Abstract
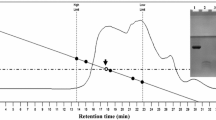
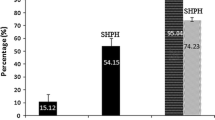
Marine red alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis is the main cultured seaweed in China with potent economic and ecological value. In this paper, the algal protein was hydrolyzed using trypsin, flavourzyme, papain and alkaline protease. Among them, the trypsin hydrolysate exhibited the highest angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activity and was fractionated into three molecular weight of >10 kDa, 3–10 kDa and <3 kDa. The <3 kDa fraction showed the highest ACE inhibitory activity of 78.15 ± 1.56% (2.0 mg/mL) and was used for further purification. An ACE inhibitory peptide was isolated from the <3 kDa fraction by Sephadex G-25, G-15 gel chromatography and ÄKTA pure system. The molecular mass and amino acid sequence of the purified peptide were identified as Gln-Val-Glu-Tyr (QVEY; MW, 537.57 Da) by MALDI-TOF/TOF–MS and MALDI-TOF/TOF–MS/MS, respectively. The peptide showed an IC50 value of 474.36 μM (0.255 mg/mL). The present study indicated that the marine red alga G. lemaneiformis can provide good protein sources, and the hydrolyzed bioactive peptides could be a potential source of functional food ingredients against hypertension.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zaman MA, Oparil S, Calhoun DA (2002) Drugs targeting the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. Nat Rev Drug Discov 1:621–636
Ondetti MA, Rubin B, Cushman DW (1977) Design of specific inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme: new class of orally active antihypertensive agents. Science 196:441–444
Cooper WO, Hernandezdiaz S, Arbogast PG, Dudley JA, Dyer S, Gideon PS, Hall K, Ray WA (2006) Major congenital malformations after first-trimester exposure to ACE inhibitors. N Engl J Med 354:2443–2451
Wijesekara I, Kim SK (2010) Angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors from marine resources: prospects in the pharmaceutical industry. Mar Drugs 8:1080–1093
Lau CC, Abdullah N, Shuib AS, Aminudin N (2014) Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from edible mushroom Agaricus bisporus (JE Lange) Imbach identified by LC–MS/MS. Food Chem 148:396–401
Garcia-Mora P, Frias J, Peñas E, Zieliński H, Giménez-Bastida JA, Wiczkowski W, Zielińska D, Martínez-Villaluenga C (2015) Simultaneous release of peptides and phenolics with antioxidant, ACE-inhibitory and anti-inflammatory activities from pinto bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L. var. pinto) proteins by subtilisins. J Funct Foods 18:319–332
Gangopadhyay N, Wynne K, O’Connor P, Gallagher E, Brunton NP, Rai DK, Hayes M (2016) In silico and in vitro analyses of the angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity of hydrolysates generated from crude barley (Hordeum vulgare) protein concentrates. Food Chem 203:367–374
Wang FJ, Yin XY, Regenstein JM, Wang JZ (2016) Separation and purification of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from walnuts (Juglans regia L.) meal. Eur Food Res Technol 242:911–918
Lacroix IME, Meng G, Cheung IWY, Li-Chan ECY (2016) Do whey protein-derived peptides have dual dipeptidyl-peptidase IV and angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activities? J Funct Foods 21:87–96
Fu Y, Young JF, Løkke MM, Lametsch R, Aluko RE, Therkildsen M (2016) Revalorisation of bovine collagen as a potential precursor of angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides based on in silico and in vitro protein digestions. J Funct Foods 24:196–206
Cudennec B, Violle N, Chataigné G, Drevet P, Bisson JF, Dhulster P, Ravallec R (2016) Evidence for an antihypertensive effect of a land snail (Helix aspersa) by-product hydrolysate-Identification of involved peptides. J Funct Foods 22:602–611
Larsen R, Eilertsen KE, Elvevoll EO (2011) Health benefits of marine foods and ingredients. Biotechnol Adv 29:508–518
Fitzgerald C, Gallagher E, Tasdemir D, Hayes M (2011) Heart health peptides from macroalgae and their potential use in functional foods. J Agr Food Chem 59:6829–6836
Lu N, Ding Y, Zang XN, Zhang XC, Chen H, Mu XS (2013) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of glutathione peroxidase and glutathione reductase from Gracilaria lemaneiformis under heat stress. J Appl Phycol 25:1925–1931
Wen X, Peng C, Zhou H, Lin Z, Lin G, Chen S, Li P (2006) Nutritional composition and assessment of Gracilaria lemaneiformis Bory. J Integr Plant Biol 48:1047–1053
Chang L, Sui Z, Fu F, Zhou W, Wang J, Kang KH, Zhang S, Ma J (2014) Relationship between gene expression of UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase and agar yield in Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis (Rhodophyta). J Appl Phycol 26:2435–2441
Qi Z, Liu H, Li B, Mao Y, Jiang Z, Zhang J, Fang J (2010) Suitability of two seaweeds, Gracilaria lemaneiformis and Sargassum pallidum, as feed for the abalone Haliotis discus hannai Ino. Aquaculture 300:189–193
Fan Y, Wang W, Song W, Chen H, Teng A, Liu A (2012) Partial characterization and anti-tumor activity of an acidic polysaccharide from Gracilaria lemaneiformis. Carbohyd Polym 88:1313–1318
Jiang W, Fu Y, Yang F, Yang Y, Liu T, Zheng W, Zeng L, Chen T (2014) Gracilaria lemaneiformis polysaccharide as integrin-targeting surface decorator of selenium nanoparticles to achieve enhanced anticancer efficacy. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6:13738–13748
Kang Y, Li H, Wu J, Xu X, Sun X, Zhao X, Xu N (2016) Transcriptome profiling reveals the antitumor mechanism of polysaccharide from marine algae Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis. PLoS One 11:e0158279
Liao X, Yang L, Chen M, Yu J, Zhang S, Ju Y (2015) The hypoglycemic effect of a polysaccharide (GLP) from Gracilaria lemaneiformis and its degradation products in diabetic mice. Food Funct 6:2542–2549
Shalaby SM, Zakora M, Otte J (2006) Performance of two commonly used angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition assays using FA-PGG and HHL as substrates. J Dairy Res 73:178–186
Henda YB, Labidi A, Arnaudin I, Bridiau N, Delatouche R, Maugard T, Piot JM, Sannier F, Thiéry V, Bordenave-Juchereau S (2013) Measuring angiotensin-I converting enzyme inhibitory activity by micro plate assays: comparison using marine cryptides and tentative threshold determinations with captopril and losartan. J Agr Food Chem 61:10685–10690
Minkiewicz P, Dziuba J, Iwaniak A, Dziuba M, Darewicz M (2008) BIOPEP database and other programs for processing bioactive peptide sequences. J AOAC Int 91:965–980
Gobbetti M, Ferranti P, Smacchi E, Goffredi F, Addeo F (2000) Production of angiotensin-I-converting-enzyme-inhibitory peptides in fermented milks started by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus SS1 and Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris FT4. Appl Environ Microb 66:3898–3904
Li GH, Qu MR, Wan JZ, You JM (2007) Antihypertensive effect of rice protein hydrolysate with in vitro angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory activity in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 16:275–280
Hayes M, Stanton C, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP (2007) Putting microbes to work: dairy fermentation, cell factories and bioactive peptides. Part II: bioactive peptide functions. Biotechnol J 2:435–449
van Platerink CJ, Janssen HGM, Haverkamp J (2008) Application of at-line two-dimensional liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for identification of small hydrophilic angiotensin I-inhibiting peptides in milk hydrolysates. Anal Bioanal Chem 391:299–307
Balti R, Bougatef A, Sila A, Guillochon D, Dhulster P, Nedjar-Arroume N (2015) Nine novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle protein hydrolysates and antihypertensive effect of the potent active peptide in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Food Chem 170:519–525
Suetsuna K, Chen JR (2001) Identification of antihypertensive peptides from peptic digest of two microalgae, Chlorella vulgaris and Spirulina platensis. Mar Biotechnol 3:305–309
Sheih IC, Fang TJ, Wu TK (2009) Isolation and characterisation of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the algae protein waste. Food Chem 115:279–284
Ko SC, Kang N, Kim EA, Kang MC, Lee SH, Kang SM, Lee JB, Jeon BT, Kim SK, Park SJ, Park PJ, Jung WK, Kim D, Jeon YJ (2012) A novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from a marine Chlorella ellipsoidea and its antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Process Biochem 47:2005–2011
Wu H, He HL, Chen XL, Sun CY, Zhang YZ, Zhou BC (2008) Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from shark meat hydrolysate. Process Biochem 43:457–461
Jimsheena VK, Gowda LR (2010) Arachin derived peptides as selective angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors: structure-activity relationship. Peptides 31:1165–1176
Mojica L, Chen K, Mejía EG (2015) Impact of commercial precooking of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) on the generation of peptides, after pepsin-pancreatin hydrolysis, capable to inhibit dipeptidyl peptidase-IV. J Food Sci 80:H188–H198
Pan S, Wang S, Jing L, Yao D (2016) Purification and characterisation of a novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory peptide derived from the enzymatic hydrolysate of Enteromorpha clathrata protein. Food Chem 211:423–430
Chen JC, Wang J, Zheng BD, Pang J, Chen LJ, Lin HT, Guo X (2016) Simultaneous determination of 8 small antihypertensive peptides with tyrosine at the C-terminal in Laminaria japonica hydrolysates by RP-HPLC method. J Food Process Pres 40:492–501
Wu Q, Cai QF, Yoshida A, Sun LC, Liu YX, Liu GM, Su WJ, Cao MJ (2016) Purification and characterization of two novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from R-phycoerythrin of red algae (Bangia fusco-purpurea). Eur Food Res Technol:1–11
Suetsuna K, Nakano T (2000) Identification of an antihypertensive peptide from peptic digest of wakame (Undaria pinnatifida). J Nutr Biochem 11:450–454
Sato M, Hosokawa T, Yamaguchi T, Nakano T, Muramoto K, Kahara T, Funayama K, Kobayashi A, Nakano T (2002) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from wakame (Undaria pinnatifida) and their antihypertensive effect in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Agr Food Chem 50:6245–6252
Suetsuna K, Maekawa K, Chen JR (2004) Antihypertensive effects of Undaria pinnatifida (wakame) peptide on blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Nutr Biochem 15:267–272
Suetsuna K (1998) Purification and identification of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitors from the red alga Porphyra yezoensis. J Mar Biotechnol 6:163–167
Wu H, Xu N, Sun X, Yu H, Zhou C (2015) Hydrolysis and purification of ACE inhibitory peptides from the marine microalga Isochrysis galbana. J Appl Phycol 27:351–361
Qian ZJ, Heo SJ, Oh CH, Kang DH, Jeong SH, Park WS, Choi IW, Jeon YJ, Jung WK (2013) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide isolated from biodiesel byproducts of marine microalgae, Nannochloropsis oculata. J Biobased Mater Bio 7:135–142
Samarakoon KW, Kwon ON, Ko JY, Lee JH, Kang MC, Kim D, Lee JB, Lee JS, Jeon YJ (2013) Purification and identification of novel angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides from cultured marine microalgae (Nannochloropsis oculata) protein hydrolysate. J Appl Phycol 25:1595–1606
Lu J, Ren DF, Xue YL, Sawano Y, Miyakawa T, Tanokura M (2010) Isolation of an antihypertensive peptide from alcalase digest of Spirulina platensis. J Agr Food Chem 58:7166–7171
Cheung HS, Wang FL, Ondetti MA, Sabo EF, Cushman DW (1980) Binding of peptide substrates and inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. Importance of the COOH-terminal dipeptide sequence. J Biol Chem 255:401–407
Fahmi A, Morimura S, Guo HC, Shigematsu T, Kida K, Uemura Y (2004) Production of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from sea bream scales. Process Biochem 39:1195–1200
Balti R, Nedjar-Arroume N, Adjé EY, Guillochon D, Nasri M (2010) Analysis of novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle proteins. J Agr Food Chem 58:3840–3846
Wijesekara I, Qian ZJ, Ryu B, Ngo DH, Kim SK (2011) Purification and identification of antihypertensive peptides from seaweed pipefish (Syngnathus schlegeli) muscle protein hydrolysate. Food Res Int 44:703–707
Salampessy J, Reddy N, Kailasapathy K, Phillips M (2015) Functional and potential therapeutic ACE-inhibitory peptides derived from bromelain hydrolysis of trevally proteins. J Funct Foods 14:716–725
Lassoued I, Mora L, Barkia A, Aristoy M, Nasri M, Toldrá F (2016) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides FQPSF and LKYPI identified in Bacillus subtilis A26 hydrolysate of thornback ray muscle. Int J Food Sci Tech 51:1604–1609
Li GH, Le GW, Shi YH, Shrestha S (2004) Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins and their physiological and pharmacological effects. Nutr Res 24:469–486
FitzGerald RJ, Meisel H (2000) Milk protein-derived peptide inhibitors of angiotensin-I-converting enzyme. Brit J Nutr 84:33–37
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Key Program of Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (LZ17D060001) and the Ningbo Science and Technology Bureau of China (2016C10034). This research was also sponsored by KC Wong Magna Fund in Ningbo University, and Li Dak Sum Yip Yio Chin Kenneth Li Marine Biopharmaceutical Development Fund, National 111 Project of China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests existed.
Compliance with ethics requirements
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cao, D., Lv, X., Xu, X. et al. Purification and identification of a novel ACE inhibitory peptide from marine alga Gracilariopsis lemaneiformis protein hydrolysate. Eur Food Res Technol 243, 1829–1837 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-017-2886-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00217-017-2886-2