Abstract
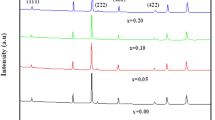
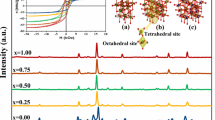
Modern fundamental science is fascinated by spinel ferrite's unique properties and potential applications. The sol–gel method was used to prepare the spinel ferrites. The synthesized samples have formula MgSmxFe2−xO4 (x = 0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.10). The structural properties of all the samples were measured by X-ray diffraction analysis. All the samples have a cubic spinel structure, while few traces of the secondary phase were observed in the last two samples. The magnetic properties of all the samples were measured from + 2000 to – 2000 Oe. The narrow loops of all the samples proved their soft nature. The Curie temperature was decreased with the substitution of samarium ions. The saturation magnetization and remanence decreased with the substitution of samarium ions, while coercivity was enhanced. The magnetic moments have the same trend as magnetization, while the anisotropy constant was increased with the substitution of rare-earth ions. All these parameters suggested that these prepared samples may be suitable for high-density magnetic recording applications.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.M.T. Farid, M. Morsi, T.I. Al-Muhimeed, A.A. AlObaid, O.A. Alamri, H. Albalawi, S.R. Ejaz, R.Y. Khosa, S. Mehmood, Z. Ali, Optoelectronic and thermoelectric properties of A3AsN (A = Mg, Ca, Sr and Ba) in cubic and orthorhombic phase. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 13, 1485–1495 (2021)
M.S. Shah, F. Yasmeen, S.R. Ejaz, R.Y. Khosa, M. Imran, M.A. Assiri, I. Ahmad, N. Ahmad, A.R. Khan, H.M.T. Farid, Structure, electronic, magnetic and thermoelectric properties of the highly Mg-rich intermetallic NdNiMg15 by hybrid density functional theory. J. Electron. Mater. 50, 3976–3985 (2021)
R. Ramzan, M. Tariq, M.N. Ashiq, H. Albalawi, I. Ahmad, M.H. Alhossainy, S.R. Ejaz, R.Y. Khosa, H.M.T. Farid, H.M. Khan, T.I. Al-Muhimeedh, A.A. AlObaid, Effect of yttrium ion on electrical and magnetic properties of barium based spinel ferrites. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 12, 1104–1112 (2021)
A. Hakeem, T. Alshahrani, G. Muhammad, M.H. Alhossainy, A. Laref, A.R. Khan, I. Ali, H.M.T. Farid, T. Ghrib, S.R. Ejaz, R.Y. Khosa, Magnetic, dielectric and structural properties of spinel ferrites synthesized by sol–gel method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 11, 158–169 (2021)
A. Hakeem, T. Alshahrani, I. Ali, M.H. Alhossainy, R.Y. Khosa, G. Muhammad, A.R. Khan, H.M.T. Farid, Synthesis and characterization of composites for microwave devices. Chin. J. Phys. 70, 232–239 (2021)
T.H. Flemban, M.C. Sequeira, Z. Zhang, S. Venkatesh, E. Alves, K. Lorenz, Identifying the influence of the intrinsic defects in Gd-doped ZnO thin-films. J. Appl. Phys. 119(6), 065301 (2016)
I. Ali, M.U. Islam, M.N. Ashiq, M.A. Iqbal, H.M. Khan, N. Karamat, Effect of Tb–Mn substitution on DC and AC conductivity of Y-type hexagonal ferrite. J. Alloys Compd. 579, 576 (2013)
C.V. Ramana, Y.D. Kolekar, K.K. Bharathi, B. Sinha, K. Ghosh, Correlation between structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties of manganese substituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 114, 183907 (2013)
T.H. Flemban, V. Singaravelu, A.A.S. Devi, I.S. Roqan, Homogeneous vertical ZnO nanorod arrays with high conductivity on an in situ Gd nanolayer. RSC Adv. 5(115), 94670–94678 (2015)
C. Radhakrishnamurthy, S.D. Likhite, P. Sahasrabudhe, In situ magnetic measurements on igneous rock bodies. Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Chem. Sci.) 87A, 245–254 (1978)
P.N. Vasambekar, C.B. Kolekar, A.S. Vaingankar, Cation distribution and susceptibility study of Cd–Co and Cr3+ substituted Cd–Co ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 186, 333–341 (1998)
R.V. Upadhyay, G.L. Baldha, A simplified model to calculate Curie temperature of ferrimagnetic spinels. Indian J. Phys. 63A, 835–838 (1989)
A. Hakeem, T. Alshahrani, H.M.T. Farid, A.R. Khan, M.H. Alhossainy, A. Laref, I. Ali, Manganese-based spinel ferrites for microwave absorption. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 2557–2563 (2021)
S. Yousaf, I. Ahmad, M. Kanwal, T. Alshahrani, H.H. Alhashim, N.A. Kattan, H.M.T. Farid, A. Riaz, T. Mehran, A. Laref, Structural and electrical properties of Ba-substituted spinel ferrites. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 122, 105488 (2021)
S. Munir, I. Ahmad, A. Laref, M.T. Farid, Effect of Nd-substitution on hexagonal ferrites for memory devices. J. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 126, 722 (2020)
H.M.T. Farid, I. Ahmad, I. Ali, S.M. Ramay, A. Mahmood, Study of spinel ferrites with addition of small amount of metallic elements. J. Electroceram. 42, 57–66 (2019)
K.Y. Butt, S. Aman, A.A. AlObaid et al., The study of structural, magnetic and dielectric properties of spinel ferrites for microwave absorption applications. Appl. Phys. A 127, 714 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-04827-9
G. Wang, Y. Ma, Z. Wei et al., Development of multifunctional cobalt ferrite/graphene oxide nanocomposites for magnetic resonance imaging and controlled drug delivery. Chem. Eng. J. 289, 150–160 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2015.12.072
S.-H. Xu, D.-L. Feng, D.-X. Li et al., Preparation of magnetic photocatalyst TiO2 supported on NiFe2O4 and effect of magnetic carrier on photocatalytic activity. Chin. J. Chem. 26, 842–846 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/cjoc.200890156
S. Arasi, R.V. Antony, M. Joseph, Impact of dysprosium (Dy3+) doping on size, optical and dielectric properties of titanium dioxide nanoparticles grown by low temperature hydrothermal method. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 3170–3177 (2017)
A. Iftikhar, S. Yousaf, A.F.A. Ahmed et al., Erbium-substituted Ni0.4Co0.6Fe2O4 ferrite nanoparticles and their hybrids with reduced graphene oxide as magnetically separable powder photocatalyst. Ceram. Int. 46(1), 1203–1210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.08.176
Y.M. Shulga, S.A. Baskakov, Y.V. Baskakova et al., Supercapacitors with graphene oxide separators and reduced graphite oxide electrodes. J. Power Sources 279, 722–730 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.032
A. Rahman, H. Sabeeh, S. Zulfiqar et al., Structural, optical and photocatalytic studies of trimetallic oxides nanostructures prepared via wet chemical approach. Synth. Met. 259, 116228 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2019.116228
S. Yousaf, S. Zulfiqar, M. Shahid et al., Electrochemical energy storage properties studies of Cu0.2Ni0.8O-reduced graphene oxide nano-hybrids. Ceram. Int. 46(9), 14304–14310 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.02.115
F. Saffari, P. Kameli, M. Rahimi et al., Effects of co-substitution on the structural and magnetic properties of NiCoxFe2−xO4 ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 41(6), 7352–7358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.02.038
A. Saini, P. Kumar, B. Ravelo et al., Magneto-dielectric properties of doped ferrite based nanosized ceramics over very high frequency range. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 19(2), 911–916 (2016)
M.A. Yousuf, M.M. Baig, N.F. Al-Khalli et al., The impact of yttrium cations (Y3+) on structural, spectral and dielectric properties of spinel manganese ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 45(8), 10936–10942 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.02.174
K. Tanbir, M.P. Ghosh, R.K. Singh et al., Effect of doping different rare earth ions on microstructural, optical, and magnetic properties of nickel–cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 31(1), 435–443 (2020)
T. Shanmugavel, S.G. Raj, G.R. Kumar et al., Cost effective preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline nickel ferrites (NiFe2O4) in low temperature regime. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 27(2), 176–181 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jksus.2014.12.006
S. Yousaf, S. Zulfiqar, M.N. Shahi et al., Tuning the structural, optical and electrical properties of NiO nanoparticles prepared by wet chemical route. Ceram. Int. 46(3), 3750–3758 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.10.097
F. Withers, T.H. Bointon, M.F. Craciun et al., All-graphene photodetectors. ACS Nano 7(6), 5052–5057 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1021/nn4005704
C. Singh, A. Goyal, S. Singhal, Nickel-doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles: efficient catalysts for the reduction of nitroaromatic compounds and photo-oxidative degradation of toxic dyes. Nanoscale 6, 7959–7970 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1039/C4NR01730G
A.R.O. Rodrigues, I.T. Gomes, B.G. Almeida et al., Magnetic liposomes based on nickel ferrite nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17(27), 18011–18021 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CP01894C
M. Mushtaq, M. Imran, S. Baig et al., Synthesis, structural and biological studies of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 48, 3–565 (2015)
K.M.F. Shahil, A.A. Balandin, Graphene–multilayer graphene nanocomposites as highly efficient thermal interface materials. Nano Lett. 12(2), 861–867 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/nl203906r
N.-U. Ain, W. Shaheen, B. Bashir et al., Electrical, magnetic and photoelectrochemical activity of rGO/MgFe2O4 nanocomposites under visible light irradiation. Ceram. Int. 42, 12401–12408 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.04.179
A.S. Hassanien, A.A. Ak, A.H. Saaedi, Synthesis, crystallography, microstructure, crystal defects, and morphology of BixZn1−xO nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel technique. CrystEngComm 20, 1716–1730 (2018)
A.A. Akl, S.A. Mahmoud, S.M. Al-Shomar, A.S. Hassanien, Improving microstructural properties and minimizing crystal imperfections of nanocrystalline Cu2O thin films of different solution molarities for solar cell applications. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 74C, 183–192 (2018)
R. Yogamalar, R. Srinivasan, A. Vinu, K. Ariga, A.C. Bose, X-ray peak broadening analysis in ZnO nanoparticles. Solid State Commun. 149, 1919–1923 (2009)
W.S. Mohamed, A.M. Abu-Dief, Synthesis, characterization and photocatalysis enhancement of Eu2O3–ZnO mixed oxide nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. Solids. 116, 375–385 (2018)
A.M. Abu-Dief, W.S. Mohamed, α-Bi2O3 nanorods: synthesis, characterization and UV-photocatalytic activity. Mater. Res. Express 4, 035039 (2017)
S. Aman, N. Ahmad, M.H. Alhossainy, H. Albalawi, M. Morsi, T.I. Al-Muhimeed, A.A. AlObaid, Structural, magnetic, electrical and microwave properties of spinel ferrites. J. Rare Earths (2021). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jre.2021.04.015
S. Aman, M.B. Tahir, N. Ahmad, The enhanced electrical and dielectric properties of cobalt-based spinel ferrites for high-frequency applications. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 32, 22440–22449 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-021-06730-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zelai, T. Structural and magnetic properties of samarium-substituted spinel ferrites. Appl. Phys. A 127, 864 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05002-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00339-021-05002-w