Abstract
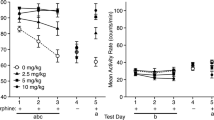
The present investigation sought (a) to establish the efficacy of morphine and ethanol as discriminative stimuli when each is paired with the administration of saline and (b) to compare, in a qualitative sense, the stimulus properties of the two drugs. Additional experiments examined the effects of treatment with naloxone or l-propranolol upon morphine and ethanol-mediated discriminated responding. Finally, the stereospecificity of the stimuli produced by morphine was determined by a comparison, in morphine-trained rats, of levorphanol and dextrorphan. Discriminated responding developed rapidly in both the morphine and ethanol groups. In tests in which ethanol was administered to morphine-trained animals and vice versa, no similarity to stimulus properties was apparent. Antagonism of discriminated responding induced by morphine and ethanol was attempted using naloxone and l-propranolol. Naloxone blocked the actions of morphine but was without effect upon ethanol. No evidence of antagonism of either drug by propranolol was found. When a range of doses of levorphanol (0.1–3 mg/kg) and dextrorphan (3–100 mg/kg) was tested in morphine trained animals, only levorphanol was able to substitute for morphine. The present results suggest that the stimulus properties of morphine represent typical opiate effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry, H., III: Classification of drugs according to their discriminable effects in rats. Fed. Proc. 33, 1814–1824 (1974)
Barry, H., III, Koepfer, E., Lutch, J.: Learning to discriminate between alcohol and nondrug condition. Psychol. Rep. 16, 1072 (1965)
Barry, H., III, Kubena, R. K.: Discriminative stimulus characteristics of alcohol, marijuana and atropine. In: Drug addiction, J. M. Singh, L. H. Miller, and H. Lal, eds., pp. 3–16. Mt. Kisco, N.Y.: Futura 1972
Belleville, R. E.: Control of behavior by drug-produced internal stimuli. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 5, 95–105 (1964)
Black, W. C., Grosz, H. J.: Propranolol antagonism of morphine-influenced behavior. Brain Res. 65, 362–367 (1974)
Conger, J. J.: The effects of alcoholism on conflict behavior in the albino rat. Quart. J. Stud. Alcohol 12, 1–29 (1951)
DeFeudis, F. V., Grosz, H. J.: Effects of propranolol on the binding of (14C) morphine to particulate fractions of mouse brain. Brain Res. 47, 510–514 (1972)
Goldstein, A.: Biostatistics. New York-London: MacMillan 1964
Grosz, H. J.: Successful treatment of a heroin addict with propranolol: Implications for opiate addiction treatment and research. J. Indiana med. Ass. 65, 505–509 (1972a)
Grosz, H. J.: Narcotic withdrawal symptoms in heroin users treated with propranolol. Lancet 1972b II, 564–566
Hill, H. E., Jones, B. E., Bell, E. C.: State dependent control of discrimination by morphine and pentobarbital. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 305–313 (1971)
Hirschhorn, I. D., Rosecrans, J. A.: A comparison of the stimulus effects of morphine and lysergic acid diethylamide. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2, 361–366 (1974)
Hirschhorn, I. D., Winter, J. C.: Mescaline and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) as discriminative stimuli. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 22, 64–71 (1971)
Hollister, L. F.: Chemical psychoses, pp. 32–44. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas 1968
Jaffe, J. H.: Narcotic analgesics. In: The pharmacologic basis of therapeutics, 4th ed. L. Goodman and A. Gilman, eds., p. 262. New York: MacMillan 1972
Kelleher, R. T., Morse, W. H.: Determinents of the specificity of behavioral effects of drugs. In: Reviews of physiology, biochemistry and experimental pharmacology, Vol. 60, pp. 2–56. New York: Springer 1968
Kubena, R. K., Barry, H., III: Generalization by rats of alcohol and atropine stimulus characteristics to other drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 15, 196–206 (1969a)
Kubena, R. K., Barry, H., III: Two procedures for training differential responses in alcohol and nondrug conditions. J. pharm. Sci. 58, 99–101 (1969b)
Krimmer, E. C., Barry, H., III: Discriminability of pentobarbital and alcohol tested by two lever choice in shock escape. Pharmacologist 15, 236 (1973)
Martin, W. R.: Opioid antagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 19, 463–521 (1967)
Mendelson, J. H., Rossi, A. M., Bernstein, J.: Effects of propranolol on behavior of alcoholics following acute alcohol intake. 157 Abs., 5th International Congress on Pharmacology, San Francisco, July 23–28, 1972
Mendelson, J. H., Rossi, A. M., Bernstein, J. G., Kuehnle, J.: Propranolol and behavior of alcohol addicts after acute alcohol ingestion. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 15, 571–578 (1974)
Overton, D. A.: State-dependent learning produced by depressant and atropine-like drugs. Psychopharmacologia (Berl.) 10, 6–31 (1966)
Overton, D. A.: Experimental methods for the study of state-dependent learning. Fed. Proc. 33, 1800–1813 (1974)
Reynolds, G. S.: A primer of operant conditioning. Glenview, Ill.: Scott, Foresman 1968
Rosecrans, J. A., Goodloe, M. H., Bennett, G. J., Hirschhorn, I.D.: Morphine as a discriminative cue: Effects of amine depletors and naloxone. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 21, 252–257 (1973)
Schechter, M. D.: Ethanol as a discriminative cue: Reduction following depletion of brain serotonin. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 24, 278–281 (1973)
Schechter, M. D.: Effect of propranolol, d-amphetamine, and caffeine on ethanol as a discriminative cue. Europ. J. Pharmacol. 29, 52–57 (1974)
Smith, A., Hayashida, K., Kim, Y.: Inhibitions by propranolol of ethanol-induced narcosis. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 22, 644–645 (1970)
Winer, B. J.: Statistical principles in experimental design, 2nd ed. New York-London: McGraw-Hill 1971
Winter, J. C.: A comparison of the stimulus properties of mescaline and 2,3,4-trimethoxyphenylethylamine. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 185, 101–107 (1973)
Winter, J. C.: Hallucinogens as discriminative stimuli. Fed. Proc. 33, 1825–1832 (1974a)
Winter, J. C.: The effects of 3,4-dimethoxyphenylethylamine in rats trained with mescaline as a discriminative stimulus. J. Pharmacol. exp. Ther. 189, 741–747 (1974b)
Winter, J. C.: Propranolol and morphine: A lethal interaction. Arch. int. Pharmacodyn. 212, 195–198 (1974c)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Winter, J.C. The stimulus properties of morphine and ethanol. Psychopharmacologia 44, 209–214 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428896
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00428896