Abstract
Rationale
Opioid receptor antagonists reliably alter the expression or extinction of ethanol’s conditioned motivational effects as indexed by the place conditioning procedure, suggesting endogenous opioids are normally involved. These studies examined how exogenous stimulation of opioid receptors alters ethanol’s conditioned rewarding and aversive effects.
Objectives
Drugs that either directly (morphine) or indirectly (ethanol) stimulate opioid receptors were tested for their effects on the expression and extinction of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference (CPP) and conditioned place aversion (CPA).
Methods
Male DBA/2J mice were exposed to unbiased ethanol (2 g/kg) conditioning procedures that produced either CPP (experiments 1–2) or CPA (experiments 3–4). Morphine (0, 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg) was injected before three post-conditioning tests in experiments 1 and 3, whereas ethanol (0, 1, 2, or 3 g/kg) was injected before tests in experiments 2 and 4. All groups received vehicle on test 4 to determine whether the drug pretreatments altered the course of extinction.
Results
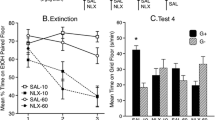
Morphine dose-dependently enhanced CPP expression (experiment 1), but ethanol dose-dependently reduced CPP expression (experiment 2). Test 4 showed no differences between drug-treated mice and mice given vehicle on all tests. Morphine had no effect on expression or extinction of ethanol-induced CPA (experiment 3). The highest ethanol dose (3 g/kg) interfered with CPA expression, but not extinction (experiment 4).
Conclusions
Pretreatment drug effects on ethanol CPP and CPA expression were most likely a byproduct of their activity altering effects rather than opioid-receptor mediated modulation of ethanol’s conditioned motivational effects. Neither drug affected the course of extinction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altshuler HL, Phillips PE, Feinhandler DA (1980) Alteration of ethanol self-administration by naltrexone. Life Sci 26:679–688
Bechtholt AJ, Cunningham CL (2005) Ethanol-Induced Conditioned Place Preference Is Expressed Through a Ventral Tegmental Area Dependent Mechanism. Behavioral Neuroscience 119(1):213–223
Bespalov AY, Tokarz ME, Bowen SE, Balster RL, Beardsley PM (1999) Effects of test conditions on the outcome of place conditioning with morphine and naltrexone in mice. Psychopharmacology 141:118–122
Blum K, Payne JE (1991) Alcohol and the addictive brain: new hope for alcoholics from biogenetic research. Free Press, New York
Ciccocioppo R, Lin D, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2003) Reinstatement of ethanol-seeking behavior by drug cues following single versus multiple ethanol intoxication in the rat: effects of naltrexone. Psychopharmacology 168:208–215. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-002-1380-z
Ciccocioppo R, Martin-Fardon R, Weiss F (2002) Effect of selective blockade of mu(1) or delta opioid receptors on reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior by drug-associated stimuli in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:391–399
Cunningham CL (1979) Flavor and location aversions produced by ethanol. Behav Neural Biol 27:362–367
Cunningham CL (1993) Pavlovian drug conditioning. In: van Haaren F (ed) Methods in behavioral pharmacology. Elsevier, New York, pp 349–381
Cunningham CL (1995) Localization of genes influencing ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and locomotor activity in BXD recombinant inbred mice. Psychopharmacology 120:28–41
Cunningham CL (2014) Genetic relationship between ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and other ethanol phenotypes in 15 inbred mouse strains. Behav Neurosci 128:430–445
Cunningham CL (2019) Genetic relationships between ethanol-induced conditioned place aversion and other ethanol phenotypes in 15 inbred mouse strains. Brain Sci 9:209
Cunningham CL, Dickinson SD, Okorn DM (1995) Naloxone facilitates extinction but does not affect acquisition or expression of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 3:330–343
Cunningham CL, Ferree NK, Howard MA (2003) Apparatus bias and place conditioning with ethanol in mice. Psychopharmacology 170:409–422
Cunningham CL, Gremel CM, Groblewski PA (2006) Drug-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Nat Protoc 1:1662–1670
Cunningham CL, Groblewski PA, Voorhees CM (2011) Place conditioning. In: Olmstead MC (ed) Animal models of drug addiction. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 167–189
Cunningham CL, Henderson CM (2000) Ethanol-induced conditioned place aversion in mice. Behav Pharmacol 11:591–602
Cunningham CL, Henderson CM, Bormann NM (1998) Extinction of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and conditioned place aversion: effects of naloxone. Psychopharmacology 139:62–70
Cunningham CL, Niehus DR, Malott DH, Prather LK (1992) Genetic differences in the rewarding and activating effects of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacology 107:385–393
Cunningham CL, Okorn DM, Howard CE (1997) Interstimulus interval determines whether ethanol produces conditioned place preference or aversion in mice. Anim Learn Behav 25:31–42
Cunningham CL, Phillips TJ (2003) Genetic basis of ethanol reward. In: Maldonado R (ed) Molecular biology of drug addiction. Humana Press, Totowa, pp 263–294
Cunningham CL, Shields CN (2018a) Effects of sex on ethanol conditioned place preference, activity and variability in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 173:84–89
Cunningham CL, Shields CN (2018b) Effects of multi-modal cues on conditioned place preference in C57BL/6J and DBA/2J mice. Psychopharmacology 235:3535–3543
Cunningham CL, Smith R, McMullin C (2003) Competition between ethanol-induced reward and aversion in place conditioning. Learn Behav 31:273–280
Cunningham CL, Tull LE, Rindal KE, Meyer PJ (2002) Distal and proximal pre-exposure to ethanol in the place conditioning task: tolerance to aversive effect, sensitization to activating effect, but no change in rewarding effect. Psychopharmacology 160:414–424
Davis M (1979) Morphine and naloxone: effects on conditioned fear as measured with the potentiated startle paradigm. Eur J Pharmacol 54:341–347
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1985) Ethanol preferentially stimulates dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats. Eur J Pharmacol 115:131–132
Font L, Houck CA, Cunningham CL (2017) Naloxone effects on extinction of ethanol- and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in mice. Psychopharmacology 234:2747–2759
Froehlich JC, Harts J, Lumeng L, Li TK (1990) Naloxone attenuates voluntary ethanol intake in rats selectively bred for high ethanol preference. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 35:385–390
Gianoulakis C (1998) Alcohol-seeking behavior: the roles of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and the endogenous opioid system. Alcohol Health Res World 22:202–210
Gianoulakis C (2001) Influence of the endogenous opioid system on high alcohol consumption and genetic predisposition to alcoholism. J Psychiatry Neurosci 26:304–318
Gremel CM, Cunningham CL (2007) Role of test activity in ethanol-induced disruption of place preference expression in mice. Psychopharmacology 191:195–202
Gremel CM, Young EA, Cunningham CL (2011) Blockade of opioid receptors in anterior cingulate cortex disrupts ethanol-seeking behavior in mice. Behav Brain Res 219:358–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2010.12.033
Herz A (1997) Endogenous opioid systems and alcohol addiction. Psychopharmacology 129:99–111
Jamensky NT, Gianoulakis C (1997) Content of dynorphins and kappa-opioid receptors in distinct brain regions of C57BL/6 and DBA/2 mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:1455–1464
Kuzmin A, Sandin J, Terenius L, Ogren SO (2003) Acquisition, expression, and reinstatement of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice: effects of opioid receptor-like 1 receptor agonists and naloxone. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:310–318
Liang J, Li Y, Ping X, Yu P, Zuo Y, Wu L, Han JS, Cui C (2006) The possible involvement of endogenous ligands for mu-, delta- and kappa-opioid receptors in modulating morphine-induced CPP expression in rats. Peptides 27:3307–3314
Linakis JG, Cunningham CL (1979) Effects of concentration of ethanol injected intraperitoneally on taste aversion, body temperature and activity. Psychopharmacology 64:61–65
Marinelli PW, Funk D, Harding S, Li Z, Juzytsch W, Lê AD (2009) Roles of opioid receptor subtypes in mediating alcohol-seeking induced by discrete cues and context. Eur J Neurosci 30:671–678. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06851.x
Middaugh LD, Bandy AL (2000) Naltrexone effects on ethanol consumption and response to ethanol conditioned cues in C57BL/6 mice. Psychopharmacology 151:321–327
Neisewander JL, Pierce RC, Bardo MT (1990) Naloxone enhances the expression of morphine-induced conditioned place preference. Psychopharmacology 100:201–205
O'Brien CP, Volpicelli LA, Volpicelli JR (1996) Naltrexone in the treatment of alcoholism: a clinical review. Alcohol 13:35–39
O'Malley SS (1995) Integration of opioid antagonists and psychosocial therapy in the treatment of narcotic and alcohol dependence. J Clin Psychiatry 56(Suppl 7):30–38
O'Malley SS, Jaffe AJ, Chang G, Rode S, Schottenfeld R, Meyer RE, Rounsaville B (1996) Six-month follow-up of naltrexone and psychotherapy for alcohol dependence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:217–224
Orsini C, Bonito-Oliva A, Conversi D, Cabib S (2005) Susceptibility to conditioned place preference induced by addictive drugs in mice of the C57BL/6 and DBA/2 inbred strains. Psychopharmacology 181:327–336. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-2259-6
Overton DA (1983) State-dependent learning and drug discriminations. In: Iversen LL, Iversen SD, Snyder SH (eds) Handbook of psychopharmacology, vol 18. Springer, pp 59–127
Pastor R, Font L, Miquel M, Phillips TJ, Aragon CM (2011) Involvement of the beta-endorphin neurons of the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus in ethanol-induced place preference conditioning in mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:2019–2029. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1530-0277.2011.01553.x
Phillips TJ, Wenger CD, Dorow JD (1997) Naltrexone effects on ethanol drinking acquisition and on established ethanol consumption in C57BL/6J mice. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 21:691–702
Reid LD, Hunter GA (1984) Morphine and naloxone modulate intake of ethanol. Alcohol 1:33–37
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2003) Addiction. Annu Rev Psychol 54:25–53
Shelton KL, Dukat M, Allan AM (2004) Effect of 5-HT3 receptor over-expression on the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:1161–1171
Shipton EA, Shipton EE, Shipton AJ (2018) A review of the opioid epidemic: what do we do about it? Pain Ther 7:23–36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40122-018-0096-7
Tzschentke TM (2007) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict Biol 12:227–462
Vezina P, Stewart J (1987) Morphine conditioned place preference and locomotion: the effect of confinement during training. Psychopharmacology 93:257–260
Volpicelli JR, Clay KL, Watson NT, O'Brien CP (1995) Naltrexone in the treatment of alcoholism: predicting response to naltrexone. J Clin Psychiatry 56(Suppl 7):39–44
Winslow BT, Onysko M, Hebert M (2016) Medications for alcohol use disorder. Am Fam Physician 93:457–465
Winter JC (1975) The stimulus properties of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacologia 44:209–214
Wróbel M (2011) Acquisition and expression of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference in mice is inhibited by naloxone. Pharmacol Rep 63:79–85
Wyvell CL, Berridge KC (2000) Intra-accumbens amphetamine increases the conditioned incentive salience of sucrose reward: enhancement of reward “wanting” without enhanced “liking” or response reinforcement. J Neurosci 20:8122–8130
Acknowledgments
Research reported in this paper was supported by the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism of the National Institutes of Health under award number R01AA007702. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cunningham, C.L., Bakner, L., Schuette, L.M. et al. Morphine and ethanol pretreatment effects on expression and extinction of ethanol-induced conditioned place preference and aversion in mice. Psychopharmacology 238, 55–66 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05658-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-020-05658-x