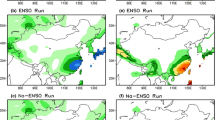
Abstract
By using the multi-taper method (MTM) of singular value decomposition (SVD), this study investigates the interdecadal evolution (10- to 30-year cycle) of precipitation over eastern China from 1951 to 2015 and its relationship with the North Pacific sea surface temperature (SST). Two significant interdecadal signals, one with an 11-year cycle and the other with a 23-year cycle, are identified in both the precipitation and SST fields. Results show that the North Pacific SST forcing modulates the precipitation distribution over China through the effects of the Pacific Decadal Oscillation (PDO)-related anomalous Aleutian low on the western Pacific subtropical high (WPSH) and Mongolia high (MH). During the development stage of the PDO cold phase associated with the 11-year cycle, a weakened WPSH and MH increased the precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin, whereas an intensified WPSH and MH caused the enhanced rain band to move northward to North China during the decay stage. During the development stage of the PDO cold phase associated with the 23-year cycle, a weakened WPSH and MH increased the precipitation over North China, whereas an intensified WPSH and the weakened MH increased the precipitation over South China during the decay stage. The 11-year and 23-year variabilities contribute differently to the precipitation variations in the different regions of China, as seen in the 1998 flooding case. The 11-year cycle mainly accounts for precipitation increases over the Yangtze River Basin, while the 23-year cycle is responsible for the precipitation increase over Northeast China. These results have important implications for understanding how the PDO modulates the precipitation distribution over China, helping to improve interdecadal climate prediction.
摘 要
本研究利用多窗谱分析—奇异值分解(MTM-SVD)方法, 研究了中国东部降水的年代际演变(10–30年的周期)及其与北太平洋海表温度(SST)的关系. 在1951–2015年期间, 中国降水和北太平洋SST场都具有两个重要的年代际信号, 其周期分别为11年和23年. 通过太平洋年代际振荡(PDO)相关的阿留申低压异常对西太平洋副热带高压(WPSH)和蒙古高压(MH)的影响, 北太平洋SST强迫可以调节中国降水的年代际变化. 对于11年周期, 在PDO负位相(PDO−)的发展期, WPSH和MH的减弱使长江流域的降水增多; 而在PDO–衰退期, WPSH和MH的增强导致雨带北移至华北地区. 对于23年周期, 在PDO−发展期, WPSH和MH的减弱使华北地区的降水增多; 在PDO–衰退期, WPSH偏强而MH偏弱则有利于华南的降水增多. 如1998年洪水事件的个例所示, 11年和23年周期变率对中国不同地区降水变化的贡献存在差异: 11年周期主要是长江流域降水增多的原因, 而23年周期是东北地区降水增多的原因. 这些结果阐明了PDO是如何调节中国降水年代际变化的过程和机制, 对提高气候年代际预测的能力具有重要意义.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adler, R. F., and Coauthors, 2003: The version-2 global precipitation climatology project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979-present). Journal of Hydrometeorology, 4, 1147–1167, https://doi.org/10.1175/1575-7521(2000)004<1147:TVGPCP>2.0.CO;2.
Chang, C.-P., Y. S. Zhang, and T. Li, 2000: Interannual and inter-decadal variations of the East Asian summer monsoon and Tropical Pacific SSTs. Part I: Roles of the subtropical ridge. J. Climate, 13, 4310–4325, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2000)013<4310:iaivot>2.0.co;2.
Chen, J., Z. P. Wen, R. G. Wu, X. Wang, C. He, and Z. S. Chen, 2017: An interdecadal change in the intensity of interannual variability in summer rainfall over southern China around early 1990s. Climate Dyn., 48, 191–207, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-016-3069-8.
Chen, W., J. Feng, and R. G. Wu, 2013: Roles of ENSO and PDO in the link of the East Asian winter monsoon to the following summer monsoon. J. Climate, 26, 622–635, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-12-00021.1.
Chen, Z. S., Z. P. Wen, R. G. Wu, P. Zhao, and J. Cao, 2014: Influence of two types of El Niños on the East Asian climate during boreal summer: A numerical study. Climate Dyn., 43, 469–481, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-013-1943-1.
Compo, G. P., and Coauthors, 2011: The twentieth century reanalysis project. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 137, 1–28, https://doi.org/10.1002/qj.776.
Deng, W. T., Z. B. Sun, G. Zeng, and D. H. Ni, 2009: Interdecadal variation of summer precipitation pattern over eastern China and its relationship with the North Pacific SST. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 33, 835–846, https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2009.04.16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Deser, C., A. S. Phillips, and J. W. Hurrell, 2004: Pacific inter-decadal climate variability: Linkages between the tropics and the North Pacific during boreal winter since 1900. J. Climate, 17, 3109–3124, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(2004)017<3109:PICVLB>2.0.CO;2.
Ding, Y. H., Z. Y. Wang, and Y. Sun, 2008: Inter-decadal variation of the summer precipitation in East China and its association with decreasing Asian summer monsoon. Part I: Observed evidences. International Journal of Climatology, 28, 1139–1161, https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.1615.
Ding, Y. H., P. Liang, Y. J. Liu, and Y. C. Zhang, 2020: Multiscale variability of Meiyu and its prediction: A new review. J. Geo-phys. Res., 125, e2019JD031496, https://doi.org/10.1029/2019JD031496.
Dong, X., and F. Xue, 2016: Phase transition of the Pacific decadal oscillation and decadal variation of the East Asian summer monsoon in the 20th century. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 33, 330–338, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-015-5130-7.
Fan, Y., and K. Fan, 2017: Pacific decadal oscillation and the decadal change in the intensity of the interannual variability of the South China Sea summer monsoon. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 10, 162–167, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2016.1256189.
Feng, Licheng, Rong-Hua Zhang, Xue Han, Bo Yu and Chuan Gao., 2021: On the second-year warming in late 2019 over the tropical Pacific and its triggering mechanism attributed to Indian Ocean effects. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 38(12), 2153–2166, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-021-1234-4.
Gao, C., M. N. Chen, L. Zhou, L. C. Feng, and R.-H. Zhang, 2022: The 2020–2021 prolonged La Nina evolution in the tropical Pacific. Science China Earth Sciences, 65, 2248–2266, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-022-9985-4.
Hu, J. Y., R.-H. Zhang, and C. Gao, 2019: A hybrid coupled ocean-atmosphere model and its simulation of ENSO and atmospheric responses. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 36, 643–657, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8197-8.
Hu, J. Y., H. N. Wang, C. Gao, and R.-H. Zhang, 2022a: Inter-decadal wind stress variability over the tropical Pacific causes ENSO diversity in an intermediate coupled model. Climate Dynamics, 60, 1831–1847, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-022-06414-x.
Hu, P., W. Chen, S. F. Chen, L. Wang, and Y. Y. Liu, 2022b: The weakening relationship between ENSO and the South China Sea summer monsoon onset in recent decades. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 39(3), 443–455, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-021-1208-6.
Jo, H.-S., S.-W. Yeh, and S.-K. Lee, 2015: Changes in the relationship in the SST variability between the tropical Pacific and the North Pacific across the 1998/1999 regime shift. Geophys. Res. Lett., 42, 7171–7178, https://doi.org/10.1002/2015GL065049.
Kalnay, E., and Coauthors, 1996: The NCEP/NCAR 40-year reanalysis project. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77, 437–472, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1996)077<0437:TNYRP>2.0.CO;2.
Kitoh, A., 2017: The Asian monsoon and its future change in climate models: A review. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 95, 7–33, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2017-002.
Latif, M., and T. P. Barnett, 1996: Decadal climate variability over the North Pacific and North America: Dynamics and predictability. J. Climate, 9, 2407–2423, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1996)009<2407:DCVOTN>2.0.CO;2.
Lau, K.-M., and M.-T. Li, 1984: The monsoon of East Asia and its global associations-A survey. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 65, 114–125, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1984)065<0114:TMOEAA>2.0.CO;2.
Li, J. P., and C. Q. Ruan, 2018: The North Atlantic-Eurasian teleconnection in summer and its effects on Eurasian climates. Environmental Research Letters, 13, 024007, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/aa9d33.
Li, J. P., F. Zheng, C. Sun, J. Feng, and J. Wang, 2019: Pathways of influence of the northern hemisphere mid-high latitudes on East Asian climate: A review. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 36, 902–921, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-019-8236-5.
Li, S. L., L. R. Ji, W. T. Lin, and Y. Q. Ni, 2001: The maintenance of the blocking over the Ural mountains during the second Meiyu period in the summer of 1998. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 18, 87–105, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-001-0006-4.
Li, X. Y., and R. Y. Lu, 2018: Subseasonal change in the seesaw pattern of precipitation between the Yangtze River basin and the tropical western North Pacific during summer. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 35, 1231–1242, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-018-7304-6.
Lin, Y.-F., J.-Y. Yu, C.-R. Wu, F. Zheng, 2021: The footprint of the 11-year solar cycle in Northeastern Pacific SSTs and its influence on the Central Pacific El Nino. Geophysical Research Letters, 48, e2020GL091369, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020GL091369.
Liu, J. P., H.-L. Ren, W. J. Li, and J. Q. Zuo, 2018: Remarkable impacts of Indian Ocean sea surface temperature on inter-decadal variability of summer rainfall in Southwestern China. Atmosphere, 9, 103, https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9030103.
Lü, J. M., C. W. Zhu, J. H. Ju, and X. Lin, 2014: Interdecadal variability in summer precipitation over East China during the past 100 years and its possible causes. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 38, 782–794, https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.1401.13227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Mann, M. E., and J. Park, 1994: Global-scale modes of surface temperature variability on interannual to century timescales. J. Geophys. Res., 99, 2 5819–2 5833, https://doi.org/10.1029/94JD02396.
Mann, M. E., and J. Park, 1999: Oscillatory spatiotemporal signal detection in climate studies: A multiple-taper spectral domain approach. Advances in Geophysics, 41, 1–131, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-2687(08)60026-6.
Mann, M. E., B. A. Steinman, D. J. Brouillette, and S. K. Miller, 2021: Multidecadal climate oscillations during the past millennium driven by volcanic forcing. Science, 371, 1014–1019, https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc5810.
Mantua, N. J., 1999: The Pacific decadal oscillation: A brief overview for non-specialists. Encyclopedia of Environmental Change. Joint Institute for the Study of the Atmosphere and Oceans University of Washington, Seattle, Washington, USA.[Available online from http://research.jisao.washington.edu/pdo/]
Mantua, N. J., S. R. Hare, Y. Zhang, J. M. Wallace, and R. C. Francis, 1997: A Pacific interdecadal climate oscillation with impacts on salmon production. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 78, 1069–1080, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0477(1997-078<1069:APICOW>2.0.CO;2.
Peng, D. D., and T. J. Zhou, 2017: Why was the arid and semiarid northwest China getting wetter in the recent decades. J. Geophys. Res., 122, 9060–9075, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016JD026424.
Qian, C., and T. J. Zhou, 2014: Multidecadal variability of North China aridity and its relationship to PDO during 1900–2010. J. Climate, 27, 1210–1222, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-13-00235.1.
Rayner, N. A., D. E. Parker, E. B. Horton, C. K. Folland, L. V. Alexander, D. P. Rowell, E. C. Kent, and A. Kaplan, 2003: Global analyses of sea surface temperature, sea ice, and night marine air temperature since the late nineteenth century. J. Geophys. Res., 108, 4407, https://doi.org/10.1029/2002JD002670.
Ren, G. Y., Y. H. Ding, Z. C. Zhao, J. Y. Zheng, T. W. Wu, G. L. Tang, and Y. Xu, 2012: Recent progress in studies of climate change in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 29, 958–977, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-012-1200-2.
Samel, A. N., and X. Z. Liang, 2003: Understanding relationships between the 1998 Yangtze River flood and northeast Eurasian blocking. Climate Research, 23, 149–158, https://doi.org/10.3354/cr023149.
Si, D., and Y. H. Ding, 2016: Oceanic forcings of the interdecadal variability in East Asian summer rainfall. J. Climate, 29, 7633–7649, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-15-0792.1.
Simmonds, I., D. H. Bi, and P. Hope, 1999: Atmospheric water vapor flux and its association with rainfall over China in summer. J. Climate, 12, 1353–1367, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1999)012<1353:Awvfai>2.0.CO;2.
Sun, C., F. Kucharski, J. P. Li, F. F. Jin, I. S. Kang, and R. Q. Ding, 2017: Western tropical Pacific multidecadal variability forced by the Atlantic multidecadal oscillation. Nature Communications, 8, 15998, https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms15998.
Thomson, D. J., 1982: Spectrum estimation and harmonic analysis. Proceedings of the IEEE, 70, 1055–1096, https://doi.org/10.1109/PROC.1982.12433.
Wei, F. Y., T. Zhang, and X. Han, 2013: MTM-SVD approach and its application in the spatio-temporal variability analysis of SST of the Indian Ocean and precipitation of South China. Marine Science Bulletin, 32, 133–140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Wu, J. J., and Z. W. Wu, 2019: Inter-decadal change of the spring North Atlantic Oscillation impact on the summer Pamir-Tienshan snow cover. International Journal of Climatology, 39, 629–642, https://doi.org/10.1002/joc.5831.
Wu, M. M., and L. Wang, 2019: Enhanced correlation between ENSO and western North Pacific monsoon during boreal summer around the 1990s. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. Lett., 12, 376–384, https://doi.org/10.1080/16742834.2019.1641397.
Xian, P., and C. Y. Li, 2003: Interdecadal modes of sea surface temperature in the North Pacific Ocean and its evolution. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 861–868. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Xu, J. J., and J. C. L. Chan, 2002: Interannual and interdecadal variability of winter precipitation over China in relation to global sea level pressure anomalies. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 19, 914–926, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-002-0055-3.
Yang, Q., Z. G. Ma, X. G. Fan, Z. L. Yang, Z. F. Xu, and P. L. Wu, 2017: Decadal modulation of precipitation patterns over Eastern China by sea surface temperature anomalies. J. Climate, 30, 7017–7033, https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-16-0793.1.
Yang, X. Q., Y. M. Zhu, Q. Xie, X. J. Ren, and G. Y. Xu, 2004: Advances in studies of Pacific decadal oscillation. Chinese Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 28, 979–992, https://doi.org/10.3878/j.issn.1006-9895.2004.06.15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhai, J. Q., X. F. Zeng, B. D. Su, and T. Jiang, 2009: Patterns of dryness/wetness in China before 2050 projected by the ECHAM5 model. Climate Change Research, 5, 220–225. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Zhang, J. Y., L. Wang, S. Yang, W. Chen, and J. L. Huangfu, 2016a: Decadal changes of the wintertime tropical tropospheric temperature and their influences on the extratropical climate. Science Bulletin, 61, 737–744, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1054-6.
Zhang, L., K. Fraedrich, X. H. Zhu, F. Sielmann, and X. F. Zhi, 2015: Interannual variability of winter precipitation in Southeast China. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 119, 229–238, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-014-1111-5.
Zhang, Q., C. Y. Xu, Z. Zhang, Y. D. Chen, and C. L. Liu, 2009: Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation over China, 1951–2005. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 95, 53–68, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00704-007-0375-4.
Zhang, Q., Y. J. Zheng, V. P. Singh, M. Luo, and Z. H. Xie, 2017a: Summer extreme precipitation in eastern China: Mechanisms and impacts. J. Geophys. Res., 122, 2766–2778, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016jd025913.
Zhang, R., Q. Y. Min, and J. Z. Su, 2017b: Impact of El Niño on atmospheric circulations over East Asia and rainfall in China: Role of the anomalous western North Pacific anticyclone. Science China Earth Sciences, 66, 1124–1132, https://doi.org/10.1007/s11430-016-9026-x.
Zhang, R.-H., and S. Levitus, 1997: Structure and cycle of decadal variability of upper-ocean temperature in the North Pacific. J. Climate, 10, 710–727, https://doi.org/10.1175/1520-0442(1997)010<0710:SACODV>2.0.CO;2.
Zhang, R.-H. and C. Gao, 2016: The IOCAS intermediate coupled model (IOCAS ICM) and its real-time predictions of the 2015–16 El Niño event. Science Bulletin, 66 (13), 1061–1070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1064-4. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-016-1064-4.
Zhang, R.-H., L. M. Rothstein, and A. J. Busalacchi, 1998: Origin of upper-ocean warming and El Nino change on decadal scales in the tropical Pacific Ocean. Nature, 391, 879–883, https://doi.org/10.1038/36081.
Zhang, R.-H., and Coauthors, 2020: A review of progress in coupled ocean-atmosphere model developments for ENSO studies in China. Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 38, 930–961, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00343-020-0157-8.
Zhang, R.-H., C. Gao, and L. C. Feng, 2022: Recent ENSO evolution and its real-time prediction challenges. National Science Review, 9(4), nwac052, https://doi.org/10.1093/nsr/nwac052.
Zhang, W. J., and Coauthors, 2016b: Unraveling El Niño’s impact on the East Asian Monsoon and Yangtze River summer flooding. Geophys. Res. Lett., 43, 1 1375–1 1382, https://doi.org/10.1002/2016gl071190.
Zhao, L., J. S. Wang, and H. J. Zhao, 2012: Solar cycle signature in decadal variability of monsoon precipitation in China. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 90, 1–9, https://doi.org/10.2151/jmsj.2012-101.
Zhao, S., J. P. Li, and C. Sun, 2016: Decadal variability in the occurrence of wintertime haze in central eastern China tied to the Pacific Decadal Oscillation. Scientific Reports, 6, 27424, https://doi.org/10.1038/srep27424.
Zhou, T. J., D. Y. Gong, J. Li, and B. Li, 2009: Detecting and understanding the multi-decadal variability of the East Asian summer monsoon recent progress and state of affairs. Meteor. Z., 18, 455–467, https://doi.org/10.1127/0941-2948/2009/0396.
Zhou, T. J., B. Wu, and L. Dong, 2014: Advances in research of ENSO changes and the associated impacts on Asian-Pacific climate. Asia-Pacific Journal of Atmospheric Sciences, 50, 405–422, https://doi.org/10.1007/s13143-014-0043-4.
Zhou, W., C. Li, and J. C. L. Chan, 2006: The interdecadal variations of the summer monsoon rainfall over South China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys., 93, 165–175, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00703-006-0184-9.
Zhu, Y. L., H. J. Wang, W. Zhou, and J. H. Ma, 2011: Recent changes in the summer precipitation pattern in East China and the background circulation. Climate Dyn., 36, 1463–1473, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-010-0852-9.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the reviewers for their precious and insightful comments, which greatly helped improve our manuscript. This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 42030410), Laoshan Laboratory (No. LSKJ202202403-2), the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB40000000), and the Startup Foundation for Introducing Talent of NUIST.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Article Highlights
• The precipitation over eastern China and the SST in the North Pacific exhibit two dominant interdecadal cycles in their local fractional variance spectrum.
• The covarying patterns of precipitation, SST, and related atmospheric fields are analyzed for the processes and mechanisms associated with the PDO.
• The relative contributions of the two interdecadal variabilities to precipitation anomalies over different regions of China are illustrated using the 1998 flooding case.
Electronic Supplementary Material to
376_2023_3011_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Synergistic Interdecadal Evolution of Precipitation over Eastern China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation during 1951–2015
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, M., Zhang, RH., Hu, J. et al. Synergistic Interdecadal Evolution of Precipitation over Eastern China and the Pacific Decadal Oscillation during 1951–2015. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 41, 53–72 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-3011-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-023-3011-z