Abstract
Background
The effect of laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication (LTF) for the treatment of laryngopharyngeal reflux (LPR) is unclear. The purpose of this study is to investigate the feasibility and effectiveness of LTF for the treatment of LPR-related symptoms and disease-specific quality of life (QoL) up to 3-year follow-up.
Materials and methods
Observational cohort study (2015–2019). Patients suffering from LPR were included. Preoperative evaluation included esophagogastroduodenoscopy, esophageal manometry and 24-h pH/impedance study. Symptoms and QoL were measured with the reflux symptom index (RSI) and the laryngopharyngeal reflux–health-related quality of life (LPR–HRQL) validate questionnaires at baseline and during follow-up.
Results
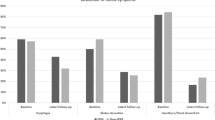
Eighty-six patients were included. Twenty-three (27%) patients had pure LPR while 63 (73%) presented with combined LPR/GERD. Cough (89.7%), dyspnea/choking (39.6%) and asthma (25.6%) were the most commonly reported extraesophageal symptoms. The median (interquartile range, IQR) total RSI score before operation and at 3-month, 6-month, 1-year, 2-year and 3-year follow-up was 36.1 (10.3), 9.58 (12.3), 11.8 (10.2), 12.4 (9.6), 12.0 (13.1) and 10.1 (12.0), respectively. The median (IQR) total LPR–HRQL score before operation and at 3-month, 6-month, 1-year, 2-year and 3-year follow-up was 57.4 (22.2), 13.4 (14.9), 15.2 (12.8), 11.4 (10.9) and 11.9 (13.5), respectively. The subscores “voice,” “cough,” “throat” and “swallow” showed a significant improvement after intervention. Compared to baseline, each per-year follow-up pairwise comparison was significantly improved (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
LTF seems feasible, effective and promising for the treatment of LPR with improved symptoms and disease-specific patients’ quality of life perception up to 3-year follow-up.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
El-Serag HB, Sweet S, Winchester CC, Dent J (2014 Jun) Update on the epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a systematic review. Gut 63(6):871–880
Ahmad I, Batch AJG (2004) Acid reflux management: ENT perspective. J Laryngol Otol 118:25–30
Koufman JA, Aviv JE, Casiano RR, Shaw GY (2002) Laryngopharyngeal refux: position statement of the committee on speech, voice, and swallowing disorders of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 127(1):32–35
Thoman DS, Hui TT, Spyrou M, Phillips EH (2002) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery and its effect on cough in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Gastrointest Surg. 6(1):17–21
Lundell L, Miettinen P, Myrvold HE, Pedersen SA, Liedman B, Hatlebakk JG, Julkonen R, Levander K, Carlsson J, Lamm M, Wiklund I (2001) Continued (5-year) followup of a randomized clinical study comparing antirefux surgery and omeprazole in gastroesophageal refux disease. J Am Coll Surg 192(2):172–179
Galmiche JP, Hatlebakk J, Attwood S, Ell C, Fiocca R, Eklund S, Langstrom G, Lind T, Lundell L (2011) Laparoscopic antireflux surgery vs esomeprazole treatment for chronic GERD: the LOTUS randomized clinical trial. JAMA 305(19):1969–1977
Koch OO, Kaindlstorfer A, Antoniou SA, Asche KU, Granderath FA, Pointner R (2012 ) Laparoscopic nissen versus toupet fundoplication: objective and subjective results of a prospective randomized trial. Surg Endosc 26(2):413–422
Nord JH (2004) Extraesophageal symptoms: What role for the Proton-Pump inhibitors? Am J Med 117:56S–62S
Freedberg DE, Kim LS, Yang YX (2017) The risks and benefits of long-term use of proton-pump inhibitors: expert review and best practice advice from the American Gastroenterological Association. Gastroenterology 152(4):706–715
Farrell TM, Richardson WS, Trus TL, Smith CD, Hunter JG (2001) Response of atypical symptoms of gastro-oesophageal reflux to antireflux surgery. Br J Surg 88:1649–1652
Catania RA, Kavic SM, Roth JS, Lee TH, Meyer T, Fantry GT, Castellanos PF, Park A (2007 Dec) Laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication effectively relieves symptoms in patients with laryngopharyngeal reflux. J Gastrointest Surg 11(12):1579–1587
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Amin MR, Koufman JA (2002) Symptoms and findings of laryngopharyngeal reflux. Ear Nose Throat J 81(S2):10–13
Bona D, Aiolfi A, Asti E, Bonavina L. Laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease and hiatus hernia: proposal for standardization using the "critical view" concept. Updates Surg. 2020 Mar 4. doi: 10.1007/s13304–020–00732–7. [Epub ahead of print]
Aiolfi A, Cavalli M, Saino G, et al. Laparoscopic posterior cruroplasty: a patient tailored approach. Hernia. 2020 Apr 25. doi: 10.1007/s10029–020–02188–5. [Epub ahead of print]
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2001) Laryngopharyngeal reflux symptoms improve before changes in physical findings. Laryngoscope 111:979–981
Belafsky PC, Postma GN, Koufman JA (2002) Validity and reliability of the Reflux Symptom Index (RSI). J Voice 16:274–277
Carrau RL, Khidr A, Gold KF, Crawley JA, Hillson EM, Koufman JA, Pashos CL (2005) Validation of a quality-of-life instrument for laryngopharyngeal reflux. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:315–320
Kohn GP, Price RR, DeMeester SR, Zehetner J, Muensterer OJ, Awad Z, Mittal SK, Richardson WS, Stefanidis D, Fanelli RD (2013) SAGES Guidelines Committee. Guidelines for the management of hiatal hernia. Surg Endosc 27(12):4409–4428
R Core Team. R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing [cited 2019 December 30]. www.r-project.org
Lechien JR, Akst LM, Hamdan AL et al (2019 May) Evaluation and management of laryngopharyngeal reflux disease: state of the art review. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 160(5):762–782
Lechien JR, Schindler A, Robotti C et al (2019 Jun) Laryngopharyngeal reflux disease in singers: pathophysiology, clinical findings and perspectives of a new patient-reported outcome instrument. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis 136(3S):S39–S43
Oelschlager BK, Chang L, Pope CE, Pellegrini CA (2005) Typical GERD symptoms and esophageal pH monitoring are not enough to diagnose pharyngeal reflux. J Surg Res 128:55–60
Oelschlager BK, Eubanks TR, Maronian N, Hillel A, Oleynikov D, Pope CE, Pellegrini CA (2002) Laryngoscopy and pharyngeal pH are complementary in the diagnosis of gastroesophageal–laryngeal reflux. J Gastrointest Surg 6:189–194
Patel DA, Blanco M, Vaezi MF (2018 Sep) Laryngopharyngeal reflux and functional laryngeal disorder: perspective and common practice of the general gastroenterologist. Gastroenterol Hepatol (N Y) 14(9):512–520
Kawamura O, Aslam M, Rittmann T, Hofmann C, Shaker R (2004) Physical and pH properties of gastroesophagopharyngeal refluxate: a 24-hour simultaneous ambulatory impedance and pH monitoring study. Am J Gastroenterol 99(6):1000–1010
Richter JE (2005) Review article: extraoesophageal manifestations of gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 22(suppl 1):70–80
El-Serag HB, Lee P, Buchner A, Inadomi JM, Gavin M, McCarthy DM (2001) Lansoprazole treatment of patients with chronic idiopathic laryngitis: a placebo-controlled trial. Am J Gastroenterol 96(4):979–983
Mainie I, Tutuian R, Shay S et al (2006) Acid and non-acid reflux in patients with persistent symptoms despite acid suppressive therapy: a multicentre study using combined ambulatory impedance-pH monitoring. Gut 55(10):1398–1402
Zhang C, Hu ZW, Yan C, Wu Q, Wu JM, Du X, Liu DG, Luo T, Li F, Wang ZG (2017) Nissen fundoplication vs proton-pump inhibitors for laryngopharyngeal refux based on ph-monitoring and symptom-scale. World J Gastroenterol 23(19):3546–3555
Krill JT, Naik RD, Higginbotham T, Slaughter JC, Holzman MD, Francis DO, Garrett CG, Vaezi MF (2017) Association between response to acid-suppression therapy and efcacy of antireflux surgery in patients with extraesophageal refux. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(5):675–681
Oelschlager BK, Eubanks TR, Oleynikov D, Pope C, Pellegrini CA (2002) Symptomatic and physiologic outcomes after operative treatment for extraesophageal reflux. Surg Endosc 16:1032–1036
Sifrim D, Dupont L, Blondeau K, Zhang X, Tack J, Janssens J (2005 Apr) Weakly acidic reflux in patients with chronic unexplained cough during 24 hour pressure, pH, and impedance monitoring. Gut 54(4):449–454
Chen RYM, Thomas RJS (2000) Results of laparoscopic fundoplication where atypical symptoms coexist with oesophageal reflux. ANZ J Surg 70:840–842
Westcott CJ, Hopkins MB, Bach K, Postma GN, Belafsky PC, Koufman JA (2004) Fundoplication for laryngopharyngeal reflux disease. J Am Coll Surg 199:23–30
Carroll TL, Nahikian K, Asban A, Wiener D (2016 Sep) Nissen fundoplication for laryngopharyngeal reflux after patient selection using dual pH, full column impedance testing: a pilot study. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 125(9):722–728
Novitsky YW, Zawacki JK, Irwin RS, Hussey VM, Callery MP (2002) Chronic cough due to gastroesophageal reflux disease: efficacy of antireflux surgery. Surg Endosc 16:567–571
Spivak H, Smith CD, Phichith A, Galloway K, Waring JP, Hunter JG (1999) Asthma and gastroesophageal reflux: fundoplication decreases need for systemic corticosteriods. J Gastrointest Surg 3:477–482
Koch OO, Antoniou SA, Kaindlstorfer A, Asche KU, Granderath FA, Pointner R (2012 Oct) Effectiveness of laparoscopic total and partial fundoplication on extraesophageal manifestations of gastroesophageal reflux disease: a randomized study. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 22(5):387–391
Zhang C, Wu J, Hu Z, Yan C, Gao X, Liang W, Liu D, Li F, Wang Z (2016 Aug 17) Diagnosis and anti-reflux therapy for GERD with respiratory symptoms: a study using multichannel intraluminal impedance-pH monitoring. PLoS ONE 11(8):e0160139
Amer MA, Smith MD, Khoo CH, Herbison GP, McCall JL (2018 Oct) Network meta-analysis of surgical management of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease in adults. Br J Surg 105(11):1398–1407
Higgins RM, Gould JC (2020 Feb) The pros and cons of partial versus total fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A 30(2):117–120
Aiolfi A, Asti E, Bernardi D et al (2018 Apr) Early results of magnetic sphincter augmentation versus fundoplication for gastroesophageal reflux disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg 52:82–88
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Literature search: A.A, AS, ER and MC. Study designs: AA and DB. Data collection: AA, LB, AS, GB, ER and GS. Data analysis: AA, GB and DB. Data interpretation: AA, GB and DB. Writing: AA, DK and DB. Manuscript critical revision: all authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and is in accordance with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Figure 1
Reflux symptom index (RSI) The RSI was calculated preoperatively, and at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 2 years and 3 years after laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication (LTF). The red line indicates the RSI 13 threshold and the black interrupted line indicates the RSI 19 threshold. An RSI above the threshold score of 19 defines the presence of pathologic LPR. The shaded box bounds the 25–75% confidence interval, the error bars bound the 10–90% confidence interval. The solid line within the box represents the median. (JPJ 36 kb)
Figure 2
laryngopharyngeal reflux–health-related quality of life score (LPR–HRQL). The LPR–HRQL was calculated preoperatively, and at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 2 years and 3 years after laparoscopic Toupet fundoplication (LTF). The shaded box bounds the 25–75% confidence interval, the error bars bound the 10–90% confidence interval. The solid line within the box represents the median. (JPJ 27 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aiolfi, A., Cavalli, M., Saino, G. et al. Laparoscopic Toupet Fundoplication for the Treatment of Laryngopharyngeal Reflux: Results at Medium-Term follow-Up. World J Surg 44, 3821–3828 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05653-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-020-05653-5