Abstract
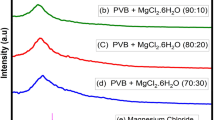
Development of high ionic conducting solid polymer electrolyte is the most challenging and ever-growing research area in science. The present study concentrated on the preparation of gellan gum–based magnesium ion conducting solid biopolymer electrolytes for electrochemical device applications. The magnesium ion conducting solid biopolymer electrolyte has been developed by solution casting technique with 1.0-g gellan gum with different concentrations of Mg (ClO4)2 salts. The prepared polymer electrolytes were characterized by XRD, FTIR, and DSC. The ionic conductivity of the polymer electrolytes has been analyzed by AC impedance analysis; the polymer electrolyte of 1.0-g gellan gum with 0.5 wt % of Mg (ClO4)2 has the maximum ionic conductivity of 1.063 × 10–2 S cm−1 at room temperature. The Mg2+ ion movements have been confirmed by Wagner’s planarization method. By using Evan’s polarization method, the cationic transference number has been obtained at 0.33 for the high conducting polymer electrolyte. The electrochemical stability of the polymer has been studied by using LSV; the high conducting polymer electrolyte is stable up to 2.86 V. The magnesium primary battery has been fabricated with the help of high conducting polymer electrolyte and its performance also studied. The magnesium battery has an open-circuit voltage of 2.52 V.















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu ID, Chang FC (2007) Determination of the interaction within polyester –based solid polymer electrolyte using FTIR spectroscopy. Polymer 48:989–996
Pandey GP, Hashmi SA (2013) Ionic liquid 1- ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetracyanoborate-based gel polymer electrolyte for electrochemical capacitors. J Mater Chem 1:3372–3378
Singh R, Polu AR, Bhattacharya B, Rhee HW, Varlikli C, Singh PK (2016) Perspectives for solid biopolymer electrolytes in dye sensitized solar cell and battery application. Renew Sust Energ Rev 65:1098–1117
Hashmi SA, Latham RJ, Linford RG, Schlindwein WS (1997) Studies on all solid state electric double layer capacitors using proton and lithium ion conducting polymer electrolytes. J Chem Soc Faraday Trans 93(23):4177–4182
Arockia Mary I, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Srikumar SR, Ponraj T, Moniha V (2019) Lithium ion conducting polymer membrane based on K- carrageenan complexed with lithium bromide and its electrochemical applications. Ionics 25:5839–5855
Armand M (1994) The history of polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 69(3–4):309–319
Avachat AM, Dash RR, Shrotriya SN (2011) Recent investigations of plant based natural gums, mucilages and resins in novel drug delivery systems. Indian J Pharm Educ Res 45:86–99
Shamsudin IJ, Ahmad A, Hassan NH, Kaddami H (2016) Biopolymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl-carrageenan and imidazolium ionic liquid. Ionics 22(6):841–851
Monisha S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Milton Frankiln Benial A, Premalatha M (2016) Preparation and characterization of cellulose actetate and lithium nitrate for advance electrochemical devices. Ionics 23:2697–2706
Buraidah MH, Teo LP, Majid SR, Yahya R, Taha RM, Arof AK (2010) Characterizations of chitosan-based polymer electrolyte photovoltaic cells. Int J Photoenergy 1–7. https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/805836
Ahmad Khair AS, Arof AK (2010) Conductivity studies of starch based polymer electrolytes. Ionics 16:123–129
Kiruthika S, Malathi M, Selvasekarapandian S, Tamilarasan K, Moniha V, Manjuladevi R (2019) Eco-friendly biopolymer electrolyte, pectin with magnesium nitrate salt for application in electrochemical devices. J Solid State Electrochem 23:2181–2193
Sampathkumar L, ChristoperSelvin P, Selvasekarapandian S, Perumal P, Chitra R, Muthukrishnan M (2019) Synthesis and characteristics of biopolymer electrolyte based on tamarind seed polysaccharide, lithium perchlorate and ethylene carbonate for electrochemical applications. Ionics 25:1067–1082
Selvalakshmi S, Mathavan T, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2017) Study on NH4I composition effect in agar-agar based biopolymer electrolyte. Ionics 23:2791–2797
Shanmugapriya S, Karthika M, Selvesekarapandian S, Manjuladevi R (2018) Preparation and characterization of polymer electrolyte based on biopolymer I-Carrageenan with magnesium nitrate. Solid State Ionics 327(1):136–149
Meera Naachiyar R, Ragam S, Selvesekarapandian S, Vengadesh Krishna M, Buvaneshwari P (2021) Development of biopolymer electrolyte membrane using Gellan gum biopolymer incorporated with NH4SCN for electro-chemical application. Ionics 27(8):3415–3429
Jansson PE, Lindberg B, Sandford PA (1998) Structural studies of gellan gum, an extracellular polysaccharide elaborated by Pseudomonas elodea. Carbohyd Res 124:135–139
Fialho AM, Moreira M, Granja AT, Popescu O, Hoffmann K, Sa-Correia I (2008) Occurrence, production and applications of gellan gum: current state and perspectives. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79(6):889–900
Milas M, Shi X, Rinaudo M (1990) On the physicochemical properties of gellan gum. Biopolymers 30:451
Neto MJ, Sentanin F, Espernaca JMSS, Medeiros MJ, Pawlika A, de-Zea Bermudez V, Silva MM (2015) Gellan gum-Ionic liquid membranes for electrchromic device application. Solid State Ionics 274:64–70
Singh R, Bhattacharya B, Rhee H-W, Singh PK (2015) Solid gellan gum polymer electrolyte for energy application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:9365–9372
Ramlli MA, Isa MIN (2016) Structural and ionic transport properties of protonic conducting solid biopolymer electrolytes based on carboxymethyl cellulose doped ammonium fluoride. J Phys Chem B 120(44):11567–11573
Mahalakshmi M, Selvanayagam S, Selvasekarapandian S, Moniha V, Manjuladevi R, Sangeetha P (2019) Characterization of biopolymer electrolytes based on cellulose acetate with magnesium perchlorate for energy storage devices. J Sci Adv Mater Devices 4:276–284
Ponraj T, Ramalingam A, Selvasekarapandian S, Srikumar R, Manjuladevi R (2020) Mg-ion conducting triblock copolymer electrolyte based on poly (VdCl-co-AN-co-MMA) with magnesium nitrate. Ionics 26:789–800
Venkata Narayanan NS, Ashok Raj BV, Sampath S (2009) Magnesium ion conducting, room temperature molten electrolytes. Electrochem Commun 11:2027–2031
Huie MM, Bock DC, Takeuchia ES, Marschilok AC, Takeuchi KJ (2015) Cathode materials for magnesium and magnesium ion based batteries. Coord Chem Rev 287:15–27
Majid SR, Sabadini RC, Kancki J, Pawlicka A (2014) Impedance analysis of gellan gum- poly (vinyl pyrrolidone) membranes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 604:84–95
Halim NFA, Majid SR, Arof AK, Kajzar F, Pawlicka A (2012) Gellan Gum-LiI Gel polymer electrolytes. Mol Cryst Liq Cryst 554(1):232–238
Noor IM (2020) Determination of charge carrier transport properties of gellan gum –lithium triflate solid polymer electrolyte from vibrational spectroscopy. High Perform Polym 32(2):168–174
Noor ISM, Majid SR, Arof AK, Djurado D, ClaroNeto S, Pawlicka A (2012) Characteristics of gellan gum-LiCF3SO3 polymer electrolytes. Solid State Ionics 225:649–653
Ponmani S, Kalaiselvimary J, Ramesh Prabhu M (2018) Structural, electrical, and electrochemical properties of poly(vinylidene fluoride-co-hexaflouropropylene)/poly(vinyl acetate)-based polymer blend electrolytes for rechargeable magnesium ion batteries. J Solid State Electrochem 22(2):2605–2615
Mangalam R, Thamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Jayakumar S, Manjuladevi R (2016) Polyvinyl pyrrolidone/Mg(ClO4)2 solid polymer electrolyte: structural and electrical studies. Ionics 23(10):2837–2843
Perera K, Dissanayake MAK, Bandaranayake PWS (2004) Ionic conductivity of a gel polymer electrolyte based on Mg (ClO4)2 and polyacrylonitrile. Mater Res Bull 39:1745–1751
Oh J-S, Ko J-M, Kim D-W (2004) Preparation and characterization of gel polymer electrolytes for solid state magnesium batteries. J Electrochimica Acta 50:903–906
Tripathi SK, Jain A, Gupita A, Mishra M (2012) Electrical and electrochemical studies on magnesium ion-based polymer gel electrolytes. J Solid State Electrochem 16(5):1799–1806
Hodge RM, Edward GH, Simon GP (1996) Water absorption and states of water in semi crystalline poly (vinyl alcohol) films. Polymer 37:1371–1376
Inbavalli D, Selvasekarapandian S, Sanjeeviraja C, Baskaran R, Kawamura J, Masuda Y (2013) Structural, thermal, morphological and electrical conductivity analysis of proton conducting tri block copolymer P(VdCl-Co-AN-Co-MMA) based electrolytes. Int J Electroactive Mater 1:71–78
Singh R, Bhattacharya B, Rhee H-W, Singh PK (2015) Solid gellan gum polymer electrolyte for energy application. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40:9365–9372
Rathod SG, Bhajantri R, Ravindrachary V (2016) Influence of transport parameters on conductivity of lithium poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan composites. J Elastomers Plast 48(5):442–455
Karthikeyan S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M, Monisha S, Boopathi Aristatil G, Arun A, Madeswaran S (2016) Proton-conducting I-Carrageenan-based biopolymer electrolyte for fuel cell application. Ionics 23:2775–2780
Baskaran R, Selvasekarapandian S, Kuwata N, Kawamura N, Hattori T (2006) ac impedance, DSC and FT-IR investigations on (x)PVAc–(1–x)PVdF blends with LiClO4. Mater Chem Phys 98(1):55–61
Ponmani S (2018) Ramesh Prabhu M (2018) Sulfonate based ionic liquid incorporated polymer electrolytes for magnesium secondary battery. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 10(1080/03602559):1520259
Chitra R, Sathya P, Selvasekarapandian S, Meyvel S (2019) Synthesis and characterization of iota-carrageenan biopolymer electrolyte with lithium perchlorate and succinonitrile (plasticizer). Polym Bull 77:1555–1579
Nithya S, Selvasekarapandian S, Premalatha M (2016) Synthesis and characterization of proton-conducting polymer electrolyte based on polyacrylonitrile. Ionics 23(10):2767–2774
Ramasamy M, Thamilselvan Malayandi S, Srinivasalu J, Ramasamy M (2017) Magnesium ion conducting polyvinyl alcohol-polyvinyl pyrrolidone based blend polymer electrolyte. Ionics 23(7):1771–1781
Sangeetha P, Selvakumar TM, Selvasekarapandian S, Srikumar SR, Manjuladevi R, Mahalakshmi M (2019) Preparation and characterization of biopolymer k-carrageenan with MgCl2 salt and its application to electrochemical devices. Ionics. https://doi.org/10.1007/sl1581-019-03193-0
Kiruthika S, Malathi M, Selvesekarapandian S, Tamilarasan K, Maheswari T (2019) Conducting biopolymer electrolyte based on pectin with magnesium chloride salt for magnesium battery applications. Polym Bull. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00.289-019-03071-9.(2019)
Boukamp BA (1986) A non linear least squares fit procedure for analysis of immittance data of electrochemical systems. Solid State Ionics 20(1):31–44
Ponraj T, Ramalingam A, Selvasekarapandian S, Srikumar R, Manjuladevi R (2021) Plasticized solid polymer electrolyte based on triblock copolymer poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile-co-methyl methacrylate) for magnesium ion batteries. Polym Bull 78:35–57
Shanmugapriya S, Karthika M, Selvesekarapandian S, Manjuladevi R, Monisha S (2018) Study of biopolymer I-carrageenan with magnesium perchlorate. Ionics 24(12):3861–3875
Manjuladevi R, Tamilselvan M, Selvasekarapandian S, Mangalam R, Premalatha M, Monisha S (2017) Mg-ion conducting blend polymer electrolyte based on poly(vinyl-alcohol)-poly(acrylonitrile) with magnesium perchlorate. Solid State Ionics 308:90–100
Kiruthika S, Malathi M, Selvasekarapandian S, Tamilarasan K, Maheshwari T (2020) Conducting biopolymer electrolyte based on pectin with magnesium chloride salt for magnesium battery application. Polym Bull 77:6299–6317
Hambali D, Zainol NH, Othman L, Md Isa KB, Osman Z (2019) Magnesium ion conducting gel polymer electrolytes based on poly(vinylidene chloride-co-acrylonitrile) (PVdC-co-AN): a comparative study between magnesium trifluoromethane sulfonate (MgTf2) and magnesium bis (trifluoromethanesulfonimide) (Mg(TFSI)2). Ionics 25:1187–1198
Reddy CVS, Sharma AK, Rao VN (2003) Conductivity and discharge characteristics of polyblend (PVP+PVA+KIO3) electrolytes. J Power Sources 114(2):338–345a
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buvaneshwari, P., Mathavan, T., Selvasekarapandian, S. et al. Preparation and characterization of biopolymer electrolyte based on gellan gum with magnesium perchlorate for magnesium battery. Ionics 28, 3843–3854 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04597-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-022-04597-1