Abstract
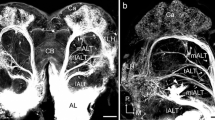
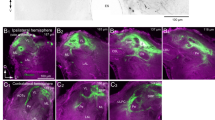
A detailed account is given by the octopaminergic innervation of the antennal heart in Schistocerca gregaria using various immunohistochemical methods. Anterograde axonal filling illustrates the unilateral innervation on the medial ventral surface of the pumping muscle of the antennal heart via the paired corpora cardiaca nerve III. In addition, antibody staining revealed that ascending axons of this nerve terminate at the ampullae of the antennal heart forming synaptoid structures and extensive neurohaemal release sites. Due to the innervation by two dorsal unpaired median neurons, the presence of the biogenic amines octopamine and tyramine could be visualized by immunocytochemistry in an insect antennal heart for the first time. The data suggest that tyramine acts as a precursor and not purely as an independent transmitter. While the octopaminergic fibers innervating the pumping muscle of the antennal heart indicate a cardioregulatory role, we conclude that octopamine released from the neurohaemal area is pumped into the antennae and an involvement in the modulation of the antennal sensory sensitivity is discussed.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atwood HL, Govind CK, Wu CF (1993) Differential ultrastructure of synaptic terminals on ventral longitudinal abdominal muscles in Drosophila larvae. J Neurobiol 24:1008–1024
Bayer R (1968) Untersuchungen am Kreislaufsystem der Wanderheuschrecke (Locusta migratoria migratorioides R. et F., Orthopteroidea) mit besonderer Berücksichtigung des Blutdruckes. Z vgl Physiol 58:76–135
Beattie TM (1976) Autolysis in axon terminals of a new neurohaemal organ in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Tissue Cell 8:305–310
Benfenati F, Bähler M, Jahn R, Greengard P (1989) Interactions of synapsin I with small synaptic vesicles. J Cell Biol 108:1863–1872
Beutel RG, Friedrich F, Ge S-Q, Yang X-K (2014) Insect morphology and phylogeny. De Gruyter, Berlin
Blumer MJ, Gahleitner P, Narzt T, Handl C, Ruthensteiner B (2002) Ribbons of semithin sections: an advanced method with a new type of diamond knife. J Neurosci Methods 120:11–16
Boppana S, Hillyer JF (2014) Hemolymph circulation in insect sensory appendages: functional mechanics of antennal accessory pulsatile organs (auxiliary hearts) in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J Exp Biol 217:3006–3014. doi:10.1242/jeb.106708
Bräunig P (1990) The morphology of suboesophageal ganglion ceils innervating the nervus corporis cardiaci III of the locust. Cell Tissue Res 260:95–108
Bräunig P, Pflüger HJ (2001) The unpaired median neurons of insects. Adv Insect Physiol 28:185–266
Brigaud I, Grosmaitre X, François MC, Jacquin-Joly E (2009) Cloning and expression pattern of a putative octopamine/tyramine receptor in antennae of the noctuid moth Mamestra brassicae. Cell Tissue Res 335:455–463. doi:10.1007/s00441-008-0722-5
Bullerjahn A, Mentel T, Pflüger HJ, Stevenson PA (2006) Nitric oxide: a co-modulator of efferent peptidergic neurosecretory cells including a unique octopaminergic neuron innervating locust heart. Cell Tissue Res 325:345–360. doi:10.1007/s00441-006-0188-2
Clark J, Lange AB (2003) Octopamine modulates spermathecal muscle contractions in Locusta migratoria. J Comp Physiol A Neuroethol Sens Neural Behav Physiol 189:105–114. doi:10.1007/s00359-002-0375-x
Crossman AR, Kerkut GA, Pitman RM, Walker RJ (1971) Electrically excitable nerve cell bodies in the central ganglion of two insect species Periplaneta americana and Schistocerca gregaria. Investigation of cell geometry and morphology by intracellular dye injection. Comp Biochem Physiol A 40:579–594
da Silva R, Lange AB (2008) Tyramine as a possible neurotransmitter/neuromodulator at the spermatheca of the African migratory locust, Locusta migratoria. J Insect Physiol 54:1306–1313. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2008.07.001
Dacks AM, Dacks JB, Christensen TA, Nighorn AJ (2006) The cloning of one putative octopamine receptor and two putative serotonin receptors from the tobacco hawkmoth, Manduca sexta. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 36:741–747. doi:10.1016/j.ibmb.2006.07.002
Dolzer J, Krannich S, Fischer K, Stengl M (2001) Oscillations of the transepithelial potential of moth olfactory sensilla are influenced by octopamine and serotonin. J Exp Biol 204:2781–2794
Donini A, Lange AB (2004) Evidence for a possible neurotransmitter/neuromodulator role of tyramine on the locust oviducts. J Insect Physiol 50:351–361. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2004.02.005
Downer RGH, Hiripi L, Juhos S (1993) Characterization of the tyraminergic system in the central nervous system of the locust, Locusta migratoria migratoides. Neurochem Res 18:1245–1248
Duch C, Mentel T, Pflüger HJ (1999) Distribution and activation of different types of octopaminergic DUM neurons in the locust. J Comp Neurol 403(1):119–134
Dukas R (2008) Evolutionary biology of insect learning. Annu Rev Entomol 53:145–160. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.53.103106.093343
Evans PD (1985) Octopamine. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry and pharmacology, vol 11. Pergamon Press, Oxford UK, pp 499–530
Farooqui T (2007) Octopamine-mediated neuromodulation of insect senses. Neurochem Res 32:1511–1529. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9344-7
Ferber M, Pflüger HJ (1990) Bilaterally projecting neurons in pregenital abdominal ganglia of the locust: anatomy and peripheral targets. J Comp Neurol 302:447–460. doi:10.1002/cne.903020303
Ferber M, Pflüger HJ (1992) An identified dorsal unpaired median neuron and bilaterally projecting neurons exhibiting bovine pancreatic polypeptide/FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in abdominal ganglia of the migratory locust. Cell Tissue Res 267:85–98
Flecke C, Stengl M (2009) Octopamine and tyramine modulate pheromone-sensitive olfactory sensilla of the hawkmoth Manduca sexta in a time-dependent manner. J Comp Physiol A 195:529–545. doi:10.1007/s00359-009-0429-4
Fox LE, Soll DR, Wu CF (2006) Coordination and modulation of locomotion pattern generators in Drosophila larvae: effects of altered biogenic amine levels by the tyramine beta hydroxylase mutation. J Neurosci 26:1486–1498. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4749-05.2006
Fussnecker BL, Smith BH, Mustar JA (2006) Octopamine and tyramine influence the behavioral profile of locomotor activity in the honey bee (Apis mellifera). J Insect Physiol 52:1083–1092
Gadenne C, Barrozo RB, Anton S (2016) Plasticity in insect olfaction: to smell or not to smell? Annu Rev Entomol 61:317–333. doi:10.1146/annurev-ento-010715-023523
Galizia CG (2014) Olfactory coding in the insect brain: data and conjectures. Eur J Neurosci 39:1784–1795. doi:10.1111/ejn.12558
Goosey MW, Candy DJ (1982) The release and removal of octopamine by tissues of the locust Schistocerca americana gregaria. Insect Biochem 12:681–685. doi:10.1016/0020-1790(82)90057-9
Grosmaitre X, Marion-Poll F, Renou M (2001) Biogenic amines modulate olfactory receptor neurons firing activity Mamestra brassicae. Chem Senses 26:653–661
Hansson BS, Christensen TA (1999) Functional characteristics of the antennal lobe. In: Hansson BS (ed) Insect olfaction. Springer, Berlin, pp 125–161
Hassler R, Chung JW (1976) The discrimination of nine different types of synaptic boutons in the fundus striati (nucleus accumbens septi). Cell Tissue Res 168:489–505. doi:10.1007/BF00215999
Heinrich R, Jacobs K, Lakes-Harlan R (1998) Tracing of a neuronal network in the locust by pressure injection of markers into a synaptic neuropil. J Neurosci Methods 80:81–89
Hertel W, Penzlin H (1992) Function and modulation of the antennal heart of Periplaneta americana (L.). Acta Biol Hung 43:113–125
Hertel W, Richter M (1997) Contributions to physiology of the antenna-heart in Periplaneta americana (L.) (Blattodea: Blattidae). J Insect Physiol 43:1015–1021. doi:10.1016/S0022-1910(97)00073-5
Hertel W, Pass G, Penzlin H (1985) Electrophysiological investigation of the antennal heart of Periplaneta americana and its reaction to proctolin. J Insect Physiol 31:563–572
Hertel W, Pass G, Penzlin H (1988) The effects of the neuropeptide proctolin and of octopamine on the antennal heart of Periplaneta americana. Symp Biol Hung 36:351–362
Hertel W, Richter M, Rapus J, Eckert M, Penzlin H (1995) The role of proctolin in the antenna-heart beat acceleration of Periplaneta americana (L.). Acta Biol Hung 46:491–506
Hertel W, Neupert S, Eckert M (2012) Proctolin in the antennal circulatory system of lower Neoptera: a comparative pharmacological and immunohistochemical study. Physiol Entomol 37:160–170
Hillier NK, Kavanagh RMB (2015) Differential octopaminergic modulation of olfactory receptor neuron responses to sex pheromones in Heliothis virescens. PLoS One 10:17. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0143179
Honegger HW, Allgäuer C, Klepsch U, Welker J (1990) Morphology of antennal motoneurons in the brains of two crickets, Gryllus bimaculatus and Gryllus campestris. J Comp Neurol 291:256–268
Hoyle G (1975) Evidence that insect dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons are octopaminergic. J Exp Zool 193(3):425–431
Imms AD (1939) On the antennal musculature in insects and other arthropods. Q J Microsc Sci 81:273–320
Jung JW, Kim JH, Pfeiffer R, Ahn YJ, Page TL, Kwon HW (2013) Neuromodulation of olfactory sensitivity in the peripheral olfactory organs of the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. PLoS One 8(11):e81361
Kalogianni E, Pflüger HJ (1992) The identification of motor and unpaired median neurons innervating the locust oviduct. J Exp Biol 168:177–198
Keil TA (1999) Morphology and development of the peripheral olfactory organs. In: Hansson BS (ed) Insect olfaction. Springer, Berlin, pp 5–47
Kononenko NL, Wolfenberg H, Pflüger HJ (2009) Tyramine as an independent transmitter and a precursor of octopamine in the locust central nervous system: an immunocytochemical study. J Comp Neurol 512(4):433–452. doi:10.1002/cne.21911
Kurylas AE, Rohlfing T, Krofczik S, Jenett A, Homberg U (2008) Standardized atlas of the brain of the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria. Cell Tissue Res 333(1):125–145
Lam F, Mcneil JN, Cn Donly (2013) Octopamine receptor gene expression in three lepidopteran species of insect. Peptides 41:66–73. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2012.03.034
Lange AB (2009) Tyramine: from octopamine precursor to neuroactive chemical in insects. Gen Comp Endocrinol 162:18–26. doi:10.1016/j.ygcen.2008.05.021
Lange AB, Orchard I (1986) Identified octopaminergic neurons modulate contractions of locust visceral muscle via adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate (cyclic AMP). Brain Res 363:340–349
Lange AB, Chan KK, Stay B (1993) Effect of allatostatin and proctolin on antennal pulsatile organ and hindgut muscle in the cockroach, Diploptera punctata. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 24:79–92. doi:10.1002/arch.940240203
Lehman HK (1990) Circadian control of Manduca sexta flight. Soc Neurosci Abs 16:1334
Linn CE, Roelofs WL (1986) Modulatory effects of octopamine and serotonin on male sensitivity and periodicity of response to sex pheromone in the cabbage looper moth, Trichoplusia ni. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 3:161–171
Linn CE, Campbell MG, Roelofs WL (1992) Photoperiod cues and the modulatory action of octopamine and 5-Hydroxytryptamine on locomotor and pheromone response in male gypsy moth, Lymantria dispar. Arch Insect Biochem 20:265–284
Linn CE, Campell MG, Poole KR, Wu WQ, Roelofs WL (1996) Effects of photoperiod on the circadian timing of pheromone response in male Trichoplusia ni: relationship to the modulatory action of octopamine. J Insect Physiol 42:881–891
Matheson T (1997) Octopamine modulates the responses and presynaptic inhibition of proprioreceptive sensory neurones in the locust Schistocerca gregaria. J Exp Biol 200:1317–1325
Mercer AR, Menzel R (1982) The effects of biogenic amines on conditioned and unconditioned responses to olfactory stimuli in the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol 145:363–368
Merlin C, Lucas P, Rochat D, François MC, Maïbèche-Coisne M, Jacquin-Joly E (2007) An antennal circadian clock and circadian rhythms in peripheral pheromone reception in the moth Spodoptera littoralis. J Biol Rhythms 22:502–514. doi:10.1177/0748730407307737
Michels B, Diegelmann S, Tanimoto H, Schwenkert I, Buchner E, Gerber B (2005) A role for synapsin in associative learning: the Drosophila larva as a study case. Learn Mem 12:224–231. doi:10.1101/lm.92805
Miller TA (1985) Structure and physiology of the circulatory system. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology, vol 3. Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp 289–353
Nagaya Y, Kutsukake M, Chigusb SI, Komatsu A (2002) A trace amine, tyramine, functions as a neuromodulator in Drosophila melanogaster. Neurosci Lett 329:324–328
Neckameyer WS, Leal SM (2009) Biogenic amines as circulating hormones in insects. In: Pfaff DW et al (eds) Hormones, brain and behavior, 2nd edn, part 2. Academic Press, Amsterdam, pp 967–1003. doi:10.1016/B978-008088783-8.00028-0
Orchard I, Lange AB (1985) Evidence for octopaminergic modulation of an insect visceral muscle. J Neurobiol 16:171–181. doi:10.1002/neu.480160303
Orchard I, Lange AB (1986) Neuromuscular transmission in an insect visceral muscle. J Neurobiol 17:359–372
Orchard I, Lange AB (1987) The release of octopamine and proctolin from an insect visceral muscle: effects of high-potassium saline and neural stimulation. Brain Res 413:251–258
Papaefthimiou C, Theophilidis G (2011) Octopamine—a single modulator with double action on the heart of two insect species (Apis mellifera macedonica and Bactrocera oleae): acceleration vs. inhibition. J Insect Physiol 57:316–325. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.11.022
Pass G (1985) Gross and fine structure of the antennal circulatory organ in cockroaches (Blattodea, Insecta). J Morphol 185:255–268
Pass G (1991) Antennal circulatory organs in Onychophora, Myriapoda and Hexapoda: functional morphology and evolutionary implications. Zoomorphology 110:145–164
Pass G (1998) Accessory pulsatile organs. In: Harrison F, Locke M (eds) Microscopic anatomy of invertebrates, vol 11B. Wiley, New York, pp 621–640
Pass G (2000) Accessory pulsatile organs: evolutionary innovations in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 45:495–518
Pass G, Agricola H, Birkenbeil H, Penzlin H (1988a) Morphology of neurons associated with the antennal heart of Periplaneta americana (Blattodea, Insecta). Cell Tissue Res 253:319–326
Pass G, Sperk G, Agricola H, Baumann E, Penzlin H (1988b) Octopamine in a neurohaemal area within the antennal heart of the American cockroach. J Exp Biol 135:495–498
Pass G, Gereben-Krenn BA, Merl M, Plant J, Szucsich NU, Tögel M (2006) Phylogenetic relationships of the orders of Hexapoda: contributions from the circulatory organs for a morphological data matrix. Arthropod Syst Phylogeny 64:165–203
Pawlowa M (1895) Über ampullenartige Blutcirculationsorgane im Kopfe verschiedener Orthopteren. Zool Anz 18:7–13
Pophof B (2000) Octopamine modulates the sensitivity of silkmoth pheromone receptor neurons. J Comp Physiol A 186:307–313
Pophof B (2002) Octopamine enhances moth olfactory responses to pheromones, but not those to general odorants. J Comp Physiol A 188:659–662
Predel R (2001) Peptidergic neurohaemal system of an insect: mass spectrometric morphology. J Comp Neurol 436:363–375. doi:10.1002/cne.1073
Predel R, Neupert S, Wicher D, Gundel M, Roth S, Derst C (2004) Unique accumulation of neuropeptides in an insect: FMRFamide-related peptides in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. Eur J Neurosci 206:1499–1513. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2004.03598.x
Ramirez JM, Pearson KG (1991) Octopamine induces bursting and plateau potentials in insect neurons. Brain Res 549:332–337
Richter M, Hertel W (1997) Contributions to the physiology of the antenna–heart in Periplaneta americana (L.) (Blattodea: Blattidae). J Insect Physiol 43:1015–1021
Rillich J, Stevenson PA, Pflüger HJ (2013) Flight and walking in locusts–cholinergic co-activation, temporal coupling and its modulation by biogenic amines. PLoS One 8:e62899
Roeder T (1999) Octopamine in invertebrates. Prog Neurobiol 59:533–561
Roeder T (2005) Tyramine and octopamine: ruling behavior and metabolism. Annu Rev Entomol 50:447–477. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.50.071803.130404
Schendzielorz T, Schirmer K, Stolte P, Stengl M (2015) Octopamine regulates antennal sensory neurons via daytime-dependent changes in cAMP and IP-3 levels in the hawkmoth Manduca sexta. PLoS One 10:e0121230
Schneider D (1964) Insect antennae. Annu Rev Entomol 9:103–122
Sombati S, Hoyle G (1984) Generation of specific behaviors in a locust by local release into neuropil of the natural neuromodulator octopamine. J Neurobiol 15:481–506
Stelinski LL, Miller JR, Gut LJ (2003) Increased EAG responses of tortricid moths after prolonged exposure to plant volatiles: evidence for octopamine-mediated sensitization. J Insect Physiol 49:845–856. doi:10.1016/S0022-1910(03)00136-7
Stengl M (2010) Pheromone transduction in moths. Front Cell Neurosci 4:1–5. doi:10.3389/fncel.2010.00133
Stevenson PA (1999) Colocalisation of taurine- with transmitter-immunoreactivities in the nervous system of the migratory locust. J Comp Neurol 404:86–96
Stevenson PA, Kutsch W (1986) Basic circuitry of an adult-specific motor program completed with embryogenesis. Naturwissenschaften 71:741–743
Stevenson PA, Pflüger HJ (1994) Colocalisation of octopamine and FMRFamide related peptide in identified heart projecting (DUM) neurons in the locust revealed by immunocytochemistry. Brain Res 638:117–125
Stevenson PA, Spörhase-Eichmann U (1995) Localization of octopaminergic neurons in insects. Comp Biochem Phys A 110:203–215
Stocker B (2011) Locust thoracic dorsal unpaired median (DUM) neurons: differential activation and peripheral distribution of octopamine and tyramine, Dissertation. Freie Universität Berlin, Berlin
Suggs JM, Jones TH, Murphree SC, Hillyer JF (2016) CCAP and FMRFamide-like peptides accelerate the contraction rate of the antennal accessory pulsatile organs (auxiliary hearts) of mosquitoes. J Exp Biol 219:2388–2395. doi:10.1242/jeb.141655
Tsai JP, Tung LC, Lee MC, Lin JT (2004) The effects of octopamine on the cardiac output of cockroach by using computer-based video analysis on measuring stroke volume. Taiwana 49:7–15
Vergoz V, McQuillan HJ, Geddes LH, Pullar K, Nicholson BJ, Paulin MG, Mercer AR (2009) Peripheral modulation of worker bee responses to queen mandibular pheromone. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:20930–20935. doi:10.1073/pnas.0907563106
Verlinden H, Vleugels R, Marchal E, Badisco L, Pflüger HJ, Blenau W, Broeck JV (2010) The role of octopamine in locusts and other arthropods. J Insect Physiol 56:854–867. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2010.05.018
von Nickisch-Rosenegk E, Krieger J, Kubick S, Laage R, Strobel J, Strotmann J, Breer H (1996) Cloning of biogenic amine receptors from moths (Bombyx mori and Heliothis virescens). Insect Biochem Mol Biol 26:817–827
Watson AH (1984) The dorsal unpaired median neurons of the locust metathoracic ganglion: neuronal structure and diversity, and synapse distribution. J Neurocytol 13:303–327
Wirkner CS, Tögel M, Pass G (2013) The arthropod circulatory system. In: Minelli A, Boxshall G, Fusco G (eds) Arthropod biology and evolution, molecules, development, morphology. Springer, Berlin, pp 343–391
Woodring AP, Stoltzman CA, Stay B (1992) Allatostatins in the nerves of the antennal pulsatile organ muscle of the cockroach Diploptera punctata. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 20:253–263
Zhukovskaya MI (2007) Aminergic regulation of pheromone sensillae in the cockroach Periplaneta americana. J Evol Biochem Physiol 43:318–326
Zhukovskaya MI (2008) Selective regulation of sensitivity to odors of different behavioral significance in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana. Physiol Entomol 33:162–166
Zhukovskaya MI (2012) Modulation by octopamine of olfactory responses to nonpheromone odorants in the cockroach, Periplaneta americana L. Chem Senses 37:421–429
Zhukovskaya MI, Kapitsky SV (2006) Activity modulation in cockroach sensillum: the role of octopamine. J Insect Physiol 52:76–86
Zornik E, Paisley K, Nichols R (1999) Neural transmitters and a peptide modulate Drosophila heart rate. Peptides 20:45–51
Acknowledgements
We thank John Plant for linguistic assistance. The support of the DFG (DFG FOR 1363, Pf128/30-1) and of the Austrian Science Fund FWF P 23251 is gratefully acknowledged. Furthermore, special thanks go to Heike Wolfenberg, Konstantin Lehmann, and Leonard Nadler for their immense support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antemann, V., Pass, G. & Pflüger, HJ. Octopaminergic innervation and a neurohaemal release site in the antennal heart of the locust Schistocerca gregaria . J Comp Physiol A 204, 131–143 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1213-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-017-1213-5