Abstract
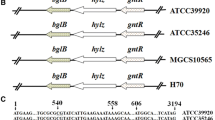
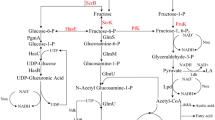
The biosynthetic pathway for hyaluronic acid (HA) has been proposed; however, a thorough genetic and functional analysis is required to further elucidate the roles of genes involved in HA production. Previously, we developed a markerless gene-deletion system for Streptococcus zooepidemicus and confirmed that hasA is essential for HA synthesis. Here, we constructed a comprehensive set of deletion mutants and investigated the roles of ten additional predicted genes in the HA synthetic pathway. Phenotypic assays revealed that all ten genes play a role in cell growth and/or HA synthesis. As expected, the deletion of hasA or hasB abolished HA production with little effect on growth, while the deletion of genes that are also required for peptidoglycan biosynthesis (hasE, glmM, and glmS) significantly reduced cell growth and HA production. Either of the glmU homologues (hasD and gcaD) was sufficient for optimal growth and the mucoid phenotype, while no double mutant could be isolated. Of the two UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGPase) paralogues, the operon-encoded hasC1 was responsible for 65 % of the activity, while hasC2 was responsible for the remaining 35 %. The deletion of hasC1 had no effect on cell growth and caused only a moderate decrease in the UDP-glucose level and HA production. The deletion of both hasC1 and hasC2 resulted in a severe growth defect and negligible UDP-glucose accumulation, HA production, and pyrophosphorylase activity. Of the two phosphoglucomutase paralogues, pgm1 and pgm2, the former is responsible for around 10 % of activity, while the latter is responsible for 90 %. The deletion of pgm1 showed no apparent effect on HA synthesis and growth, while the deletion of pgm2 resulted in the abolishment of HA synthesis and a significantly slower growth. These results should guide the metabolic engineering of S. zooepidemicus to improve HA productivity and quality.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beres SB, Sesso R, Pinto S, Hoe NP, Porcella SF, DeLeo FR, Musser JM (2008) Genome sequence of a Lancefield group C Streptococcus zooepidemicus strain causing epidemic nephritis: new information about an old disease. PLoS One 3(8):e3026
Blank LM, Hugenholtz P, Nielsen LK (2008) Evolution of the hyaluronic acid synthesis (has) operon in Streptococcus zooepidemicus and other pathogenic streptococci. J Mol Evol 67(1):13–22
Brody S, Tatum E (1967) Phosphoglucomutase mutants and morphological changes in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci 58(3):923
Chen WY, Marcellin E, Hung J, Nielsen LK (2009) Hyaluronan molecular weight is controlled by UDP-N-acetylglucosamine concentration in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. J Biol Chem 284(27):18007–18014
Chen WY, Marcellin E, Steen JA, Nielsen LK (2014) The role of hyaluronic acid precursor concentrations in molecular weight control in Streptococcus zooepidemicus. Mol Biotechnol 56(2):147–156
Chong BF, Nielsen LK (2003) Aerobic cultivation of Streptococcus zooepidemicus and the role of NADH oxidase. Biochem Eng J 16(2):153–162
Crater DL, Dougherty BA, van de Rijn I (1995) Molecular characterization of hasC from an operon required for hyaluronic acid synthesis in group A streptococci: demonstration of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase activity. J Biol Chem 270(48):28676–28680
Daran JM, Dallies N, Thines‐Sempoux D, Paquet V, François J (1995) Genetic and biochemical characterization of the UGP1 gene encoding the UDP‐glucose pyrophosphorylase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 233(2):520–530
DeAngelis PL, Papaconstantinou J, Weigel PH (1993) Molecular cloning, identification, and sequence of the hyaluronan synthase gene from group A Streptococcus pyogenes. J Biol Chem 268(26):19181–19184
Dillard JP, Vandersea MW, Yother J (1995) Characterization of the cassette containing genes for type 3 capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis in Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med 181(3):973–983
Dougherty BA, van de Rijn I (1993) Molecular characterization of hasB from an operon required for hyaluronic acid synthesis in group A streptococci: demonstration of UDP-glucose dehydrogenase activity. J Biol Chem 268(10):7118–7124
Fraenkel D, Levisohn S (1967) Glucose and gluconate metabolism in an Escherichia coli mutant lacking phosphoglucose isomerase. J Bacteriol 93(5):1571–1578
Froman BE, Tait RC, Gottlieb L (1989) Isolation and characterization of the phosphoglucose isomerase gene from Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet 217(1):126–131
Izawa N, Serata M, Sone T, Omasa T, Ohtake H (2011) Hyaluronic acid production by recombinant Streptococcus thermophilus. J Biosci Bioeng 111(6):665–670
Kleczkowski LA, Geisler M, Ciereszko I, Johansson H (2004) UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase: an old protein with new tricks. Plant Physiol 134(3):912–918
Liu L, Wang M, Du G, Chen J (2008) Enhanced hyaluronic acid production of Streptococcus zooepidemicus by an intermittent alkaline-stress strategy. Lett Appl Microbiol 46(3):383–388
Liu L, Liu Y, Li J, Du G, Chen J (2011) Microbial production of hyaluronic acid: current state, challenges, and perspectives. Microb Cell Factories 10:99. doi:10.1186/1475-2859-10-99
Lu M, Kleckner N (1994) Molecular cloning and characterization of the pgm gene encoding phosphoglucomutase of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 176(18):5847–5851
Mengin-Lecreulx D, van Heijenoort J (1993) Identification of the glmU gene encoding N-acetylglucosamine-1-phosphate uridyltransferase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 175(19):6150–6157
Mengin-Lecreulx D, van Heijenoort J (1996) Characterization of the essential gene glmM encoding phosphoglucosamine mutase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 271(1):32–39
Mesak LR, Dahl MK (2000) Purification and enzymatic characterization of PgcM: a β-phosphoglucomutase and glucose-1-phosphate phosphodismutase of Bacillus subtilis. Arch Microbiol 174(4):256–264
Mollerach M, López R, García E (1998) Characterization of the galU gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae encoding a uridine diphosphoglucose pyrophosphorylase: a gene essential for capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis. J Exp Med 188(11):2047–2056
Olsen LR, Vetting MW, Roderick SL (2007) Structure of the E. coli bifunctional GlmU acetyltransferase active site with substrates and products. Protein Sci 16(6):1230–1235
Prasad SB, Ramachandran KB, Jayaraman G (2012) Transcription analysis of hyaluronan biosynthesis genes in Streptococcus zooepidemicus and metabolically engineered Lactococcus lactis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 94(6):1593–1607
Seibold GM, Eikmanns BJ (2013) Inactivation of the phosphoglucomutase gene pgm in Corynebacterium glutamicum affects cell shape and glycogen metabolism. Biosci Rep 33(4):645–654
Sun X, Yang D, Wang Y, Geng H, He X, Liu H (2013) Development of a markerless gene deletion system for Streptococcus zooepidemicus: functional characterization of hyaluronan synthase gene. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 97(19):8629–8636
Watzele G, Tanner W (1989) Cloning of the glutamine: fructose-6-phosphate amidotransferase gene from yeast; pheromonal regulation of its transcription. J Biol Chem 264(15):8753–8758
Wessels MR, Moses AE, Goldberg JB, DiCesare TJ (1991) Hyaluronic acid capsule is a virulence factor for mucoid group A streptococci. Proc Natl Acad Sci 88(19):8317–8321
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the research foundation of Tianjin Science and Technology Commission (13RCGFSY19400) and the Tianjin Municipal High School Science and Technology Development Fund Program (20130602).
Authors’ contributions
L.H. designed the research; L.H., Z.Y., L.K., and Z.Q. performed the research; L.H., Q.Z., and N.L. analyzed the data; and L.H., Q.Z., and N.L. wrote the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 2037 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Luo, K., Zhao, Q. et al. Genetic and biochemical characterization of genes involved in hyaluronic acid synthesis in Streptococcus zooepidemicus . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 3611–3620 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7286-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-016-7286-1