes to Upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum. Crop Sci 19:481–484
Diouf L, Magwanga RO, Gong W, He S, Pan Z et al (2018) QTL mapping of fiber quality and yield-related traits in an intra-specific Upland cotton using genotype by sequencing (GBS). Int J Mol Sci 19(2):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020441
Draye X, Peng C, Jiang CX, Decanini L, Delmonte TA et al (2005) Molecular dissection of interspecific variation between Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense (cotton) by a backcross-self approach: II. Fiber fineness. Theor Appl Genet 111:764–771
Fang DD, Hinze LL, Percy RG, Li P, Deng D et al (2013) A microsatellite-based genome-wide analysis of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars from major cotton-growing countries. Euphytica 191:391–401
Fang L, Wang Q, Yan H, Jia Y, Chen J et al (2017) Genomic analyses in cotton identify signatures of selection and loci associated with fiber quality and yield traits. Nat Genet 49:1089–1098
Fu Y, Yuan DD, Hu WJ, Cai CP, Guo WZ (2013) Development of Gossypium barbadense chromosome 18 segment substitution lines in the genetic standard line TM-1 of Gossypium hirsutum and mapping of QTLs related to agronomic traits. Acta Agron Sin 53:1512–1517
Guo W, Cai C, Wang C, Han Z, Song X et al (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176:527–541
Guo X, Guo Y, Ma J, Wang F, Sun M et al (2013) Mapping heterotic loci for yield and agronomic traits using chromosome segment introgression lines in cotton. J Integr Plant Biol 55:759–774
Guo Y, Guo X, Wang F, Wei Z, Zhang S et al (2014) Molecular tagging and marker-assisted selection of fiber quality traits using chromosome segment introgression lines (CSILs) in cotton. Euphytica 200:239–250
Hou M, Cai C, Zhang S, Guo W, Zhang T et al (2013) Construction of microsatellite-based linkage map and mapping of nectarilessness and hairiness genes in Gossypium tomentosum. J Genet 92:445–459
Keerio A, Shen C, Nie Y, Ahmed M, Zhang X et al (2018) QTL Mapping for fiber quality and yield traits based on introgression lines derived from Gossypium hirsutum × G. tomentosum. Int J Mol Sci 19:243. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010243
Lan MJ, Yang ZM, Shi YZ, Ge RH, Li AG et al (2011) Assessment of substitution lines and identification of QTL related to fiber yield and quality traits in BC4F2 and BC4F3 populations from Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense. Sci Agric Sin 14:3086–3097
Li C, Wang X, Dong N, Zhao H, Xia Z et al (2013) QTL analysis for early-maturing traits in cotton using two Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) crosses. Breed Sci 63:154–163
Li L, Zhao S, Su J, Fan S, Pang C et al (2017) High-density genetic linkage map construction by F2 populations and QTL analysis of early-maturity traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). PLoS One 12(8):e0182918
Liang QZ, Cheng H, Hua H, Li ZH, Hua JP (2013) Construction of a linkage map and QTL mapping for fiber quality traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Sci Bull 58:3233–3243
Liu D, Liu F, Shan X, Zhang J, Tang S et al (2015) Construction of a high-density genetic map and lint percentage and cottonseed nutrient trait QTL identification in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Genet Genom 290:1683–1700
Ma Z, He S, Wang X, Sun J, Zhang Y et al (2018) Resequencing a core collection of Upland cotton identifies genomic variation and loci influencing fiber quality and yield. Nat Genet 50:803–813
Meyer RS, Purugganan MD (2013) Evolution of crop species: genetics of domestication and diversification. Nat Rev Genet 14:840–852
Nie X, Tu J, Wang B, Zhou X, Lin Z (2015) A BIL population derived from G. hirsutum and G. barbadense provides a resource for cotton genetics and breeding. PLoS One 10:e0141064
Ooijen V (2001) JoinMap-Version 3.0, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Res Int, Wageningen
Paterson AH, Lander ES, Hewitt JD, Peterson S, Lincoln SE et al (1988) Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors by using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature 335:721–726
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:122–127
Qin H, Guo W, Zhang YM, Zhang T (2008) QTL mapping of yield and fiber traits based on a four-way cross population in Gossypium hirsutum L. Theor Appl Genet 117:883–894
Rong J, Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C et al (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Rong J, Feltus FA, Waghmare VN, Pierce GJ, Peng WC et al (2007) Meta-analysis of polyploid cotton QTL shows unequal contributions of subgenomes to a complex network of genes and gene clusters implicated in lint fiber development. Genetics 176:2577–2588
Said JI, Knapka JA, Song M, Zhang J (2015a) Cotton QTLdb: a cotton QTL database for QTL analysis, visualization, and comparison between Gossypium hirsutum and G. hirsutum × G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genom 290:1615–1625
Said JI, Song M, Wang H, Lin Z, Zhang X et al (2015b) A comparative meta-analysis of QTL between intraspecific Gossypium hirsutum and interspecific G. hirsutum × G. barbadense populations. Mol Genet Genom 290:1003–1025
Shang L, Wang Y, Wang X, Liu F, Abdugheni A et al (2016) Genetic analysis and QTL detection on fiber traits using two recombinant inbred lines and their backcross populations in Upland cotton. G3 Genes Genom Genet 6:2717–2724
Shen X, Zhang T, Guo W, Zhu X, Zhang X (2006) Mapping fiber and yield QTLs with main, epistatic, and QTL × environment interaction effects in recombinant inbred lines of Upland cotton. Crop Sci 46:61–66
Shen X, Guo W, Lu Q, Zhu X, Yuan Y et al (2007) Genetic mapping of quantitative trait loci for fiber quality and yield trait by RIL approach in Upland cotton. Euphytica 155:371–380
Shi Y, Li W, Li A, Ge R, Zhang B et al (2015) Constructing a high-density linkage map for Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense and identifying QTLs for lint percentage. Chin Bull Bot 57:450–467
Si Z, Chen H, Zhu X, Cao Z, Zhang T (2017) Genetic dissection of lint yield and fiber quality traits of G. hirsutum in G. barbadense background. Mol Breed 37:9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11032-016-0607-3
Smith CW, Coyle GG (1997) Association of fiber quality parameters and within-boll yield components in Upland cotton. Crop Sci 37:1775–1779
Song W, Wang M, Su W, Lu Q, Xiao X et al (2017) Genetic and phenotypic effects of chromosome segments introgressed from Gossypium barbadense into Gossypium hirsutum. PLoS One 12:e0184882
Su J, Fan S, Li L, Wei H, Wang C et al (2016) Detection of favorable QTL alleles and candidate genes for lint percentage by GWAS in Chinese Upland cotton. Front Plant Sci 7:1576
Tan Z, Fang X, Tang S, Zhang J, Liu D et al (2015) Genetic map and QTL controlling fiber quality traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 203:615–628
Tang S, Teng Z, Zhai T, Fang X, Liu F et al (2015) Construction of genetic map and QTL analysis of fiber quality traits for Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 201:195–213
Van Berloo R (2008) GGT 2.0: Versatile Software for visualization and analysis of genetic data. J Hered 99:232–236
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wang Y, Huang H (2008) Genetics research into crop domestication and its application in soybean breeding. Chin Bull Bot 25:221–229
Wang JK, Wan XY, Crossa J (2006) QTL mapping of grain length in rice (Oryza sativa L.) using chromosome segment substitution lines. Genet Res 88:93–104
Wang J, Wan X, Li H, Pfeiffer WH, Crouch J et al (2007) Application of identified QTL-marker associations in rice quality improvement through a design-breeding approach. Theor Appl Genet 115:87–100
Wang P, Ding YZ, Lu QX, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2008) Development of Gossypium barbadense chromosome segment substitution lines in the genetic standard line TM-1 of Gossypium hirsutum. Chin Sci Bull 53:1512–1517
Wang P, Zhu Y, Song X, Cao Z, Ding Y et al (2012) Inheritance of long staple fiber quality traits of Gossypium barbadense in G. hirsutum background using CSILs. Theor Appl Genet 124:1415–1428
Wang H, Huang C, Guo H, Li X, Zhao W et al (2015) QTL Mapping for fiber and yield traits in Upland cotton under multiple environments. PLoS One 10:e0130742
Wang H, Huang C, Zhao W, Dai B, Shen C et al (2016) Identification of QTL for fiber quality and yield traits using two immortalized backcross populations in Upland cotton. PLoS One 11(12):e0166970
Wang M, Tu L, Min L, Lin Z, Wang P et al (2017) Asymmetric subgenome selection and cis-regulatory divergence during cotton domestication. Nat Genet 49:579–587
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Percival AE (1992) Genetic diversity in Gossypium hirsutum and the origion of Upland cotton. Am J Bot 79:1291–1310
Wendel JF, Brubaker CL, Seelanan T (2010) The origin and evolution of Gossypium: In: Stewart JM, Oosterhuis DM, Heitholt JJ, Mauney JR (eds) Physiology of cotton. Springer Netherlands, Dordrecht, pp 1–18
Xi ZY, He FH, Zeng RZ, Zhang ZM, Ding XH et al (2006) Development of a wide population of chromosome single-segment substitution lines in the genetic background of an elite cultivar of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genome 49:476–484
Xu P, Gao J, Cao Z, Chee PW, Guo Q et al (2017) Fine mapping and candidate gene analysis of qFL-chr1, a fiber length QTL in cotton. Theor Appl Genet 130:1309–1319
Yu J, Kohel RJ, Smith CW (2010) The construction of a tetraploid cotton genome wide comprehensive reference map. Genomics 95:230–240
Zhang J, Guo W, Zhang T (2002) Molecular linkage map of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L.) with a haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 105:1166–1174
Zhang ZS, Hu MC, Zhang J, Liu DJ, Zheng J et al (2009) Construction of a comprehensive PCR-based marker linkage map and QTL mapping for fiber quality traits in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 24:49–61
Zhang JF, Dan YZ, Liang Y, Gu YJ, Zhang BC et al (2012a) Evaluation of yield and fiber quality traits of chromosome segment substitution lines population (BC5F3 and BC5F34) in cotton. J Plant Genet Resour 13:773–781
Zhang K, Zhang J, Ma J, Tang S, Liu D et al (2012b) Genetic mapping and quantitative trait locus analysis of fiber quality traits using a three-parent composite population in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Breed 29:335–348
Zhang WW, Pan JS, He HL, Zhang C, Li Z et al (2012c) Construction of a high density integrated genetic map for cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 124:249–259
Zhang S, Wang T, Liu Q, Gao X, Zhu X et al (2015) Quantitative trait locus analysis of boll-related traits in an intraspecific population of Gossypium hirsutum. Euphytica 203:121–144
Zhang S, Feng L, Xing L, Yang B, Gao X et al (2016) New QTLs for lint percentage and boll weight mined in introgression lines from two feral landraces into Gossypium hirsutum acc TM-1. Plant Breed 135:90–101
Zhao L, Lv Y, Cai C, Tong X, Chen X et al (2012) Toward allotetraploid cotton genome assembly: integration of a high-density molecular genetic linkage map with DNA sequence information. BMC Genom 13:539. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-539
Zhu YJ, Wang P, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2010) Mapping QTLs for lint percentage and seed index using Gossypium barbadense chromosome segment introgression lines. Acta Agron Sin 36:1318–1323
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Dr Kunbo Wang, professor of Cotton Research Institute of Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, for kindly providing us with the seeds and pollens of Gossypium hirsutum races latifolium accs. TX-34 and TX-48 and punctatum acc. TX-114 at Hainan wild cotton growing garden.
Funding
This programme was financially supported in part by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2016YFD0100203) and Jiangsu Collaborative Innovation Centre for Modern Crop Production. The funding body has had no role in the design of the study and collection, analysis and interpretation of data or in writing the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in the reported research.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by Stefan Hohmann.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, L., Zhang, S., Xing, L. et al. QTL analysis for yield and fibre quality traits using three sets of introgression lines developed from three Gossypium hirsutum race stocks. Mol Genet Genomics 294, 789–810 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01548-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-019-01548-w