Abstract
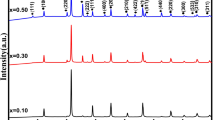
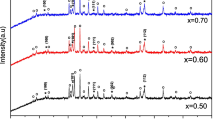
In this work, multiferroic composites of (1−x) Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3 + x Ni0.6Zn0.25La0.15Fe2O4 (x = 0.0, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7, 0.9 and 1.0) have been synthesized using solid-state reaction method and their different properties have been systematically investigated. X-ray diffraction (XRD) studies reveal the formation of cubic structure for perovskite and cubic spinel structure for ferrite phases with crystallite sizes in the range of 17.79–28.21 nm. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) analyses show that the boundaries between Ca-doped BaTiO3 (BCT) and La-doped Ni-Zn ferrite (NZLFO) phases are very clear which indicates small atomic diffusion. The average grain size was found to vary from 2.27 to 0.83 µm with increasing ferrite content. The M-H hysteresis loops obtained from vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM) measurements show as the content of the ferrite phase is increased the saturation magnetization and the remnant magnetization increase but the coercive field and thereby the magneto crystalline anisotropy energy decreases. High dielectric constant values are observed at low frequencies but it decreases with the frequency up to about 7 MHz and beyond which becomes frequency-independent. AC conductivity of the composites derived from dielectric constant and loss tangent values can be described by the hopping mechanism.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. Herrera Diez, R. Kruk, K. Leistner, J. Sort, Magnetoelectric materials, phenomena, and devices. APL Mater. 9, 050401 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0053631
Y. Slimani, S. Shirsath, E. Hannachi, M. Almessiere, M. Aouna, N. Aldossary et al., (BaTiO3)1‐x + (Co0.5Ni0.5Nb0.06Fe1.94O4)x nanocomposites: Structure, morphology, magnetic and dielectric properties. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 104, 5648–5658 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1111/jace.17931
Y. Slimani, M. Almessiere, S. Shirsath, E. Hannachi, G. Yasin, A. Baykal et al., Investigation of structural, morphological, optical, magnetic and dielectric properties of (1−x) BaTiO3/xSr0.92Ca0.04Mg0.04Fe12O19 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 510, 66933 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2020.166933
Y. Jia, S. Or, J. Wang, H. Chan, X. Zhao, H. Luo, High magnetoelectric effect in laminated composites of giant magnetostrictive alloy and lead-free piezoelectric ceramic. J. Appl. Phys. 101, 104103 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2732420
K. Verma, S. Singh, S. Tripathi, R. Kotnala, Multiferroic Ni0.6Zn0.4Fe2O4-BaTiO3 nanostructures: Magnetoelectric coupling, dielectric, and fluorescence. J. Appl. Phys. 116, 124103 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4896118
C. Deng, Y. Zhang, J. Ma, Y. Lin, C. Nan, Magnetoelectric effect in multiferroic heteroepitaxial BaTiO3–NiFe2O4 composite thin films. Acta Mater. 56, 405–412 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actamat.2007.10.004
M. Bichurin, V. Petrov, R. Petrov, Direct and inverse magnetoelectric effect in layered composites in electromechanical resonance range: a review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3548–3550 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.086
K. Sadhana, S. Ramana Murthy, S. Jie, Y. Xie, Y. Liu, Q. Zhan et al., Magnetic field induced polarization and magnetoelectric effect of Ba0.8Ca0.2TiO3-Ni0.2Cu0.3Zn0.5Fe2O4 nanomultiferroic. J. Appl. Phys. 113, 17C731 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4795820
G. Liu, C. Nan, Z. Xu, H. Chen, Coupling interaction in multiferroic BaTiO3–CoFe2O4 nanostructures. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 38, 2321–2326 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1088/0022-3727/38/14/005
Y. Slimani, A. Selmi, E. Hannachi, M. Almessiere, G. AlFalah, L. AlOusi et al., Study on the addition of SiO2 nanowires to BaTiO3: Structure, morphology, electrical and dielectric properties. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 156, 110183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2021.110183
I. Szafraniak-Wiza, L. Kozielski, T. Sebastian, Preparation and properties of Ba1−xCaxTiO3 nanopowders obtained by mechanochemical synthesis. Phase Trans. 89, 803–807 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1080/01411594.2016.1198962
K. Lhoussain, E. Abdelilah, S. Salaheddine, Dielectric study of calcium doped barium titanate Ba1−xCaxTiO3 ceramics. Int. J. Phys. Sci. 11, 71–79 (2016). https://doi.org/10.5897/ijps2015.4415
R. Varatharajan, R. Jayavel, C. Subramanian, Growth and characterization of ferroelectric Ba1−xCaxTiO3 single crystals. Ferroelectrics 215, 169–180 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150199808229560
M. Mhareb, Y. Slimani, Y. Alajerami, M. Sayyed, E. Lacomme, M. Almessiere, Structural and radiation shielding properties of BaTiO3 ceramic with different concentrations of Bismuth and Ytterbium. Ceram. Int. 46, 28877–28886 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.08.055
Y. Slimani, B. Unal, E. Hannachi, A. Selmi, M. Almessiere, M. Nawaz et al., Frequency and dc bias voltage dependent dielectric properties and electrical conductivity of BaTiO3SrTiO3/(SiO2)x nanocomposites. Ceram. Int. 45, 11989–12000 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.03.092
Y. Slimani, A. Selmi, E. Hannachi, M. Almessiere, A. Baykal, I. Ercan, Impact of ZnO addition on structural, morphological, optical, dielectric and electrical performances of BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 9520–9530 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01284-2
Y. Slimani, A. Selmi, E. Hannachi, M. Almessiere, M. Mumtaz, A. Baykal et al., Study of tungsten oxide effect on the performance of BaTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 30, 13509–13518 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01718-x
Y. Slimani, B. Unal, M. Almessiere, E. Hannachi, G. Yasin, A. Baykal et al., Role of WO3 nanoparticles in electrical and dielectric properties of BaTiO3–SrTiO3 ceramics. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 7786–7797 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-03317-7
M. Savinov, V. Trepakov, S. Kamba, S. Kapphan, J. Petzelt, R. Pankrath et al., Dielectric and infrared response of Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3. Ferroelectrics 295, 31–38 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1080/714040620
A. Korkmaz, S. Güner, Y. Slimani, H. Gungunes, M. Amir, A. Manikandan et al., Microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of vanadium-substituted nickel spinel nanoferrites. J. Supercond. Novel Magn. 32, 1057–1065 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10948-018-4793-6
Y. Wang, X. Wu, W. Zhang, W. Chen, Synthesis and electromagnetic properties of La-doped Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 90–95 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2015.09.044
X. Wu, W. Wu, L. Qin, K. Wang, S. Ou, K. Zhou et al., Structure and magnetic properties evolution of nickel-zinc ferrite with lanthanum substitution. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 379, 232–238 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.12.057
O. Hemeda, A. Tawfik, A-Al-Sharif, M. Amer, B. Kamal, D. El Refaay, et al., DC conductivity and magnetic properties of piezoelectric–piezomagnetic composite system. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 4118–4126 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.07.028
X. Feng, Z. Xiangchun, L. Liangchao, L. Hui, J. Jing, Synthesis, magnetic properties and microstructure of Ni–Zn–Cr ferrites doped with lanthanum. J. Rare Earths 25, 232–235 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1016/s1002-0721(07)60477-3
Y. Dasan, B. Guan, M. Zahari, L. Chuan, Substitution on structure, morphology and magnetic properties of nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrite. PLoS ONE 12, e0170075 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0170075
A. Abdeen, Electric conduction in Ni–Zn ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 185, 199–206 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1016/s0304-8853(97)01144-x
M. Hossain, Effect of rare earth metal substitution on the structural, magnetic and transport properties of Ni–Zn ferrites, MPhil Thesis, Khulna University of Engineering and Technology, Khulna, Bangladesh (2017), http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.12228/130.
K. Patankar, S. Joshi, B. Chougule, Dielectric behaviour in magnetoelectric composites. Phys. Lett. A 346, 337–341 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physleta.2005.06.099
Y. Shen, J. Sun, L. Li, Y. Yao, C. Zhou, R. Su et al., The enhanced magnetodielectric interaction of (1–x) BaTiO3–xCoFe2O4 multiferroic composites. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2, 2545–2551 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4TC00008K
R. Zhang, C. Deng, L. Ren, Z. Li, J. Zhou, Dielectric, ferromagnetic and magnetoelectric properties of BaTiO3–Ni0.7Zn0.3Fe2O4 composite ceramics. Mater. Res Bulln. 48, 4100–4104 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.materresbull.2013.06.026
H. Yang, H. Wang, L. He, L. Shui, X. Yao, Polarization relaxation mechanism of Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3/Ni0.8Zn0.2Fe2O4 composite with giant dielectric constant and high permeability. J. Appl. Phys. 108, 074105 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.3490782
J. Boomgaard, A. van Run, J. Van Suchtelen, Piezoelectric-piezomagnetic composites with magnetoelectric effect. Ferroelectrics 14, 727–728 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150197608236711
S. Lokare, D. Patil, B. Chougule, Structural, dielectric and magnetoelectric effect in (x) BaTiO3 + (1−x) Ni0.93Co0.02Mn0.05Fe2O4 ME composites. J. Alloys Compd. 453, 58–63 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2006.11.161
M. Kanakadurga, P. Raju, S. Murthy, Preparation and characterization of BaTiO3+MgCuZnFe2O4 nanocomposites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 341, 112–117 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2013.04.037
A. Kumar, C. Lekha, S. Vivek, V. Saravanan, K. Nandakumar, S. Nair, Multiferroic and magnetoelectric properties of Ba0.85Ca0.15Zr0.1Ti0.9O3–CoFe2O4 core–shell nanocomposite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 418, 294–299 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.02.065
R. Xu, S. Zhang, F. Wang, Q. Zhang, Z. Li, Z. Wang et al., The study of microstructure, dielectric and multiferroic properties of (1 − x) Co0.8Cu0.2Fe2O4-x Ba0.6Sr0.4TiO3 composites. J. Electron. Mater. 48, 386–400 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11664-018-6718-3
Y. Liu, Y. Wu, D. Li, Y. Zhang, J. Zhang, J. Yang, A study of structural, ferroelectric, ferromagnetic, dielectric properties of NiFe2O4–BaTiO3 multiferroic composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 24, 1900–1904 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-012-1032-y
Y. Jun, W. Moon, C. Chang, H. Kim, H. Ryu, J. Kim et al., Effects of Nb-doping on electric and magnetic properties in multi-ferroic BiFeO3 ceramics. Solid State Commun. 135, 133–137 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ssc.2005.03.038
P. Victor, R. Ranjith, S. Krupanidhi, Normal ferroelectric to relaxor behavior in laser ablated Ca-doped barium titanate thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 94, 7702 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.1618914
M. Mahmoudi, H. Hosseinkhani, M. Hosseinkhani, S. Boutry, A. Simchi, W. Shane, K. Journeay, S.L. Subramani, Magnetic resonance imaging tracking of stem cells in vivo using iron oxide nanoparticles as a tool for the advancement of clinical regenerative medicine. Chem. Rev. 111, 253–280 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1021/cr1001832
M. Almessiere, Y. Slimani, H. Sayed, A. Baykal, I. Ercan, Microstructural and magnetic investigation of vanadium-substituted Sr-nanohexaferrite. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 471, 124–132 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.054
D. Ghosh, H. Han, J. Nino, G. Subhash, J. Jones, Synthesis of BaTiO3-20wt%CoFe2O4 Nanocomposites via Spark Plasma Sintering. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 95, 2504–2509 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1551-2916.2012.05221.x
A. Fawzi, A. Sheikh, V. Mathe, Multiferroic properties of Ni ferrite—PLZT composites. Physica B 405, 340–344 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phyYsb.2009.08.090
M. Hakim, S. Nath, S. Sikder, K. Hanium Maria, Cation distribution and electromagnetic properties of spinel type Ni–Cd ferrites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 7, 1316–1321 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpcs.2013.04.011
M. Khedhri, N. Abdelmoula, H. Khemakhem, R. Douali, F. Dubois, Structural, spectroscopic and dielectric properties of Ca-doped BaTiO3. Appl. Phys. A. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-019-2487-y
S.K. Sen, T.C. Paul, S. Dutta, M.N. Hossain, M.N.H. Mia, XRD peak profile and optical properties analysis of Ag-doped h-MoO3 nanorods synthesized via hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 1768–1786 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02694-y
P.V. Ramana, K.S. Rao, K.H. Rao, Influence of iron content on the structural and magnetic properties of Ni-Zn ferrite nanoparticles synthesized by PEG assisted sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn Mater. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.06.065
K. Brinkman, T. Iijima, K. Nishida, T. Katoda, H. Funakubo, The influence of acceptor doping on the structure and electrical properties of sol–gel derived BiFeO3 thin films. Ferroelectrics 357, 35–40 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1080/00150190701527597
A. Abdel Aal, T. Hammad, M. Zawrah, I. Battisha, A. Abou Hammad, FTIR study of nanostructure perovskite BaTiO3 doped with both Fe3+and Ni2+ions prepared by sol–gel technique. Acta Phys. Pol., A 126, 1318–1321 (2014). https://doi.org/10.12693/APhysPolA.126.1318
L. Wang, H. Kang, D. Xue, C. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of Ba0.5Sr0.5TiO3 nanoparticles. J. Cryst. Growth. 311, 605–607 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcrysgro.2008.09.069
X. Wang, L. Zhang, H. Liu, J. Zhai, X. Yao, Dielectric nonlinear properties of BaTiO3–CaTiO3–SrTiO3 ceramics near the solubility limit. Mater. Chem. Phys. 112, 675–678 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2008.06.020
A. Gadkari, T. Shinde, P. Vasambekar, Synthesis, characterization and magnetic properties of La3+ added Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. J. Alloy. Compd. 509, 966–972 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2010.08.155
H. Kumar, J. Singh, R. Srivastava, P. Negi, H. Agrawal, K. Asokan, FTIR and electrical study of dysprosium doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Nanosci. 2014, 1–10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/862415
B. Das, A. Hossain, Rietveld refined structure, ferroelectric, magnetic and magnetoelectric response of Gd- substituted Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite and Ca, Zr co-doped BaTiO3 multiferroic composites. J. Alloy. Compd. 867, 159068 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.159068
I. Esha, F. Toma, M. Al-Amin, M. Khan, K. Maria, Synthesis of type-II based (1−x) Ba0.6(Ca1/2Sr1/2)0.4Ti0.5Fe0.5O3 + (x) Ni0.40Zn0.45Cu0.15Fe1.9Eu0.1O4 composites via standard solid state reaction method and investigation of multiferroic properties. AIP Adv. 8, 125207 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1063/1.5078505
S. Mane, P. Tirmali, B. Ranjit, M. Khan, N. Khan, A. Tarale et al., Studies on magnetocapacitance, dielectric, ferroelectric, and magnetic properties of microwave sintered (1−x) (Ba0.8Sr0.2TiO3) - x (Co0.9Ni0.1Fe2O4) multiferroic composite. Solid State Sci. 81, 43–50 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2018.05.004
A. Globus, I. - Magnetization mechanismssome physical considerations about the domain wall size theory of magnetization mechanisms. Le Journal De Physique Colloques. 38, C1-1-C1-15 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1051/jphyscol:1977101
N. Gupta, M. Dimri, S. Kashyap, D. Dube, Processing and properties of cobalt-substituted lithium ferrite in the GHz frequency range. Ceram. Int. 31, 171–176 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2004.04.004
J. Maxwell, A treatise on electricity and magnetism vol II, 3rd edn. (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1955)
K. Wagner, Zur Theorie der unvollkommenen Dielektrika. Ann. Phys. 345, 817–855 (1913). https://doi.org/10.1002/andp.19133450502
C. Koops, On the dispersion of resistivity and dielectric constant of some semiconductors at audiofrequencies. Phys. Rev. 83, 121–124 (1951). https://doi.org/10.1103/physrev.83.121
V. Senthil, T. Badapanda, S. Kumar, P. Kumar, S. Panigrahi, Relaxation and conduction mechanism of PVA: BYZT polymer composites by impedance spectroscopy. J. Polym. Res. 19, 1 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-012-9838-0
K. Verma, A. Kumar, D. Varshney, Dielectric relaxation behavior of AxCo1−xFe2O4 (A=Zn, Mg) mixed ferrites. J. Alloy. Compd. 526, 91–97 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.02.089
M. Hashim, Alimuddin, S. Shirsath, S. Kumar, R. Kumar, A. Roy et al., Preparation and characterization chemistry of nano-crystalline Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite. J. Alloys Comp. 549, 348–357 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2012.08.039
A. Momin, R. Parvin, M. Shahjahan, M. Islam, H. Tanaka, A. Hossain, Interplay between the ferrimagnetic and ferroelectric phases on the large magnetoelectric coupling of xLi0.1Ni0.2Mn0.6Fe2.1O4–(1−x)Bi0.8Dy0.2FeO3 composites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31, 511–525 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-02556-7
M. Rahaman, S. Saha, T. Ahmed, D. Saha, A. Hossain, Magnetoelectric effect of (1−x) Ba0.5Sr0.5Zr0.5Ti0.5O3+(x) Ni0.12Mg0.18Cu0.2Zn0.5Fe2O4 composites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 371, 112–120 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2014.07.025
A. Jonscher, The ‘universal’ dielectric response. Nature 267, 673–679 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1038/267673a0
M. Matin, M. Hossain, M. Ali, M. Hakim, M. Islam, Enhanced dielectric properties of prospective Bi0.85Gd0.15Fe1−xCrxO3 multiferroics. Results Phys. 12, 1653–1659 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rinp.2019.01.079
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the Materials Science Division, Atomic Energy Centre, Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh and Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology (BUET), Dhaka 1000, Bangladesh for providing the experimental facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasan, Z., Rouf, H.K. & Khan, M.N.I. Structural, magnetic, dielectric and electrical properties of Ba0.77Ca0.23TiO3–Ni0.6Zn0.25La0.15Fe2O4 multiferroic composites. Appl. Phys. A 128, 311 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05441-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-022-05441-z