Abstract
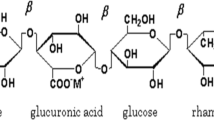
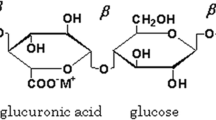
The biopolymer electrolyte based on gellan gum with various concentrations of lithium chloride salt has been prepared using solution casting technique and optimized with high ionic conductivity of 4.08 × 10–3 S cm−1 for the composition of 1 g gellan gum + 1.2 M wt% of LiCl using AC impedance analysis. XRD has been used to study the crystalline/amorphous nature of the prepared membrane. The complex formation between the polymer and the salt is analyzed using FTIR technique. DSC analysis has been done to evaluate the glass transition temperature of the prepared electrolytes. Transference number measurement was done to confirm that the conduction is due to cations. CV analysis was done to measure the cyclic stability of the prepared membrane which shows an adequate result by reciprocating the pattern for 50 cycles. Primary lithium-ion conducting battery is constructed using highest lithium-ion conducting membrane. It shows an open circuit voltage of 1.88 V.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarascon JM, Armand M (2011) Issues and challenges facing rechargeable lithium batteries. In: Materials for sustainable energy: a collection of peer-reviewed research and review articles from Nature Publishing Group, pp 171–179
Kumar LS, Selvin PC, Selvasekarapandian S, Manjuladevi R, Monisha S, Perumal P (2018) Tamarind seed polysaccharide biopolymer membrane for lithium-ion conducting battery. Ionics 24(12):3793–3803
Agrawal RC, Pandey GP (2008) Solid polymer electrolytes: materials designing and all-solid-state battery applications: an overview. J Phys D Appl Phys 41(22):223001
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Moniha V, Meyvel S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan solid biopolymer electrolytes for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25(5):2147–2157
Selvalakshmi S, Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2017) Biopolymer agar-agar doped with NH4SCN as solid polymer electrolyte for electrochemical cell application. J Appl Polym Sci 134(15):44702 (1–10)
Kaplan DL (1998) Introduction to biopolymers from renewable resources. In: Biopolymers from renewable resources. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp 1–29
Selvin PC, Perumal P, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Boopathi G, Chandra ML (2018) Study of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on K-carrageenan and NH4SCN for electrochemical devices. Ionics 24(11):3535–3542
Moniha V, Alagar M, Selvasekarapandian S, Sundaresan B, Hemalatha R, Boopathi G (2018) Synthesis and characterization of bio-polymer electrolyte based on iota-carrageenan with ammonium thiocyanate and its applications. J Solid State Electrochem 22(10):3209–3223
Khiar AA, Arof AK (2010) Conductivity studies of starch-based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16(2):123–129
Monisha S, Selvasekarapandian S, Mathavan T, Benial AMF, Manoharan S, Karthikeyan S (2016) Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on cellulose acetate for potential applications in energy storage devices. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 27(9):9314–9324
Rasali NMJ, Nagao Y, Samsudin AS (2019) Enhancement on amorphous phase in solid biopolymer electrolyte based alginate doped NH4NO3. Ionics 25(2):641–654
Muthukrishnan M, Shanthi C, Selvasekarapandian S, Manjuladevi R, Perumal P, Selvin PC (2019) Synthesis and characterization of pectin-based biopolymer electrolyte for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25(1):203–214
Singh R, Bhattacharya B, Rhee HW, Singh PK (2015) Solid gellan gum polymer electrolyte for energy application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40(30):9365–9372
Noor IM (2020) Determination of charge carrier transport properties of gellan gum–lithium triflate solid polymer electrolyte from vibrational spectroscopy. High Perform Polym 32(2):168–174
Noor ISM, Majid SR, Arof AK, Djurado D, Neto SC, Pawlicka A (2012) Characteristics of gellan gum–LiCF3SO3 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 225:649–653
Neto MJ, Sentanin F, Esperança JMSS, Medeiros MJ, Pawlicka A, de Zea Bermudez V, Silva MM (2015) Gellan gum—Ionic liquid membranes for electrochromic device application. Solid State Ionics 274:64–70
Majid SR, Sabadini RC, Kanicki J, Pawlicka A (2014) Impedance analysis of gellan gum-poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) membranes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 604(1):84–95
Kumar GG, Munichandraiah N (2000) Effect of plasticizers on magnesium-poly (ethyleneoxide) polymer electrolyte. J Electroanal Chem 495(1):42–50
Chieng BW, Ibrahim NA, Yunus WMZW, Hussein MZ (2014) Poly (lactic acid)/poly (ethylene glycol) polymer nanocomposites: effects of graphene nanoplatelets. Polymers 6(1):93–104
Chandra MVL, Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Study of PVAc-PMMA-LiCl polymer blend electrolyte and the effect of plasticizer ethylene carbonate and nanofiller titania on PVAc-PMMA-LiCl polymer blend electrolyte. J Polym Eng 37(6):617–631
Naachiyar RM, Ragam M, Selvasekarapandian S, Krishna MV, Buvaneshwari P (2021) Development of biopolymer electrolyte membrane using Gellan gum biopolymer incorporated with NH4SCN for electro-chemical application. Ionics 27(8):3415–3429
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semicrystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37(8):1371–1376
Hong T, Yin JY, Nie SP, Xie MY (2021) Applications of infrared spectroscopy in polysaccharide structural analysis: progress, challenge and perspective. Food Chem: X 12:100168
Setyaningrum DL, Riyanto S, Rohman A (2013) Analysis of corn and soybean oils in red fruit oil using FTIR spectroscopy in combination with partial least square. Int Food Res J 20(4):1977
Cassanelli M, Norton I, Mills T (2017) Effect of alcohols on gellan gum gel structure: bridging the molecular level and the three-dimensional network. Food Struct 14:112–120
Halim NFA, Majid SR, Arof AK, Kajzar F, Pawlicka A (2012) Gellan gum-LiI gel polymer electrolytes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 554(1):232–238
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Benial AMF (2017) Preparation and characterization of cellulose acetate and lithium nitrate for advanced electrochemical devices. Ionics 23(10):2697–2706
Vijaya N, Selvasekarapandian S, Hirankumar G, Karthikeyan S, Nithya H, Ramya CS, Prabu M (2012) Structural, vibrational, thermal, and conductivity studies on proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on poly (N-vinylpyrrolidone). Ionics 18(1–2):91–99
Selvalakshmi S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2019) Characterization of biodegradable solid polymer electrolyte system based on agar-NH4Br and its comparison with NH 4 I. J Solid State Electrochem 23(6):1727–1737
Perumal P, Selvin PC, Selvasekarapandian S, Sivaraj P (2019) Structural and electrical properties of bio-polymer pectin with LiClO4 solid electrolytes for lithium ion polymer batteries. Mater Today: Proc 8:196–202
Boukamp BA (1986) A package for impedance/admittance data analysis. Solid State Ionics 18:136–140
Kumar LS, Selvin PC, Selvasekarapandian S (2021) Impact of lithium triflate (LiCF3SO3) salt on tamarind seed polysaccharide-based natural solid polymer electrolyte for application in electrochemical device. Polym Bull 78(4):1797–1819
Boopathi G, Pugalendhi S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S, Aristatil G (2017) Development of proton conducting biopolymer membrane based on agar–agar for fuel cell. Ionics 23(10):2781–2790
Nithya H, Selvasekarapandian S, Selvin PC, Kumar DA, Kawamura J (2012) Effect of propylene carbonate and dimethylformamide on ionic conductivity of P (ECH-EO) based polymer electrolyte. Electrochim Acta 66:110–120
Prodromakis T, Papavassiliou C (2009) Engineering the Maxwell-Wagner polarization effect. Appl Surf Sci 255(15):6989–6994
Mary IA, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Chitra R, Chandra ML, Ponraj T (2020) Lithium ion conducting biopolymer membrane based on K-carrageenan with LiNO 3. Ionics 26(9):4311–4326
Hemalatha R, Alagar M, Selvasekarapandian S, Sundaresan B, Moniha V, Boopathi G, Selvin PC (2019) Preparation and characterization of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on PVA, amino acid proline, and NH4Cl and its applications to electrochemical devices. Ionics 25(1):141–154
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S, Meyvel S (2020) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan biopolymer electrolyte with lithium perchlorate and succinonitrile (plasticizer). Polym Bull 77(3):1555–1579
Selvasekarapandian S, Hema M, Kawamura J, Kamishima O, Baskaran R (2010) Characterization of PVA—NH4NO3 polymer electrolyte and its application in rechargeable proton battery. J Phys Soc Jpn 79:163–168
Genova FKM, Selvasekarapandian S, Karthikeyan S, Vijaya N, Pradeepa R, Sivadevi S (2015) Study on blend polymer (PVA-PAN) doped with lithium bromide. Polym Sci, Ser A 57(6):851–862
Premalatha M, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Monisha S, Selvalakshmi S, Pandi DV (2017) Tamarind seed polysaccharide (TSP)-based Li-ion conducting membranes. Ionics 23(10):2677–2684
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aafrin Hazaana, S., Joseph, A., Selvasekarapandian, S. et al. Development and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on gellan gum (GG) with lithium chloride (LiCl) for the application of electrochemical devices. Polym. Bull. 80, 5291–5311 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04316-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00289-022-04316-w